# 2019q3 Homework2 (lab0)
<contributed by:`xl86305955`>
###### tags:`sysprog2019` `list` `Homework2`
## 作業要求
實驗目標為實作 queue
* first in, first out (FIFO)
* last in, first out (LIFO)
### 結構

### 功能
實現以下功能:
* qnew:Create a new, empty queue.
* qfree:Free all storage used by a queue.
* qinserthead:Attempt to insert a new element at the head of the queue (LIFO discipline).
* qinserttail:Attempt to insert a new element at the tail of the queue (FIFO discipline).
* qremovehead:Attempt to remove the element at the head of the queue.
* qsize:Compute the number of elements in the queue.
--
## 實驗環境
```shell
$ uname -a
Linux fred-System-Product-Name 4.15.0-64-generic #73-Ubuntu SMP Thu Sep 12 13:16:13 UTC 2019 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
$ gcc --version
gcc (Ubuntu 7.4.0-1ubuntu1~18.04.1) 7.4.0
```
----
## 文件閱讀
* [C Programming Lab: Assessing Your C Programming Skills](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~213/labs/cprogramminglab.pdf)
* [Linked Lists](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~iliano/courses/18S-CMU-CS122/handouts/10-linkedlist.pdf)
* [如何寫一個 Git Commit Message](https://blog.louie.lu/2017/03/21/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%AF%AB%E4%B8%80%E5%80%8B-git-commit-message/)
----
## 資料總覽
從 github 上將文件 clone 下來
```
$ git clone https://github.com/sysprog21/lab0-c
```
資料夾裡有:
```
$ ls
console.c harness.c LICENSE qtest qtest.dSYM queue.h README.md report.h traces
console.h harness.h Makefile qtest.c queue.c queue.o report.c scripts
```
其中,在 `README.md` 中有對這些檔案的解釋:
```
You will handing in these two files
* queue.h : Modified version of declarations including new fields you want to introduce
* queue.c : Modified version of queue code to fix deficiencies of original code
Tools for evaluating your queue code
* Makefile : Builds the evaluation program qtest
* README.md : This file
* scripts/driver.py : The C lab driver program, runs qtest on a standard set of traces
Helper files
* console.{c,h} : Implements command-line interpreter for qtest
* report.{c,h} : Implements printing of information at different levels of verbosity
* harness.{c,h} : Customized version of malloc and free to provide rigorous testing framework
* qtest.c : Code for qtest
Trace files
* traces/trace-XX-CAT.cmd : Trace files used by the driver. These are input files for qtest.
* They are short and simple.
* We encourage to study them to see what tests are being performed.
* XX is the trace number (1-15). CAT describes the general nature of the test.
* traces/trace-eg.cmd : A simple, documented trace file to demonstrate the operation of qtest
```
本次作業將針對 `queue.h` 及 `queue.c` 做修改
### 測試資料
使用`$ make test` 測試,內容尚未實作,得分為 `0`:
```
+++ TESTING trace trace-15-perf:
# Test performance of insert_tail, size, and reverse
ERROR: Insertion of gerbil failed (1 failures total)
ERROR: Computed queue size as 1431655765, but correct value is 1000000
ERROR: Computed queue size as 1431655765, but correct value is 1000000
--- trace-15-perf 0/7
--- TOTAL 0/100
```
----
## 實作
### Queue structure
`Queue` 中包含:
* 指向 Queue 頭端指標 `head`
* 指向 Queue 尾端指標 `tail`
* 可用來實現尾端插入,時間為 O(1)
* 紀錄 Queue 的大小 `int size`
* 計算 `queue size` 大小,時間為 O(1)
```clike
/* Queue structure */
typedef struct {
list_ele_t *head;
list_ele_t *tail;
int size;
} queue_t;
```
### Linked list element structure
每個 element 包含:
* 指向 element 中 string 的指標 `value`
* 指向下個 element 的指標 `next`
```clike
typedef struct ELE {
char *value;
struct ELE *next;
} list_ele_t;
```
### q_insert_head()
#### 功能
* Attempt to insert element at head of queue.
* Return true if successful.
* Return false if q is NULL or could not allocate space.
* Argument s points to the string to be stored.
* The function must explicitly allocate space and copy the string into it.
#### 作法
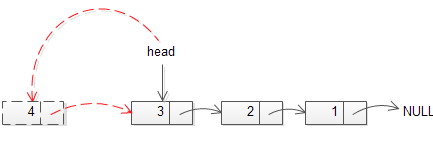
step 1: 新增一個節點 `newh`
step 2: 加入 `newh` 之值
step 3: 設定 `newh` 的下個節點為目前的 head
step 4: 將 head 設定為 `newh`
step 5: Queue size 加一
#### 實作
```clike
bool q_insert_head(queue_t *q, char *s)
{
if (q == NULL) {
return false;
}
list_ele_t *newh;
newh = malloc(sizeof(list_ele_t));
if (newh != NULL) {
newh->value = strdup(s);
if (q->head == NULL || q->tail == NULL) {
newh->next = NULL;
q->tail = newh;
} else {
newh->next = q->head;
}
q->head = newh;
q->size += 1;
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
```
#### 注意事項
* `return false` 時機:
* q 為 NULL
* 新增節點失敗時
* 若是 `newh` 為第一個節點 ,則需將 `tail` 指標指向 `newh`
#### 實測功能
```
cmd>new
q = []
cmd>ih 1
q = [1]
cmd>ih 2
q = [2 1]
cmd>ih 3
q = [3 2 1]
cmd>ih str 1000
q = [str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str ... ]
cmd>quit
Freeing queue
```
#### 有關新增字串
沿著程式中註解 `/* Don't forget to allocate space for the string and copy it */` 搜尋,找到 `strdup` 之函式:
```clike
char * strdup(const char *str1);
```
[cppreferece.com](https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/experimental/dynamic/strdup) 上的解釋,功能為複製字串,使用後需要自己釋放記憶體:
> Returns a pointer to a null-terminated byte string, which is a duplicate of the string pointed to by str1. The returned pointer must be passed to free to avoid a memory leak.
相關實作方式, [stackoverflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/252782/strdup-what-does-it-do-in-c) 上有更詳盡的說明:
```clike
char *strdup(const char *src) {
char *dst = malloc(strlen (src) + 1); // Space for length plus nul
if (dst == NULL) return NULL; // No memory
strcpy(dst, src); // Copy the characters
return dst; // Return the new string
}
```
### q_insert_tail()
#### 功能
* Attempt to insert element at tail of queue.
* Return true if successful.
* Return false if q is NULL or could not allocate space.
* Argument s points to the string to be stored.
* The function must explicitly allocate space and copy the string into it.
#### 作法
step 1: 新增一個節點 `newt`
step 2: 加入 `newt` 之值
step 3: 設定 `newt` 的下個節點為 NULL
step 4: 將原先 tail 節點的下一個結點設為 `newt`
step 5: 將 tail 設定為 `newt`
step 6: Queue size 加一
```clike
bool q_insert_tail(queue_t *q, char *s)
{
if (q == NULL)
return false;
list_ele_t *newt;
newt = malloc(sizeof(*newt));
if (newt != NULL) {
newt->value = strdup(s);
if (newt->value == NULL) {
free(newt);
return false;
}
if (q->head == NULL && q->tail == NULL) {
q->head = newt;
} else {
q->tail->next = newt;
}
newt->next = NULL;
q->tail = newt;
q->size += 1;
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
```
#### 注意事項:
* 因為在 Queue 中加入 `tail` 指標,因此 `q_insert_tail()` 得以在 O(1) 中實現
* 大致作法與 `qinsert_head` 相似,需注意新增時 `head` 與 `tail` 指標相關事宜
#### 實測功能:
```
cmd>new
q = []
cmd>it 1
q = [1]
cmd>it 2
q = [1 2]
cmd>it 3
q = [1 2 3]
cmd>quit
Freeing queue
```
### q_free()
#### 功能
* Free all storage used by queue
* 若 Queue 是空的,則不做任何動作
#### 作法
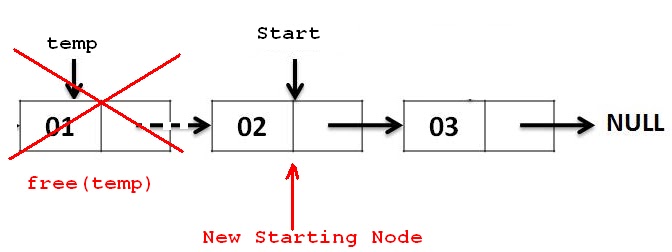
step 1: 新增節點 `tmp`
step 2: `tmp` 指向 `head`
step 3: 將 `head` 設為原先 `head` 的下一個
step 4: 釋放原先 `head` 中 value 所佔的空間
step 5: 釋放 `tmp` 指標 ,回到 `step 1` 重複直到 `head` 為 NULL
step 6: 釋放 `q` 指標
```clike
void q_free(queue_t *q)
{
if (q == NULL)
return;
while (q->head != NULL) {
list_ele_t *tmp;
tmp = q->head;
q->head = q->head->next;
free(tmp->value);
free(tmp);
}
free(q);
}
```
#### 注意事項
原先程式:
```clike
void q_free(queue_t *q)
{
if (q == NULL)
return;
while (q->head != NULL) {
list_ele_t *tmp;
tmp = q->head;
q->head = q->head->next;
free(tmp);
}
free(q);
}
```
使用 `$valgrind ./qtest` 測試,雖然 `free` 但是記憶體並未完整被釋放,觀察 `valgrind` 顯示中的訊息:
```
$ valgrind ./qtest
cmd>new
cmd>new
q = []
cmd>ih str 1000
cmd>ih str 1000
q = [str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str ... ]
cmd>quit
cmd>quit
Freeing queue
ERROR: Freed queue, but 1001 blocks are still allocated
==13472== 64 bytes in 1 blocks are still reachable in loss record 1 of 2
==13472== at 0x4C2FB0F: malloc (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_memcheck-amd64-linux.so)
==13472== by 0x10CFF7: test_malloc (harness.c:130)
==13472== by 0x10D3E3: q_new (queue.c:27)
==13472== by 0x109402: do_new (qtest.c:108)
==13472== by 0x10BD43: interpret_cmda (console.c:218)
==13472== by 0x10BDE6: interpret_cmd (console.c:239)
==13472== by 0x10CCA4: cmd_select (console.c:605)
==13472== by 0x10CE0E: run_console (console.c:642)
==13472== by 0x10A872: main (qtest.c:583)
==13472==
==13472== 44,000 bytes in 1,000 blocks are still reachable in loss record 2 of 2
==13472== at 0x4C2FB0F: malloc (in /usr/lib/valgrind/vgpreload_memcheck-amd64-linux.so)
==13472== by 0x10CFF7: test_malloc (harness.c:130)
==13472== by 0x10D227: test_strdup (harness.c:189)
==13472== by 0x10D4B2: q_insert_head (queue.c:70)
==13472== by 0x1096B5: do_insert_head (qtest.c:166)
==13472== by 0x10BD43: interpret_cmda (console.c:218)
==13472== by 0x10BDE6: interpret_cmd (console.c:239)
==13472== by 0x10CCA4: cmd_select (console.c:605)
==13472== by 0x10CE0E: run_console (console.c:642)
==13472== by 0x10A872: main (qtest.c:583)
==13472==
```
延著註解方向思考 `/* How about freeing the list elements and the strings? */` 是否是在釋放 linked list 中字串中的資料並未被釋放,因為在 q_insert_head() 中,使用了 `strdup(char *s)`配置了額外記憶體,因此需注意在使用後需自行 free 掉
:::success
增加一行 `free (tmp->value)` 即可改善此問題
:::
#### 實測功能
```
cmd>ih str 1000
q = [str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str ... ]
cmd>free
q = NULL
```
### q_remove_head()
#### 功能
* Attempt to remove element from head of queue.
* Return true if successful.
* Return false if queue is NULL or empty.
* If sp is non-NULL and an element is removed, copy the removed string to *sp(up to a maximum of bufsize-1 characters, plus a null terminator.)
* The space used by the list element and the string should be freed.
#### 作法
remove head 相對比 remove list 上的任意節點相對簡單,觀念上與 `q_free()` 一樣,但是這邊有額外要求要複製被刪除節點中的數值,其大小最大為 bufsize -1
:::info
bufsize 在 qtest.c 檔中定義大小為 256
:::
```clike
bool q_remove_head(queue_t *q, char *sp, size_t bufsize)
{
if (q == NULL)
return false;
if (q->size == 0)
return false;
if (sp != NULL) {
strncpy(sp, q->head->value, bufsize - 1);
sp[bufsize - 1] = '\0';
}
list_ele_t *tmp;
tmp = q->head;
if (q->head != NULL)
q->head = q->head->next;
free(tmp->value);
free(tmp);
q->size -= 1;
return true;
}
```
#### 注意事項
* 在 `q_remove_head` 中,在 free 節點時亦需要做釋放節點中 value 之動作,加入動作後問題得以改善
#### 實測功能
```
q = [3 2 1]
cmd>rh
Removed 3 from queue
q = [2 1]
cmd>rh
Removed 2 from queue
q = [1]
cmd>rh
Removed 1 from queue
q = []
```
#### 有關複製字串
沿著複製、限制大小等需求,找到 `strncpy` 之函式,在 C99 版本下 [cpprefernce](https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/string/byte/strncpy) 做以下解釋,以下擷取部份:
> Copies at most count characters of the character array pointed to by src to the character array pointed to by dest, stopping at the first null character.
在複製字串時,會根據限制大小,簡單來說就是複製部份字串,測試如下:
```clike
int main(void)
{
char src[] = "hi";
char dest[6] = "abcdef"; // no null terminator
strncpy(dest, src, 5); // writes five characters 'h', 'i', '\0', '\0', '\0' to dest
printf("strncpy(dest, src, 5) to a 6-byte dest gives : ");
for (size_t n = 0; n < sizeof dest; ++n) {
char c = dest[n];
c ? printf("'%c' ", c) : printf("'\\0' ");
}
}
```
output:
```clike
strncpy(dest, src, 5) to a 6-byte dst gives : 'h' 'i' '\0' '\0' '\0' 'f'
```
:::info
若無指定成 `\0` 則為空白,output 為:
strncpy(dest, src, 5) to a 6-byte dest gives : 'h' 'i' '' '' '' 'f'
:::
### q_size()
#### 功能
* Return number of elements in queue.
* Return 0 if q is NULL or empty
#### 作法
因為先前在 Queue 結構中加入 size 欄位,使得得到 Queue size 變得相當簡單,也使得此功能在 O(1) 完成
```clike
int q_size(queue_t *q)
{
if (q == NULL || q->head == NULL) {
return 0;
} else
return q->size;
}
```
:::info
若未紀錄 size 值,則需走訪整個 Linked list 計算 node 總數,時間為 O(n)
:::
#### 實測功能
```
cmd>new
q = []
cmd>ih str 1000
q = [str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str str ... ]
cmd>size
Queue size = 1000
```
### q_reverse()
#### 功能
* Reverse elements in queue
* No effect if q is NULL or empty
#### 作法
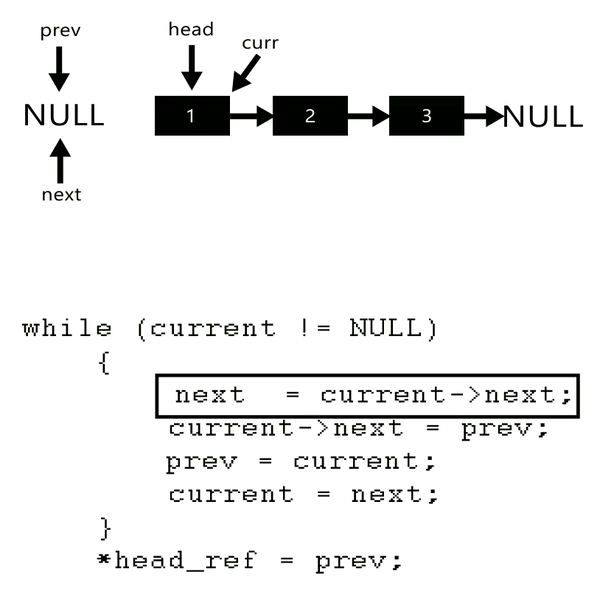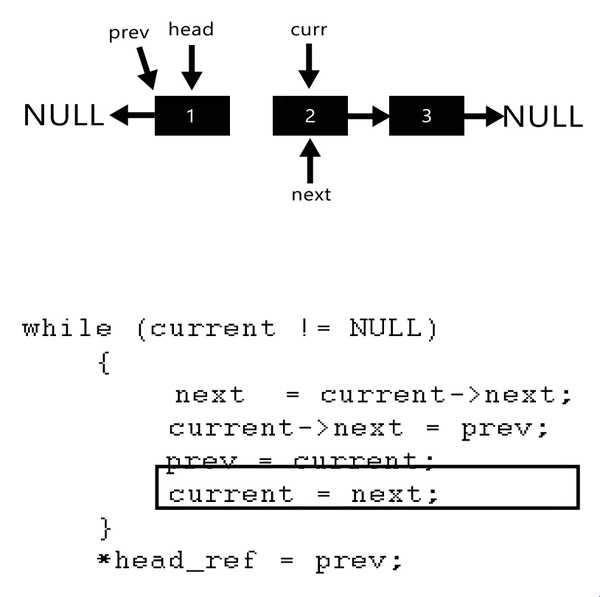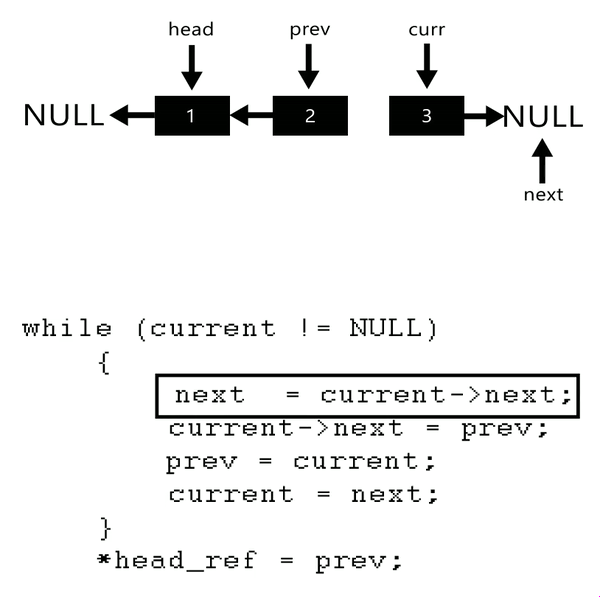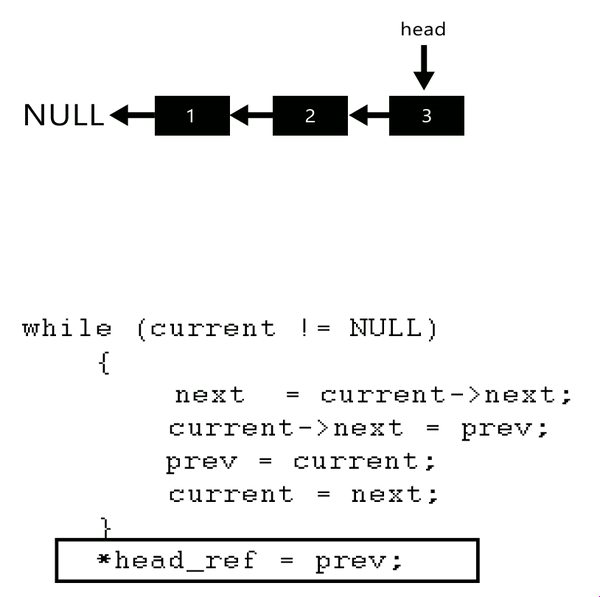
step 1: 新增三個節點 `prev`、 `current`、 `next` ,將 `curr` 指向目前的 `head`
step 2: 將 `tail` 指標指向 `head`
step 3: 將 `curr` 的下個節點設為 `next`
step 4: 將 `prev` 設為 `curr` 的下個節點
step 5: 將 `prev` 設為 `curr`
step 6: 將 `curr` 設為 `next`
step 7: 返回步驟 `3` ,重複直到 `curr` 指到 NULL
step 8: 將 prev 設為 `head`
如圖所示:
```clike
void q_reverse(queue_t *q)
{
if (q == NULL || q->size <= 1)
return;
list_ele_t *prev;
list_ele_t *curr;
list_ele_t *next;
prev = NULL;
curr = q->head;
next = NULL;
q->tail = q->head;
while (curr != NULL) {
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
q->head = prev;
}
```
#### 注意事項
* 最後 `curr` 會指向 NULL ,因此 `head` 為 `prev`
#### 實測功能
```
q = [5 4 3 2 1]
cmd>reverse
cmd>reverse
q = [1 2 3 4 5]
```
----
## 測試結果
測試程式正確性:
```
$ make test
scripts/driver.py
--- Trace Points
--- TOTAL 100/100
```
測試程式 memory 使用情形:
```
$ make valgrind
cp qtest /tmp/qtest.RvdGVO
chmod u+x /tmp/qtest.RvdGVO
sed -i "s/alarm/isnan/g" /tmp/qtest.RvdGVO
scripts/driver.py -p /tmp/qtest.RvdGVO --valgrind
--- Trace Points
--- trace-15-perf 7/7
--- TOTAL 100/100
```
## 疑難雜症
### 格式問題
若是程式沒有按照編排規則, git hooks 會發會作用,在 commit 時會出現以下提示訊息:
```
$ git commit
--- /tmp/tmp.mqgOs23CNd/queue.c 2019-10-01 13:08:54.657806586 +0800
+++ /tmp/tmp.mqgOs23CNd/.merge_file_wFQJ9r.y4D0ly 2019-10-01 13:08:54.685806165 +0800
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ queue_t *q_new()
if (q == NULL)
return false;
/* What if malloc returned NULL? */
- q->head = NULL;
+ q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0; /* Size initialize */
return q;
[!] queue.c does not follow the consistent coding style.
```
解決方法:
step 1: 輸入 `$clang-format -i queue.c` ,使用 clang-format 將程式編排至風格一致
step 2: 再將檔案新增 `$git add queue.c`
step 3: 重新 commit 後即解決問題
### 有關 pre-commit
打開在 `/.git/hooks` 目錄中的 `pre-commit.hook` 檔,紀錄 `pre-commit` 要做的檢查,包含 `diff` , `clang-format` 與 `cppcheck`:
```
$ cat ../../scripts/pre-commit.hook
#!/usr/bin/env bash
CPPCHECK_OPTS="-I. -I./include --error-exitcode=1 ."
RETURN=0
CLANG_FORMAT=$(which clang-format)
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "[!] clang-format not installed. Unable to check source file format policy." >&2
exit 1
fi
CPPCHECK=$(which cppcheck)
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "[!] cppcheck not installed. Unable to perform static analysis." >&2
exit 1
fi
DIFF=$(which colordiff)
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
DIFF=diff
fi
FILES=`git diff --cached --name-only --diff-filter=ACMR | grep -E "\.(c|cpp|h)$"`
for FILE in $FILES; do
nf=`git checkout-index --temp $FILE | cut -f 1`
tempdir=`mktemp -d` || exit 1
newfile=`mktemp ${tempdir}/${nf}.XXXXXX` || exit 1
basename=`basename $FILE`
source="${tempdir}/${basename}"
mv $nf $source
cp .clang-format $tempdir
$CLANG_FORMAT $source > $newfile 2>> /dev/null
$DIFF -u -p -B "${source}" "${newfile}"
r=$?
rm -rf "${tempdir}"
if [ $r != 0 ] ; then
echo "[!] $FILE does not follow the consistent coding style." >&2
RETURN=1
fi
if [ $RETURN -eq 1 ]; then
echo "" >&2
echo "Make sure you indent as the following:" >&2
echo " clang-format -i $FILE" >&2
echo
fi
done
# static analysis
$CPPCHECK $CPPCHECK_OPTS >/dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
RETURN=1
echo "" >&2
echo "Fail to pass static analysis." >&2
echo
fi
exit $RETURN
```
#### diff
* 功能:比較同檔案不同版本間的差異
使用 `git log ` 檢視先前 commit ,再使用 `git diff` 可比較兩版本間之差異,實測如下:
```
$ git log
Free node value in remove head
commit 0a3dc04a6fc10a0357e71c4493b3151921a72cc6
Author: Fred <xl86305955@freddy50407@gmail.com>
Date: Tue Oct 1 13:58:57 2019 +0800
Fix freed block problems while freeing
commit 2f215325a2f0c69f7c851bf27ba3c5a0629b54f4
Author: Fred <xl86305955@freddy50407@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Sep 30 23:26:22 2019 +0800
```
```
$ git diff 0a3dc 2f215
diff --git a/queue.c b/queue.c
index f8e6d79..52bdabd 100644
--- a/queue.c
+++ b/queue.c
@@ -42,7 +42,6 @@ void q_free(queue_t *q)
while (q->head != NULL) {
list_ele_t *tmp;
tmp = q->head;
- free(tmp->value);
q->head = q->head->next;
free(tmp);
}
```
#### cppcheck
有時過的了 compiler ,卻不一定過的了 `cppcheck`
`cppcheck` 負責找出一些由 programmer 犯下的錯但 compiler 能接受的 code
>Cppcheck is a static analysis tool for C/C++ code. It provides unique code analysis to detect bugs and focuses on detecting undefined behaviour and dangerous coding constructs. The goal is to detect only real errors in the code (i.e. have very few false positives
像是指標用完沒有釋放,就在 `cppcheck` `memory leak` 檢查範疇中
* 功能:
* Automatic variable checking
* Bounds checking for array overruns
* Classes checking (e.g. unused functions, variable initialization and memory duplication)
* Usage of deprecated or superseded functions according to Open Group
* Exception safety checking, for example usage of memory allocation and destructor checks
* Memory leaks, e.g. due to lost scope without deallocation
* Resource leaks, e.g. due to forgetting to close a file handle
* Invalid usage of Standard Template Library functions and idioms
* Miscellaneous stylistic and performance errors
#### clang-format
* 功能:能自訂排版風格,在每次 commit 的時候保持整體風格一致
像是這次的 `clang-format` 中,下面寫法就是非法的:
```clike
if (q == NULL) return;
```
會被修改成:
```clike
if (q == NULL) {
return;
}
```
以下為這次 `clang-format` 中紀錄的內容:
```
$ cat .clang-format
BasedOnStyle: Chromium
Language: Cpp
MaxEmptyLinesToKeep: 3
IndentCaseLabels: false
AllowShortIfStatementsOnASingleLine: false
AllowShortCaseLabelsOnASingleLine: false
AllowShortLoopsOnASingleLine: false
DerivePointerAlignment: false
PointerAlignment: Right
SpaceAfterCStyleCast: true
TabWidth: 4
UseTab: Never
IndentWidth: 4
BreakBeforeBraces: Linux
AccessModifierOffset: -4
```
搜尋之下發現,`clang` 是一種基於 llvm (low level virtual machine) 發展出的編譯器,原先 Apple 都使用 GCC 編譯 ,但是 Apple 推崇的 Object-C GCC 並不買單,因此 Apple 開始發展此編譯器

## 研究自動測試機制
### Makefile
* 目的:程式在撰寫時,會依據各式需求分隔成各式 `.c` ,`.h` 檔,因此要成為最終可執行檔前,所有程式皆必須被編譯才行,但是一個一個慢慢編譯又太麻煩。因此只要寫好 `Makefile` 檔,編譯器會根據 `makefile` 檔內容,透過 `$ make` 指令,編譯所有相關程式,並彙整出可執行檔。
因為在成為最終可執行檔前,寫好的程式會透過編譯器一層一層的轉換,因此我們必須先瞭解編譯時編譯器到底為我們做了哪些事
以下為GCC 編譯器的四個步驟:

Step 1: Preprocessor
* 主要功能:
* 清除註解
* 巨集替換
* 將 include 的檔案展開
利用 `$ gcc -E .c -o .i` 可產出 `.i` 檔
Step 2: Compiler
* 主要功能:
* 檢查程式正確性並轉成組合語言
以 hello world 為例
```
$ gcc -S helloworld.i -o helloworld.s
$ cat helloworld.s
.file "helloworld.c"
.text
.section .rodata
.LC0:
.string "hello world"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB0:
.cfi_startproc
pushq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 16
.cfi_offset 6, -16
movq %rsp, %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 6
leaq .LC0(%rip), %rdi
call puts@PLT
movl $0, %eax
popq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa 7, 8
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE0:
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 7.4.0-1ubuntu1~18.04.1) 7.4.0"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
```
Step 3: Assembler
* 主要功能:
* 透過 Assembler 將組合語言轉成機器看得懂的 machine language
Step 4: Linker
* 主要功能(取自CS:APP p.466):
* 符號解析(Symbol Resolution):Object files define and referencesymbols. The purpose of symbol resolution is toassociate each symbol reference with exactly one symbol definition
* 重新定位 (Relocation):compilers and assemblers generate code and data sections that start at address 0. Thelinkerrelocatesthese sections by associating a memory location with each symbol definition, andthen modifying all of the references to those symbols so thatthey point to this memory location
延伸閱讀:[链接器(linker)的作用](https://www.cnblogs.com/immortal-worm/p/5819036.html)

參考資料:[Everything you want to know about GCC](https://medium.com/@meghamohan/everything-you-want-to-know-about-gcc-fa5805452f96)
了解編譯過程後知道因為層與層之中檔案具相依關係,`makefile` 撰寫方式則是由上層往下層書寫,冒號左邊為最大的集合,右邊則為所有與最大集合相依的所有檔案

這次 makefile 內容:
```
$ cat Makefile
CC = gcc
CFLAGS = -O0 -g -Wall -Werror
GIT_HOOKS := .git/hooks/applied
all: $(GIT_HOOKS) qtest
$(GIT_HOOKS):
@scripts/install-git-hooks
@echo
queue.o: queue.c queue.h harness.h
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c queue.c
qtest: qtest.c report.c console.c harness.c queue.o
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o qtest qtest.c report.c console.c harness.c queue.o
test: qtest scripts/driver.py
scripts/driver.py
valgrind_existence:
@which valgrind 2>&1 > /dev/null
valgrind: qtest valgrind_existence
$(eval patched_file := $(shell mktemp /tmp/qtest.XXXXXX))
cp qtest $(patched_file)
chmod u+x $(patched_file)
sed -i "s/alarm/isnan/g" $(patched_file)
scripts/driver.py -p $(patched_file) --valgrind
@echo
@echo "Test with specific case by running command:"
@echo "scripts/driver.py -p $(patched_file) --valgrind -t <tid>"
clean:
rm -f *.o *~ qtest /tmp/qtest.*
rm -rf *.dSYM
(cd traces; rm -f *~)
```
最後加入了 `clean` 的動作,是因為在編譯時會產生出很多中間檔,刪除後使資料夾內的內容不會太過雜亂
延伸閱讀:
* [Makefile的寫法](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E1_uuFWibuM)
* [Makefile 語法和示範](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/SySTMXPvl?type=view)
### 評分方式
在 `README.md` 中寫到:
>scripts/driver.py : The C lab driver program, runs qtest on a standard set of traces
`scripts/driver.py` 也被寫在 `makefile` 裡,用來實現 `make test` 指令。檔案是用 python 撰寫,在 `./traces` 資料夾中有每個測驗對應的測試資料,以 `trace-03-ops` 為例子:
```
# Test of insert_head, insert_tail, reverse, and remove_head
--- trace-03-ops 6/6
```
對應的測試資料儲存在 `./scripts/trace-03-ops.cmd` ,以下為其中內容:
```
$ cat trace-03-ops.cmd
# Test of insert_head, insert_tail, reverse, and remove_head
option fail 0
option malloc 0
new
ih dolphin
ih bear
ih gerbil
reverse
it meerkat
it bear
it gerbil
reverse
it squirrel
reverse
rh squirrel
ih vulture
reverse
rh gerbil
rh bear
rh meerkat
rh gerbil
rh bear
rh dolphin
rh vulture
```
以下節錄跑測試資料的函式:
```python
$ cat driver.py
#!/usr/bin/python
import subprocess
import sys
import getopt
# Driver program for C programming exercise
class Tracer:
traceDirectory = "./traces"
qtest = "./qtest"
command = qtest
verbLevel = 0
autograde = False
useValgrind = False
traceDict = {
1 : "trace-01-ops",
2 : "trace-02-ops",
3 : "trace-03-ops",
4 : "trace-04-ops",
5 : "trace-05-ops",
6 : "trace-06-string",
7 : "trace-07-robust",
8 : "trace-08-robust",
9 : "trace-09-robust",
10 : "trace-10-malloc",
11 : "trace-11-malloc",
12 : "trace-12-malloc",
13 : "trace-13-perf",
14 : "trace-14-perf",
15 : "trace-15-perf"
}
traceProbs = {
1 : "Trace-01",
2 : "Trace-02",
3 : "Trace-03",
4 : "Trace-04",
5 : "Trace-05",
6 : "Trace-06",
7 : "Trace-07",
8 : "Trace-08",
9 : "Trace-09",
10 : "Trace-10",
11 : "Trace-11",
12 : "Trace-12",
13 : "Trace-13",
14 : "Trace-14",
15 : "Trace-15"
}
def runTrace(self, tid):
if not tid in self.traceDict:
print("ERROR: No trace with id %d" % tid)
return False
fname = "%s/%s.cmd" % (self.traceDirectory, self.traceDict[tid])
vname = "%d" % self.verbLevel
clist = [self.command, self.qtest, "-v", vname, "-f", fname]
try:
retcode = subprocess.call(clist)
except Exception as e:
print("Call of '%s' failed: %s" % (" ".join(clist), e))
return False
return retcode == 0
```
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet