# O-RAN Introductions
## What is O-RAN and its Characteristics
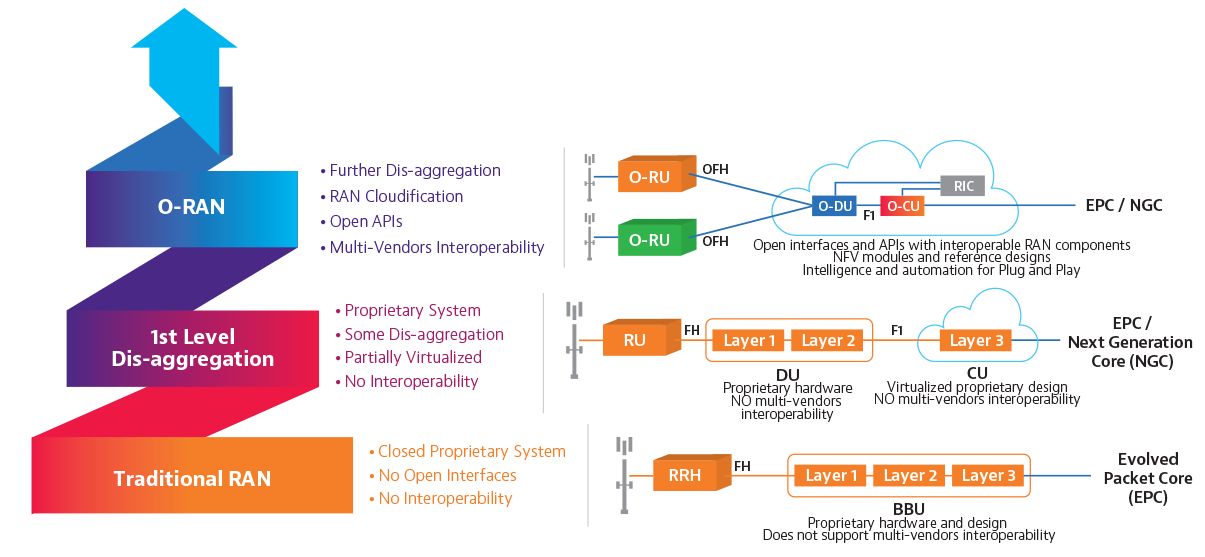
O RAN (Open RAN) refers to industry-wide standards for RAN (Radio Access Network) interfaces; it supports interoperation between vendors’ equipment. As a result, the technology offers network flexibility at a lower cost.
:::info
It is a disaggregated approach to deploying mobile fronthaul and midhaul networks built entirely on cloud native principles.
:::
O-RAN technology decomposed the existing Baseband Unit (BBU) into two functional components, a **Distributed Unit (DU)** and **Central Unit (CU)**. Conforming to modern control user plane separation (CUPS) constructs, the Central Unit can be further decoupled into distinct **control plane (CU-CP)** and **user plane (CU-UP)** functions, replacing the monolithic BBU with the CU/DU allows for new deployment models.
### Key Components of O-RAN
* **Open Interfaces**: O-RAN defines open, standardized interfaces between various components of the RAN, such as between the radio unit (RU), distributed unit (DU), centralized unit (CU), and the core network.
* **Virtualization**: O-RAN promotes the virtualization of RAN functions, allowing them to run on standard, off-the-shelf hardware using virtualized network functions (VNFs) or containerized microservices.
* **Software-Defined Networking (SDN)**: O-RAN leverages SDN principles to enable centralized control and programmability of the RAN which allows operators to dynamically allocate resources and optimize network performance and new use cases.
* **Intelligence and Automation**: O-RAN introduces intelligence and automation into the RAN through advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI technologies to enable autonomous network management, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource utilization.
* **Cloud-Native Architecture:** O-RAN embraces cloud-native principles, such as microservices, containerization, and orchestration, to build a more agile, scalable, and resilient RAN infrastructure. This approach aligns with the broader industry trend towards cloud-native and edge computing technologies.
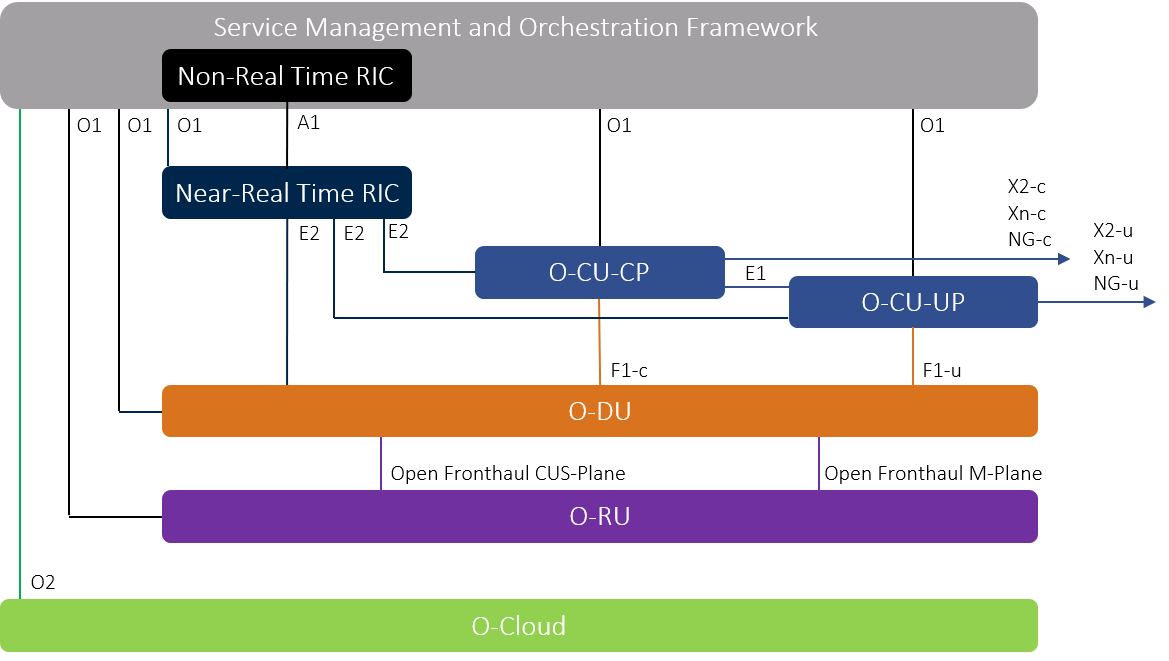
## O-RAN Architecture

### Service Management and Orchestration Framework (SMO)
Includes an integration fabric and data services for the functions it manages. **It allows managed functions to interoperate and communicate** within the O-RAN. The SMO connects to and manages the RICs, O-Cloud, the O-CU, and O-DU.
### RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC)
There are two types of RICs
* non-real-time
* near-real-time.
Both are logical functions for **controlling and optimizing the elements and resources** of an O-RAN. A near-real-time RIC controls and optimizes elements and resources with granular data collection and communication over the E2 interface.
### O-Cloud
A cloud computing platform made up of the physical infrastructure nodes using the O-RAN architecture.
### O-RAN central unit (O-CU)
Logical node that hosts protocols:
* Radio Resource Control (RRC)
* Service data adaptation protocol (SDAP)
* Packet data convergence protocol (PDCP).
### O-RAN distributed unit (O-DU)
A logical node that hosts protocols
* Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol,
* Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol,
* Physical Interface (PHY).
### O-RAN Radio unit (O-RU)
It processes radio frequencies received by the physical layer of the network. The processed radio frequencies are sent to the O-DU through a front haul interface.
## O-RAN and 5G
5G defines the overall framework and capabilities of next-generation wireless networks, while O-RAN focuses specifically on redefining the architecture of the **RAN component** to be more open and flexible, aligning with the broader industry trends towards virtualization, open interfaces, and software-defined networking.
### 5G
5G only refers to the **fifth generation of wireless technology**, it encompasses a broad range of technologies, standards, and use cases. While 5G defines the overall framework and capabilities of the next-generation wireless network, it **does not specify the detailed architecture of the radio access network (RAN)** or the implementation of specific network components.
### O-RAN
While 5G defines the overall framework and capabilities of next-generation wireless networks, O-RAN focuses specifically on **redefining the architecture of the RAN component** to be more open and flexible, aligning with the broader industry trends towards virtualization, open interfaces, and software-defined networking.
Also O-RAN principles and concepts can be applied to 4G networks as well, not just 5G. While O-RAN was initially developed to address challenges in 5G network deployments, its principles of open interfaces, virtualization, and standardized hardware and software can also benefit 4G LTE networks.