# 2D Array-1
---
## Agenda
1. Intro to 2D Arrays
2. Indexing and taking Input
3. Print matrix row by row and column by column
4. print matrix in wave form
5. Max of matrix.
6. Max of every row
---
### Introduction
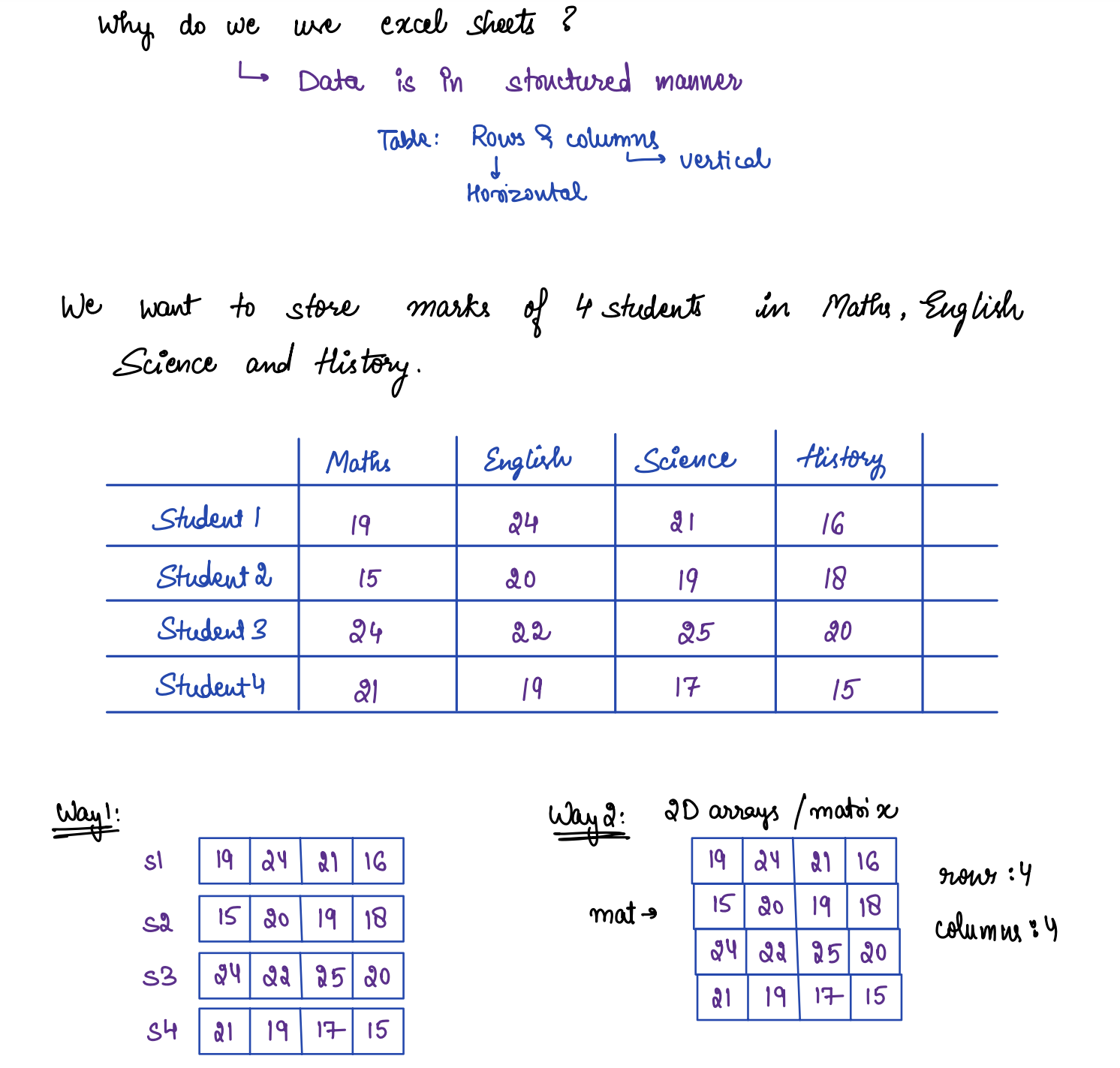
Two-dimensional arrays can be defined as arrays within an array. 2D arrays is a collection of 1d Arrays.
#### Syntax:
```java
datatype name[][] = new datatype[rows][cols]
```
>**Note:** When we create 2D matrix by int default all values are equal to 0.
---
# Question
What is N representing in the line given below?
int[][] mat = new int[N][M];
# Choices
- [ ] Number of Column
- [x] Number of Row
- [ ] Total Element
---
# Question
What is M representing in the line given below?
int[][] mat = new int[N][M];
# Choices
- [x] Number of Column
- [ ] Number of Row
- [ ] Total Element
---
# Question
How to create a matrix with 2 rows and 5 columns?
# Choices
- [x] int[][] mat = new int[2] [5];
- [ ] int[] mat = new int[2] [5];
- [ ] int[][] mat = new int[5] [2];
---
# Question
How to create a matrix with 5 columns and 7 rows?
# Choices
- [x] int mat[ ] [ ] = new int[7] [5];
- [ ] int mat[ ] = new int[5] [7];
- [ ] int mat[ ] [ ] = new int[5] [7];
---
# Question
How to create a matrix with size M * N having M = 5 and N = 7
# Choices
- [ ] int mat[ ] [ ] = new int[7] [5];
- [ ] int mat[ ] = new int[5] [7];
- [x] int mat[ ] [ ] = new int[5] [7];
---
### Indexing and Properties:
* We can access ith row and jth column of matrix `mat[][]` by:
mat[i][j]
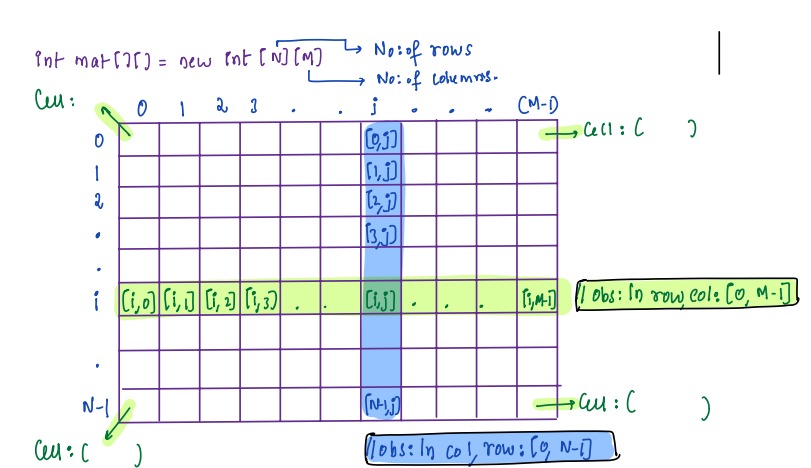
* If we iterate on a row, column changes and if we iterate on a column, row changes. For example, in above figure we can see that if we iterate on ith row, column number changes from `[0,M - 1]`.
* Similarly, in above figure we can see that if we iterate on jth row, row number changes from `[0,N - 1]`.
* In a matrix `mat[][]`, mat.length will be equal to total number of rows in a matrix and `mat[0].length` will be equal to total number of columns.
**Number of rows =** array.length
**Number of columns =** array[0].length
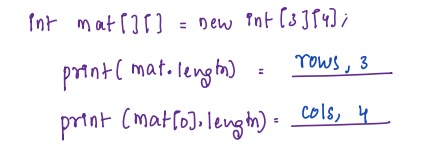
---
# Question
What will be the index of top left cell in a given matrix, mat of size N * M?
# Choices
- [ ] mat[0][M]
- [x] mat[0][0]
- [ ] mat[top][left]
- [ ] mat[N][0]
---
# Question
What will be the index of top right cell in a given matrix, mat of size N * M?
# Choices
- [x] mat[0][M-1]
- [ ] mat[N - 1][0]
- [ ] mat[N][0]
- [ ] mat[bottom][left]
---
# Question
What will be the index of bottom right cell in a given matrix, mat of size N * M?
# Choices
- [ ] mat[N - 1][0]
- [x] mat[N - 1][M - 1]
- [ ] mat[N][M]
- [ ] mat[bottom][right]
---
# Question
What will be the index of bottom left cell in a given matrix, mat of size N * M?
# Choices
- [x] mat[N - 1][0]
- [ ] mat[N - 1][M - 1]
- [ ] mat[N][M]
- [ ] mat[bottom][right]
---
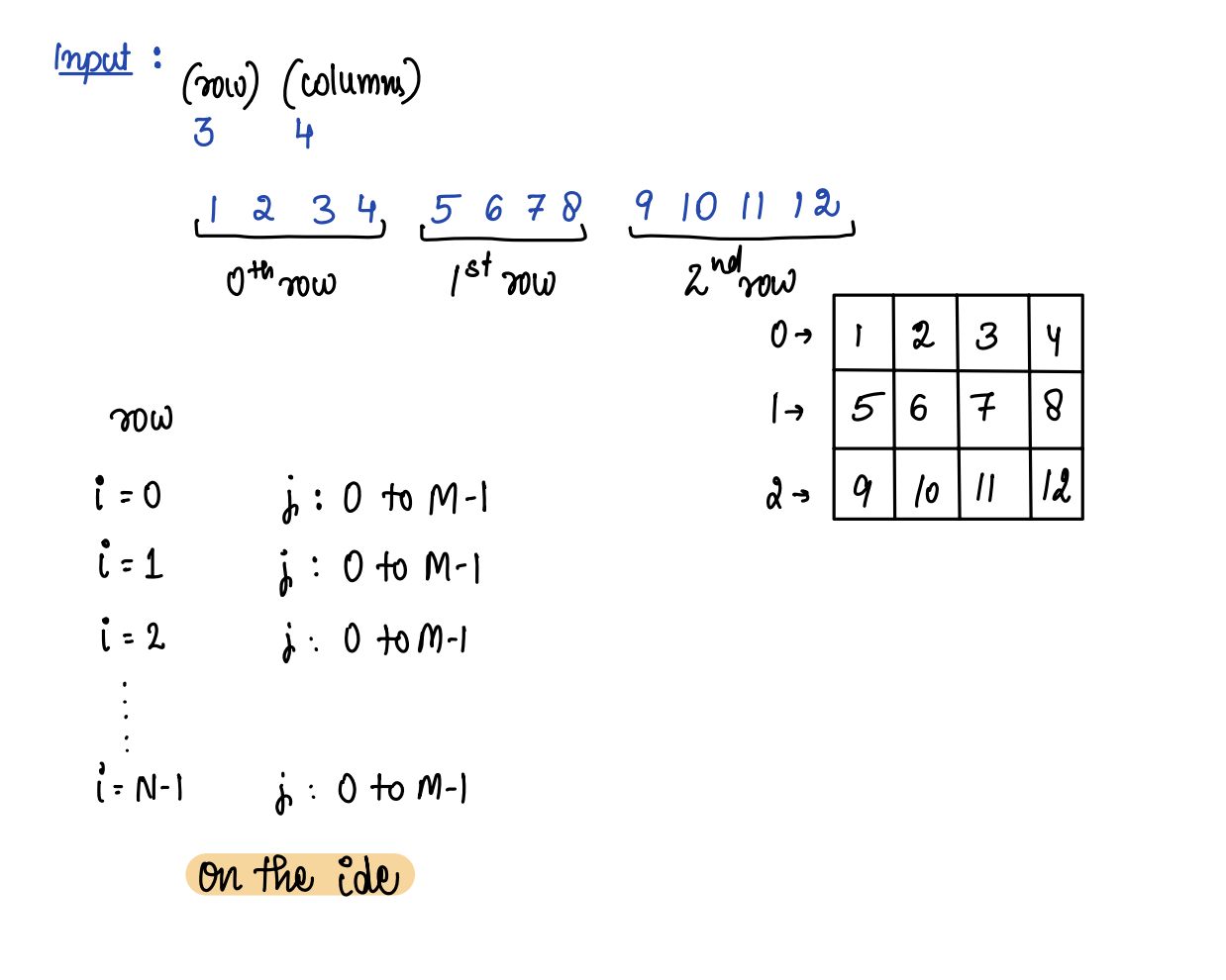
### Taking input from user
Create a matrix having N rows and M columns fill the
matrix by taking input from the user
**Input**: rows = 3, columns = 4
**Code:**
```java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Enter the number of rows
int N = scanner.nextInt();
// Enter the number of columns
int M = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] matrix = new int[N][M];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
}
```
---
# Question
Print the 0th index row of the given matrix.
```plaintext
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
```
# Choices
- [x] 1 2 3 4
- [ ] 1 5 9
- [ ] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
---
### Printing 0th Row
Given a matrix, you are required to print its 0th row.
#### Observation
To print the 0th row of the matrix, we can directly access the elements in the 0th row and print them.
#### Example
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| ----- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 2 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
The 0th row of the matrix would be: **1 2 3 4**
#### Pseudocode
```java
void printZeroRow(int mat[][]) {
int n = mat.length;
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) // columns
{
System.out.print(mat[0][c] + " ");
}
}
```
---
### Print Matrix Row by Row and Column by Column
Given a matrix, print every row in new line.
#### Example
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 2 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
**Output :**
```plaintext
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
```
#### Code
```java
void printmat(int mat[][]){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
for(int r = 0; r < n; r++)//rows
{
for(int c = 0; c < m; c++) //columns
{
System.out.print(mat[r][c] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
```
---
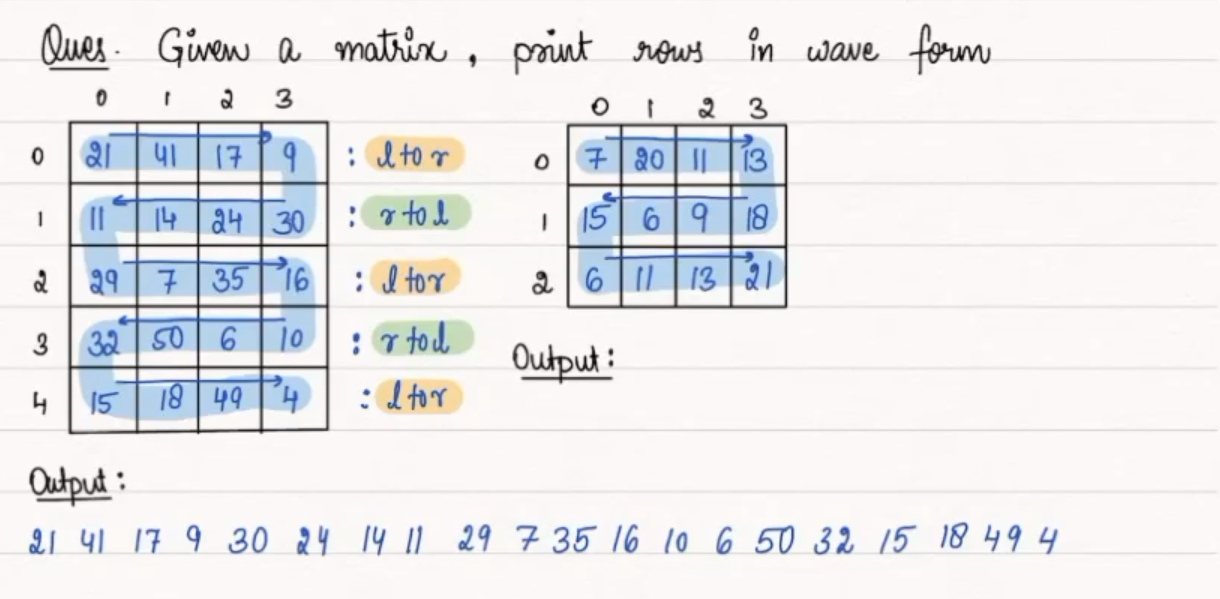
### Printing Row in wave form
Given a matrix, print rows and column in wave form.
#### Observation
First we will rum loop for rows from index 0 to n-1 where n is the number of rows. Inside this loop we will run another loop for columns from 0 to m-1, where m is total number of columns. Inside this loop we will print the value at row i and column j.
#### Example 1
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 0 | 21 | 41 | 17 | 9 |
| 1 | 11 | 14 | 24 | 30 |
| 2 | 29 | 7 | 35 | 16 |
| 3 | 32 | 50 | 6 | 10 |
| 4 | 15 | 18 | 49 | 4 |
**Output :**
```plaintext
21 41 17 30 24 14 11 29 7 35 16 10 6 50 32 15 18 49 4
```
#### Observation
* For even rows we will traverse columns from 0 to m - 1 index.
* For odd rows we will traverse columns from m - 1 to 0 index.
#### Pseudocode
```java
void printWaveArray(int mat[][]){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
for(int r = 0; r < n; r++)//rows
{
if(r % 2 == 0){
for(int c = 0; c < m; c++) //columns
{
System.out.print(mat[r][c] + " ");
}
}
else{
for(int c = m - 1; c >= 0; c--) //columns
{
System.out.print(mat[r][c] + " ");
}
}
}
}
```
---
# Question
Print the 0th index column of the given matrix.
```plaintext
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
```
# Choices
- [ ] 1 2 3 4
- [x] 1 5 9
- [ ] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
---
### Print 0th column
Given a matrix, print 0th column.
#### Example
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 2 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
The 0th col of the matrix would be: **1 5 9**
#### Observation
We will run a single loop for i for rows from index 0 to n-1, where n is total number of rows and will print `matrix[i][0]`.
#### Pseudocode
```java
void printZeroCol(int mat[][]){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
for(int r = 0; r < n; r++)//rows
{
System.out.print(mat[r][0] + " ");
}
}
```
---
### Print every column
Given a matrix, print every column in new line.
#### Exmaple 1
```java
mat[4][3] = {
{21,16,17,14},rows
{7,8,10,1},
{6,11,13,21}
}
Ans = {
{21, 7, 6}
{16, 8, 11}
{17, 10, 13}
{14, 1, 21}
}
```
| 21 | 16 | 17 | 14 |
|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 7 | 8 | 10 | 1 |
| 6 | 11 | 13 | 21 |
#### Observation
First we will rum loop for columns from index 0 to m - 1 where m is the number of columns. Inside this loop we will run another loop for rows from 0 to n - 1, where n is thw total number of columns. Inside this loop we will print the value at row i and column j.
#### Pseudocode
```java
void printmat(int mat[][]){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
for(int c = 0; c < m; c++)//rows
{
for(int r = 0; c < n; c++) //columns
{
System.out.print(mat[r][c] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
```
---
### Printing Column in Wave Form
Given a matrix, you are required to print its elements in wave form by columns.
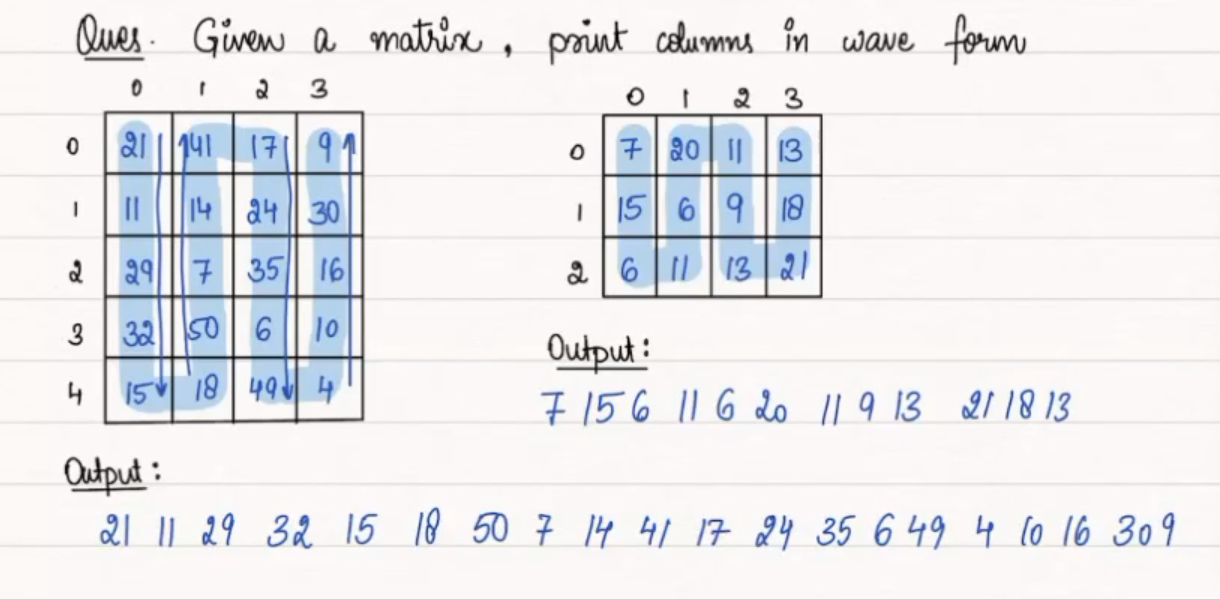
#### Observation
To print the matrix in wave form by columns, we can iterate through the columns of the matrix. For even columns, we start from the top and move downward; for odd columns, we start from the bottom and move upward. This way, we print the elements in a zigzag pattern along the columns.
#### Example
Consider the following matrix:
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 0 | 21 | 16 | 17 | 14 |
| 1 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 1 |
| 2 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 21 |
| 3 | 32 | 50 | 6 | 10 |
| 4 | 15 | 18 | 49 | 4 |
The elements in wave form by columns would be: `21 7 6 32 15 18 50 11 8 16 17 10 13 6 49`.
#### Pseudocode
```java
void printWaveArrayByColumn(int mat[][]) {
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++){ // columns
if (c % 2 == 0) {
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++){ // rows
print(mat[r][c] + " ");
}
} else {
for (int r = n - 1; r >= 0; r--){ // rows
print(mat[r][c] + " ");
}
}
}
}
```
---
### Max of matrix
Given a 2D Array A[][], return max element from this matrix.
### Example:
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 0 | 12 | 65 | 89 | 74 |
| 1 | 22 | 44 | 12 | 30 |
| 2 | 10 | 12 | 97 | 19 |
**Output:**
Max element of matrix is 97
### Idea:
1. Iterate on every element of row and column.
2. compare mat[i][j] with max element.
3. return max element.
### Psuedo Code:
```java
public class Solution {
public int solve(int[][] A) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < A[0].length; j++) {
if(max < A[i][j]) {
max = A[i][j];
}
}
}
return max;
}
}
```
---
### Max of Every Row
Given a matrix and row number, return an array containing max of all elements in that row.

#### Example 1
**mat :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | max |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| 0 | 21 | 16 | 17 | 14 | 21 |
| 1 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 21 | 21 |
| 3 | 32 | 50 | 6 | 10 | 50 |
| 4 | 15 | 18 | 49 | 4 | 49 |
**ans :**
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|:-----:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
| ans | 21 | 10 | 21 | 50 | 49 |
---
# Question
What will be the max of every row for the given matrix?
```plaintext
1 2 3 13 4
5 6 17 8 9
19 0 1 2 21
```
# Choices
- [ ] 15 19
- [ ] 4 9 21
- [x] 13 17 21
---
# Question
What should be the size of array to store max in every row for a matrix of size N * m
# Choices
- [ ] N + M
- [x] N
- [ ] M
- [ ] N * M
---
#### Observation
Size of ans array = total no of Rows
1. Create ans array
2. Iterate on every row and find max
3. Store the max of ith row at ans[i]
Dry Run wrt Above Example:
| i | Initial MAX | Iterate on ith row: j -> 0 to m-1 | Max in Row | ans[i] = max |
|:---:|:-----------:|:---------------------------------:|:----------:|:------------:|
| 0 | - INF | Iterate on 0th row: j -> 0 to m-1 | 21 | ans[0] = 21 |
| 1 | -INF | Iterate on 1st row: j -> 0 to m-1 | 10 | ans[1] = 10 |
| 2 | -INF | Iterate on 2nd row: j -> 0 to m-1 | 21 | ans[2] = 21 |
| 3 | -INF | Iterate on 3rd row: j -> 0 to m-1 | 50 | ans[3] = 50 |
| 4 | -INF | Iterate on 4th row: j -> 0 to m-1 | 49 | ans[4] = 49 |
#### Pseudocode
```java
int prinRowMax(int mat[][], int r){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)//rows
{
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(mat[i][j] > max)
{
max = mat[i][j];
}
}
ans[i] = max;
}
return ans;
}
```