# String Implementation
---
1. Introduction to Characters
2. ASCII Introduction
3. Sum of digits in the string with characters and digits
4. Replace all the characters 'x' with '$'
5. Count uppercase and lower case characters
6. Count number of characters of first string present in the second string
---
### Character:
A character represent a single symbol.
There are different types of characters:
* Uppercase characters : ['A' - 'Z']
* Lowercase characters : ['a' - 'z']
* Numeric characters: ['0' - '9']
* Special characters: ['@', '#', '\$', '%', '&'...]
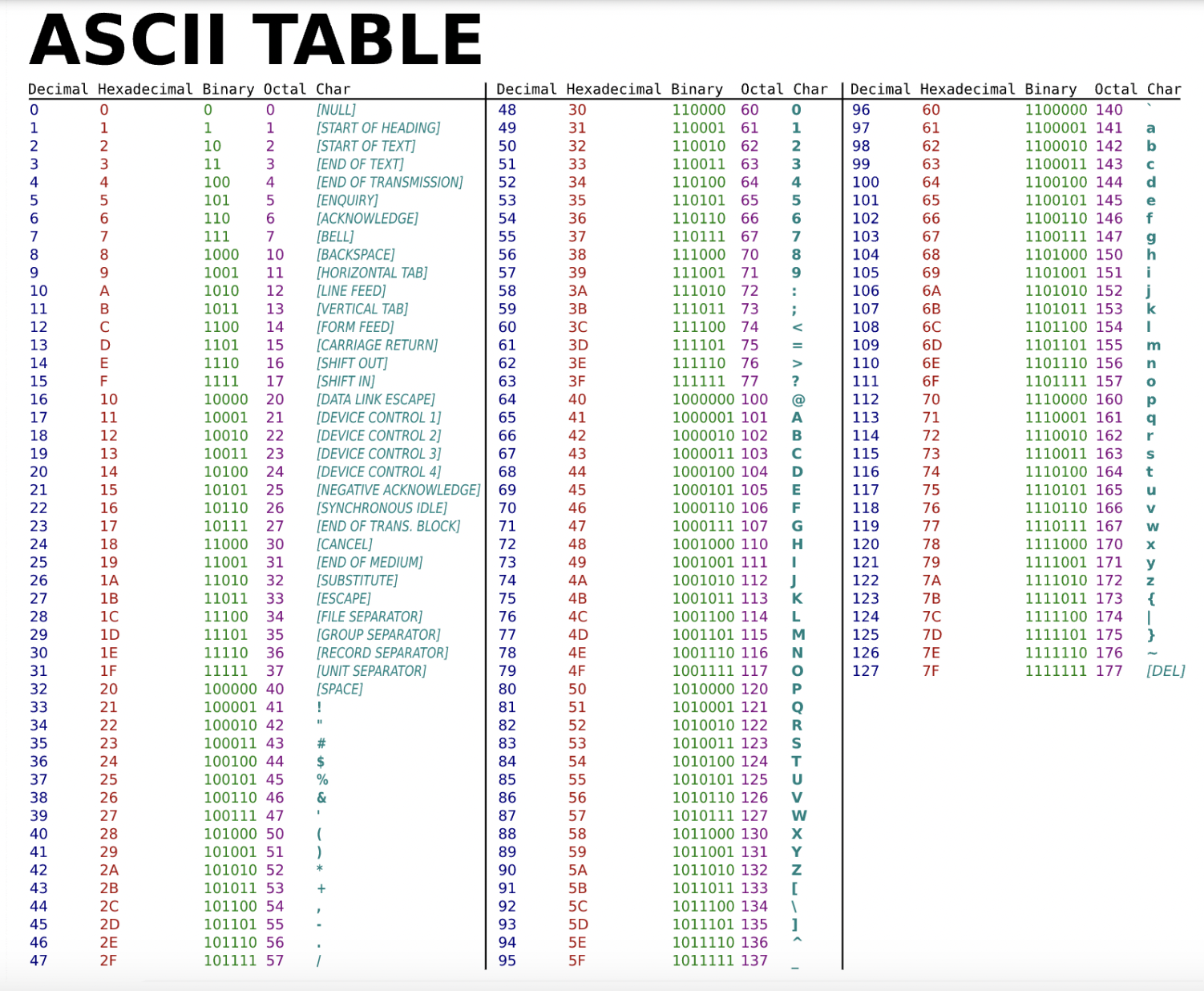
There are a total of 128 characters.
## Syntax
**Example 1:**
```java
char ch = 'a';
System.out.println(ch);
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
a
```
**Example 2:**
```java
char ch = 'ab';
System.out.println(ch);
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
Error: Only a single symbol is a character.
```
---
## Why do we need ASCII Codes?
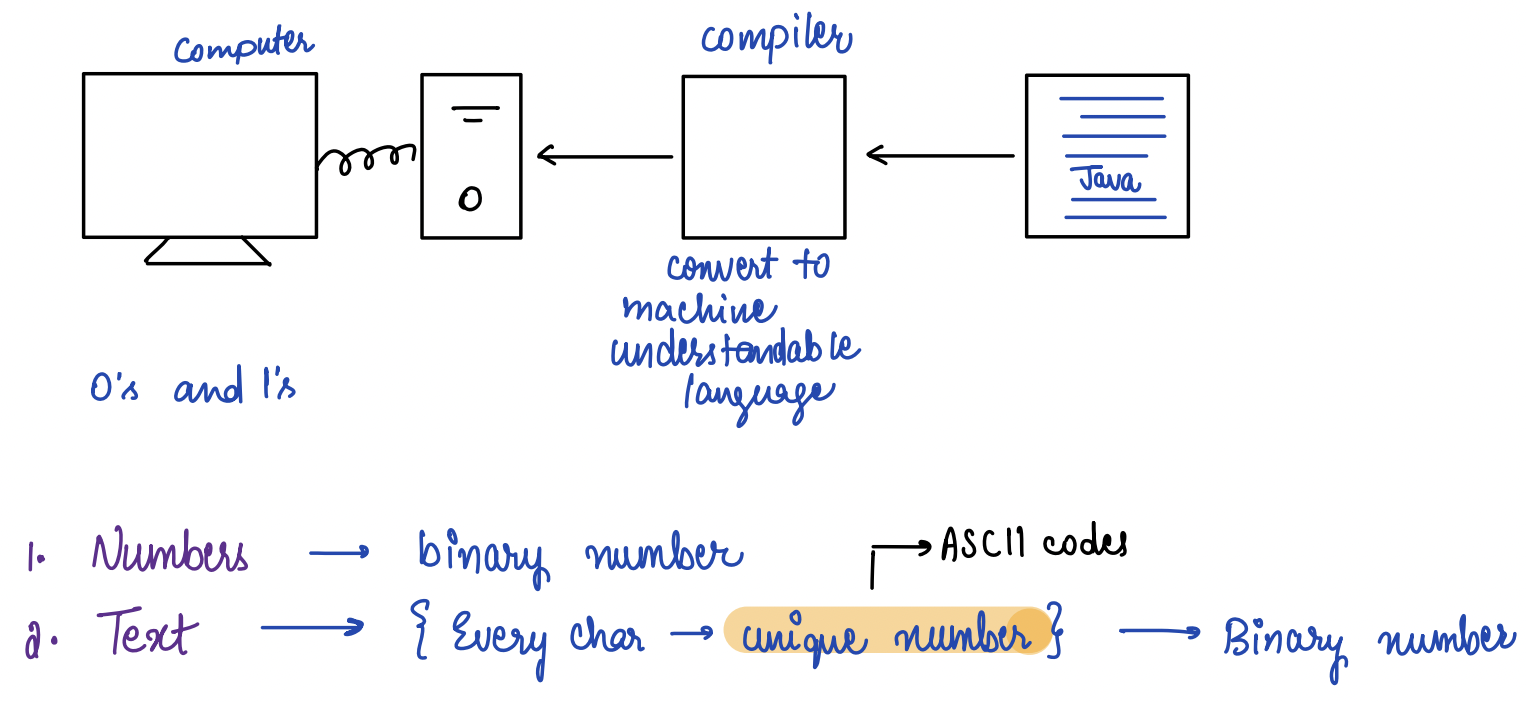
---
## ASCII Codes
ASCII stands for **American Standard Code for Information Interchange.**
These codes are a standardized system of assigning a unique numeric value to each character in the English language and other common characters, such as punctuation marks and symbols.
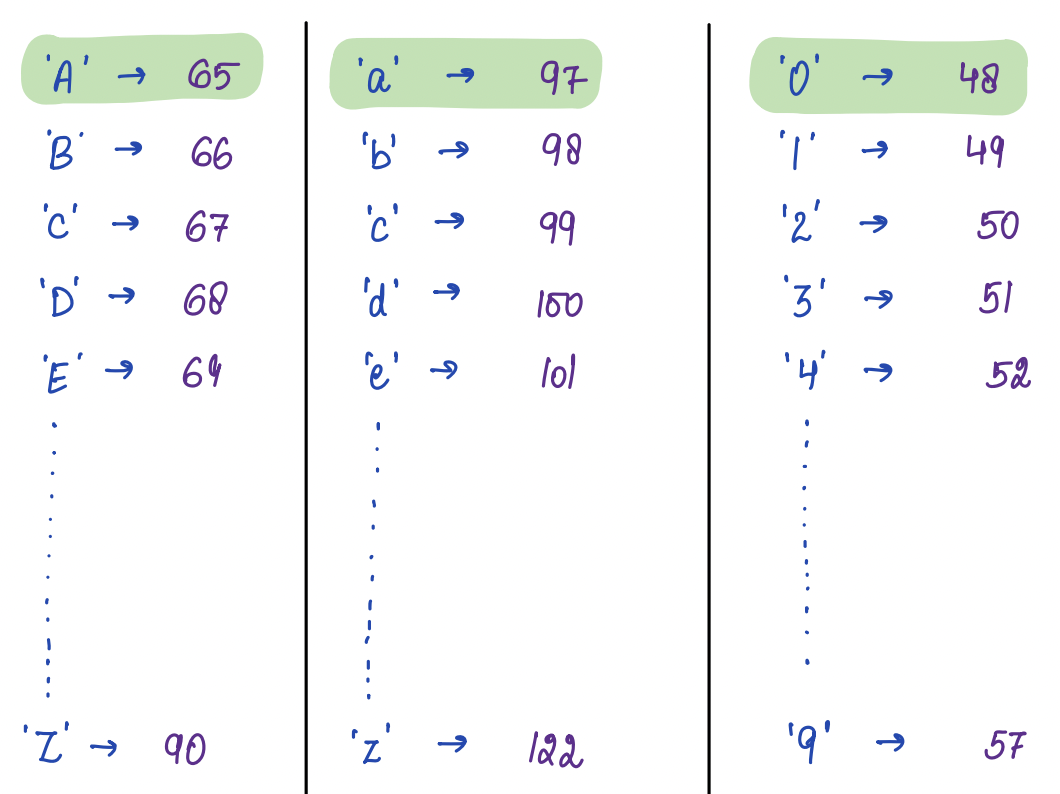
## Show the ASCII table in the class
---
#### Definition
In programming, a string is a data type used to represent a sequence of characters.
#### Syntax
The syntax for declaring and initializing a string variable in Java is:
```java
String str = "Hello World!"; // Double quotes are used to define a string
```
#### Example -
```java
String str = "How are you?"
print(str) // How are you? will be printed
```
#### Indexing
String indexing starts from 0, where the first character is at index 0, the second character is at index 1, and so on.
**Example -**
```java
String str = "Hello, World!";
System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); // Output: 'H'
System.out.println(str.charAt(7)); // Output: 'W'
```
---
### Properties of a String
Some of the most commonly used properties of a string include:
* **Length:** The length() method of the String class returns the number of characters in a string. For example,
```java
String str = "Priyanshi";
int n = str1.length(); // assigns 9 to variable n as str has 9 characters.
System.out.println(str.length()); // 9
```
* **Access a character:** The charAt(index) method of the String class returns the character at that index in a string. Indexing in string is same as that in array and starts from 0. For example,
```java
String str = "Priyanshi";
System.out.println(str.charAt(5)); // output will be 'n'.
```
* **Iterate a string:** We can iterate over the characters of a string using a loop. One way to do this is to use a for loop that iterates over the index positions of the string, and then use the charAt() method to retrieve the character at each position. For example,
```java
String str = "Priyanshi";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(i + " -> " + str.charAt(i));
}
```
* **Update a string:** In Java, strings are immutable, meaning that their contents cannot be changed after they are created.
* **Concatenating characters to String:** In Java, a character can be concatenated after a string by using the + or += operator, or through the concat() method, defined in the java. lang. String class.
```java
// Concatentaion example
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = s1 + "Everyone";
System.out.println(s2); // Output will be "Hello Everyone"
String s3 = "Hi";
s3 = s3 + 'i';
System.out.println(s3); // Output will be "Hii"
s3 = 'e' + s3;
System.out.println(s3); // Output will be "eHii"
s3 = "Bye " + s3;
System.out.println(s3); // Output will be "Bye eHii"
```
---
#### Problem statement:
Given a string s, you have to find the length of the longest word in the input string.
### Exanple 1:
Input:
hi hello bye
Output:
5
Explanation:
In the sentence "hi hello bye", hello is the longest word, whose length is 5.
---
# Question
Given string A, "coding is awesome"
find the length of the longest word in the given string.
# Choices
- [x] 7
- [ ] 6
- [ ] 5
- [ ] I dont know
---
### Explanation
In the sentence "coding is awesome", awesome is the longest word, whose length is 7.
---
```java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = scanner.nextLine();
int maxLength = 0;
int currentLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < line.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = line.charAt(i);
if (currentChar != ' ') {
currentLength++;
} else {
if (currentLength > maxLength) {
maxLength = currentLength;
}
currentLength = 0;
}
}
if (currentLength > maxLength) {
maxLength = currentLength;
}
System.out.println(maxLength);
scanner.close();
}
```
---
### Problem
Given a string A of length N and a character B, replace all occurrences of B in string A with character '@'.
**Input Format**
First line is String A
Second line is Character B
**Example:**
abcad
a
**Output:**
@bc@d
---
# Question
Given string A,"interviewbit"
String B= "i"
replace all occurrences of B in string A with character '@'.
# Choices
- [x] @nterv@ewb@t
- [ ] i@terv@ewb@t
- [ ] @ntervewb@t
- [ ] I dont know
---
### Explanation
Modified string after Replacement of i at 1st, 7th, and 11th position is @nterv@ewb@t
---
### Idea:
1. Initialization: Create an empty string result.
2. Iterate: Loop through each character in the input string.
3. Check and Replace: If the current character matches the target character, append '@' to the result; otherwise, append the current character.
4. Final Result: Return the modified string (result).
### Psuedo code
```java
static String replaceCharacter(String str, char targetChar) {
String result = "";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = str.charAt(i);
if (currentChar == targetChar) {
result += '@';
} else {
result += currentChar;
}
}
return result;
}
```
---
### Problem:
Given a string, Count uppercase and lower case characters and print the values.
### Example:
String str="Hello World"
**Output:**
Uppercase: 2
Lowercase: 8
---
# Question
Given string ElePHant
Count number of Uppercase character first, then lowercase characters.
# Choices
- [ ] 3 lowercase<br>5 uppercase
- [x] 3 uppercase<br>5 lowercase
- [ ] 5 uppercase<br>9 lowercase
- [ ] I dont know
---
```java
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scn.next();
int c1 = 0;
int c2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
c1++;
} else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
c2++;
}
}
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
}
```
---
### Problem:
Count number of characters of first string present in the second string.
### Example:
String A=abbd
String B=aabb
Output:
Number of common characters: 3(a,b,b)
### Pseudo Code
```java
static int countCommonCharacters(String str1, String str2) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = str1.charAt(i);
for (int j = 0; j < str2.length(); j++) {
if (currentChar == str2.charAt(j)) {
count++;
break; // Break the inner loop once a common character is found
}
}
}
return count;
}
```
------