## [232\. Implement Queue using Stacks](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (`push`, `peek`, `pop`, and `empty`).
Implement the `MyQueue` class:
- `void push(int x)` Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
- `int pop()` Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
- `int peek()` Returns the element at the front of the queue.
- `boolean empty()` Returns `true` if the queue is empty, `false` otherwise.
**Notes:**
- You must use **only** standard operations of a stack, which means only `push to top`, `peek/pop from top`, `size`, and `is empty` operations are valid.
- Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
**Example 1:**
**Input**
\["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"\]
\[\[\], \[1\], \[2\], \[\], \[\], \[\]\]
**Output**
\[null, null, null, 1, 1, false\]
**Explanation**
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: \[1\]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: \[1, 2\] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is \[2\]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
**Constraints:**
- `1 <= x <= 9`
- At most `100` calls will be made to `push`, `pop`, `peek`, and `empty`.
- All the calls to `pop` and `peek` are valid.
解法:使用兩個 stacks
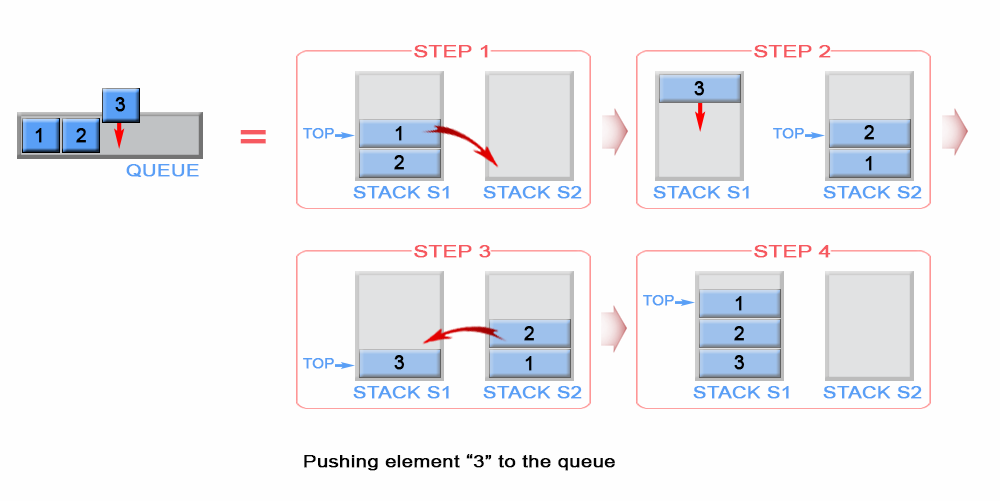
```cpp
class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue() {}
void push(int x) {
// 後進來的會維持在最上層
// 如果 s1 推了 1, 2, 3,3 會在最上面
s1.push(x);
}
int pop() {
peek();
int temp = s2.top(); s2.pop();
return temp;
}
int peek() {
// s2 用來儲存 s1 的反轉順序,如果 s2 裡面有值,直接回傳 s2.top();
if(!s2.empty()) return s2.top();
// 如果 s1 還有值,將元素丟到 s2 儲存,反轉順序
while(!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.top()); s1.pop();
}
return s2.top();
}
bool empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
private:
stack<int> s1; // push 進去的元素先裝在這,最後一個元素會維持在最上層
stack<int> s2; // 將 s1 的元素 pop() 到 s2,反轉順序
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
```
:::success
- 時間複雜度:$O(N)$
- 空間複雜度:$O(N)$
:::