---
title: How to Find Pythagorean Triplet in an Array? - Scaler Topics
description: Learn what is a Pythagorean triplet in an array and how to find it. Scaler Topics also explains Pythagoras's theorem along with examples.
author: Pawan Harwani
category: Miscellaneous
---
:::section{.abstract}
## Introduction
Pythagoras theorem is a theorem in geometry which says that in a right angled triangle, square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides. Pythagorean triplet is a set of `3` numbers that satisfies pythagoras theorem.
According to pythagoras theorem, in a right angled triangle, square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides. Pythagoras theorem has many real life applications from architecture to navigation systems.
For example, if we know height of the roof and length to cover it then we can use pythagoras theorem to find the diagonal length of the roof's slope.

Another example, pythagoras theorem can be used in two dimensional navigation systems.
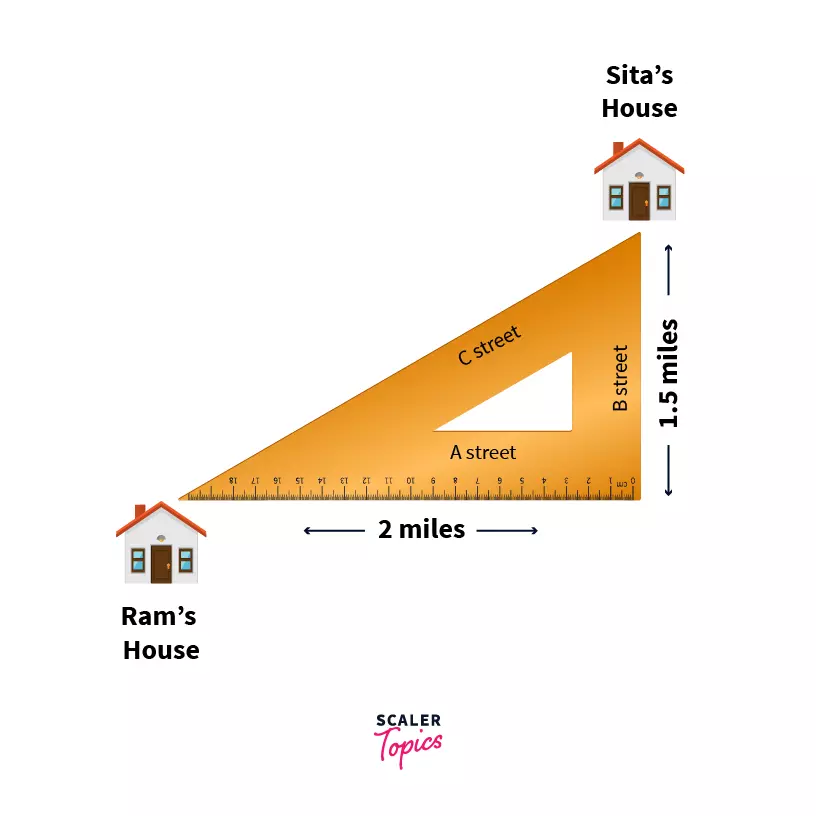
Suppose you are standing at a place and there is place `A` north to you at some distance and there is another place `B` east to you at some distance then using pythagoras theorem to find the shortest distance between places `A and B`.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Methods to Find Pythagorean Triplet in an Array
1. ### Naive Method
**Steps :**
1. Run a nested loop that will pick 3 elements from the array namely `a, b, c`.
2. Check if `a, b, c` follows pythagoras theorem.
```cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to check if pythagorian triplet
// is present in the array
bool isTripletPresent(int arr[], int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
for(int k = j + 1; k < n; k++)
{
int a = arr[i] * arr[i], b = arr[j] * arr[j], c = arr[k] * arr[k];
// checking if square of any one side is equal to
// sum of squares of other two sides
if(a == b + c || b == a + c || c == a + b)
return true;
}
}
}
// triplet is not present
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int arr[n] = {4, 6, 3, 7, 5};
if(isTripletPresent(arr, n))
cout<<"YES\n";
else
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
```
**Time Complexity:** $O(n^3)$ since we are running nested loop with 3 levels.
**Space Complexity:** `O(1)` since we are not using any extra space.
2. ### Using Sorting
**Steps:**
1. Square every number in the array.
2. Sort the array in ascending order.
3. Let's say we want to find a triplet `(i,j,k)` (where `i,j,k` are indices in the array) such that `arr[i] = arr[j] + arr[k]`.
4. For finding the triplet `(i,j,k)` we will run a loop from the end of the array fixing `i` and then we will apply meet in the middle technique in the array from `0 to i - 1` to find the pair (j,k) such that `arr[i] = arr[j] + arr[k]`.
5. If `arr[j] + arr[k] = arr[i]` then a triplet is found, else if `arr[j] + arr[k] > arr[i]` then decrement `k` i.e `k- -`, else increment `j` i.e `j++`.
6. If triplet is not found then decrement `i` i.e `i- -` and repeat step 5.
```cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to check if pythagorian triplet
// is present in the array
bool isTripletPresent(int arr[], int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i] * arr[i];
sort(arr, arr + n);
for(int i = n - 1; i > 1 ; i--)
{
int j = 0, k = i - 1;
while(j < k)
{
if(arr[i] == arr[j] + arr[k])
return true;
if(arr[i] > arr[j] + arr[k])
j++;
else
k--;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int arr[n] = {4, 6, 3, 7, 5};
if(isTripletPresent(arr, n))
cout<<"YES\n";
else
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
```
**Time Complexity:** $$O(n^2)$$ since we are running nested loop with 2 levels.
**Space Complexity:** `O(1)` since we are not using any extra space.
3. ### Using Hashing
**Steps :**
1. Store every number of the array in the hash array.
2. Let's say we want 3 numbers namely `a, b, c` satisfying pythagoras theorem i.e $$a^2 + b^2 = c^2$$
3. For step 2, run a nested loop trying all possible combinations of a and b, then we will check for c in the hash array, if c exist then triplet exist otherwise not.
```cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to check if pythagorian triplet
// is present in the array
bool isTripletPresent(int arr[], int n)
{
// stores maximum number in the array
int max1 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
max1 = max(max1, arr[i]);
// hash array
vector<int> hash(max1 + 1, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
hash[arr[i]]++;
// nested loop to explore all possibilities
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
hash[arr[i]]--;
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
hash[arr[j]]--;
int a = arr[i] * arr[i], b = arr[j] * arr[j];
int c = sqrt(a + b);
// checking availability of c in the hash array
// if present return true
if(c <= max1 && c * c == a + b && hash[c] > 0)
return true;
hash[arr[j]]++;
}
hash[arr[i]]++;
}
// triplet not present
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int arr[n] = {5, 6, 4, 7, 3};
if(isTripletPresent(arr, n))
cout<<"YES\n";
else
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
```
**Time Complexity:** $$O(n^2)$$ since we are running nested loop with 2 levels.
**Space Complexity:** `O(max1)` where `max1` is the maximum number in the array.
4. ### Using STL
**Steps:**
1. Store every number of the array in an unordered map.
2. Let's say we want 3 numbers namely `a, b, c` satisfying pythagoras theorem i.e $$a^2 + b^2 = c^2$$
3. For step 2, run a nested loop trying all possible combinations of `a` and `b`, then we will check for `c` in the map, if c exist then triplet exist otherwise not.
```cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to check if pythagorian triplet
// is present in the array
bool isTripletPresent(int arr[], int n)
{
// stores frequency of numbers
//from the array
unordered_map<int,int> mp;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
mp[arr[i]]++;
// nested loop to explore all possibilities
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
mp[arr[i]]--;
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
mp[arr[j]]--;
int a = arr[i] * arr[i], b = arr[j] * arr[j];
int c = sqrt(a + b);
// checking availability of c in the map
// if present return true
if(c * c == a + b && mp[c] > 0)
return true;
mp[arr[j]]++;
}
mp[arr[i]]++;
}
// triplet not present
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int arr[n] = {5, 6, 4, 7, 3};
if(isTripletPresent(arr, n))
cout<<"YES\n";
else
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
```
**Time Complexity:** $$O(n^2)$$ since we are running nested loop with 2 levels.
**Space Complexity:** `O(n)`.
5. ### Using Set (A better hash-based approach)
**Steps:**
1. First square every array elements and then sort them in increasing order.
2. Run two loops where the outer loop starts from the last index of the array to the second index (0 based indexing is assumed) and the inner loop starts from outerLoopIndex – 1 to the start
3. Create a set to store the elements in between outerLoopIndex and innerLoopIndex.
4. Check if there is a number in the set which is equal to arr[outerLoopIndex] – arr[innerLoopIndex]. If yes, then return “True”.
```cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isTripletPresent(int arr[],int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i]*arr[i]; //square each element
sort(arr, arr + n);//sort the array
for(int i = n - 1; i > 1; i--)
{
unordered_set<int> s;
for(int j = i - 1; j >- 1; j--)
{
if(s.count(arr[i] - arr[j])) // if the pythagorean condition satisfied
return true;
s.insert(arr[j]);
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n=5;
int arr[] = {3, 2, 4, 6, 5};
if (isTripletPresent(arr, n))
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
return 0;
}
```
**Time Complexity:** `O(n^2)` since we are running nested loop with 2 levels.
**Space Complexity:** `O(n)`.
:::
:::section{.summary}
## Conclusion
In this article we learned :
1. Pythagoras theorem which says in a right angled triangle, square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
2. How to find pythagorean triplet in the given array using different approaches like naive approach, sorting, hashing, and STL.
## Related Topics
* [Must Do Maths for DS-Algo](https://www.scaler.com/event/master-fundamentals-for-coding-interviews-must-do-mathematics-for-ds-algo/)
:::