# Hexaware
## Java
what is Java?
what is flow control?
What is short circuiting?
what is a constructor?
2.
### Java Reflection API
Java Reflection is a process of examining or modifying the run time behavior of a class at run time.
The java.lang.Class class provides many methods that can be used to get metadata, examine and change the run time behavior of a class.
The java.lang and java.lang.reflect packages provide classes for java reflection.
[link](https://www.javatpoint.com/java-reflection#:~:text=Java%20Reflection%20is%20a%20process%20of%20examining%20or,and%20java.lang.reflect%20packages%20provide%20classes%20for%20java%20reflection.)
### Java 8
* forEach method
* functional interface
* Stream API
* method reference
*
### pillars of OOP
#### encapsulation
#### abstraction
##### interface vs abstract class
An abstract class allows you to create functionality that subclasses can implement or override. An interface only allows you to define functionality, not implement it.
#### inheritance
* single level inheritance
* multi level inheritance
* Hierarchical inheritance
multiple inheritance is not supported by Java. Multiple inheritance is that a class can inherit properies from more than one parent class.
#### polymorphism
### Differences between JDK, JRE and JVM
1. JDK (Java Development Kit) is a Kit that provides the environment to develop and execute(run) the Java program. JDK is a kit(or package) that includes two things, Development Tools like compilers, debuggers. Another one is JRE.
JRE (to execute your java program).
2. JRE (Java Runtime Environment) is an installation package that provides an environment to only run(not develop) the java program onto your machine. It contains some class libraries, supporting files and JVM.
3. JVM (Java virtual machine).Both JRE and JDK has JVM and JVM is responsible for executing the java program. it is a interpreter that convert java bytecode into machine code.
#### Garbage collection
garbage collection in Java is an automatic process. The garbage collector find the unused objects in heap, delete those objects and release the memory.+
#### Difference between Primitive vs Reference variable
1. primitive type stores value. objects store reference.
2. Comparison using == operator
3. The first difference between primitive and reference types is that the former can never be null
4. Stack vs Heap: primitive type is created in stack, on the other hand, object is created in heap.
5. Memory consumption or Size: Primitive variables take less memory than reference variables because they don't need to maintain object metadata
Read more: https://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2015/09/difference-between-primitive-and-reference-variable-java.html#ixzz7ZL68OYsc
#### What is an array?
An array is a collection of similar data elements stored at contiguous memory locations. It is the simplest data structure where each data element can be accessed directly by only using its index number.
#### Wrapper class
Wrapper classes provide a way to use primitive data types as objects.
### DataStructure
#### Stack
A stack is a special area of computer’s memory which stores temporary variables created by function. In stack, variables are declared, stored and initialized during runtime.
This is the temporary memory where variable values are stored when their methods are invoked. After the method is finished, the memory containing those values is cleared to make room for new methods.
References, primitives live on the stack
Even though objects live in the heap the reference to those objects live in the stack
#### Heap
It’s created by the Java Virtual Machine when it starts. The memory is used as long as the application is running. When an object is created, it is always created in Heap and has global access.
#### ArrayList
>It’s a dynamically resizing array which have the benefit of an array while offering flexibility in size. arraylist grow its capacity whenever we run out of space.
* What is collection?
> A Collection is a group of individual objects represented as a single unit.
* Tell me about list in Java ?
> Its a interface in java. We use ArrayList and LinkedList ...and more
* What is big O(n)?
> Big O Notation refers to the complexity of a given algorithm. n refers to the size of the input.
#### Interface
An interface only contains abstract method and static variable. The interface in Java is a blueprint of a class.
> default interface can have implementation.
* scope: scope defines where a certain variable or method is accessible in a program. There are three types of scope. Class scope, method scope and block scope.
* override variable
* what is method signature?
* It's the combination of the method name and the parameter list.
* StringBuilder is faster and preferred over StringBuffer for the single-threaded program. If thread safety is needed, then StringBuffer is used.
* Comparable is meant for objects with natural ordering which means the object itself must know how it is to be ordered. For example Roll Numbers of students. Whereas, Comparator interface sorting is done through a separate class.
* A basic differentiating feature is that using comparable we can use only one comparison. Whereas, we can write more than one custom comparators as you want for a given type.
* final: final is a non-access modifier. If we make a class as final, the class can't be extended. A final method can't be override. The value of a final variable cannot be changeed.
* finalize: The finalize() method is called the finalizer. Finalizers get invoked when JVM figures out that this particular instance should be garbage collected.
* The finally statement defines a code block to run regardless of the result.
* JDBC: JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is the Java API that manages connecting to a database,
### Exception
* https://beginnersbook.com/2013/04/user-defined-exception-in-java/
* exception handling: Exception handling ensures that the flow of the program doesn't break when an exception occurs.
what are exceptios?
> exception is an unwanted or unexpected event, which occurs during the execution of a program that disrupt the normal flow of the program.
Errors
> Errors usually occur in the abnormal conditions. For example: OutOfMemoryError, StackOverflowError. It's a bad idea to catch an error and program is not possible to recover from an error.
` When an error occurs, the method creates an object and hands it off to the runtime system. The object, called an exception object, contains information about the error, including its type and the state of the program when the error occurred. Creating an exception object and handing it to the runtime system is called throwing an exception. `
### Thread
A thread in Java is the direction or path that is taken while a program is being executed.
#### Creating thread
* thread:two ways to create a thread,
* Extending java.lang.Thread class.
* Implementing Runnable interface
> Thread Class vs Runnable Interface
> We can achieve basic functionality of a thread by extending Thread class because it provides some inbuilt methods like yield(), interrupt() etc. that are not available in Runnable interface.
> If we extend the Thread class, our class cannot extend any other class because Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance. But, if we implement the Runnable interface, our class can still extend other base classes.
> Using runnable will give you an object that can be shared amongst multiple threads.
#### thread deadlock
If thread 1 locks A, and tries to lock B, and thread 2 has already locked B, and tries to lock A, a deadlock arises. Thread 1 can never get B, and thread 2 can never get A. In addition, neither of them will ever know. They will remain blocked on each their object, A and B, forever. This situation is a deadlock.
#### using thread
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17756255/accessing-a-variable-of-a-thread-from-another-thread-in-java
### Stream
Stream api is used to process collections of objects and it supports various methods which can be pipelined to produce the desired result.
* Stream: Stream is an API that is introduced in Java 8 which is used to process collections of objects. A stream is a sequence of objects that supports various methods which can be pipelined to produce the desired result.
#### intermediate operations
#### terminal operations
* Collections:The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate the group of objects.
### Functional interface and lambdas
1. A functional interface is an interface that contains only one abstract method and it often goes with lambda expressions.
3. Comparator and Runnable are examples of functional interfaces.
* lambdas: A lambda expression is a short block of code which takes in parameters and returns a value. Lambda expressions are similar to methods.
#### method references
Reference to an Instance Method of a Particular Object.
Method references are a special type of lambda expressions. They're often used to create simple lambda expressions by referencing existing methods.
### String pool
String Pool is a storage area in Java heap.
>Each time a string literal is created, the JVM checks the string literal pool first. If the string already exists in the string pool, a reference to the pooled instance returns. If the string does not exist in the pool, a new String object initializes and is placed in the pool.
#### Difference Between == and .equals() Method in Java
== is an operator and it compares references. .equals is a method and it compares content.
## data struceture
big o of 1 time complexit
## SQL
* what is outer join?
> outer join returns all records that have value either in left or right table.
The **INNER JOIN** keyword selects records that have matching values in both tables.
SQL function and procedure.
SQL trigger
Triggers are special types of stored procedures (SQL Statements) that are automatically executed when operations are performed on a table within the database. It is not possible to invoke triggers on-demand. The triggers are more like event handlers since they are executed on a specific occasion. A trigger is triggered only whenever an action (INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE) is performed on the table on which it is defined.
* many to many relation
1. **one to one:** When a row in a table is related to only one role in another table and vice versa,we say that is a **one to one relationship**. This relationship can be created using *Primary key-Unique foreign key constraints*.
2. **one to many:** This is where a row from one table can have multiple matching rows in another table this relationship is defined as a **one to many relationship**.
3. many to many: A row from one table can have multiple matching rows in another table, and a row in the other table can also have multiple matching rows in the first table this relationship is defined as a **many to many relationship**.
*
## Spring
### Inversion of control
Inversion of Control (IoC) is a design principle that allows classes to be loosely coupled and, therefore, easier to test and maintain.
### Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection (DI) is a programming technique that makes a class independent of its dependencies
Dependency injection is a pattern we can use to implement IoC, where the control being inverted is setting an object's dependencies.
Connecting objects with other objects, or “injecting” objects into other objects, is done by an assembler rather than by the objects themselves.
#### dependecies injection: Dependency injection is a programming technique that makes a class independent of its dependencies.
diff:
1. constructor Injection does not allow you to construct an object until your dependencies are ready. On the other hand, we can not guarantee that certain dependency is injected or not if we use setter injection.
2. setter injection is more readable.
3. setter can be overridden.
Read more: https://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2012/11/difference-between-setter-injection-vs-constructor-injection-spring-framework.html#ixzz7WDqYiMwn
* What are some stereotype annotations?
>@Repository, @Service, @Controller
* @Controller vs @ RestController: @RestController annotation is a special controller used in RESTful Web services, and it’s the combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody annotation.
### spring boot vs spring:
Spring Boot is basically an extension of the Spring framework. It has autoconfiguration that can speed up and simplify development.
<!-- Spring Boot provides a number of starter dependencies for different Spring modules. -->
### spring
Spring framework is a java EE (Enterprise Edition) framework that is used to build applications.
### ApplicationContext
`ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationcontext/student-bean-config.xml");`
### bean life cycle
> The lifecycle of any object means when & how it is born, how it behaves throughout its life, and when & how it dies. Similarly, the bean life cycle refers to when & how the bean is instantiated, what action it performs until it lives, and when & how it is destroyed. In this article, we will discuss the life cycle of the bean.
### Scope of Bean in spring
1. singleton 2. prototype 3. request 4. session 5. application 6. websocket
### Spring IoC container
Spring Ioc container create and manage all objects in Java.
It creates the objects, configures and assembles their dependencies, manages their entire life cycle. The Container uses Dependency Injection(DI) to manage the components that make up the application.
### AOP:
AOP stands for Aspect-Oriented Programming. AOP uses aspects instead of objects like OOP does. This allows handling of cross-cutting concerns, which are parts of a program that rely upon other parts or that affect other parts of a program entirely. Concerns that are handled in an application many times are: logging, security, and data transfer.
### Spring MVC
* A Spring MVC is a Java framework which is used to build web applications. It follows the Model-View-Controller design pattern. It implements all the basic features of a core spring framework like Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection.
## Angular
### Component
A component encapsulate data, html template, and the logic
angular life cycle: In Angular, every component has a life-cycle, a number of different stages it goes through from initializing to destroying.
> 8 stages
> ngOnChanges
> ngOnInit
> ngDoCheck
> ngAfterContentInit
> ngAfterContentChecked
> ngAfterViewInit
> ngAfterViewChecked
> ngOnDestroy
* augular component: Components are the main building block for Angular applications. an html, a typeScript class, a css selector.
### Angular directive
Directives are classes that add additional behavior to elements in the Angular applications. For example we can use ngif to show or hide particular element on the page.
### angular observable
Observables are used to handle asychronous operation like HTTP response.
### Angular Data Binding
* Interpolation
* property binding
* event binding
* two-way-data-binding: Two-way binding gives components in your application a way to share data. Use two-way binding to listen for events and update values simultaneously between parent and child components.
### Angular expression
Expressions are used to bind application data to HTML. Expressions are written inside double curly braces such as in {{ expression}}.
## RESTFUL
REST is a set of guidelines that software can use to communicate over the internet.
A REST API (also called a “RESTful” API) is a specific type of API that follows these guidelines.
## design pattern
Singleton Pattern, Factory Pattern
### Factory design pattern
We define an interface and let the subclasses decide which object to instantiate. We use Factory method to create the object we want.
## DAO pattern
The Data Access Object is basically an object or an interface that provides access to an database.
## throw vs throws
**Throw**: The throw keyword in Java is used to explicitly throw an exception from a method or any block of code.
**Throws:** throws is a keyword in Java which is used in the signature of method to indicate that this method might throw one of the listed type exceptions. The caller to these methods has to handle the exception using a try-catch block.
my explanation: throws is a key word we use in a method. it indicate that the method might throw one of the listed exceptions.
## Docker
We haven't covered it yet. But I know Ducker is a deployment platform that helps developers building, running, and shipping their application. Docker packages up everything applications need and run it on any machine with docker.
## Microservices
Microservices are an architectural style that develops a single application as a set of small services.
https://microservices.io/patterns/microservices.html
## Devops
### What is DevOps?
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increase an organization’s efficiency to deliver application and services. This allows deploying code to production faster and in an automated way.
### AWS
#### EC2
Where EC2 is like a remote computer running Windows or Linux, S3 is simply a storage service for storing large binary files.
#### S3
simple stroage service. It's a webservice that we can storing data there.
## Questions to ask
How would you describe a typical day in this position?
What's the most important thing I should accomplish in first ninty days?
What's your management style?
how would you describe the company culture?
#### Difference between method and function?
The difference is that a method is associated with an object, while a function is not.
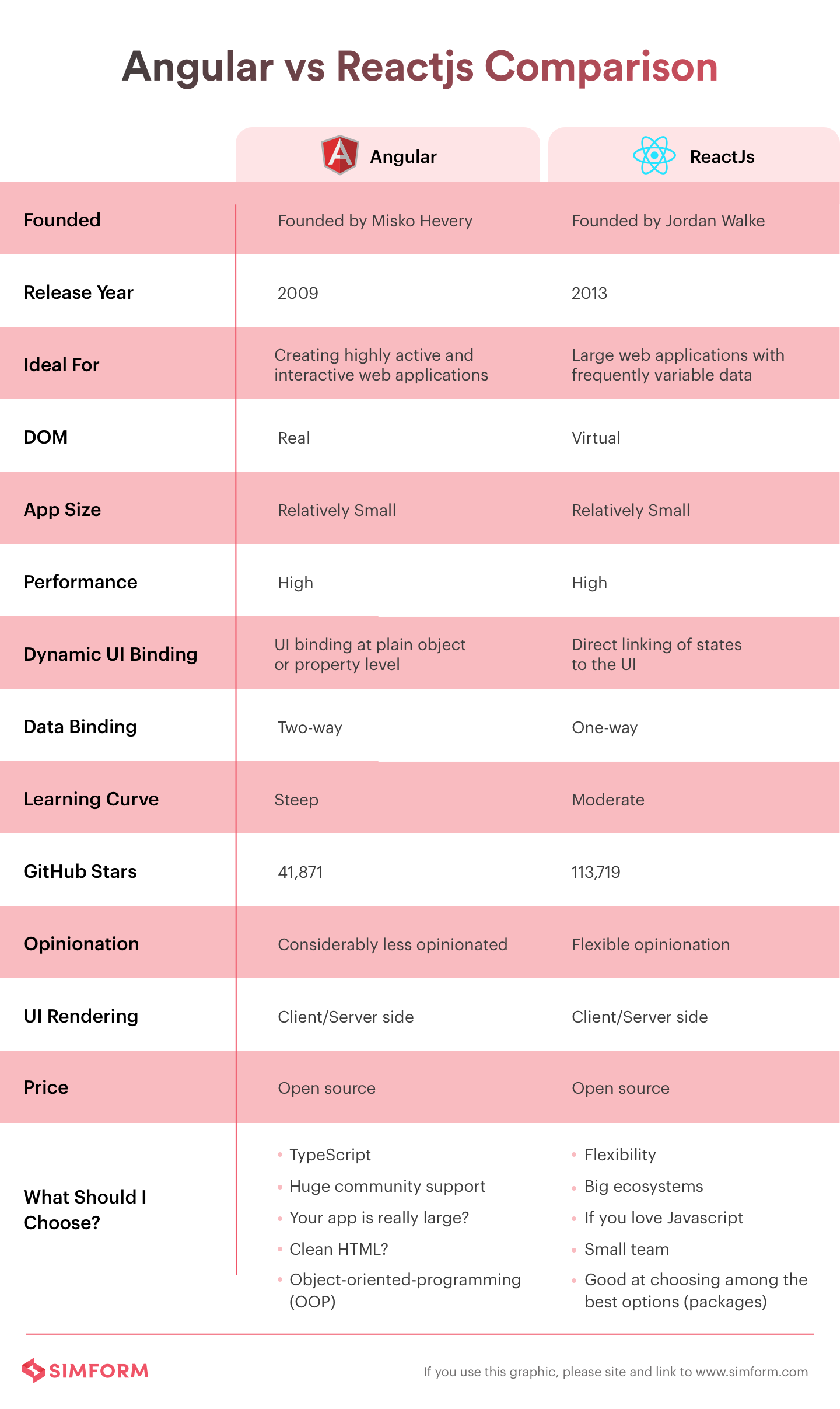
#### React vs Angular
marker interface
collections vs collection
some input take object
### 5 years
As a mid-level software developer, I see myself progressing into a senior role within five years and taking on more responsibility.
angularjs lifecyle scope
filter
beanlife
### Agile
xml bean
two ways to autowired an object
spring beanfactory and spring applicationcontext
context.getBean
spring container
-----------
1. what is Angular component vs angular service?
2. service: Service is a piece of reusable code with a focused purpose. A code that you will use across muService is a piece of reusable code with a focused purpose. A code that you will use across multiple components in your application.
Our components need to access the data. You can write data access code in each Component, but this is very inefficient and breaks the rule of single responsibility. The Component should focus on presenting the data to the user.
The task of receiving data from the back-end server should be delegated to another class. We call a class a service class because it provides each Component with the data it needs.ltiple components in your application.
Our components need to access the data. You can write data access code in each Component, but this is very inefficient and breaks the rule of single responsibility. The Component should focus on presenting the data to the user.
The task of receiving data from the back-end server should be delegated to another class. We call a class a service class because it provides each Component with the data it needs.
3.what design pattern?