# 2018q3 Homework1
contributed by < [osamchiu](https://github.com/osamchiu) >
- [x] 開發工具和規格標準篇
- [x] 指標篇
- [x] 函式呼叫篇
- [x] 遞迴呼叫篇
- [x] 前置處理器應用篇
- [ ] goto 和流程控制
- [ ] linked list 和非連續記憶體操作
- [ ] 技巧篇
- [ ] GNU/Linux 開發工具
## 開發工具和規格標準篇
> C is quirky, flawed, and an enormous success. Although accidents of history surely helped, it evidently satisfied a need for a system implementation language efficient enough to displace assembly language, yet sufficiently abstract and fluent to describe algorithms and interactions in a wide variety of environments. —— Dennis M. Ritchie
在以前寫C的時候根本沒有想那麼多,就當成了一個普通的語言再用,其實到頭來也變成雖然已經過了幾年,但是對C而言沒什麼深度的瞭解。
### license
##### GPLv3
做動態連結時有較大的限制
##### MIT License
別把作者名字塗掉就可以用(夠簡單)
==對於compiler而言,是不是可以認知為如果我不是抄襲他們的原始碼,只是單純利用他們的compiler我就等於可以免費使用? 即使我的程式是有收益的??==
:::info
是的,在不違反當地法規 (如美國對加密演算法的出口管制) 的前提下,MIT License 允許你使用該授權的編譯器自由地編譯程式碼,後者也能自由地運用,包含商業行為
:notes: jserv
:::
==謝謝老師回答 請問GPLv3也是如此嗎?==
:::info
GPLv3 的狀況複雜一點,要看 GPLv3 授權的編譯器產生的程式碼是否附帶同樣 GPLv3 的程式碼,這部分要對照 [Exceptions to GNU Licenses](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/exceptions.html) 來解讀。
請花點時間讀 GPLv3 一類的授權條款,一輩子受用的
:notes: jserv
:::
==好的 謝謝老師 我再看看詳細內容 感謝你回答!==
### 有趣的地方
終端機其實是檔案
### compiler的由來
編譯器開發 C的編譯器怎麼來?
C0>C1>...>CN bootstrapping
## 指標篇
>A pointer type may be derived from a function type, an object type, or an incomplete type, called the referenced type. A pointer type describes an object whose value provides a reference to an entity of the referenced type. A pointer type derived from the referenced type T is sometimes called ‘‘pointer to T’’. The construction of a pointer type from a referenced type is called ‘‘pointer type derivation’’.
>Array, function, and pointer types are collectively called derived declarator types. A declarator type derivation from a type T is the construction of a derived declarator type from T by the application of an array-type, a function-type, or a pointer-type derivation to T.
不管什麼在C裡面只有call by value
```C=1
int B = 2;
void func(int *p) { p = &B; }
int main() {
int A = 1, C = 3;
int *ptrA = &A;
func(ptrA);
printf("%d\n", *ptrA);
return 0;
}
```
```graphviz
digraph structs {
node[shape=record]
{rank=same; structa,structb,structc}
structp [label="p|<p>&B"]
structptr [label="<name_ptr> ptrA|<ptr> &A"];
structb [label="<B> B|2"];
structa [label="<A> A|1"];
structc [label="<C> C|3"];
structptr:ptr -> structa:A:nw
structp:p -> structb:B:nw
}
```
```clike=1
int B = 2;
void func(int **p) { *p = &B; }
int main() {
int A = 1, C = 3;
int *ptrA = &A;
func(&ptrA);
printf("%d\n", *ptrA);
return 0;
}
```
```graphviz
digraph structs {
node[shape=record]
{rank=same; structa,structb,structc}
structp [label="p(in func)|<p> &ptrA"]
structadptr [label="&ptrA(temp)|<adptr> &ptrA"]
structptr [label="<name_ptr> ptrA|<ptr> &B"];
structb [label="<B> B|2"];
structa [label="<A> A|1"];
structc [label="<C> C|3"];
structptr:ptr -> structb:B:nw
structadptr:adptr -> structptr:name_ptr:nw
structp:p -> structptr:name_ptr:nw
}
```
對C而言function就是只有複製傳copy的
所以傳pointer to pointer就是等於把原先的pointer的value(另一個address)複製一份傳入function
這樣才能真的改變到
## 函式呼叫篇
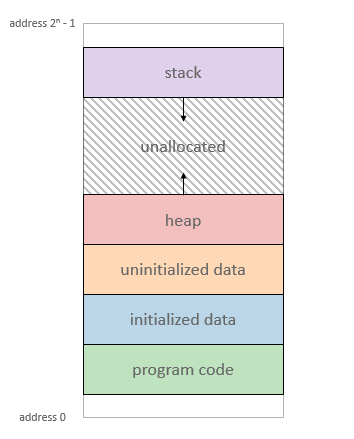
把整個函數的部分複習了一遍
## 遞迴呼叫篇
#### 對於Recursive在compiler的效率
以老師提供之費氏數列程式碼 利用godbolt進行實驗
- comiplier version:X86-64 gcc 8.2
``` C
//test code
int fib(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
return fib(n - 1) + fib (n - 2);
}
int fib1(int n, int a, int b) {
if (n == 0) return a;
return fib(n - 1 , b, a + b);
}
```
- C++
``` ASM
fib(int, int, int):
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 16
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-4], edi
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-8], esi
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-12], edx
cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-4], 0
jne .L2
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-8]
jmp .L3
.L2:
mov edx, DWORD PTR [rbp-8]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-12]
add edx, eax
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-4]
lea ecx, [rax-1]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-12]
mov esi, eax
mov edi, ecx
call fib(int, int, int)
nop
.L3:
leave
ret
fib1(int, int, int):
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 16
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-4], edi
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-8], esi
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-12], edx
cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-4], 0
jne .L5
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-8]
jmp .L6
.L5:
mov edx, DWORD PTR [rbp-8]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-12]
add edx, eax
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-4]
lea ecx, [rax-1]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-12]
mov esi, eax
mov edi, ecx
call fib(int, int, int)
nop //==here==
.L6:
leave
ret
```
- C
``` ASM
fib:
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
push rbx
sub rsp, 24
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-20], edi
cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-20], 0
jne .L2
mov eax, 0
jmp .L3
.L2:
cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-20], 1
jne .L4
mov eax, 1
jmp .L3
.L4:
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-20]
sub eax, 1
mov edi, eax
call fib
mov ebx, eax
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-20]
sub eax, 2
mov edi, eax
call fib
add eax, ebx
.L3:
add rsp, 24
pop rbx
pop rbp
ret
fib1:
push rbp
mov rbp, rsp
sub rsp, 16
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-4], edi
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-8], esi
mov DWORD PTR [rbp-12], edx
cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-4], 0
jne .L6
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-8]
jmp .L7
.L6:
mov edx, DWORD PTR [rbp-8]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-12]
add edx, eax
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-4]
lea ecx, [rax-1]
mov eax, DWORD PTR [rbp-12]
mov esi, eax
mov edi, ecx
call fib1 //==here==
.L7:
leave
ret
```
==發現在C的版本裡面直接call fib1
而在C++版本中呼叫後會有一個nop(查資料後發現是延時等待)
仔細思考後來是想不太到為什麼會有這樣的差異==
ps:同樣程式碼在x86-64 gcc 7.3卻沒有該nop指令
:::info
和 optimization order 有關,你可以新增編譯參數 `-march=native -mtune=native -Ofast` 再重新編譯
:notes: jserv
:::
#### file loading的包裝型態
在FILE以及DIR的函式內部回傳利用FILE* 以及DIR*作為回傳
可以有效的包裝讀取以及實際存取的狀況
## 前置處理器應用篇
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet