# Merge Sort
###### tags: `演算法` `資料結構`
{%hackmd @rpyapp/theme %}
[toc]
## What is Merge Sort
合併排序是一種 Divide and Conquer 的演算法,它是將一個 array 分解為幾個 sub array,直到每個 sub array 由一個元素組成,然後以產生排序列表的方式合併這些子列表。
大致分成三個步驟:
1. **切分**: 將未排序的 array 劃分為 sub array,當每個 sub array 就是每個 element 時。
2. **比較合併**: 將相鄰的兩個 sub array ,互相比較第一個 element ,並取較小值則為以排序值,以排序值可以用新 array 存或是用 index 的方式將其隔開。
3. 重複該過程,直到所有 sub array 都合併成一個 array 。
### >>下圖1、8、2、9 為切分過程,當切到 sub array 只包含 1 element 時開始比較合併的
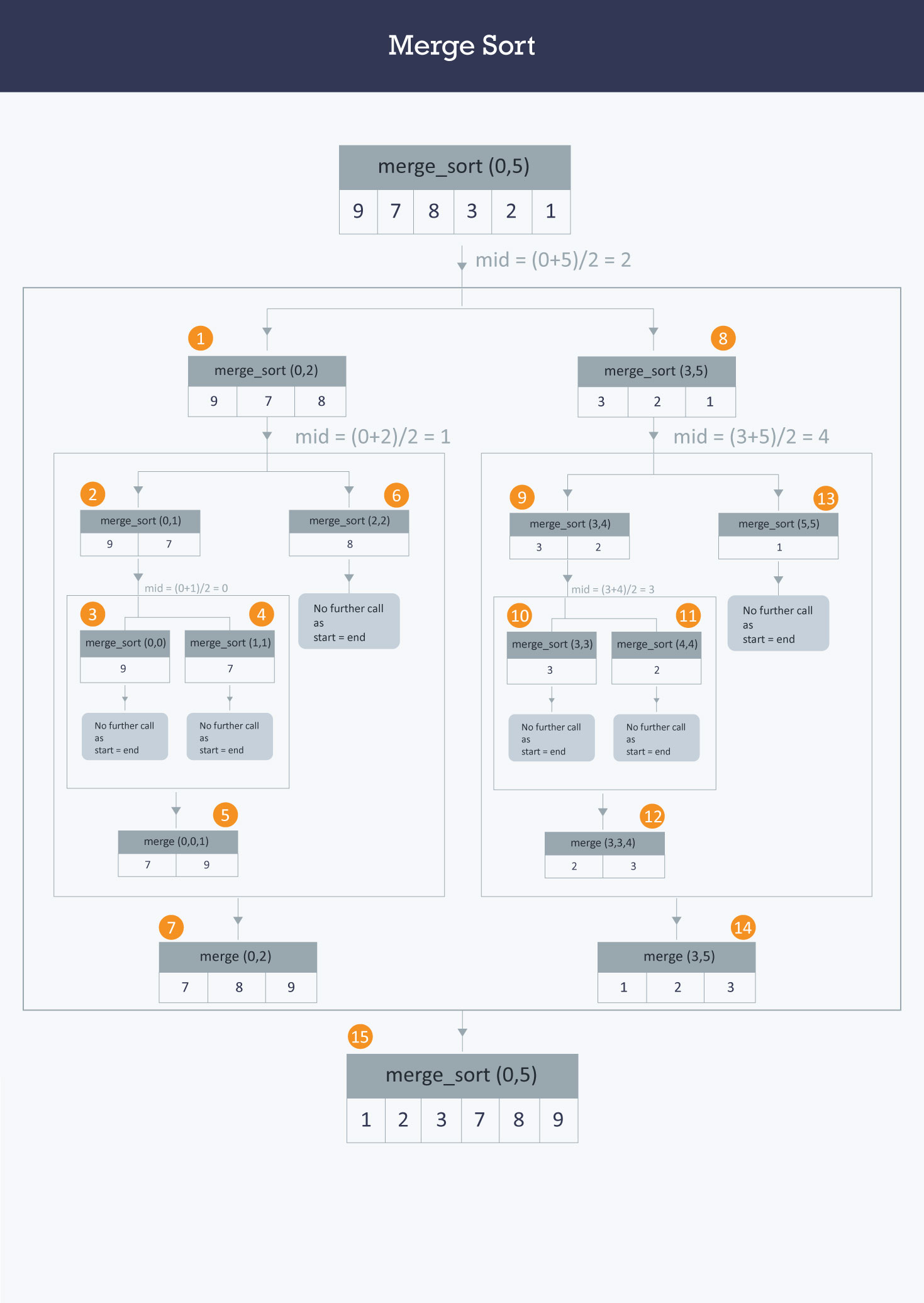
>[來源網站](https://www.hackerearth.com/zh/practice/algorithms/sorting/merge-sort/tutorial/)
### >>下圖為另一張流程圖,在切分和合併比較清楚
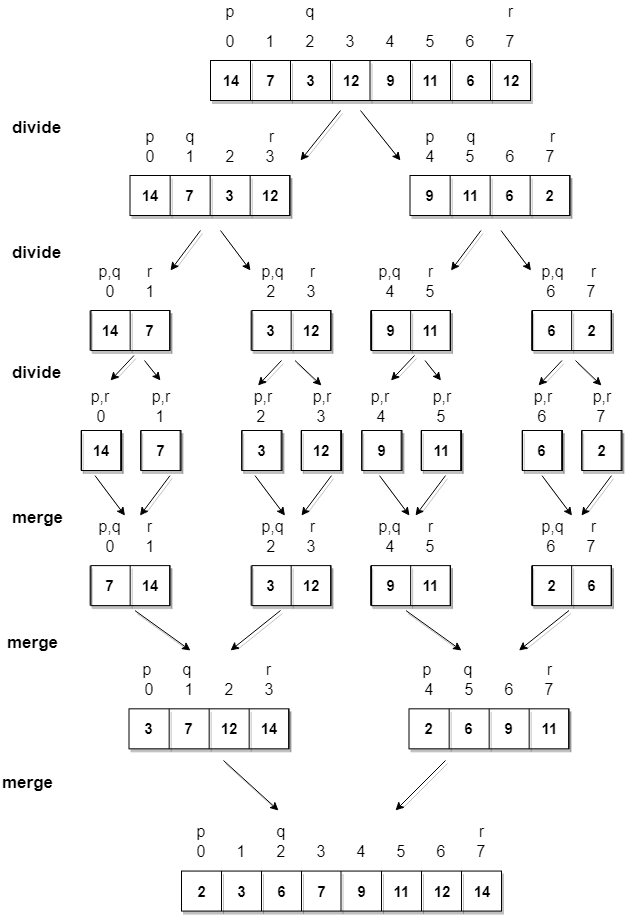
>[圖片來源](https://www.studytonight.com/data-structures/merge-sort)
## Divide and Conquer
如何使一個大且複雜的問題更容易解決,而分而治之(Divide and Conquer) 就是一種方式,它的想法是將大問題切分稱須多小問題,然後各個擊破。
以英國舉例,當英國人來到印度時,他們可以與宗教信仰不同的國家和睦相處,工作勤奮、天真、且很團結。聽起來很棒,但是對英國來說卻不好管制。因此,他們採取了分而治之的政策。他們通過煽動地方國王之間的對抗,使他們相互對抗,將問題分為較小的問題,這對他們來說非常有效。 在歷史上,“分而治之”(Divide and Rule) 是一項政治策略,但是在演算法的世界裡,他表示的是我們以某種方式將一個問題分解為較小的子問題,最終解決整個問題將變得更加容易。
分而治之的概念涉及三個步驟:
1. Divide : 將問題分為多個小問題。
2. Conquer : 分別解決每個較不複雜的子問題。
3. Combine : 結合子問題的解決方案以找到實際問題的解決方案。
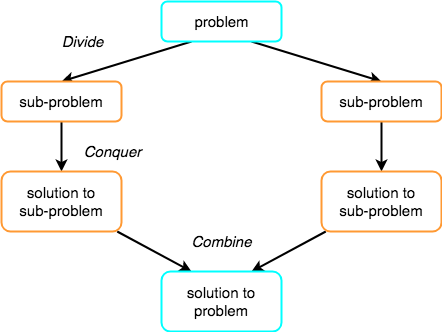
> [來源網站](https://www.studytonight.com/data-structures/merge-sort)
## Complexity Analysis of Merge Sort
Merge Sort is quite fast, and has a time complexity of O(n*log n). It is also a stable sort, which means the "equal" elements are ordered in the same order in the sorted list.
In this section we will understand why the running time for merge sort is O(n*log n).
As we have already learned in Binary Search that whenever we divide a number into half in every stpe, it can be represented using a logarithmic function, which is log n and the number of steps can be represented by log n + 1(at most)
Also, we perform a single step operation to find out the middle of any subarray, i.e. O(1).
And to merge the subarrays, made by dividing the original array of n elements, a running time of O(n) will be required.
Hence the total time for mergeSort function will become n(log n + 1), which gives us a time complexity of O(n*log n).
- **Worst Case Time Complexity** [ Big-O ]: O(n*log n)
- **Best Case Time Complexity** [Big-omega]: O(n*log n)
- **Average Time Complexity** [Big-theta]: O(n*log n)
- **Space Complexity: O(n)**
Time complexity of Merge Sort is O(n*Log n) in all the 3 cases (worst, average and best) as merge sort always divides the array in two halves and takes linear time to merge two halves.
It requires equal amount of additional space as the unsorted array. Hence its not at all recommended for searching large unsorted arrays.
It is the best Sorting technique used for sorting Linked Lists.
- **Auxiliary Space**: O(n)
- **Algorithmic Paradigm**: Divide and Conquer
- **Sorting In Place**: No in a typical implementation
- **Stable**: Yes
>[來源網站](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/merge-sort/)
## Applications of Merge Sort
- Merge Sort is useful for sorting linked lists in O(nLogn) time.
- In the case of linked lists, the case is different mainly due to the difference in memory allocation of arrays and linked lists. Unlike arrays, linked list nodes may not be adjacent in memory. Unlike an array, in the linked list, we can insert items in the middle in O(1) extra space and O(1) time. Therefore merge operation of merge sort can be implemented without extra space for linked lists.
In arrays, we can do random access as elements are contiguous in memory. Let us say we have an integer (4-byte) array A and let the address of A[0] be x then to access A[i], we can directly access the memory at (x + i*4). Unlike arrays, we can not do random access in the linked list. Quick Sort requires a lot of this kind of access. In linked list to access i’th index, we have to travel each and every node from the head to i’th node as we don’t have a continuous block of memory. Therefore, the overhead increases for quicksort. Merge sort accesses data sequentially and the need of random access is low.
- Inversion Count Problem
- Used in External Sorting
>[來源網站](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/merge-sort/)
## Refer to
- [Merge Sort | GeeksforGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/merge-sort/)
- [Merge Sort | Studytonight](https://www.studytonight.com/data-structures/merge-sort)
- [Merge Sort | Hackerearth](https://www.hackerearth.com/zh/practice/algorithms/sorting/merge-sort/tutorial/)