---
canonical_url: https://www.scaler.com/topics/str-in-python/
title: str() in Python | str() Function in Python - Scaler Topics
description: Learn about str() function in Python. Scaler Topics explains the syntax, working of each method along with parameters, return value and examples.
author: Sushant Gaurav
category: Python
amphtml: https://www.scaler.com/topics/str-in-python/amp/
publish_date: 2022-03-30
---
# str in Python
:::section{.abstract}
## Overview
To convert a specified value or an object into a string object, we use str in python. The conversion of one data type into the other data type is known as type casting or type conversion.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Syntax of `str()` in Python
The syntax of the method, str in python is very simple:
```python
str(object, encoding = 'utf-8', errors = 'strict')
```
The encoding and errors parameters are optional parameters but the object parameter is required.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Parameters of `str()` in Python
The method - str in python takes three parameters. The parameters provided to the str() in python are:
- **object**: The object parameter is a required parameter.
- **encoding**: The encoding parameters stores the encoding of the provided object.
- **errors**: It stores the specified action that needs to be performed if the conversion or decoding fails.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Return Values of `str()` in Python
The str in python returns the string object value (string version) of the given object or number.
If we do not give any parameter in the method, it will return an empty string.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Exceptions of `str()` in Python
There are 6 types of errors that can be provided as a parameter in the str() method.
- **strict**: It is the default value for the error parameter, the strict raises a UnicodeDecodeError.
- **ignore**: We can specify ignore to ignore the unencoded Unicode.
- **replace**: The replace is used to replace the un-encodable Unicode with a question mark (?).
- **xmlcharrefreplace**: The xmlcharrefreplace is used to insert XML characters in place of the un-encodable Unicode.
- **backslashreplace**: The backslashreplace is used to insert escape sequences (`\uNNNN`) in place of un-encodable Unicode.
- **namereplace**: The namereplace is used to insert `\N{....}` escape sequence in place of un-encodable Unicode.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Example of `str()` in Python
Let us convert a number into a string object using the method, str in python.
```python
number = 55
string = str(number)
print("Converted string is:",string)
```
**Output:**
```python
The converted string is: 55
```
:::
:::section{.main}
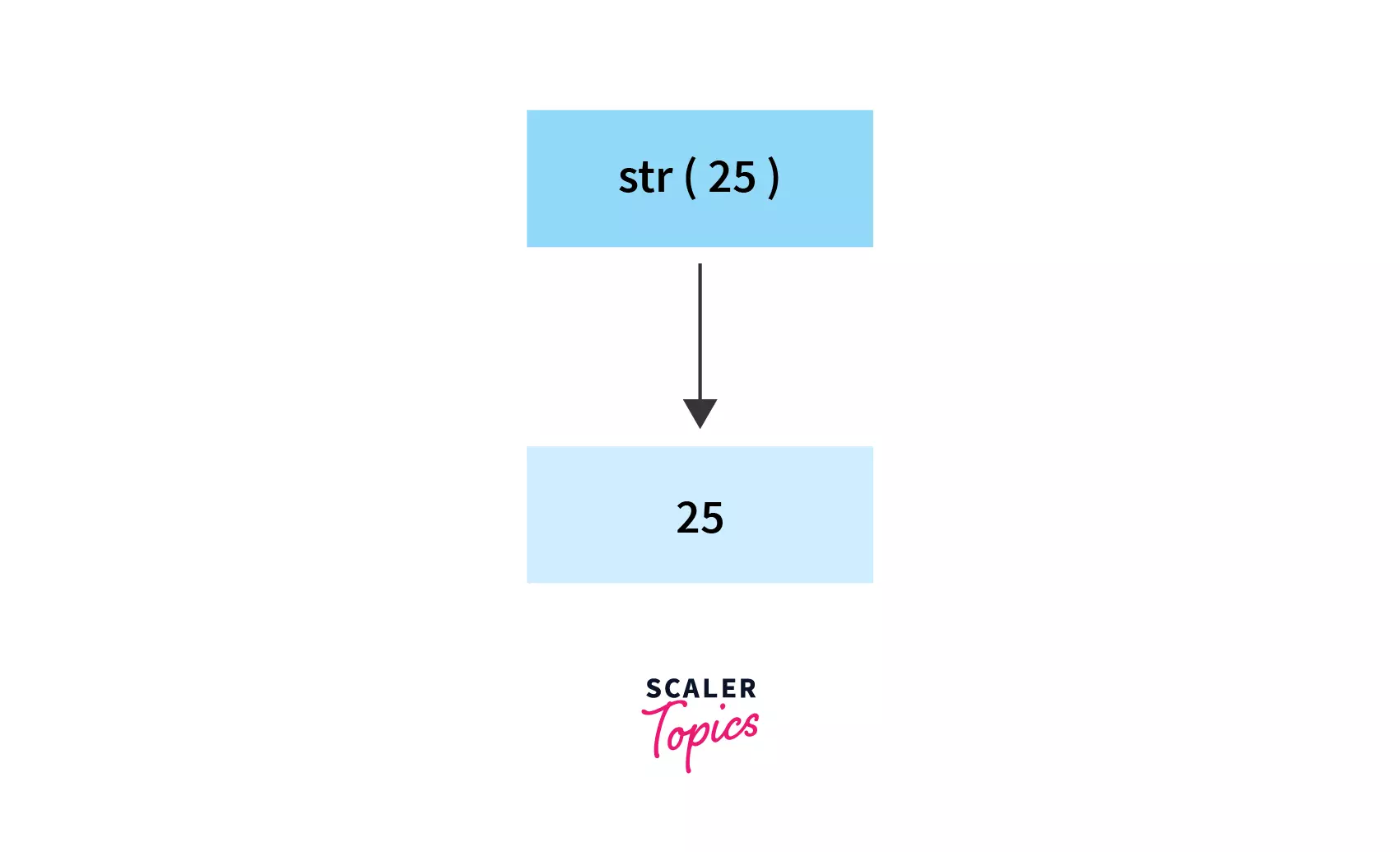
## What is `str()` in Python?
As we know, the conversion of one data type into the other data type is known as type casting or type conversion. To convert a specified value or an object into a string object, we use str in python.
:::
:::section{.main}
## How to use `str()` in Python?
We can use the str in python to convert an object to a string version of the given object or number. We need to provide the object that needs to be converted into a string.The object is any object or value(s) that is to be converted into a string object.
Along with the object, we can also provide the decoding type (like UTF-8) as well as error object the response took if the decoding fails. If we do not provide any object in the parameter, the str in python returns an empty string.If we do not provide any encoding parameter, the default value i.e. **UTF-8** is provided.
:::
:::section{.main}
## More Examples
Let us take a few examples to understand the str method in python in a better way.
### Example 1: Convert to String
Let us take a number and convert it into the string using str in python:
```python
number = 11
string = str(number)
print("Converted string is:",string)
```
**Output:**
```python
The converted string is: 11
```
:::{.tip}
**Note:**
If we do not provide the error and encoding parameter, the str() method internally calls the `__str__()` method of the object. In some cases, if the `__str__()` method is not found, the str() method invokes `repr(object)`.
:::
:::section
### Example 2: How str() works for bytes?
Whenever we provide the error and encoding parameter, the object parameter should be of the type: **bytes-like-object** or bytes or bytes-array.
Let us take an example where we specify the error and encoding parameter to understand the working of str in python in a better way.
```python
print(str(bytes('string conversion', encoding = 'utf-8', errors = 'ignore')))
```
**Output:**
```python
b'string conversion'
```
Let us provide a different encoding standard.
```python
value = bytes('string conversion', encoding = 'utf-8')
print(str(value, encoding = 'ascii'))
```
**Output:**
```python
string conversion
```
:::
:::section{.summary}
## Conclusion
- To convert a specified value or any object into a string object, we use str in python.
- The conversion of one data type into the other data type is known as type casting or type conversion.
- The str in python takes three parameters and returns an equivalent string object. Its syntax is: `str(object, encoding = 'utf-8', errors = 'strict')`.
- The object parameter is required but the encoding and errors parameters are optional.
:::
:::section{.main}
## See Also
* [int in Python](https://hackmd.io/IwmyQweVThCkVfcW9hyxbw)
* [Byte in Python](https://www.scaler.com/topics/byte-to-string-python/)
:::