---
title: How to Find Array Length in Java - Scaler Topics
description: Learn how to find Array length in Java on Scaler Topics along with syntax, examples, and code explanations.
author: Abhinav Prakash
category: Java
---
:::section{.main}
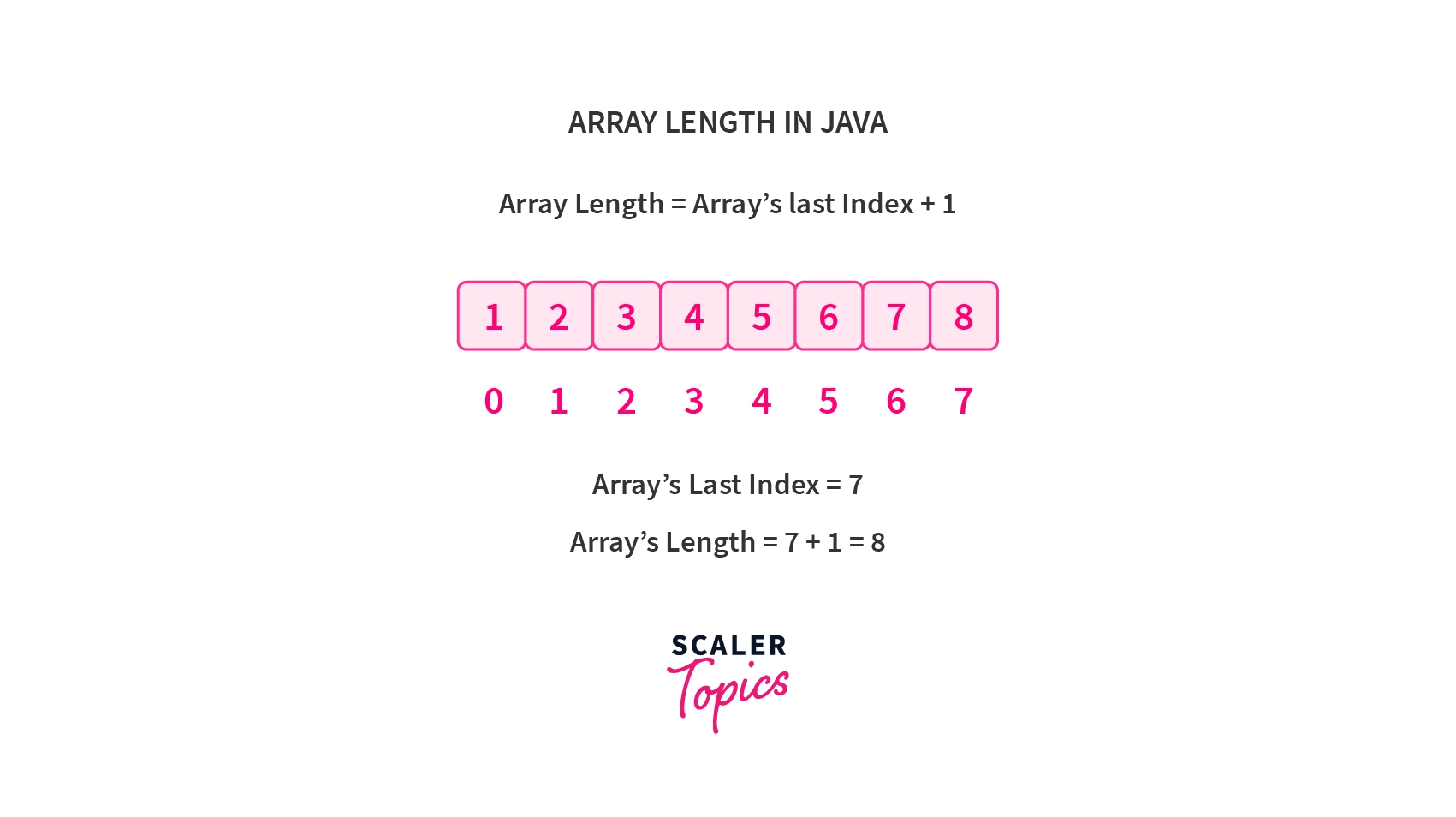
An array length in java signifies its capacity, accessible via the `length` attribute. This attribute, specific to arrays, reveals the number of elements it holds. While Java lacks a dedicated method for this, accessing `length` with the array's name provides quick insight into its size. Arrays store uniform-type elements in a fixed-size structure.
**Syntax:**
```java
// n is the size of the array
data-type[] A = new data-type[n];
int lengthOfArray = A.length;
```
:::
:::section{.main}
## Array Length Attribute
The number of elements in the array at the time of declaration is referred to as the array's size or length. The length of array in java named `A` is supplied by the following code:
```java
int len = A.length;
```
Let’s take a few examples to understand how length attributes work.
**Example: 1**
```java
// program to illustrate array length in java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[5];
int len = a.length;
System.out.println("Length of the Array is: " + len);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```java
Length of the Array is: 5
```
**Example: 2**
```java
// java program to illustrate string array length in java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] city = {
"Delhi",
"Bhubaneswar",
"Mumbai",
"Bangalore",
"Kolkata",
"Hyderabad",
};
int arrayLength = city.length;
System.out.println("The size of the array is: " + arrayLength);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```java
The size of the array is: 6
```
**Example: 3**
```java
// program to illustrate array length in java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static void len(int [] arr) {
if (arr== null) {
System.out.println("The length of empty array cann't determined.");
}
else {
int size= arr.length;
// prints the arr length
System.out.println("The size of the array is: " + size);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int [] brr= {45, 98, 45, 433, 342};
//passing null value to the len function
len(null);
//passing arr array to the function
len(arr);
//passing brr array to the function
len(brr);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
The length of empty array cann't determined.
The size of the array is: 5
The size of the array is: 5
```
:::
:::section{.main}
## Some Other Methods to Find Java Array Length
### Naive Approach
In this method, we employ a loop to iterate through each element of the array and count the number of elements encountered. This approach is commonly referred to as the "naive" method due to its simplicity and directness in determining the array length in java.
**Example:**
```java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 11, 32, 43, 24, 85, 56 };
//printing the array
System.out.println("Integer Array: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
long size = 0;
for(int i:arr){
size++;
}
System.out.println("The size of The integer array is: "+ size);
String[] brr= {"a","b","c","d","e"};
//printing the array
System.out.println("String Array: " + Arrays.toString(brr));
long sz = 0;
for(String i:brr){
sz++;
}
System.out.println("The size of The string array is: "+ sz);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
Integer Array: [11, 32, 43, 24, 85, 56]
The size of The integer array is: 6
String Array: [a, b, c, d, e]
The size of The string array is: 5
```
### Using length() Method
There is a length attribute associated with arrays. Using the length field, we can easily get the length of array in java.
**Example:**
```java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 11, 32, 43, 24, 85, 56 };
//printing the array
System.out.println("Integer Array: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
long size = arr.length;
System.out.println("The size of The integer array is: "+ size);
String[] brr= {"a","b","c","d","e"};
//printing the array
System.out.println("String Array: " + Arrays.toString(brr));
long sz = brr.length;
System.out.println("The size of The string array is: "+ sz);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
Integer Array: [11, 32, 43, 24, 85, 56]
The size of The integer array is: 6
String Array: [a, b, c, d, e]
The size of The string array is: 5
```
### Using size() Method
We can use the size() method of java.util.ArrayList class to get the number of elements in the list i.e array length in java.
**Example 1:**
```java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrlist = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//adding elements to arraylist
arrlist.add(11);
arrlist.add(32);
arrlist.add(43);
arrlist.add(24);
arrlist.add(85);
arrlist.add(56);
int size=arrlist.size();
System.out.println("The size of The array is: "+ size);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
The size of The array is: 6
```
**Example 2:**
```java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrlist = new ArrayList<String>();
//adding elements to arraylist
arrlist.add("a");
arrlist.add("b");
arrlist.add("c");
arrlist.add("d");
arrlist.add("e");
arrlist.add("f");
int size=arrlist.size();
System.out.println("The size of The array is: "+ size);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
The size of The array is: 6
```
### Using Stream API
Java 8 introduced the Stream API, which enables performing operations on arrays using functional programming paradigms. With this API, the count() method of the Stream class can be leveraged to determine the number of elements in an array.
**Example:**
```java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 11, 32, 43, 24, 85, 56 };
//printing the array
System.out.println("Integer Array: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
long size = Arrays.stream(arr).count();
System.out.println("The size of The integer array is: "+ size);
String[] brr= {"a","b","c","d","e"};
//printing the array
System.out.println("String Array: " + Arrays.toString(brr));
long sz = Arrays.stream(brr).count();
System.out.println("The size of The string array is: "+ sz);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```plaintext
Integer Array: [11, 32, 43, 24, 85, 56]
The size of The integer array is: 6
String Array: [a, b, c, d, e]
The size of The string array is: 5
```
:::
:::section{.summary}
## Conclusion
- The `array length` in java is very important attribute, with many real-life use cases.
- The length attribute is used to traverse Java arrays, opening the scope for performing various operations on the array elements.
- Among the elementary operations, we can search for a value or find the maximum or minimum value in an array using the `length` attribute in the loops.
- The last index of an array is one less than its length.
:::