# Ch6
## The Graph 定義
**資料結構**
一個graph圖表有兩個sets(集合): V,E
* V(G): 非空集合,存著**頂點vertices**
* E(G): 可以是空集合,存**著線edges**
### 方向性
**undirected graph**
* 線並沒有方向性 (v0, v1) = (v1,v0)
* v0 and v1 are adjacent()
* (v0, v1) is incident on vertices v0 and v1
**directed graph**
* 線有方向性 <v0, v1> != <v1, v0>
* <v0, v1> is incident on v0 and v1
### path
**Path**(路徑)指在圖表裡面從vertex到另一個vertex,會由一連串的線 (vp, vi1), (vi1, vi2), ...,(vin, vq)所組成
* path such as (0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 3) is also written as 0, 2, 1, 3
* path的長度(length)是指走過的線(edges)的數量
### complete and incomplete graph

## The Graph ADT
### Adjacency Matrix
「相鄰矩陣」。把一張圖上的點依序標示編號。然後建立一個方陣,記錄連接資訊。方陣中的每一個元素都代表著某兩點的連接資訊

> 圖片取自:https://web.ntnu.edu.tw/~algo/Graph.html
### Adjacency lists
「相鄰列表」。把一張圖上的點依序標示編號。每一個點,後方列出所有相鄰的點

> 圖片取自:https://web.ntnu.edu.tw/~algo/Graph.html
**資料結構**
```c=
#define MAX_VERTICES 50 /*maximum number of vertices*/
typedef struct node *node_pointer;
typedef struct node {
int vertex;
struct node *link;
};
node_pointer graph[MAX_VERTICES];
int n = 0; /* vertices currently in use*/
```
## DFS && BFS
### DFS
每個節點會記錄跟其相鄰的節點
找到一個點後,尋找該點是否還有跟其他未訪問過的節點相連

**程式碼(recursive)**
```c=
void dfs(int v){
/* depth first search of a graph begin*/
node_pointer w;
visited[v] = TRUE;
printf("%5d" , v);
for(w = graph [v]; w; w = w->link)
if (!visited[w->vertex])
dfs(w->vertex);
}
```
**Output**
```c=
0 1 3 7 4 5 2 6
```
### BFS (Queue)

**資料結構**
```c=
typedef struct queue *queue_pointer;
typedef struct queue {
int vertex;
queue_pointer link;
};
void addq(queue_pointer *, queue_pointer *, int);
int deleteq(queue_pointer *);
```
**程式碼(iterative)**
```c=
void bfs(int v){
node pointer w;
queue_pointer front, rear;
front = rear = NULL; /*initialize queue*/
printf ("%5d", v) ;
visited[v] = TRUE;
addq(&front, &rear, v);
while(front){
v = deleteq(&front) :
for(w = graph[v]; w; w = w->link){
if(!visited[w->vertex]){
printf("%5d", w->vertex)
addq(&front,&rear,w->vertex);
visited[w->vertex] = TRUE;
}
}
}
```
**Output**
```c=
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
```
## Minimum Cost Spanning Trees
每個節點都有不同的權重weight,而其中具有最小weight總和的樹,稱為Minimum Spanning Tree(MST)

> 圖片取自:http://alrightchiu.github.io/SecondRound/minimum-spanning-treeintrojian-jie.html
### 演算法
下面寫到的幾種都是屬於**貪婪演算法**
* Kruskal's algorithm
* Prim's algorithm
* Sollin’s Algorithm
### Kruskal's algorithm
Kruskal演算法的方式是從所有邊中,反覆選擇最短的邊,它的步驟是:
1. 將所有的邊依照權重由小到大排序。
2. 從最小開始,選擇不會形成環的邊,直到連接所有節點。

> 資料取自:https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/m/articles/10278295
**虛擬碼**

### Prim's algorithm
1. 先將任意節點加入到樹之中(選擇起點)
2. 選擇與樹距離最近的節點,加入到樹中,反覆此步驟直到所有節點均在樹中,即為最小生成樹。
3. 每一階段樹都會納入距離最近的節點、增加一條邊,直到連接所有的節點。
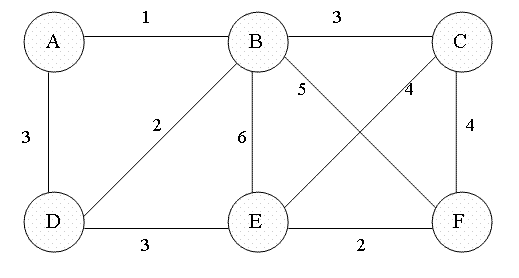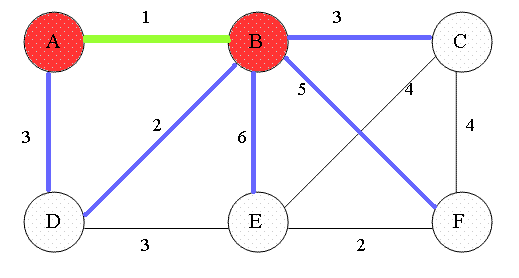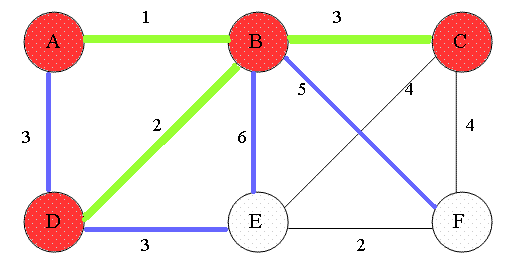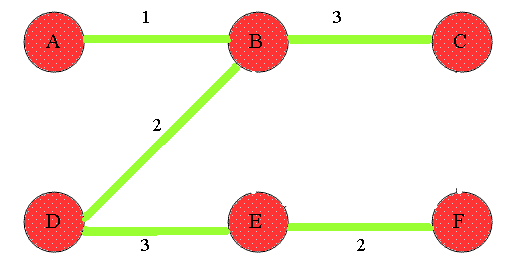
> 圖片取自:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Prim-animation.gif
**虛擬碼**

### Sollin’s Algorithm
1. 將各頂點視為獨立的一棵樹
2. 就每棵樹挑出成本最小的邊,並加入此樹
3. 刪除重複挑出的邊,只保留一份
4. 重複2~3直到只剩一棵樹,或是無邊可挑
> 取自:https://garychang.gitbook.io/data-structure/4-graph/4.3-spanning-tree/4.3.3-sollins-algorithm

**沒有虛擬碼,所以stage要會寫**

# Ch7
## Sorting(排序演算法)
### Insertion sort(插入排序法)
1. 從資料列的第二個元素開始,逐一取出每一個元素,稱為目標元素。
2. 將目標元素與已排序的資料列中的元素逐一比較,直到找到一個比目標元素大的元素或搜尋完整個已排序的資料列。
3. 將目標元素插入到適當的位置。
4. 重複上述過程直到所有的元素都已排序完成。
> 取自:https://medium.com/@ollieeryo/insertion-sort-%E6%8F%92%E5%85%A5%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%B3%95-c215ae516a7a

> 圖片取自: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/9c/Insertion-sort-example.gif
**程式碼**
```c=
void insertion_sort(element list[], int n){
/* perform a insertion sort on the list*/
int i,j;
element next;
for (i = 1; 1 < n; i++){
next = list[i];
for(j= i-1;j >= 0 && next.Key < list[j].Key;j--)
list[j+1] = list[j];
list[j+1] = next;
}
}
```
> 時間複雜度: $O(n^2)$
### Quick sort(快速排序法)
1. 先從陣列中選擇一個「樞紐」(pivot),然後將所有小於樞紐的值都移到它的左邊、將所有大於樞紐的值都移到它的右邊
2. 當樞紐完成以後,我們對左半部分再次進行同樣的處理(找到 pivot、移動位置),再處理右半部分。
* **為Unstable的演算法(排序結果不唯一)**
> 取自:https://medium.com/@amber.fragments/%E6%BC%94%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95-%E5%AD%B8%E7%BF%92%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98-12-%E5%BF%AB%E9%80%9F%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%B3%95-quick-sort-841420575b24

> 圖片取自: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/9c/Quicksort-example.gif
**程式碼**
```c=
void quicksort(element list[],int left, int right){
int pivot,i,j;
element temp;
if (left < right){
i = left; j = right + 1;
pivot = list[left].key;
do {
do
i++;
while(list[i].key < pivot);
do
j--;
while(list[j].key > pivot);
if (i < j)
SWAP(list[i],list[j],temp);
} while(i < j);
SWAP(list[left],list[j],temp);
quicksort (list,left,j-1);
quicksort (list,j+1,right);
}
}
```
> 時間複雜度: $O(n\log_2 n)$
### Merge sort(合併排序法)
基本的步驟可以分為「**拆分**」與「**合併**」:
* **拆分**
1. 把大陣列切一半成為兩個小陣列
2. 把切好的兩個小陣列再各自切一半
3. 重複步驟二直到每個小陣列都只剩一個元素
* **合併**
1. 排序兩個只剩一個元素的小陣列並合併
2. 把兩邊排序好的小陣列合併並排序成一個陣列
3. 重複步驟二直到所有小陣列都合併成一個大陣列
> 內容取自:https://medium.com/appworks-school/%E5%88%9D%E5%AD%B8%E8%80%85%E5%AD%B8%E6%BC%94%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95-%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%B3%95%E9%80%B2%E9%9A%8E-%E5%90%88%E4%BD%B5%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%B3%95-6252651c6f7e
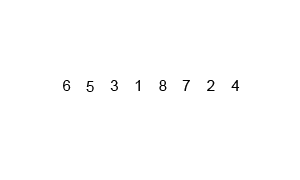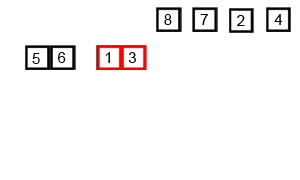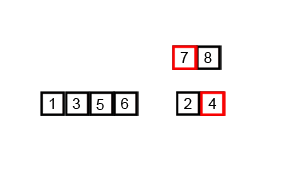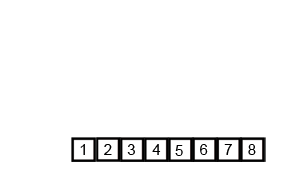
> 圖片取自:https://miro.medium.com/v2/0*K7cD17vfL7FdTTLK.gif
* Merge sort 主程式
```c=
void merge-sort(element list[], int n){
int length = 1;
element extra[MAX_SIZE];
while(length < n){
merge-pass(list,extra,n,length);
length *= 2;
merge-pass(extra,list,n,length);
length *= 2;
}
}
```
**程式碼(Iterative)**
* 排序
```c=
void merge(element list[], element sorted[], int i, int m,int n){
/* merge two sorted files: list [i],...,
* list [m], and list [m+1], .., list [n].
* These files are sorted to obtain a sorted list:
* sorted[i],..., sorted [n] */
int j,k,t;
j = m+1; /* index for the second sublist */
k = i;/* index for the sorted list */
while(i <= m && j <= n){
if (list[i].key <= list[j].key)
sorted[k++] = list[i++]
else
sorted[k++] = list [j++];
}
if (i > m) //右邊陣列剩下的元素直接複製到sorted
/* sorted[k],... sorted[n] = list[j],...,list[n] */
for (t = j; t <= n; t++)
sorted[k+t-j] = list[t];
else //左邊陣列剩下的元素直接複製到sorted
/* sorted[k],..,sorted[n] = list[i],*/
for(t = i: t <= m; t++)
sorted[k+t-i] = list[t];
```
* 合併
```c=
void merge-pass(element list[], element sorted[], int n, int length){
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<= n - 2*length;i += 2*length - 1)
merge(list,sorted,i,i + length - 1,i + 2*length - 1);
if(i + length < n)
merge(list,sorted,i,i + length - 1,n - 1);
else
for(j=i; j < n; j++)
sorted[j] = list[j];
}
```
> 時間複雜度: 總共$O(n^2)$
### Heap sort(堆積排序)
1. 把初始的Binary tree變成Max heap
2. 從最後一個(n)元素開始,將n與root比較,如果n比root小則交換
3. 將Binary tree變成Max heap
4. n - -,重複過程2~3,直到n=0(全部的節點都跟root比較過)
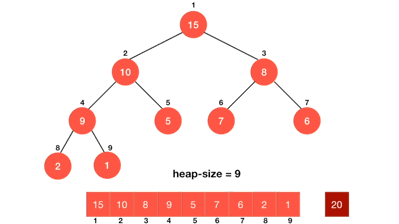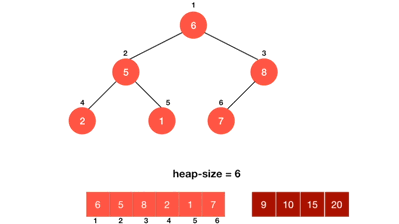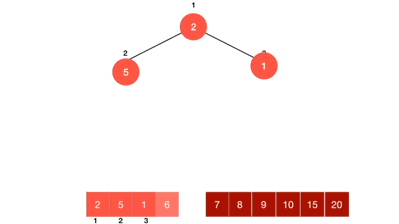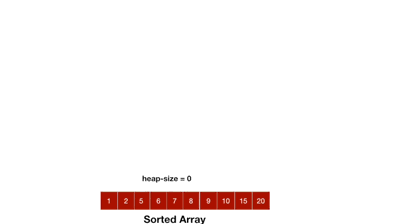
**程式碼(從小排到大)**
* Heap sort 主程式
```c=
void heapsort(element list[], int n){
/* perform a heapsort on the array*/
int i,j;
element temp;
//將binary tree調整成max heap
for(i = n/2; i > 0; i--) //bottom-up
adjust(list,i,n) ;
for(i = n-1; i > 0; i--){
SWAP(list[1],list[i+1],temp);
adjust (list, 1, i): //top-down
}
}
```
* 把Binary tree變成 Max heap
```c=
void adjust (element listl], int root, int n){
int child, rootkey;
element temp;
temp = list[root];
rootkey = list[root].key;
child = 2 * root;/*left child */
while (child <= n){
if ((child < n)&&(list[child].key < list [child+1].key))
child++;
if (rootkey > list[child].key)
//compare root and max root
break;
else { //move to parent
list[child / 2] = list[child];
child *= 2;
}
}
list[child/2] = temp;
}
```
> 時間複雜度: 總共$O(n\log_2 n)$
### Radix sort
常見的 Radix sort 依據整數的每個位數來排序,依照位數排序的先後順序,可分為兩種:
* **Least significant digit (LSD)**:從最低有效鍵值開始排序(最小位數排到大)。
* Most significant digit (MSD):從最高有效鍵值開始排序(最大位數排到小)
簡單的 **LSD Radix sort** 步驟如下:
1. LSD of each key:取得每個資料鍵值的**最小位數**(LSD)。
2. Sorting subroutine:依據該位數大小排序資料。
3. Repeating:取得下一個有效位數,並重複步驟二,至最大位數(MSD)為止。
**資料結構**
```c=
#define MAX_DIGIT 3 /* 0 to 999 */
#define RADIX_SIZE 10
typedef struct list_node *list_pointer;
typedef struct list_node {
int key[MAX_DIGIT];
list_pointer link;
};
```
**程式碼**
```c=
list_pointer radixsort(list-pointer ptr){
/*Radix Sort using a Linked list */
list-pointer front[RADIX_SIZE],rear[RADIX_SIZE];
int i, j, digit;
for (i = MAX_DIGIT-1; i >= 0; i--){
for (j = 0; j < RADIX_SIZE; j++)
front[j] = rear[j] = NULL;
while(ptr){
digit = ptr->key[i];
if(!front[digit])
front[digit] = ptr;
else
rear[digit]->link = ptr;
rear[digit] = ptr;
ptr = ptr->link; //換下一個數字
}
//reestablish the linked list for the next pass
ptr = NULL;
for(j = RADIX_SIZE-1; j >= 0; j--){
if(front[j]){
rear[j]->link = ptr;
ptr = front[j];
}
}
}
return ptr;
}
```
> 時間複雜度: O(MAX_DIGIT(RADIX_SIZE+n))
# Ch8
## Hashing 定義
是一種資料儲存與擷取之技術,當要存取 Data X 之前,必須先經過 Hashing Function 計算求出 Hashing Address (or Home Address),再到 Hash Table 中對應的 Bucket 中存取 Data X,而 Hash Table 結構是由 B 個 buckets 組成,每個 bucket 有 S 個 Slots,每個 Slot 可存一筆 Data
**Hash Table 大小 = B * S 筆**

### Hashing 優點
* 搜尋 Data 之前,**無需事先排序過**
* 再沒有 Collision 情況下,**Search time 為: $O(1)$**,與資料量 n 無關
* 保密 / 安全性高,在不知道 Hashing Function 下,很難取得 Data
* 可作為 Data 壓縮之用途
### Collision && Overflow
**Collision (碰撞)**
* 不同的 Data,例如 (x,y),經過 **Hashing function 計算後得出相同的 Hashing Address** 稱之,也就是 H (x) = H (y)。
**Overflow(溢位)**
* 當 Collision 發生後,且對應的 Bucket 已滿,則稱為 Overflow
**Collision 與 Overflow 比較**
* 有 collision 不一定會 overflow
* 若每個 bucket 只有 1 個 slot,或是只能放一筆 Data,則 Collision = Overflow
### identifier density && loading density
令 t 為 identifier 是 Hash table 裡面的總數,n 為使用 identifier 個數,B * S 為 Hash Table size
則:
$$identifier\ density = \frac{n}{t}$$
$$loading\ density(負載密度) = \frac {n}{B * S}$$
$$
Note:若 **load density 越大,代表 Hash Table 利用度高,但相對 Collision 機會也大**
> 引用自: [資料結構與演算法筆記 - Hashing (雜湊) 原理介紹 - Kenny's Blog](https://blog.kennycoder.io/2020/02/18/%E8%B3%87%E6%96%99%E7%B5%90%E6%A7%8B%E8%88%87%E6%BC%94%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98-Hashing-%E9%9B%9C%E6%B9%8A%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E4%BB%8B%E7%B4%B9/)
## Hash function
### Middle Square
將鍵值平方後,取**中間適當位數**作為 Hashing Address
例如:鍵值 = 8125,平方後 = 66015625
取中間三個位數,156 作為 Hashing Address
### Division
Mod (or Divide) 取餘數
H(X) = X % M
**M 最好滿足:**
* 非2的質數
### Folding Addition
將鍵值切成幾個相同長度之片段 $(P_1-P_n)$,再將這些片段加總,即得 Hash Address
而相加的方法有兩種:
* shift (位移)
* bounding (邊界)
例如:x = 12320324111220 ,分成五個片段
1. P1 = 123
1. P2 = 203
1. P3 = 241
1. P4 = 112
1. P5 = 020
**shift 作法**
將 $(P_1-P_n)$ 相加 = 699
**bounding 作法**
偶數的片段反向,所以:
* P2 = 302
* P4 = 211
再加總 $(P_1-P_n)$ = 897
### Digits Analysis (位數值分析)
適用於資料事先知道之情況,分析每個資料再不同位數之值域分布情況,選出之位數組成 Hashing Address
* 若分布很集中,則捨棄該位數
* 若分布散亂,則挑選該位數
拿電話號碼為例:
1. 02-7415089 => 158
1. 02-7434079 => 347
1. 02-7424139 => 243
1. 02-7458069 => 586
1. 02-7473029 => 732
根據以上的位數挑出三個數字的 Hashing Addrss
> 引用自: [資料結構與演算法筆記 - Hashing (雜湊) 原理介紹 - Kenny's Blog](https://blog.kennycoder.io/2020/02/18/%E8%B3%87%E6%96%99%E7%B5%90%E6%A7%8B%E8%88%87%E6%BC%94%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98-Hashing-%E9%9B%9C%E6%B9%8A%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E4%BB%8B%E7%B4%B9/)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet