# <center><i class="fa fa-edit"></i> **RAN Background Knowledge**</center>
:::info
**Resources**
1. https://hackmd.io/AQym4FBjRvyRA8sk1d8KQw?view#Potential-Topics
2. https://5g.systemsapproach.org/ran.html
3. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-fVHO_WCGF8
4. https://www.parallelwireless.com/wp-content/uploads/Parallel-Wireless-e-Book-Everything-You-Need-to-Know-about-Open-RAN.pdf
5. https://hackmd.io/@MingHung/5G
6. https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1sHMhI2Y5YNEaG-ImD7xDSV3FwxjZ55Jm
7. https://hackmd.io/@Min-xiang/SJcMCEaRd
:::
:::success
Learning Objective:
- Gain some background knowledge on RAN
- Able to identify key components in RAN
- Know the history of O-RAN
:::
Radio Access Network (RAN) is part of a mobile wireless telecommunication system that implements a radio access technology. It resides between a device such as a mobile phone, a computer, or any remotely controlled machine and provides connection with its core network (CN)1. It consists of a baseband unit, radio unit or remote radio unit, antennas, and software interfaces. RAN comprises of radio base stations, cell towers, and other network elements that are responsible for managing the communication between mobile devices and the core network.
## **1. Background**
- RAN is the main architectural components of cellular access networks
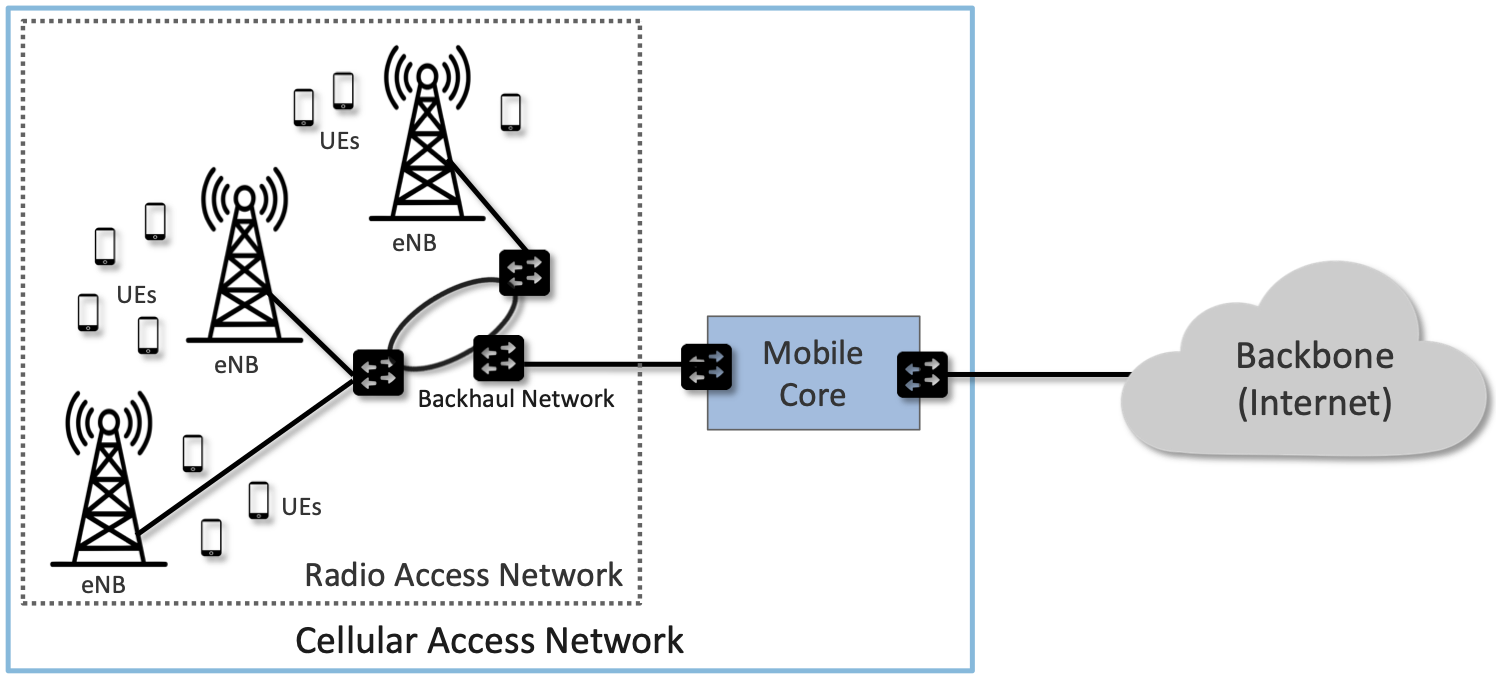
:::info
- **eNB (evolved Node B) = base station (4G, gnB in 5G, g = ***next Generation***)**
- **UE = User Equipment**
- **BBU (Baseband Unit)**
- **RRU (Remote Radio Unit)**
- **RRU handles the RF (Radio Frequency) task of the access network while BBU handles the DSP (Digital Signal Processing)**
:::
### **1.1 RAN**
#### **1.1.1 RAN**
- Starts with ***3rd Generation Partnership Project*** **(3GPP)**, RAN defines standard on how the radio spectrum is used. Making sure it is used efficiently and meets QoS requirements of every user by bringing licensed spectrum. RAN controls most of the Internet's *last mile*.
- There are three parts in networking, core network, access network, and transport network. These components each consisted of hardware and software.


- **Core Network** includes firewall, routers, gateway, etc. In the past, each vendor used to have a lot of software and hardware for the core network. But with the advancement of technology, the function of hardware nowadays have been replace by Commercial Off-The-Shelf Servers(COTS). This phenomenon is analogical to radio, video player, music player, etc turns into apps on your smartphone.

- **Access Network** can be divided into 2 main sections, BBU (Baseband Unit) and RRU (Remote Radio Unit). RRU handles the RF (Radio Frequency) task of the access network while BBU handles the DSP (Digital Signal Processing) task. Below shows the diagram of convetional access networks.

- With virtual Radio Access Network, the diagram turns into the picture below. The BBU hardware gets replace by the COTS Server rather than a proprietary hardware. This way, the operator of the access network can just leave all the hardware function of the BBU to a COTS provider which makes things easier.
#### **1.1.2 RAN Development / History**

##### Traditional RAN

In the past, all equipments were set up near the antennas which makes base station installation expensive and not efficient. Each base station require extra space and cooling system for the installation.
##### C-RAN (Cloud RAN or Centralized RAN)
C-RAN was the first effort to realizing the virtualization of the RAN functions. This development was issued by IBM, Intel, and China Mobile. The deployment of C-RAN resulted a model where the baseband unit that doing a digital process could be located not in a data center.


##### vRAN (Virtual RAN)
vRAN is basically replacing the BBU hardware by a COTS server. The software that runs on the BBU is virtualized to run on any COTS server. But the proprietary interfaces between radios and COTS-based BBU remain as they are.


##### Open RAN
The key with Open RAN is that the interface between the BBU and RRU / RRH is an open interface, so, any vendor’s software can work on any open RRU / RRH. More open interfaces enable the use of one supplier's radios with another's processors – which is not possible with CRAN or vRAN.

#### **1.1.3 How RAN Works**
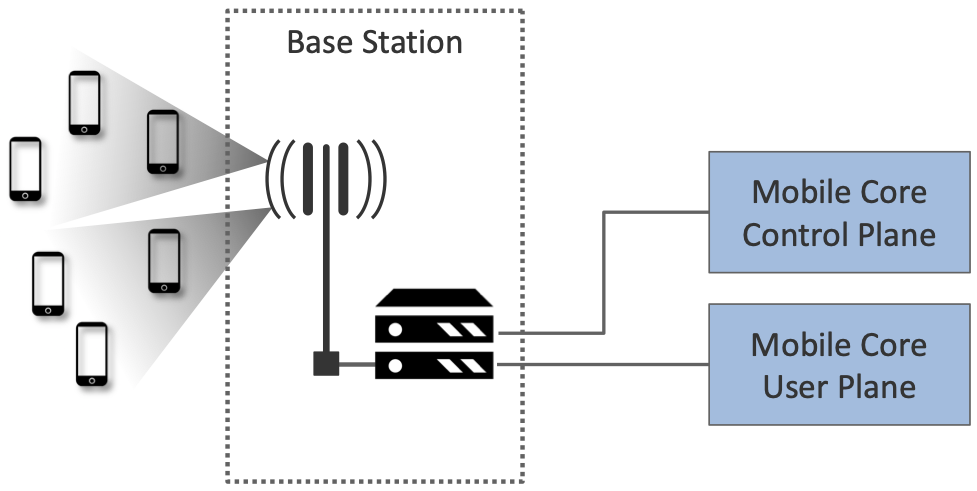
1. Each base station establishes the wireless channel for a subscriber's UE upon power-up or upon handover when the UE is active. This wireless channel is said "*to provide a bearer service*".

2. Each base station establishes "3GPP Control Plane" connectivity between the UE and the corresponding Mobile Core Control Plane component, and forwards signaling traffic (enables UE authentication, registration, and mobility tracking) between the two.

3. For each active UE, the base station establishes one or more tunnels between the corresponding Mobile Core User Plane component.

4. Base station forwards both control and user plane packets between the Mobile Core and the UE. #*Connectivity between RAN an Mobile Core is IP-based*

5. Each base station coordinates UE handovers with neighboring base stations, using direct station-to-station links.

6. Base stations coordinate wireless multi-point transmission to a UE from multiple base stations

RAN as a whole (not just a single base station) not only supports handovers, but also link aggregation and load balancing.
### **1.2 Mobile Core**
- Purposes:
- Authenticates devices prior to attaching them to the network
- Provides Internet (IP) connectivity for both data and voice services.
- Ensures this connectivity fulfills the promised QoS requirements.
- Tracks user mobility to ensure uninterrupted service.
- Tracks subscriber usage for billing and charging.
- In 4G it was called the **Evolved Packet Core (EPC)** and in 5G it is called the **Next Generation Core (NG-Core)**.


- Mobile Core divided into a Control Plan and a User Plane, an architectural feature known as **CUPS: Control and User Plane Separation**.
- **CUPS** provides architecture enhancement for separation functionality in core network, thus enabling flexible network deployment and operation by distributed/centralized deployment and the independent scaling between control plane and user plane function.
- In 5G, one of the target is the ability to segregate traffic for different usage domains into isolated network slices, each of which delivers a different level of service to a collection of devices and applications, such as slicing traffic for IoT and Video.
### **1.3 Backbone / Backhaul Network**
- Interconnects the base stations that implement the RAN with the Mobile Core which typically wired.
- ***Passive Optical Network*** (PON) that implements Fiber-to-the-Home is a prime candidate for implementing the RAN backhaul.
### **1.4 Deployment Options**
Based on 3GPP, deployment options:
#### **Standalone 4G/Stand-Alone 5G**
-> Build a new 5G base station
:::success
- The core network uses 5G architecture, no longer depends on 4G
- The transmission rate is not limited
:::
#### **Non-Standalone (4G+5G RAN) over 4G's EPC = **NSA****
-> Involves 5G base stations being deployed alongside the existing 4G base stations in a given geography to provide a data-rate and capacity boost.
-> **Control plane traffic** between the UE and the 4G Mobile Core is forwarded through **4G Base Stations**, and the **5G Base Stations** are used only to carry user traffic.


- Non-Standalone (4G+5G RAN) over 5G's NG-Core

## **2. O-RAN**
### **2.1 Brief about O-RAN**
:::success
- **Open RAN** is a **collective action** in building an open telecom network that complies to **3GPP**
- O-RAN objective:

:::
- **Open RAN** started as a movement that applies to all generations (or known as ALL Gs) for the mobile technology. In other words, we can say that Open RAN applies to 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and their development in the future.Before we begin, we must know the difference of the terms between **Open RAN**, **OpenRAN**, **O-RAN**, and **ORAN**.
* **Open RAN** is the movement in wireless telecomounications to disaggregate hardware and software and to create open interfaces between them. We can defined it as the ability to integrate, deploy and operate radio access networks using components, subsystems and software sourced from multiple suppliers, connected over open interfaces.
* **OpenRAN** could mean two different things, such as:
* One of the two groups within the Telecom Infra Project\. Telecom Infra Project is the OpenRAN project group, which is an initiative to degine and build 2G, 3G, and 4G RAN solutions based on general-purpose, vendor-neutral hardware and software defined technology.
* OpenRAN 5G NR Project Group which focuses on 5G NR.

* **O-RAN** refers to O-RAN Alliance, which publishes new RAN spesifications, releases open software for the RAN, and supports its members in testing and integration of their implementation.
* **O-RAN** term can be used to refer to Open RAN movement.
### **2.2 O-RAN Vision**




- The concept of O-RAN is the same as above, to simplify things. The main difference is, Open RAN is based on open interface as you can see in the diagram below.

- The RRU will be replaced with SDR (Software Defined Radio). BBU still the same with vRAN. The interface between SDR and BBU however is an open interface. That way, the operator of the access network can leave all the work in the interface to a vendor. That means, all the hardware and sotware work of access network (RRU, BBU, the interface between) can actually be taken care of by using vendors. In the further O-RAN approach,BBU will be seperated into CU (Central Unit) and DU (Distributed Unit) as can be seen on the image below. CU will handle the less time sensitive processing functions while DU will handle the real-time processing functions.

- The way that this "open based", "any vendor can provide the hardware and software" concept will work is to replace the specific designed hardware to a more general one. Think of it like the differences between a DVD player and calculator with computer. DVD player can only play DVD and calculator can only count. DVD player cannot count and calculator cannot play a DVD. Computer can do both. Computer is a general machine while DVD player and calculator is a specific machine. Specific machine tends to cost less, work faster and save more energy while a general machine will do the opposite because it has to be prepared to do everything. On the other hand, general machine will innovate faster because the software-driven development and will require less money to mass-produce because the market will be bigger that specific machines. This applies to ORAN. ORAN will require a more general hardware. Below is an example of a 5G O-RAN deployment with multiple vendors for the

- Deployment of the RRU used hardware from 3 different vendors, A, B, C. On the DU side, there are 3 different vendors, V2 to V4.
- **Reasons operators are looking forward to ORAN (and it all come down to cost reduction)**:
- Avoid vendor lock-in
- Multiple vendors within network will encourage price competition
- Competition will produce innovations
- Different solution based on different requirements
- Easy scaling
- Reduced time to market


:::warning
**General misconception of O-RAN**:
- Open RAN doesn't mean open source
- ORAN doesn't only apply to 4G and 5G, 2G and 3G can also use the technology
:::
### **2.3 O-RAN Architecture**
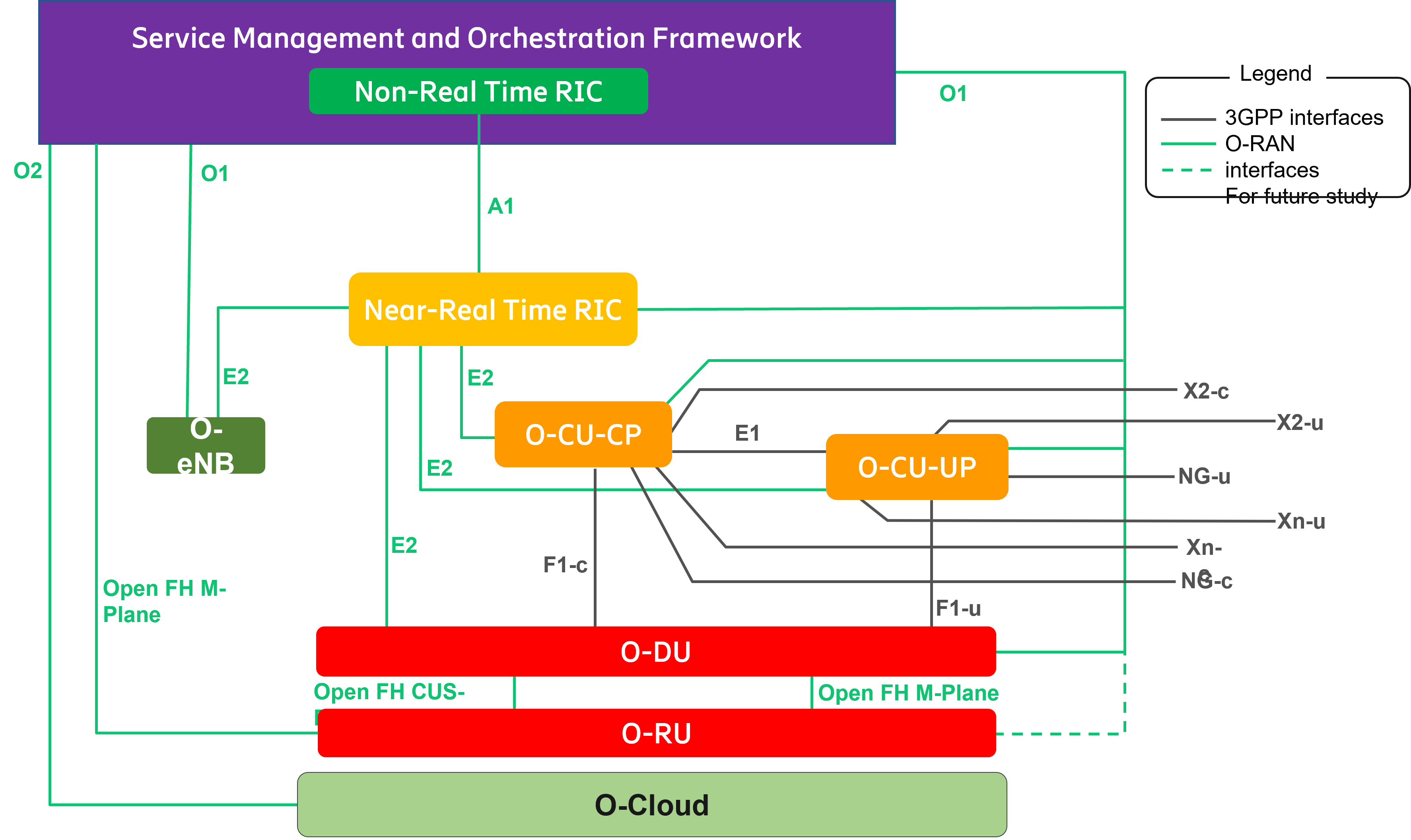
- **near-RT RIC: O-RAN near-real-time RAN Intelligent Controller**: a logical function that enables near-real-time control and optimization of O-RAN elements and resources via fine-grained data collection and actions over E2 interface.
- **non-RT RIC: O-RAN non-real-time RAN Intelligent Controller**: a logical function that enables non-real-time control and optimization of RAN elements and resources, AI/ML workflow including model training and updates, and policy-based guidance of applications/features in near-RT RIC.
- **NMS**: A Network Management System
- **O-CU**: O-RAN Central Unit: a logical node hosting RRC, SDAP and PDCP protocols
- **O-CU-CP: O-RAN Central Unit – Control Plane**: a logical node hosting the RRC and the control plane part of the PDCP protocol
- **O-CU-UP: O-RAN Central Unit – User Plane**: a logical node hosting the user plane part of the PDCP protocol and the SDAP protocol
- **O-DU: O-RAN Distributed Unit**: a logical node hosting RLC/MAC/High-PHY layers based on a lower layer functional split.
- **O-RU: O-RAN Radio Unit**: a logical node hosting Low-PHY layer and RF processing based on a lower layer functional split. This is similar to 3GPP’s “TRP” or “RRH” but more specific in including the Low-PHY layer (FFT/iFFT, PRACH extraction).
- **O1**: Interface between management entities in Service Management and Orchestration Framework and O-RAN managed elements, for operation and management, by which FCAPS management, Software management, File management shall be achieved.
- **O1***: Interface between Service Management and Orchestration Framework and Infrastructure Management Framework supporting O-RAN virtual network functions.
- **xAPP**: Independent software plug-in to the Near-RT RIC platform to provide functional extensibility to the RAN by third parties.

- **NG-RAN** is a part of the 3GPP 5G system responsible for providing Radio Access to 5G networks.
- **gNB** provides 5G NR access to the users by providing NR control
- **NG-eNB** provides LTE Radio access to the users or provides E-UTRA control
- General Principles for NG-RAN
- Logical separation of signaling and data transport networks.
- NG-RAN and 5GC functions are fully separated from transport functions.
- RRC connection mobility is fully controlled by the NG-RAN.
- The NG-RAN interfaces are defined along with the following principles:
1. The functional division across the interfaces have as few options as possible.
2. Interfaces are based on a logical model of the entity controlled through this interface.
3. One physical network element can implement multiple logical nodes.


### **2.4 O-RAN Protocol Stack to OSI Model**



- **Radio Frequency (RF)** is essentially analog/digital conversion of electromagnetic signals from the physical layer
- **Physical Layer (PHY)** controls Coding/decoding, modulation/demodulation, multi-antenna mapping and other PHY related functions and mapping transport channels to physical channels
- **Medium Access Control (MAC)** controls Multiplexing and mapping of logical channels into transport channels and HARQ and all scheduling related functions
- **Radio Link Control (RLC)** controls segmentation and retransmission, no in-sequence delivery support of data to higer protocol layers to reduce latency, and removal of concatenation to allow RLC PDUs assembled in advance
- **Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP)** provides IP header compression using Robust Header Compression (RoHC), ciphering and integrity protection. PDCP will route and duplicate for DC with split bearers
- **Service Data Application Protocol (SDAP)** exists only in the user plane in both gNB and UE, it maps QoS based bearers to radio bearers according to their quality of service requirements. This protocol stack is new in 5G NR due to new mechanism for handling QoS
- **Radio Resource Control (RRC)** exists only in the control plane in both gNB and UE, control-plane functionality operates between the RRC located in the gNB and the device. RRC is responsible for handling the RAN-related control-plane procedures
### **2.5 O-RAN Functional Split**
#### **2.5.1 RAN Functional Split 101**
- Split concept in RAN started in C-RAN which splits the Base Station function into BBU and RRU

- Starting with 5G, 3GPP introduced the DU and CU concept as the evolution path toward vRAN which introduced separate Fronthaul and Midhaul to provide more flexibility in vertical transport options

- RAN functional splits can be separated into **Vertical** and **Horizontal** splits

- **Vertical Split** allows separate optimization of Control Plane (CP) and User Plane (UP) Separation / **CUPS**, a more consistent CP in multi-vendor network environment and more challenge for a lower layer splits
- **Horizontal Split** separates CU and DU to obtain centralization gain, both in terms of performance gains and economy of scale, shift functionalities to different locations based on morphologies and transport availabilities. and make overall RAN more future proof and less costly for future generation updates.



- 3GPP has defined 8 functional split options for fronthaul networks in Technical Report 38.801 as below:
- **Option 1** (RRC/PCDP)
- **Option 2** (PDCP/RLC Split)
- **Option 3** (High RLC/Low RLC split, Intra RLC split)
- **Option 4** (RLC-MAC split)
- **Option 5** (Intra MAC split)
- **Option 6** (MAC-PHY split)
- **Option 7** (Intra PHY split)
- **Option 8** (PHY-RF split)
- These splits have huge impact on three essential components of 5G network: **Latency**, **Bandwidth**, and **Scalability**.
- Lower layer split (close to RF) means ==higher bandwidth and catering to very tight latency requirements. Bandwidth will also scales with the increase in antenna ports.==
- Higher layer split (clos to PDCP) results in a ==drastic reduction in bandwidth and relaxation of latency. This will leads to long distance between CU and RU transport.==

- **Benefits of implementing a split architecture as per 3GOO rekease 14.0**:
- Flexible HW/SW Implementation
- Allows Coordination, Load Management
- Enables adaptation to various Use Cases
- Virtualizat
- **Factors related to network deployment scenarios constraints and intended software services:**
- Need to support/implement specific QoS settings
- Need to support specific user density & load demand
- Need to adapt to Ideal & Non-Ideal Transport Networks
- **Practical Implementation Samples:**




- **Multiple Functional Splits**:

#### **2.4.3 O-RAN Split Option 7-2x**
- Split Option 7-2x is one of famous LLS split option adopted by by O-RAN fronthaul specifications. This functional splitting between Distributed Unit (O-DU) and Radio Unit (O-RU) divide the function of Phy Layer (Layer 1) named as High Phy resides in DU and Low Phy resides in RU. An overview of Split Option 7-2x is shown in below picture.



#### **2.4.4 Example Of Functional Split Deployment**

## **3. 5G**
### **3.1 5G Evolution**

- 5G is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
- Summary of each generation:
- 1980s: **1G** delivered analog voice
- Early 1990s: **2G** introduced digital voice.
- Early 2000s: **3G** brought mobile data
- 2010s: **4G LTE** ushered in the era of mobile broadband
- 2020s: **5G** is a unified, more capable air interface. It has been designed with an extended capacity to enable next-generation user experiences, empower new deployment models and deliver new services.
### **3.2 RAN Architecture Evolution**

- Reffering to [background](https://hackmd.io/PXh4Qj8tT_CdjUp7cE3Gwg?both#1-Background):
:::info
- **eNB (evolved Node B) = base station (4G, gnB in 5G, g = ***next Generation***)**
- **UE = User Equipment**
- **BBU (Baseband Unit)**
- **RRU (Remote Radio Unit)**
- **RRU handles the RF (Radio Frequency) task of the access network while BBU handles the DSP (Digital Signal Processing)**
:::


- From the figure above, each base station must independetly establish a connection with the surrounding base station to exchange information. This situation will become more complicated and the number of connections will grow exponentially, making it difficult to coordinate the interference between 4G base stations.
:::success
- **4G Advantages**: latency reduction and deployment flexibility
:::
:::danger
- **4G Disadvantages**: inefficiency of information exchange between stations
:::

| 4G BBU to 5G CU, DU| 5G CU, DU, and AAU protocol layer segmentation |
| -------- | -------- |
|  |  |
- In the 5G era, the functions of the base station and core network have been reconstructed:
- **BBU** :arrow_right: **CU and DU**
- **RRU** and **Antenna** :arrow_right: **AAU**
- According to the real-time requirements of different protocol layers:
- **CU** :arrow_right: (not require high real-time) **PDCP and RLC**
- **DU** :arrow_right: (the physical high layer) **MAC, and RLC**

- **UPF (User Plane Function)**: represents the data plane evolution of a Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS) strategy
- **connects RAN and DN**
- Encapsulation and Decapsulation of GTP-U Protocol
- Packet routing and forwarding, packet inspection
- QoS corresponds to the processing of the client
- Collect user traffic usage reports
- Here's where O-RAN plays a part:
- **DN (Data Network)**: identifies ISP, internet access, or 3rd party services

### **3.3 5G Characteristics**

- **Speed and Bandwidth**
- **Low Latency**
- **Low Power Consumption**
- **Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output)**
- **Small Cell**
- **Beamforming**
| **URRLC** | **mMTC** | **eMBB** |
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
| - Low Latency|- Emergy Optimization|- Extreme throughput
|- High Reliabbility|- High Connection Density|- Enhanced spectral Efficiency
|- High Availability|- Low Complexity|- Extended coverage
|- Loction precision|- Extended Coverage | |