---
title: Git Note
tags: Git
---
[two dots & three dots](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/462974/what-are-the-differences-between-double-dot-and-triple-dot-in-git-com)
:::info
HEAD 的代號為 @
^^^^^ = ~5
`git reset ~5` 表示 reset 到相對於HEAD 所在 commit 的五個版本以前
:::
## Convenient setup
### setup by shell script
```shell
$ git config --global core.editor "vim"
$ git config --global user.name "<NAME>"
$ git config --global user.email "<EMAIL@ADDRESS>"
$ git config --global alias.ll 'log --graph --pretty=format:"%h <%an> %ar%n comment: %s%n"'
$ git config --global alias.la 'log --graph --oneline --all'
$ git config --global alias.ls 'log --graph --oneline'
$ git config --global alias.unstage 'reset HEAD --'
$ git config --list
```
### directly edit in config file
```
[core]
editor = vim
[user]
email = "user_email"
name = "user_name"
[alias]
ll = log --graph --pretty=format:\"%h <%an> %ar%n comment: %s%n\"
la = log --graph --oneline --all
ls = log --graph --oneline
unstage = reset HEAD --
co = checkout
st = status -uno
amend = commit --amend --no-edit
```
# Overview
## terminology
- repository:
**觀念上**:儲存庫,顧名思義就是已經整理好進行歸檔的檔案所在的地方稱之。
**對應檔案**:主要為 ==.git== 目錄底下的 objects\ 及 refs\。
- storaging area:
**觀念上**:working directory 與 repository 之間的暫存區,在我們實際將 working directory 的更動內容實際裝成送進 repository 之前的暫存。也可以說是在調整這次 commit 的 working tree 長什麼樣。
**對應檔案**: 主要為 ==.git\index== 但該檔案,還會存有額外資訊來比對 working directory 中哪些檔案被更動過。
- working directory:
**觀念上**:我們實際編輯檔案的地方稱之。凡是新增、刪除、修改檔案均在此處為之。也可以說是 git 實際管理的檔案
**對應檔案**:就是 ==.git== 目錄所在的資料夾(及其底下的檔案)。但在後來 git 新增的功能中還可以另外建立 sub working-directory.
- working tree:
**觀念上**:某次 commit 。在它 commit 當下所以的檔案以及它當時的狀態。tree 這個詞源自於 git 在進行版控時會將所有的檔案壓縮為一個個 blob 物件。 在利用 tree 物件(相當於資料夾的角色)來表示 working directory 檔案即資料夾的關係。整個結構就像一個樹狀資料結構。
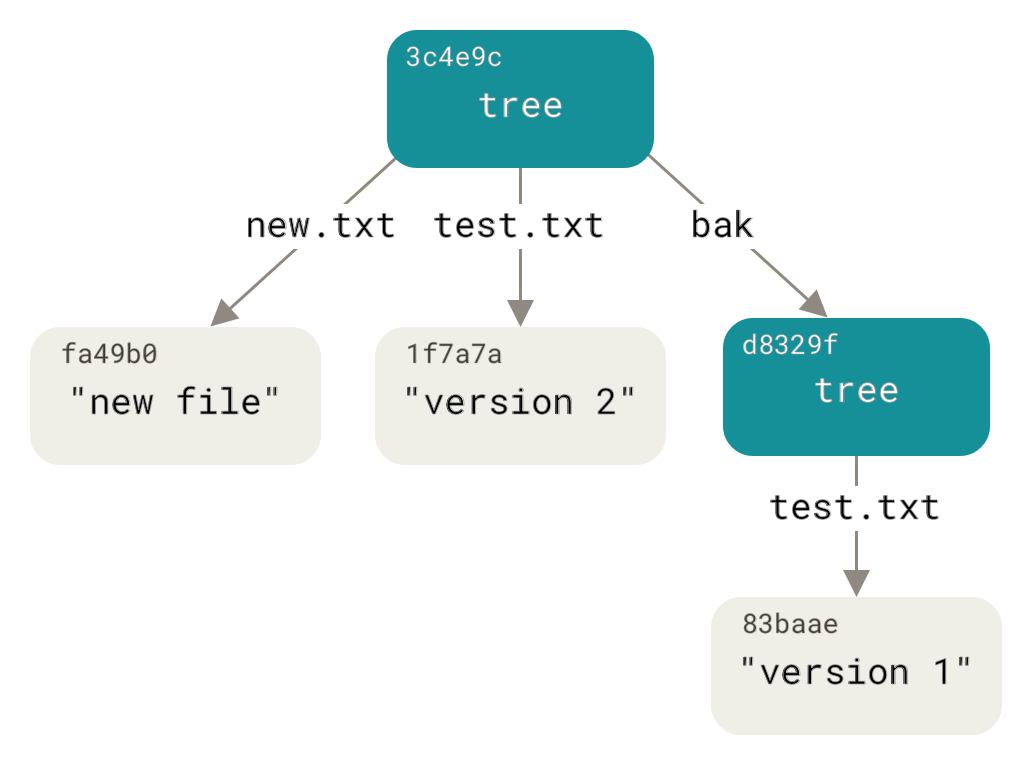
圖片來源:https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Internals-Git-Objects
> 做個比喻 working tree 就是生產設施,會產生各式各樣的產品,而 storaging area 就是倉庫前的集貨廣場。在這裡你會選擇要把哪些產品在這一梯次一起送進倉庫,在具體一點就是你會拿一個紙箱開始挑你要送進倉庫的產品(透過add指令),接著就是送進 repository 了(透過commit) 指令,再者你可能會在箱子外面貼上標籤指寫些 comment (透過 -m "\<your comment\>")
[name=改寫自**為你自己學GIT_高見龍**]
### Feature
"A **distributed** revision control system"
兩大特色
1. **distributed**: git 不需要中央 server 就可以在電腦上獨立運作。因為整個資料都是由**.git**管理,因此 .git 在版本紀錄就在,反之,就 GG 了。PS:如果想要,也是可以透過建立 server 還分享 .git 目錄達到共同開發的目的。
2. **snapshot**: git 在紀錄檔案的時候是直接將原始檔案壓縮直接塞進資料庫。所以再回溯版本的時候只要將該本所有檔案解加縮去代當前目錄就可以了。速度相當的快,有別於早期版本控制是紀錄版本差異,在回溯的時候要不斷的往回 trace 版本差異將檔案重建。
:::warning
git 也是會紀錄版本差異。但通常是在丟到遠端資料庫或是手動呼叫 garbage collection 的時候。也就是會將比較穩定。更動頻率較低的檔案改採版本差異的方式紀錄。
:::
## 如何運作
[Git Internals](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Internals-Plumbing-and-Porcelain)
# config
存放目錄
| | directory |
|--------|-----------------|
| local | repository |
| global | ~/.gitconfig |
| system | /etc/.git/config|
## 常用指令
```bash
$ git config --<global/local/system> user.name <User_name>
$ git config --<global/local/system> user.email <User_name>
$ git config --<global/local/system> alias.<alias_name> "command"
$ git config --<global/local/system> core.editor <editor_launch_command>
$ git coonfig --list # list all configuration
$ git config <key> #ex: git config user.name
```
# repository、 staging area、 working directory
## 常用指令
```bash
$ git init # 初始化當前目錄作為git repository
$ git add <file_name> # 將工作目錄的變動加入暫存區
$ git add -p <file_name> # partial add,會跳出視窗選擇要stage 的部份。
$ git reset <file_name> # 移出暫存區
$ git commit -a # 直接提交所有已 trace 的檔案
$ git commit -m "<commit message>" # 將暫存區置入儲存庫
$ git commit --amend -m "<commit message>" # 修改上一次的comment
$ git commit --amend --no-edit # 追加檔案道上一次commit 不修改comment
$ git ststus # 顯示工作區、暫存區狀態
$ git rm <file_name> # 相當於 rm <file_name> && git add <file_name>
$ git rm <file_name> --cached # 只是stop tracking不移除檔案
$ git mv <old_name> <new_name> # 改名
```
:::info
add . vs add --all
前者僅將當前目錄及其子目入底下檔案加入暫存區,後者為 repository 底下所有檔案
:::
## checkout
把 respository 底下的某個物件拉出來解壓縮,蓋掉當前目錄的檔案,預設是使用 staging area 對應的 objects 來蓋掉當前 working directory 的檔案。
```bash
$ git checkout <file_name> # checkout 特定檔案
$ git checkout . # checkout 所有檔案
$ git checkout HEAD^^ <file_name> # 把指定檔案的HEAD 打回兩個版本前
```
## log
```bash
$ git log --author="<name>" # 找特定作者
$ git log --grep="<message>" # 找特定訊息
$ git log <file_name> # 顯示特定檔案日誌
$ git log -p # 顯示日誌含修改(+,-)行資訊
$ git log --since='9am' --until='12am' --after='2017-01'
$ git log -n <num> # 只顯示 num 筆紀錄
$ git blame [-L <s>,<e>] <file_name> # 顯示檔案line_s~line_e修改紀錄(時間、作者)
```
## reflog
紀錄 HEAD 所指的地方
```
$ git reflog
$ git log -g
```
## Stash
用來暫存未完成的工作,其儲存區類似 stack
```
$ git stash # 儲存當前的工作區進度
$ git stash list # 查看目前存起來的清單{}號碼越小越新存放在stack越上面
$ git stash apply stash@{} # 將暫存進度套用到當前分支上(暫存仍保留在stash)
$ git stash drop stash@{} # 將不要的暫存丟棄
$ git stash pop stash@{} # apply + drop(暫存不pop 後由stash 刪除)
```
## Reset
Note: reset 實際上不是回溯到過去,然後把東西丟掉,而是在移動當前 branch 所指到的位置。
- 透過`git reflog` 可以查看變化
```bash
$ git reset <相對位置或絕對位置>
```
|模式 |Mixed |soft |hard |
|----------|----------|--------|------|
|工作目錄 |不變 |不變 |丟掉 |
|暫存 |丟掉 |不變 |丟掉 |
|拆出來的檔案|丟回工作目錄|丟回暫存區|直接丟掉|
> 1. soft 只是重新指向把head 移動到其他,\<commit\>
> 2. mixes 會將暫存區全部丟棄,工作區保留。此時`git status` 顯示的狀態為working tree 與\<commit\>比較的結果
# branch
branch就像一張標籤紙貼在某一次的commit上,當新的commit事件發生時新的commit物件會指向上一次HEAD所在的commit。其中,HEAD也可向像是一張標籤紙但它並不是貼在commit上,而是貼在branch上,用來表示當前所在的branch。
## 常用指令
```bash
$ git branch # 查看分支列表,*表示當前所在分支
$ git branch <branch_name> # 建立分支
$ git branch <branch_name> <SHA-1 key> # 在指定commit上建立分支
$ git branch -m <old_name> <new_name> # 更改分支名稱
$ git branch -d <branch_name> # 刪除分支,當分支有內容尚未合併會跳出警告
$ git branch -D <branch_name> # 忽略警告強制刪除分支
$ git checkout <branch_name> # 切換分支
$ git checkout -b <branch_name> # 切換分支,若分支不存在則先建立分支
$ git merge <branch_name> # 將<branch_name>所代表的分支併入當前所在分支。
$ git merge --no-ff <branch_name> # 見Q2
$ git branch --no-merged
$ git branch --merged
```
:::info
**Q1**: 如果有尚未 commit 就直接切換制其他分支?
**A1**: 如果有 blob 物件會被置換則git會跳通知請求commit。反之則直接置換blob。
**Q2**: 未甚麼合併分支的時候沒有小耳朵?
作用就是直接把 ref 設程跟合併對象一樣
**A2**: 如果是父分支與子分支進行合併會採用直接移動標籤的方式,此方式稱為fast-forward。
只有當非直系分支進行合併才會以新增commit物件的方式合併,這時會出現小耳朵,且此commit會指向兩個子分支。
如果有強迫症特別希望小耳朵的出現可以在merge時加上`--no-ff`參數放棄fast-forward。
:::
`
# Remote
這系列的指令是用來連結遠端儲存庫
- clone 下來的儲存庫預設會將將它稱作 origin
```bash
$ git remote add <簡稱> <url> # 新增儲存庫。概念上其作用就只是建立一個代號,代號內容就是後面的 url
$ git remote rename <old_name> <new_name> # 更改遠端簡稱
$ git rm <remote_name> # 刪除遠短
$ git remote # 顯示所有遠端儲存庫
$ git remote show <remote_name> # 顯示遠端儲存庫資訊
$ git fetch # 來擷取訊
$ git pull # git fetch + git merge
$ git push <remote_name> <local_branch_name>:<remote_branch_name> # 指定推上去的遠端分支名稱
```
## Tag
- 預設 push 是不會把tag push 到遠端的 要加 --tag flag 或是 push <flag_name>
- 直接 checkout 到 tag 會發生斷頭現象
- 可以透過以下指令在跳轉的時候同時建立分支 `git checkout -b <branch_name> <tag_name>`
## Remote Branch
### Tracking branck
遠端分之顧名思義就是遠端資料庫上的分資。但這邊有個比較特別的觀念是 tracking branch。其概念是在本地端生成一個遠端分之的影子,我們子能操縱影子也就是本地端的分支。
(心得:這樣的設計應該是為了符合去中心話的核心思想。我想不會希望我們每次操作都需要作連線。)
可以透過 git branch -vv 查看
### 如何建立 tracking branch?
1. clone 下來預設幫我們建立
2. git checkout --track <remote_name>/<remote_branch> # 生成一條同明得分支去接
- Note: 本地端沒有該名稱分支。且遠端中恰好只有一個同名分支`git checkout <branch_name>` 預設就會便上面的指令。
3. git checkout -b \<branch\> \<remote\>/\<remote_branch\> 直接新創一條指定分支去 track
4. git branch \[-u/--set-upstream-to\] \<remote\>/\<remote_branch\> # 用以存在的分支去承接一條上游分支
## git worktree
Git allows user to create several folder(worktree) attach to the same repository where the ".git/" located.
### Commonly used Commands
```bash
$ git worktree add <path> # create worktree at spcific folder and using the `basename <path>` as branch name
$ git worktree add <path> <branch/HASH> # create worktree at specific folder with specific index.
$ git wortree add -b <branch_name> <path> <branch/HASH> # same as above with the branch name were given
$ git worktree remove/move
$ git worktree list # show worktrees linked to this repository
$ git worktree prune # prune linked worktree list, if its corresponding folder is not exist.
```
## git clone
[sparse checkout](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/600079/how-do-i-clone-a-subdirectory-only-of-a-git-repository)
```shell
mkdir <repo>
cd <repo>
git init
git remote add -f origin <url>
git config core.sparseCheckout true
echo "some/dir/" >> .git/info/sparse-checkout
git pull origin master
```
## option "\-\-reference"
當我們去 clone 同一個 repository 兩次的時候,可以讓第二次 clone 去參照第一次 clone 的 repository 的 .git/objects,如此一來就不用去 clone 整個 folder。
## option "\-\-shared"
與 \-\-reference 類似但是改用 hard link 的方式實作。此法只在 unix 系統適用。
好處是可以避念。Base folder 被刪掉。找不到 reference 的問題。
## Other
1. [自建 server](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-on-the-Server-The-Protocols)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet