# 2024.10.14 - Progcrypto Camp - Intorduction to Account Transfer
[Aki](https://x.com/rumitoast) , Co-founder of [Mycel](https://mycel.land)
**Full docs here**:
https://hackmd.io/@taryune/ry8aX8LJkx
---
# Cross-Domain Asset Swapping
- Traditional methods in cross-chain swapping like **atomic swaps** and **smart contract-based locks** face challenges like cryptographic curve reliance, counterparty dependency, and chain-specific limitations.
- **Account transfer** is a generalized approach that treats the account as a unified object, allowing cross-chain, multi-asset transfers in a single transaction.
---
## Smart Contract-Based Asset Lock
>
[Intents Architecture in Across](https://docs.across.to/concepts/intents-architecture-in-across)
- Cross-chain Dependency: Relies on locking assets on one chain
- Dynamic Matching (AMM/OFA)
---
## Atomic Swap (HTLC)

>
> [Atomic swaps: a simple, fair exchange protocol](https://medium.com/@pierre.noizat/what-are-atomic-swaps-bc1d034634c9)
- Counterparty Dependence: Atomic swaps require both parties to agree on the swap before it begins
---
## We Still Need More Generalized Approach
- Breaking Dependency on Cryptographic Curves or Smart-Contracts
- Improving Liquidity and Flexibility in Matching
- Unified and Scalable Asset Transfer
---
## Account as Object: An Approach to Generalize Assets
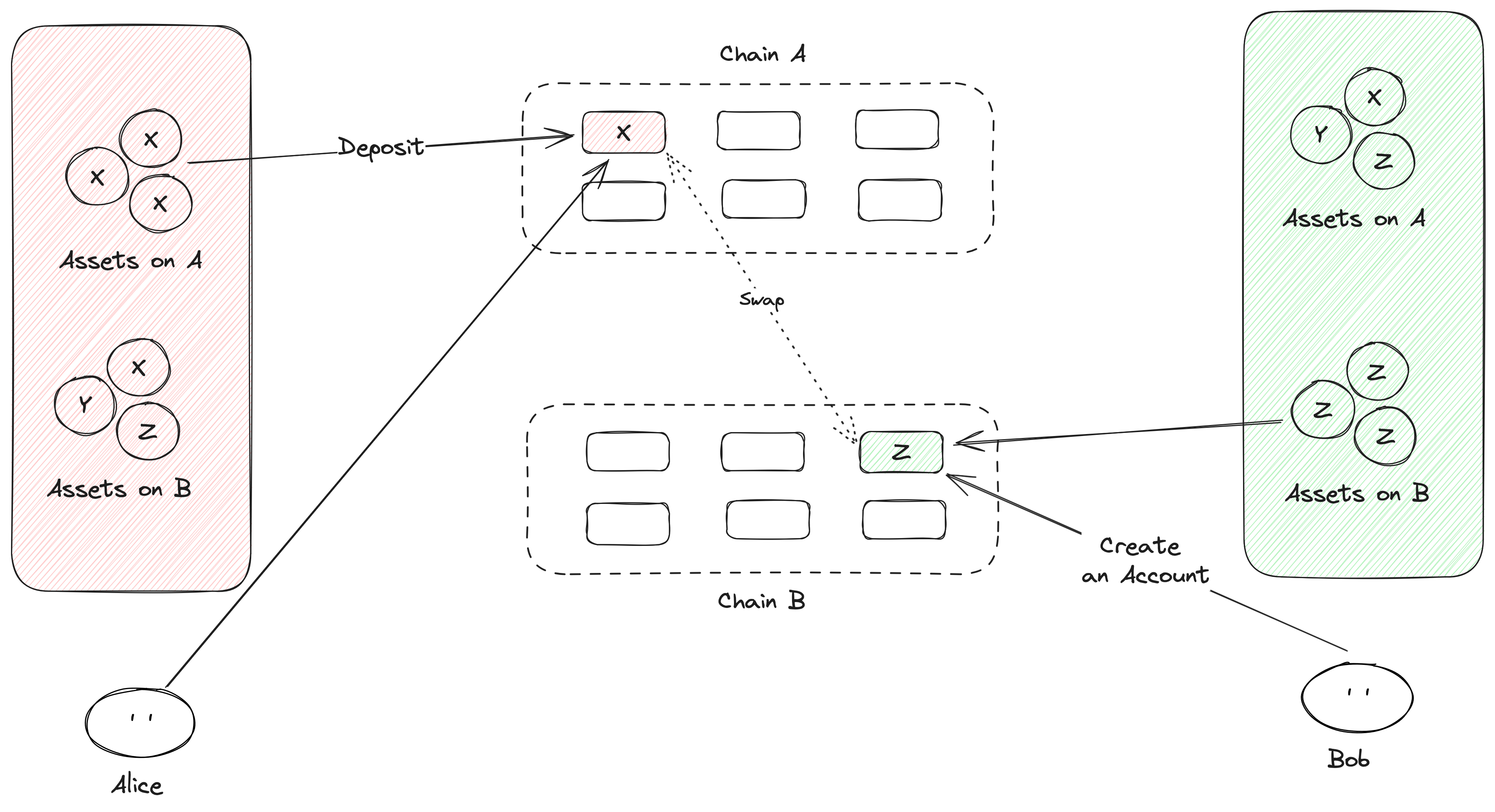
- No Dependency on Crypto Curves or State Machine Architectures
- Improving Liquidity and Flexibility in Matching
- Unified and Scalable Asset Transfer
---
## Transferable Account = Key + Ownership
- Key: The actual private key that controls the account. This key is crucial because it governs the ability to sign transactions and perform actions with the assets held in the account.
- State: The ownership state of the account, which includes information about who owns the account.
---
## Key Management
- Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS)
- Trusted Execution Environment (TEE)
- Hybrid Approaches: TSS can be applied in decentralized networks to distribute key shares, while individual participants can use TEEs to manage their share of the key securely.
---
## Swap Account
- Alice wants to swap A token for B token (Intent_A)
$$
\text{Intent}_A = (A_i, B_r, \tau_A)
$$
- Bob wants to swap B token for A token (Intent_B)
$$
\text{Intent}_B = (B_i, A_r, \tau_B)
$$
Where:
- $A_i$and $B_i$are the initial accounts of Alice and Bob, respectively.
- $A_r$and $B_r$are the requested accounts that Alice and Bob want in return.
- $\tau_A$and $\tau_B$represent the expiration times for the intents.
---
## 1. Submit Intents

---
## 2. Solve Intents

---
## 2. Solve Intents
1. **Intent Matching**:
The solver checks whether Alice’s and Bob’s intents are compatible. If they are, the system starts the swap process.
$$
\text{Match}(A_i, B_r) = \text{true} \quad \text{and} \quad \text{Match}(B_i, A_r) = \text{true}
$$
2. **Partial Transaction**:
Solver creates a partial transaction, which temporarily holds the state changes (ownership swap)
$$
K_{\text{temp}}(A_i) = B \quad \text{and} \quad K_{\text{temp}}(B_i) = A
$$
$$
\text{Tx}_{\text{partial}} = (A_i \xrightarrow{\text{temporary}} B, B_i \xrightarrow{\text{temporary}} A)
$$
---
## 3. Unlock Accounts

---
## 3. Unlock Accounts
1. **Verification**: Alice verifies the assets in her new account, making sure they match what she expected to receive from Bob. Also Bob does the same.
$$
\text{Verify}(A_r) = \text{true} \quad \text{and} \quad \text{Verify}(B_r) = \text{true}
$$
2. **Unlock and Finalize**: If both parties confirm that the assets are correct, the new owners are settled by the transaction which update the key state store.
$$
\text{Tx}_{\text{final}} = (A_i \xrightarrow{\text{final}} B, B_i \xrightarrow{\text{final}} A)
$$
$$
K(A_i) = B \quad \text{and} \quad K(B_i) = A
$$
---
## 4. Request Withdraw

---
## Comparison

---
## Sample implementation

---
## Conclusion
- Account transfer provides a generalized, scalable, and secure method for cross-chain asset transfers.
- By enabling the movement of entire portfolios across blockchains without relying on cryptographic curves or bridges, it enhances liquidity, flexibility, and interoperability.
- As DeFi evolves, account transfer offers a robust foundation for cross-chain interaction.
---