# Maths
[Class
recording](https://www.scaler.com/meetings/i/beginner-maths-1-6/archive)
[lecture
notes](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1scmwyBmYqBgTv1d8kGS7nISr8ZM2HKUJ/view?usp=share_link)
## **Content**
1. Number system
2. Binary number system
3. Decimal number system
4. Binary ⟷ decimal representation
5. Range
6. Log function
### **Meanwhile when people are joining** (5-7 mins)
- Instructor's welcome.
- Breaking ice with students.
- casual conversation to bond.
---
title: Number System
description:
duration: 200
card_type: cue_card
---
## **Number System**
- Binary system i.e **0/1**
- Decimal number system i.e **0,1,2...9**
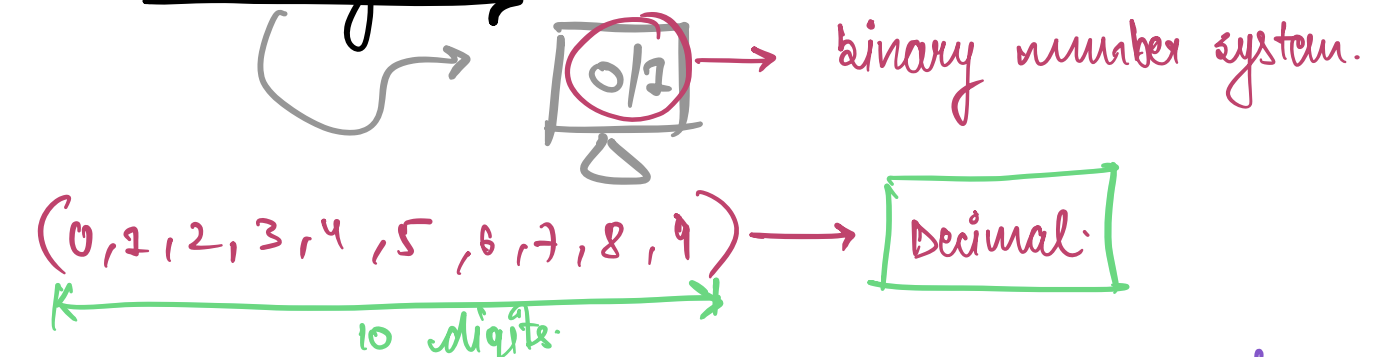
- Correct way of representing a number system is to specify its base.
e.g (183)<sub>10</sub>, (101)<sub>2</sub> etc.
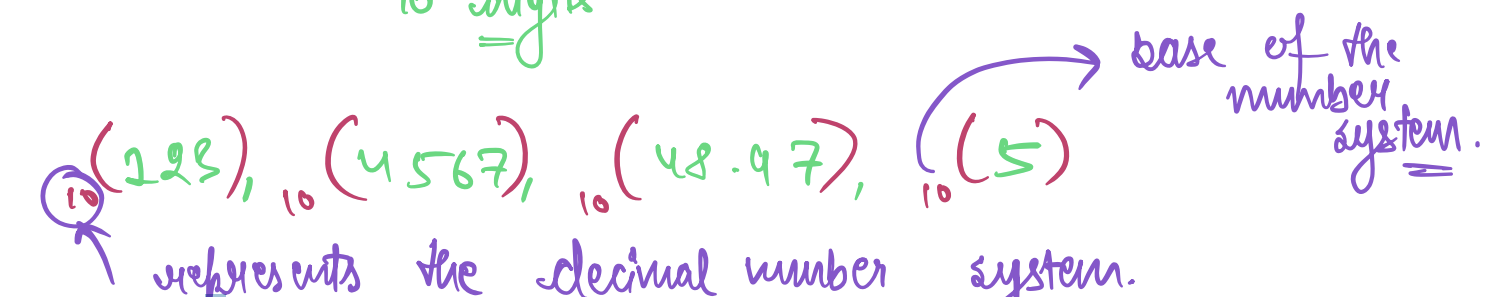
- From left to right, the digits represent increasing powers of 10
starting from 0.
- (9456)<sub>10</sub> is 6\* 10<sup>0</sup>+5\* 10<sup>1</sup>+4\*
10<sup>2</sup>+9\* 10<sup>3</sup>
- Number system to base 50, e.g (9456)<sub>50</sub> = 6\*
50<sup>0</sup>+5\* 50<sup>1</sup>+4\* 50<sup>2</sup>+9\*
50<sup>3</sup>
- (-312)<sub>10</sub> is -1\* (3\* 10<sup>2</sup>+2\*
10<sup>1</sup>+1\* 10<sup>0</sup>)
---
title: Binary number system
description:
duration: 200
card_type: cue_card
---
## **Binary number system**
- Contains **0s** and **1s** alone.
- Any number less than 2<sup>*n*</sup> can be represented by n digits
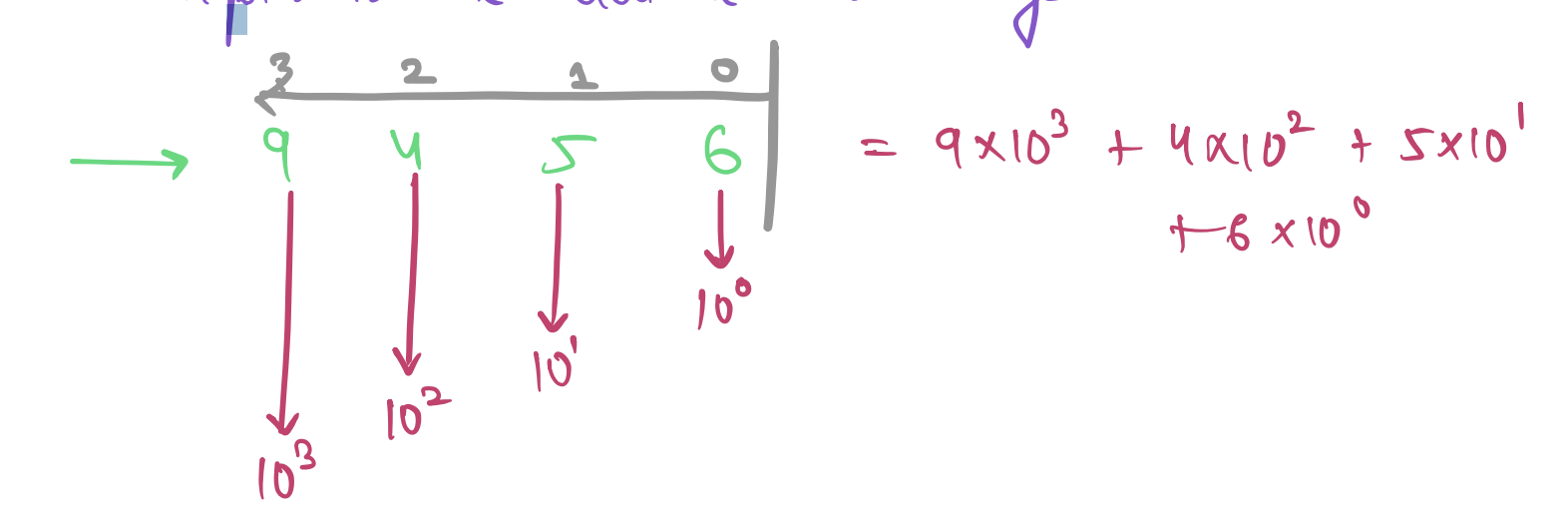
### **Question - What is the value?**
- (101)<sub>2</sub>
- (1111)<sub>2</sub>
- (00000001111)<sub>2</sub>
**Ans**:
- (101)<sub>2</sub> = 5
- (1111)<sub>2</sub> = 15
- (00000001111)<sub>2</sub> = 15
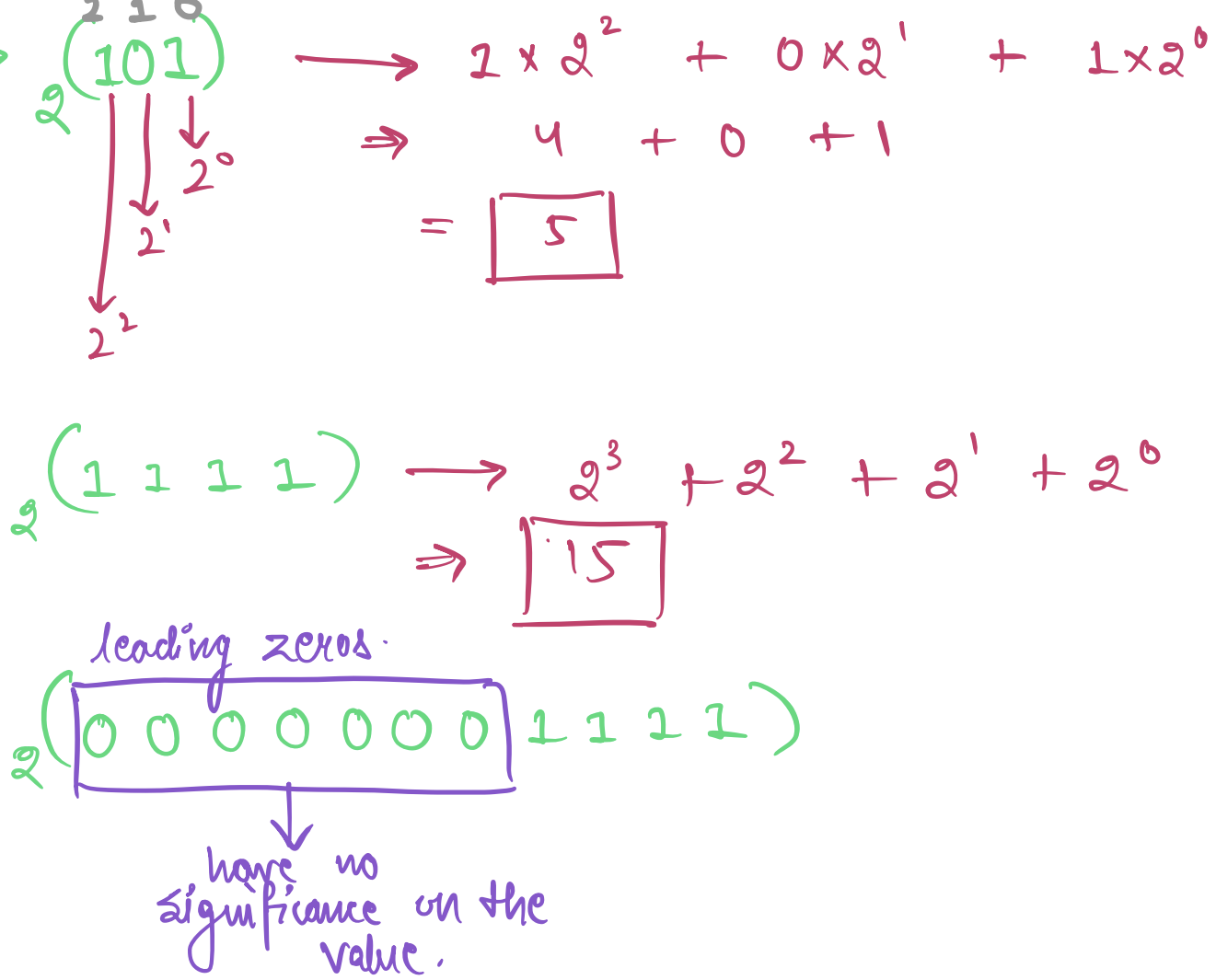
**NOTE:** Leading zeros in a number representaton has no significance.
### **Question: Write all binary numbers from 0 to 7.**

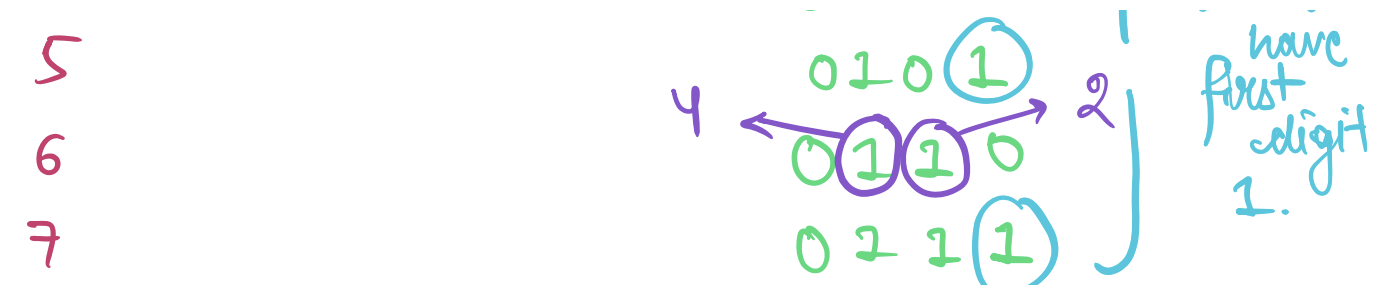
- Notice how every odd number has the unit digit 1.
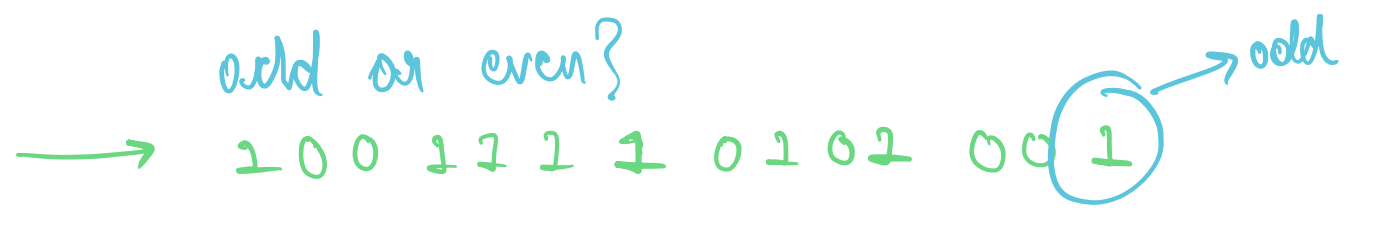
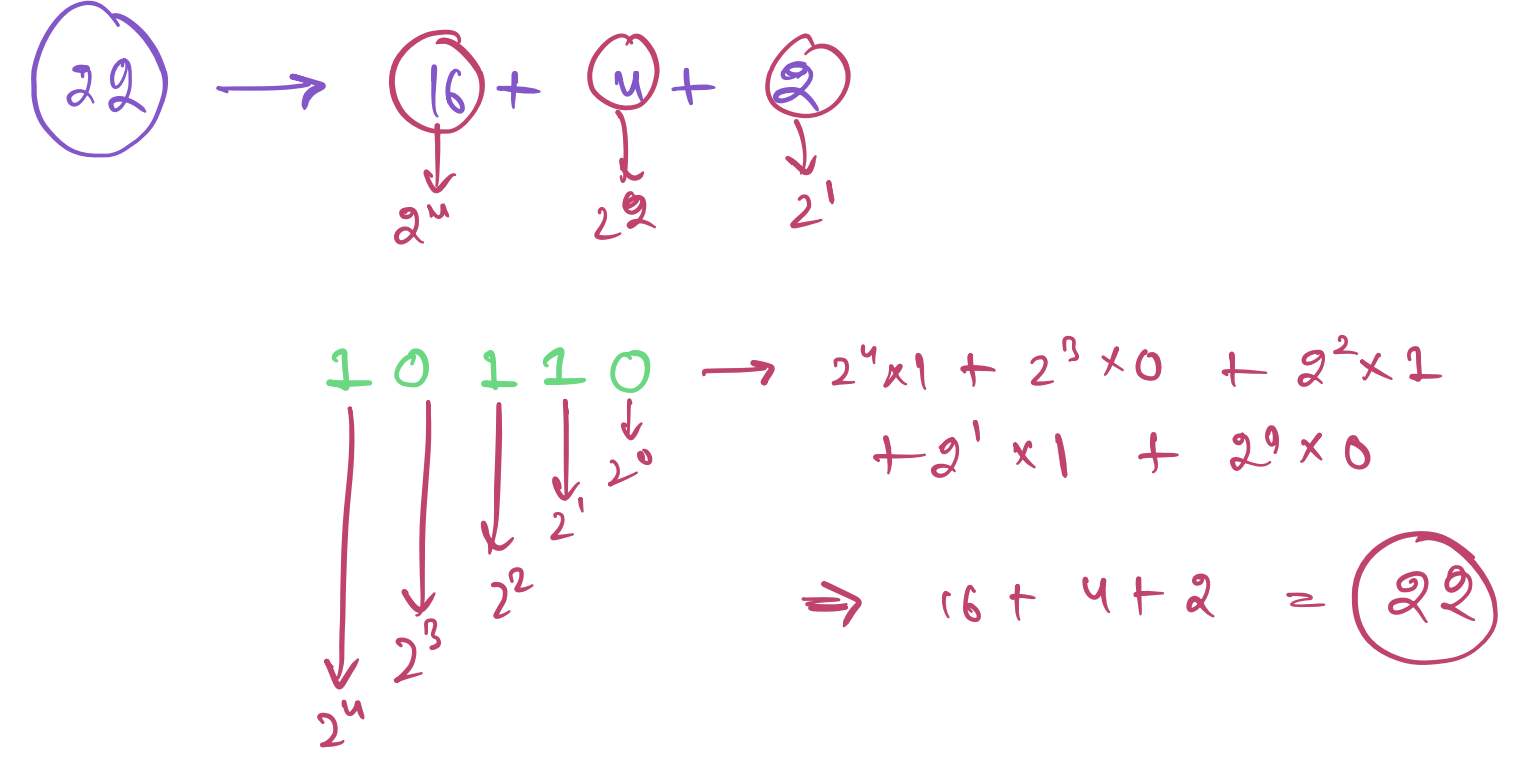
- first 1 digit of a number in binary representation occurs at the
biggest power of 2 less than the number
- for example, for 22 the largest power of 2 less than 22 is 16 or
2<sup>4</sup> , therefore first 1 occurs at 5th place from right
(starts from 0).
---
title: Converting decimal to binary
description:
duration: 300
card_type: cue_card
---
## Converting decimal to binary
- Progressively divide by the base of the number system you want to
convert it into and note down the remainder from end to start.
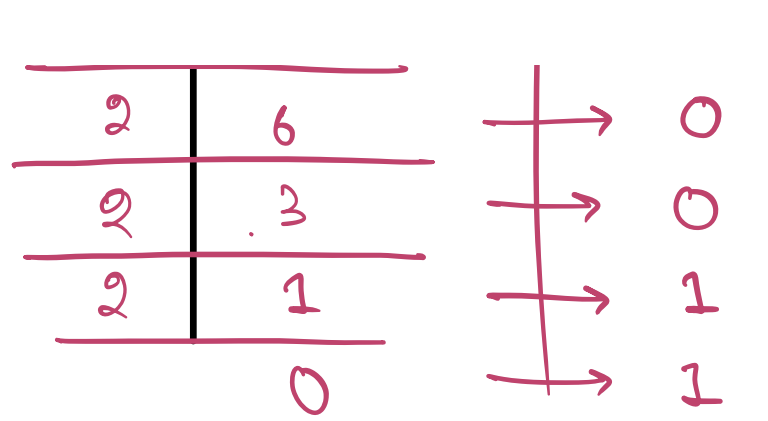
#### Question : Convert decimal number 50 to binary
**Answer:** 110010
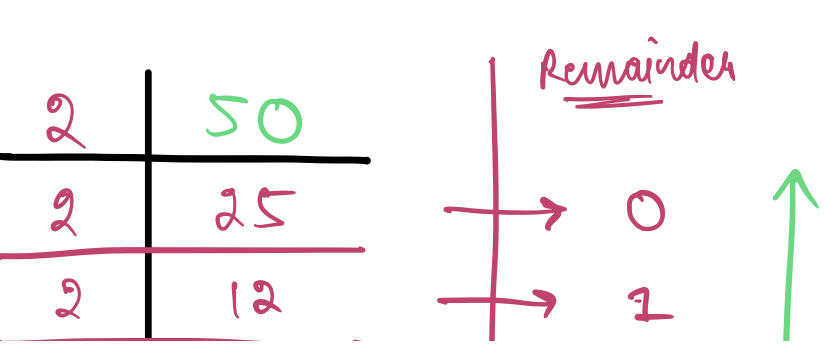
---
title: Converting Binary to Decimal conversion
description:
duration: 300
card_type: cue_card
---
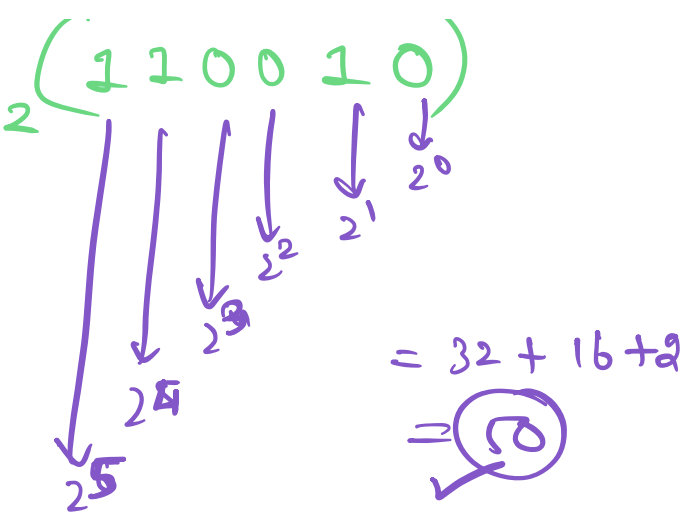
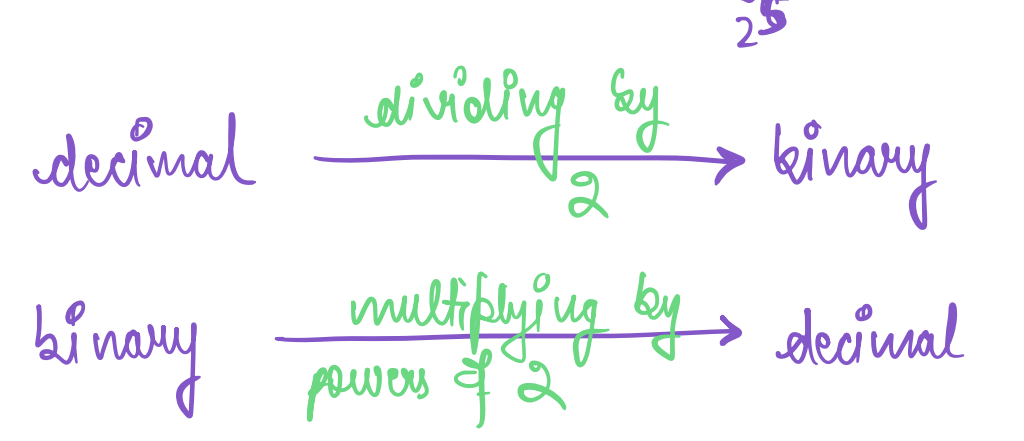
## Binary ↔ Decimal conversion
- Decimal to binary : divide by 2
- Binary to decimal : multiply powers of 2
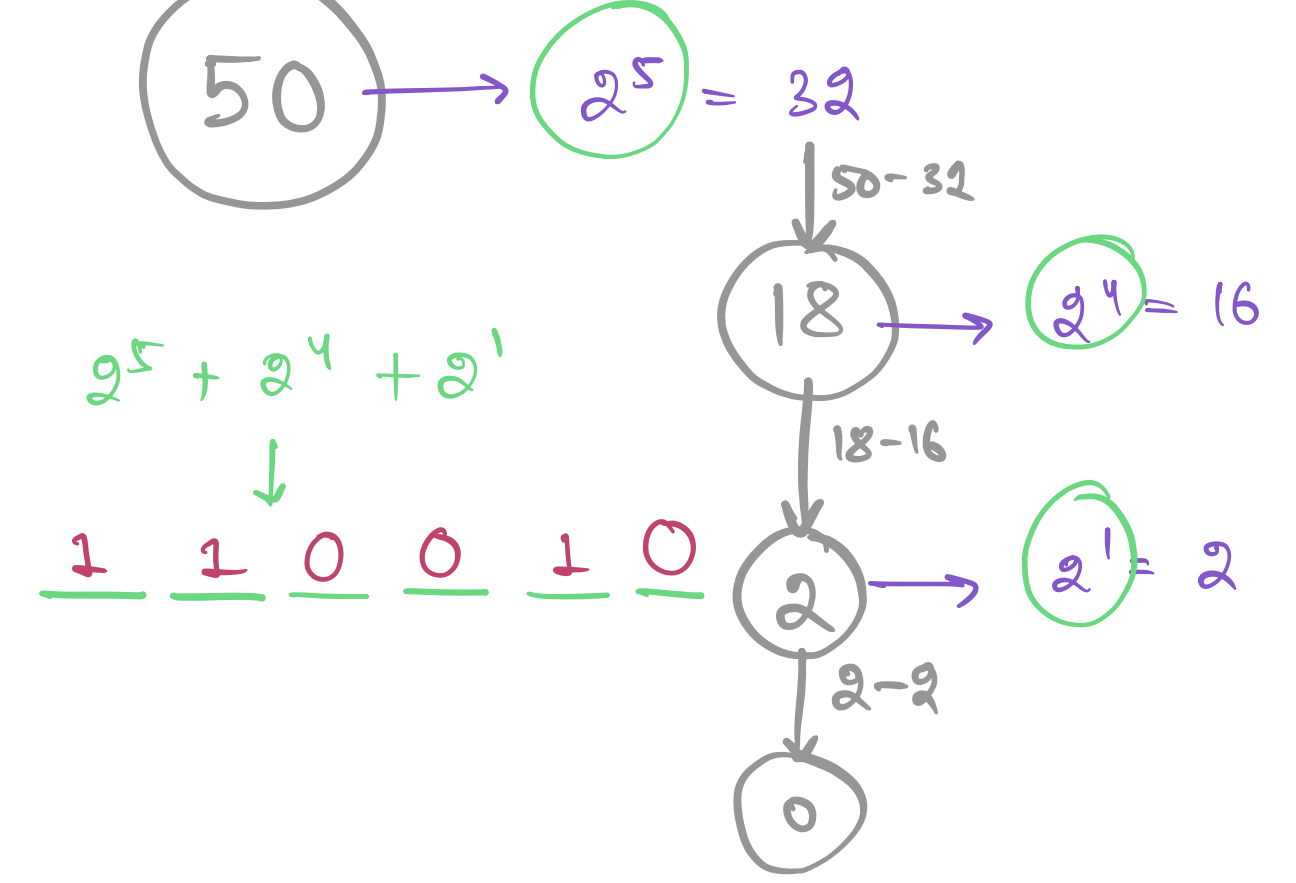
## **Decimal to binary intuitive method**
- Progressively take the largest power of **2** less than the number,
by subtracting the largest power of **2** from the number.
### **Difference between number system**
- Binary number system in just two values 0s and 1s can represent any
value of number while decimal needs 10 values (0 to 9).
---
title: Explaining Range
description:
duration: 300
card_type: cue_card
---
## Range
- `The range [1,10]` represents `[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]`
- Square brackets `[]` means the terminal values are inclusive
- In square bbrackets `[start, end]`, the number of values is
**end-start+1**
- `(1,10)` represents `[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]`
- in round brackets `()`, the terminal values are exclusive.
- `(start, end)` has **end-start-1** number of values
### **Question: Number of numbers in the range `[100, 302]`**
**Ans**: 302-100+1 = 203
### **Question: Number of numbers in the range `(100, 302)`**
**Ans**: 302-100-1 = 201
- in `( )` the start is excluded and end is excluded, it is called
mixed range.
### **Question: Number of numbers in the range `[100, 302)`**
**Ans**: 302-100 = 202
- in `[ )` the start is excluded and end is excluded, it is called
mixed range.
- Python always uses mixed range `[start,end)`
``` python=
range(1,10)
len(range(1,10))
```
```bash=
9
```
---
title: Explaining bin function
description:
duration: 300
card_type: cue_card
---
## `bin()` in python
- Gives the binary value
- Binary in python is represented by '0b' prefix
Code:
``` python=
print(bin(56)) #'ob111000
a=0b101
a #5
```
>Output
```bash=
0b111000
5
```
### **Question**: Given a number, find the digit at the unit place
**Ans**: '%'
Code:
``` python=
a = 36279734984
a % 10 #unit place digit
```
>Output
```bash=
4
```
### **Question**: Given a number, find the digit at
1. List item
2. List item
the tens place
Code:
``` python=
a = 36279734984
d = a%100
d = d // 10 #tens place digit
d
```
>Output
```bash=
8
```
### Given a number how many times should you divide by 2 to get 1?
**Ans:** `floor(log(n))`
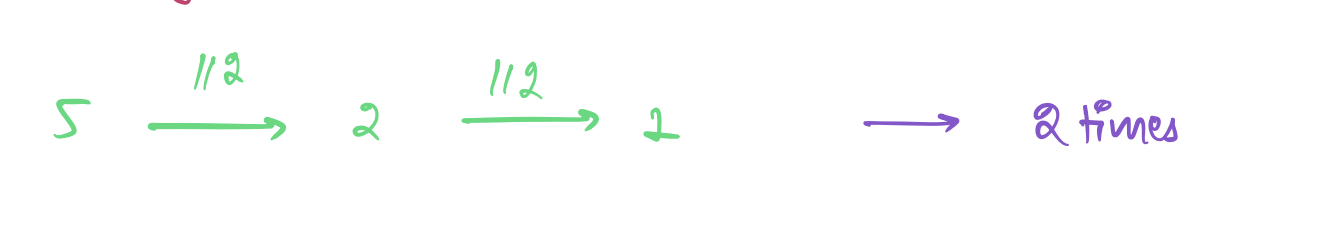
The answer would be equal to the closest power of 2 which would be equal
to `floor(log(n))`.
---
title: Explaining Log function
description:
duration: 300
card_type: cue_card
---
### **Log function**
- a<sup>*x*</sup> = b then, log<sub>*a*</sub>(b) = x
---
title: Quiz-1
description: Quiz-1
duration: 60
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
Which of the following is not a valid number system in Python?
# Choices
- [ ] Binary
- [ ] Octal
- [ ] Hexadecimal
- [x] Ternary
---
title: Quiz-2
description: Quiz-2
duration: 60
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
What is the output of the following code snippet?
```python=
a = 0b101
b = 0b110
print(bin(a|b))
```
# Choices
- [ ] 0b1010
- [x] 0b111
- [ ] 0b1001
- [ ] 0b10
---
title: Quiz-2 Explanation
description:
duration: 60
card_type: cue_card
---
### Explanation:
The \| operator performs a bitwise OR operation on the
binary representations of the two numbers. In this case, a OR b results
in the binary number 0b111.
---
title: Quiz-3
description: Quiz-3
duration: 60
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
What is the decimal equivalent of the binary number 101011?
# Choices
- [x] 43
- [ ] 45
- [ ] 47
- [ ] 49
---
title: Quiz-4
description: Quiz-4
duration: 60
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
What is the output of the following code snippet?
```python=
import math
print(math.log10(100))
```
# Choices
- [x] 2
- [ ] 10
- [ ] 100
- [ ] 0.01
---
title: Quiz-4 Explanation
description:
duration: 60
card_type: cue_card
---
### Explanation:
Explanation: The `math.log10` function in Python returns the base-10
logarithm of a number. In this case, the input to the function is 100,
which is equal to 10 raised to the power of 2 (i.e., 100 = 10^2).
Therefore, the output of `math.log10(100)` is 2.
---
title: Quiz-5
description: Quiz-5
duration: 60
card_type: quiz_card
---
# Question
What is the output of the following code snippet?
```python=
for i in range(1, 10, 2):
print(i, end=' ')
```
# Choices
- [x] 1 3 5 7 9
- [ ] 1 4 7
- [ ] 2 4 6 8
- [ ] 2 4 8