# Introduction to JavaScript
---
title: Agenda
description: Agenda.
duration: 1260
card_type: cue_card
---
## Agenda
- What is JavaScript?
- How JS runs on the Browser
- Installing Node.js
- How Node.js runs JS code
- Variables in JavaScript
- How Js is a Dynamically Typed Language
- DataTypes in JS (Primitive and Refrenece)
- Functions in JS
- Arrays in JS
- Objects in JS
---
title: Module Importance
description:
duration: 1800
card_type: cue_card
---
### **Module Importance:**
JavaScript is the backbone of modern web development. This module helps you build strong foundations in asynchronous programming, closures, scopes, event loops, and functional programming — concepts essential for tackling real-world challenges in frontend and full-stack roles.
### **Industry Relevance:**
Core JavaScript skills are universally expected in technical interviews for both product-based and service-based companies. Whether debugging asynchronous code or building dynamic UIs, JavaScript fluency is a must-have.
### **Mandatory Practice Components:**
- **Mock interviews:** Assess logical application of JavaScript in interview settings
- **Weekly contests:** Reinforce concepts through real-time coding exercises
---
### **Job Market Snapshot**
| **Company & Role** | **Responsibilities** | **Skills Required** |
|------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------|
| **Zomato**, Frontend Developer | Build and optimize dynamic UI components, ensure smooth UX on web/mobile platforms | JavaScript (ES6+), HTML/CSS, async programming |
| **Razorpay**, UI Engineer | Collaborate with backend teams, build event-driven UIs, manage component states | JavaScript, DOM manipulation, debugging skills |
| **Swiggy**, Software Engineer (Web) | Work on scalable UI features, optimize for performance and accessibility | JavaScript, React basics, async handling |
---
title: Introduction to JavaScript
description: Basics of JavaScript, how to use JavaScript. Downloading nodejs.
duration: 1260
card_type: cue_card
---
### Definition
JavaScript is a language that is used to add interactivity to your websites, web apps etc..
#### History of JavaScript
* Before JavaScript was developed, the information displayed was static which means nothing can be done by the user. **Brendan Eich** developed JavaScript in just 10 days. LiveScript was the name given before JavaScript. Due to the popularity of Java programming language, Brendan gave the name JavaScript instead of LiveScript.
* JavaScript was introduced for browsers. Browsers like Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari support JavaScript.
### How does JavaScript work in a Browser?
#### Output in JavaScript
- Show devtools
- Discuss how to run few js command, we can do it in the console tab
When you click on inspect in your browser, a console window is opened which allows you to write JavaScript code.
Using `console.log` in JavaScript we can print out anything as we do in the other programming languages in Java we use `System.out.println()`.
```javascript!
console.log("Hello");
```
#### Variable in JavaScript
To define a variable in JavaScript `var` keyword is used.
```javascript!
var a = "Scaler";
console.log(a);
```
**[Ask the learners]**
What makes the Browser run the JavaScript code?
--> There are **JavaScript Engines** that are associated with the browsers.
For example, in Chrome: V8 Engine is used, while in Firefox: Spider Monkey is used.
> As Developers cannot use developer tools and develop an application using the console of the browser, we will use VS code and link the JavaScript file with the HTML file. By using the `<script>` tag (written inside the `<body>` of the HTML file) similar to the `<style>` tag used to write the CSS code we can write JavaScript code inside the `<script>` tag.
***Running JS code***
- Create intro.html
- Discuss that just like style tag which goes in head, we have script tag for JS which goes at the end of body tag.
Why will be discussed later
- Short answer - It helps in reducing the perceived load time of the page because the visual content of the page (HTML and CSS) is displayed to the user before the JavaScript starts executing.
The last thing before closing body tag is generally the script tag where the JS code goes
The code goes like this-
```html
<body>
<script>
console.log('Hello World')
</script>
</body>
```
#### Creating External JavaScript file
Similar to CSS, an External JavaScript file can be created using the `.js` extension.
The External JavaScript file can be linked to the HTML file using `<script src=""></script>`. The `<script>` tag has a source attribute to link the JavaScript file to the HTML file.
- Create index.js file
and write basic JS code
```JS
console.log("hello From the script File")
```
- add the index.js file in script tag's src attribute in the index.html file like this-
```html
<body>
<script>
console.log('Hello World')
</script>
<script src="./index.js"></script>
</body>
```
- see the output in the Browser
---
title: Download Nodejs
description:
duration: 2100
card_type: cue_card
---
### Download Nodejs
JavaScript is used for browsers only so how can we run it in our local machines? To overcome this, Ryan Dahl came up with *Node.js* which is an open-source JavaScript runtime environment. Node.js can be downloaded using [Nodejs](https://nodejs.org). It is recommended to download the LTS (long-term support) version.
To check if Nodejs is downloaded open the terminal on a Macbook or cmd in Windows.
Run the following command to check if it is downloaded successfully.
```
node --version
```
To start using node just type `node` in your terminal it will open the node environment which will allow you to run JavaScript in your local system.
#### Applications of JavaScript
After the invention of Nodejs JavaScript could be used for the following:
* JavaScript can be used for server-side development (to create servers or applications).
* Tools and technologies used for web development like React js, Express js and MongoDB came into existence.
* Mobile development also came into existence like React Native, and Ionic used to develop mobile applications.
* Desktop application - Electron js. For example - Vs code is built on Electron js.
* Tensorflow JS in AI and Machine learning is also being used currently.
* Metaverse - AR/VR where JavaScript can be used.
<!-- ADD ECMA Standards -->
#### Use node in Vs code
There is a terminal in Vs code that can be accessed for a particular file as well by right-clicking on the file and selecting the option 'Open in Integrated Terminal' as shown in the image.
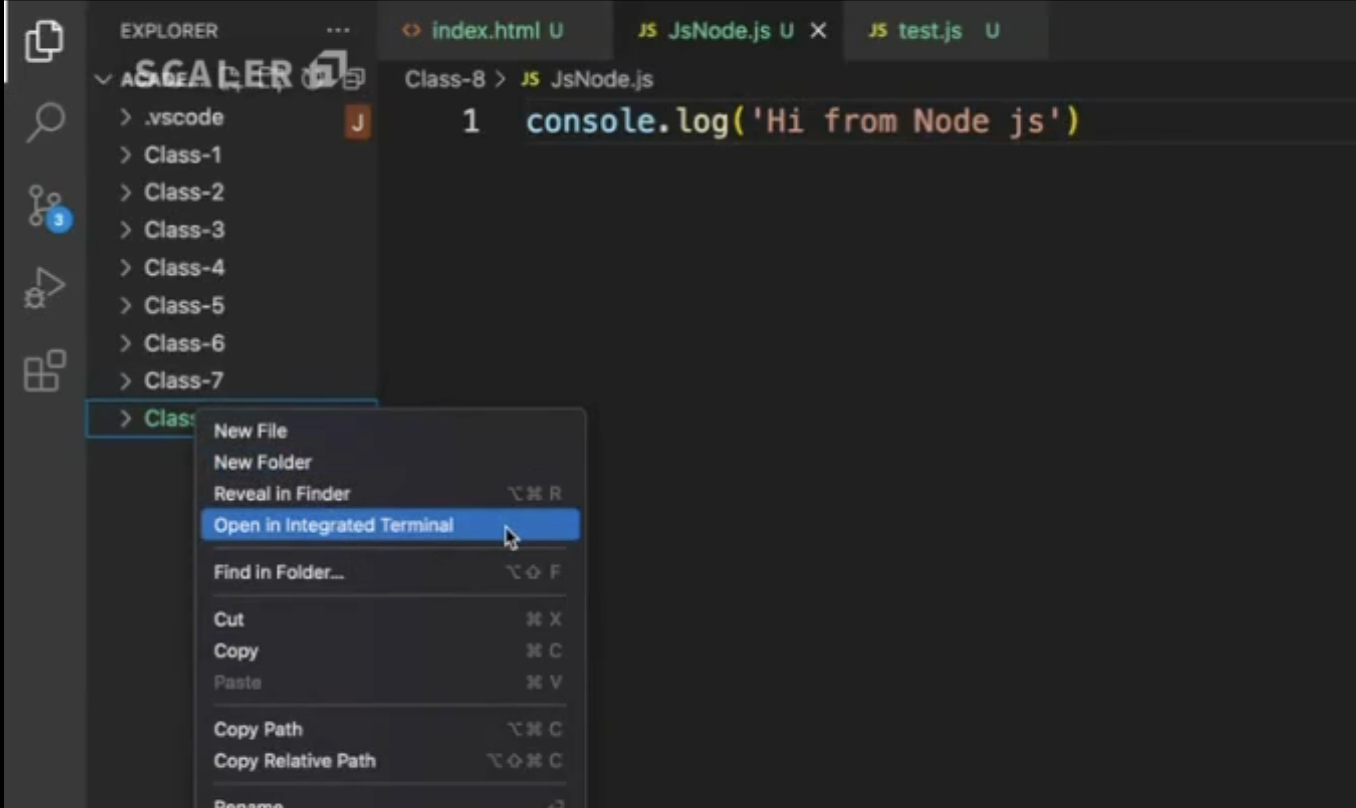
As you can see in the image, there is a file named JsNode.js which is created in folder Class-8 containing `console.log('Hi from Node js')`.
It can be accessed in the Vs code terminal by running the following command:
```
Node JsNode.js
```
The above command will give the result as:
```
Hi from Node js
```
> If there is an error while running the node js command which is commandNotFoundException then you can watch the following [video](https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sQXWVrb52kw) for Windows machines because this problem is mostly faced by Windows users.
---
title: Variables in JavaScript
description: var, let and const keywords are discussed
duration: 1800
card_type: cue_card
---
### Variables in JavaScript
**Definition**
Variables are a memory space in a system that is used to store values. These values can be a number, string, or boolean values and many more.
The `var` keyword is used in JavaScript to declare a variable.
For example:
```javascript!
var a = 30
console.log(a);
```
The result will be 30.
> JavaScript does not care about data type initialization for variables and these types of languages are known as loosely typed languages. The languages that care about data type initialization are known as strictly typed languages.
#### Dynamically Typed language
Values can be assigned to any variables anytime, anywhere with the same name, and print out all the possible output. For example:
```javascript!
var a = true
console.log(a)
var a = false
console.log(a)
```
The above code will print both true and false.
#### Problems of Var keyword
* The var keyword allows the re-declaration of variables. In ES6, two keywords: let and const were introduced which does not allow the re-declaration of variables. *(ES stands for Ecma Script which is a set of rules defined for JavaScript which keeps getting updated)*
**Example**
```javascript!
let a = 'Delhi'
console.log(a)
let a = 'Mumbai'
console.log(a)
```
The above code will throw an error named `Identifier a has already been declared`.
**Example**
```javascript!
let r = 10;
r = 30; //reinitialising the value
console.log(r)
```
- reinitializing with let is possible
* The var and let keyword allows re-initialization while const does not. The const keyword once declared will always remain constant.
Const behavior
```js
const pi = 3.14
pi = 3.15 // re-assign a variable not allowed
console.log(pi)
```
For const variables, declarations and assignment needs to be done in one line
Let's understand it using a chart:
| | Re-declaration | Re-Initialization |
| :--------: | :--------: | :--------: |
| **var** | Yes | Yes |
|**let** | No | Yes |
|**const** | No | No |
> If const is not initialised then it will throw an error. Therefore, it is necessary to declare and initialise const once.
---
title: Datatype in JavaScript
description: Two types of datatypes are discussed:- primitive and reference
duration: 3240
card_type: cue_card
---
### DataTypes in JavaScript
Datatypes are divided into two types - **Primitive Datatypes and Reference Datatypes**.
#### Primitive DataTypes
* **Numbers**
Numbers can be declared in JavaScript as shown below:
```javascript!
let a = 20
let b = 1000000000
let c = 12.57
let d = -10.12
let f = 2/0 // Infinity
let s = 'hello'/0 -> NaN
```
* **Strings**
```javascript!
let str = 'JavaScript'
let str2 = "Hello"
let str3 = `Hi, this is a string` // backticks are known as template literal
```
Hotstar cricket audience count
Backticks allow us to embed variables and expressions in string
```js
let activeUsers = 100
const message = `There are ${activeUsers} users online`
```
* **Boolean**
```javascript!
let isEven = true
let isOdd = false
```
* **Undefined**
When a variable is not defined it is set as undefined by default.
```javascript!
let a;
```
* **Null**
Null is assigned to a variable when we say that a value for this doesnt's exists or can be assigned later.
Null is a special value that represents ‘nothing’, ‘empty’ or value unknown
null is an assignment value that represents a deliberate non-value (or an empty value). It indicates the absence of any value or object.
```javascript!
let a = null
```
While both null and undefined represent "no value", the choice between them is not interchangeable. undefined is used when a value has not been assigned and is the default state, while null is used to explicitly denote a null or "empty" value.
#### Reference DataTypes
## Functions
Functions are abstract bodies defined to do a particular task.
The function is defined using the `function` keyword in JavaScript followed by the function name with parentheses.
```javascript!
//Create a beverage Vending machine
//Function Declaration
function serveBeverage(drink){
//drink is a parameter for the function
console.log(drink)
}
//call the function - function Invokation
serveBeverage('tea') //tea is an argument for drink parameter
```
The function can be called multiple times and multiple arguments can be passed.
# Arrays
The array is a data structure to store multiple values of multiple data types. The elements are stored in an indexed manner.
## Accessing array element
Any array element can be accessed by an index. If we want to access the fifth element of an array named `arr`, then we have to simply write `arr[4]`, as the array works on 0-indexing.
```javascript=
let arr = [1, 'Scaler', true, undefined, null, [1, 2, 3] ,function(){}]
console.log(arr)
// access an element with index from an array
console.log(arr[4]) // print null
let d=arr[5]
console.log(d) // print [1, 2, 3]
console.log(d[0]) // print 1
```
## Changing an array element
We can change the value of any element by its index, if we want to change the value of the fourth element of an array named `arr`, then we need to simply write `arr[3]='new value'`
```javascript=
let arr = [1, 'Scaler', true, undefined, null, [1, 2, 3]]
console.log(arr) // print [1, 'Scaler', true, undefined, null, [1, 2, 3]]
// change an array element to a different value
arr[3] = 'Mrinal'
arr[4] = 700
console.log(arr) //print [1, 'Scaler', true, 'Mrinal', 700, [1, 2, 3]]
```
## Length of an array
Gives the length of the array, length means the total number of elements in an array.
```javascript=
let arr = [1, 'Scaler', true, undefined, null, [1, 2, 3]]
console.log(arr.length) // print 6 as there are a total of 6 elements in an array.
```
## Array methods
**Push Method:**
Inserting an element into an array at the end
```javascript=
let cars = ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi']
console.log(cars) // print ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi']
cars.push('Urus')
console.log(cars) // print ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
```
**Pop Method:**
Delete the element from the end of the array
```javascript=
let cars = ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
console.log(cars) // print ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
cars.pop()
console.log(cars) // print ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi']
```
Popped elements can also be stored in another variable.
```javascript=
let cars = ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
var removedElement = cars.pop()
console.log(removedElement) // print Urus
```
**Unshift Method**
Insert an element at the start of an array(0th index).
```javascript=
let cars = ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi']
console.log(cars) // print ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi']
cars.unshift('Urus')
console.log(cars) // print ['Urus', 'Swift', 'BMW', 'Audi']
```
**Shift Method**
Remove the 0th index element of an array.
```javascript=
let cars = ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
console.log(cars) // print ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
cars.shift()
console.log(cars) // print ['BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
```
Shifted elements can also be stored in another variable.
```javascript=
let cars = ['swift', 'BMW', 'Audi', 'Urus']
var removedElement = cars.shift()
console.log(removedElement) // print swift
```
---
title: Objects
description:
duration: 1800
card_type: cue_card
---
# Objects
Objects are basically in which data is stored in the form of key-value pairs.
**Ways to create Objects**
```js
let user = new Object( ) // object constructor syntax
let anotherUser = { } // object literal syntax
console.log(user)
console.log(anotherUser)
```
You Can directly create objects by specifying properties as shown below
## Example
```javascript=
let person ={
name: 'Mrinal',
age: 24,
phone: 1234567
}
console.log(person)
// dot notation
console.log(person.age)
// bracket notation
console.log(person['phone'])
```
We can store any kind of value in an object. We can also write a function inside the object using `:`. Another object can also be created within the object and also arrays can be stored as values inside objects along with numbers strings and boolean
Let's Take an Example to have all this inside an Object
```javascript=
let captainAmerica ={
name : 'Steve Rogers',
age : 102,
// Array
allies : ['Tony', 'bruce', 'bucky']
// function inside an object
sayHi : function(){
console.log('Captain says hi')
}
// nested object
address :{
country : 'USA',
city : {
name : 'Brokkly',
pincode : 12345
}
}
// Boolean
isAvenger : true
}
// accessing age from captainAmerica object
console.log(captainAmerica.age) // prints 102
// accessing element of array allies from captainAmerica object
console.log(captainAmerica.allies[1]) // prints bruce
// accessing element from the nested object
console.log(captainAmerica.address.city)
// print complete city object
console.log(captainAmerica.address.city.pincode) // print 12345
// changing some values of an object
captainAmerica.isAvenger=false
// adding new key-value in object
captainAmerica.movies=['End Game', 'Age of Ultorn', 'Civil War']
//The above statement will create a key with movies if it is not available in the object otherwise it will update the previous value of movies.
// calling function defined within an object
captainAmerica.sayHi()
//Deleting key from an object
delete captainAmerica.age
```
---
title: Unlock & Solve
description:
duration: 600
card_type: cue_card
---
Please unlock the assignment for students by clicking this "question mark" button on top bar.
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/078/685/original/Screenshot_2024-06-19_at_7.17.12_PM.png?1718804854" width=200 />
Ask students to solve **JS Core - String Manipulation: Reverse a string** from assignment.
1. Give them 7 minutes to think while you can answer any doubts that they are having.
2. Then you can explain them the problem statement and unfold the ask.
3. The question asks to find number of set bits in given number.
### How to access problem being Instructor?
You can go to instructor dashboard and navigate through your batch, classes and then problems.(https://www.scaler.com/academy/instructor-dashboard/)