## [417\. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow](https://leetcode.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/)
There is an `m x n` rectangular island that borders both the **Pacific Ocean** and **Atlantic Ocean**. The **Pacific Ocean** touches the island's left and top edges, and the **Atlantic Ocean** touches the island's right and bottom edges.
The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an `m x n` integer matrix `heights` where `heights[r][c]` represents the **height above sea level** of the cell at coordinate `(r, c)`.
The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell's height is **less than or equal to** the current cell's height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean.
Return _a **2D list** of grid coordinates _`result`_ where _`result[i] = [ri, ci]`_ denotes that rain water can flow from cell _`(ri, ci)`_ to **both** the Pacific and Atlantic oceans_.
**Example 1:**
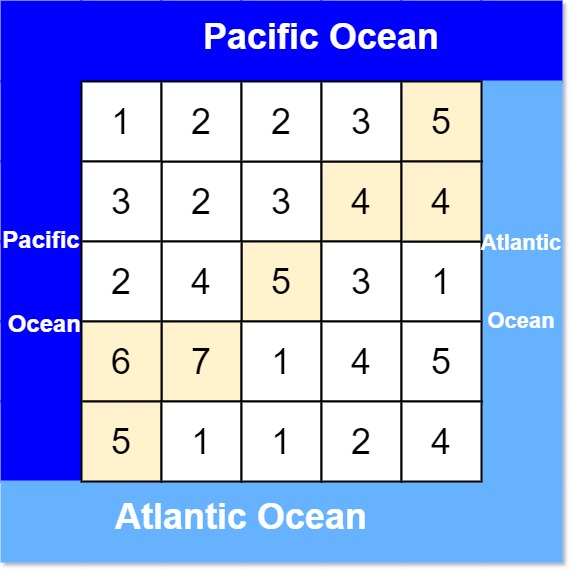
**Input:** heights = \[\[1,2,2,3,5\],\[3,2,3,4,4\],\[2,4,5,3,1\],\[6,7,1,4,5\],\[5,1,1,2,4\]\]
**Output:** \[\[0,4\],\[1,3\],\[1,4\],\[2,2\],\[3,0\],\[3,1\],\[4,0\]\]
**Explanation:** The following cells can flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, as shown below:
\[0,4\]: \[0,4\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[0,4\] -> Atlantic Ocean
\[1,3\]: \[1,3\] -> \[0,3\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[1,3\] -> \[1,4\] -> Atlantic Ocean
\[1,4\]: \[1,4\] -> \[1,3\] -> \[0,3\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[1,4\] -> Atlantic Ocean
\[2,2\]: \[2,2\] -> \[1,2\] -> \[0,2\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[2,2\] -> \[2,3\] -> \[2,4\] -> Atlantic Ocean
\[3,0\]: \[3,0\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[3,0\] -> \[4,0\] -> Atlantic Ocean
\[3,1\]: \[3,1\] -> \[3,0\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[3,1\] -> \[4,1\] -> Atlantic Ocean
\[4,0\]: \[4,0\] -> Pacific Ocean
\[4,0\] -> Atlantic Ocean
Note that there are other possible paths for these cells to flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
**Example 2:**
**Input:** heights = \[\[1\]\]
**Output:** \[\[0,0\]\]
**Explanation:** The water can flow from the only cell to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
**Constraints:**
- `m == heights.length`
- `n == heights[r].length`
- `1 <= m, n <= 200`
- `0 <= heights[r][c] <= 105`
```cpp=
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> directions = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int rows = heights.size(), cols = heights[0].size();
if(rows == 0 || cols == 0) return {};
vector<vector<int>> res;
// 分別用兩個矩陣紀錄這個格子有沒有比其他格子高
// 起始值都是 false
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(rows, vector<bool>(cols));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(rows, vector<bool>(cols));
// by rows 開始搜索,如果發現這個格子比周圍的格子高,就標記 true
// 因為要找比周圍格子高的值,起始值用 INT_MIN
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
dfs(heights, pacific, INT_MIN, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, INT_MIN, i, cols - 1);
}
// by cols 開始搜索,如果發現這個格子比周圍的格子高,就標記 true
// 因為要找比周圍格子高的值,起始值用 INT_MIN
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
dfs(heights, pacific, INT_MIN, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, INT_MIN, rows - 1, j);
}
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
res.push_back({i, j});
}
}
}
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& seen, int previous, int i, int j) {
int rows = heights.size(), cols = heights[0].size();
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= rows || j >= cols || seen[i][j] || heights[i][j] < previous)
return;
// 標記這個格子比其他人高
seen[i][j] = true;
// 四個方向深度搜索
for(auto& dir : directions)
dfs(heights, seen, heights[i][j], i + dir[0], j + dir[1]);
}
};
```
:::success
- 時間複雜度:$O(M \cdot N)$
- 空間複雜度:$O(M \cdot N)$
:::