# BoltDB Source Code Analysis
boltdb It has the following properties:
K/VType storage, use B+tree indexes.
Support namespace, each pair K/Vstored in a Bucketcase, different Bucketcan have the same key, supports nested Bucket.
Support Services ( ACID), use MVCCand COWto allow multiple transactions to read and write transactions to execute concurrently, but have read transaction may block write transactions for reading and writing little scenes.
The following code implements the most basic function:
Open file my.dbcorresponding database;
Start a write transaction
Created in the transaction Bucket: MyBucket;
In MyBucketwriting key: foo, value: bar;
Commit the transaction.
```go=
// Open the my.db data file in your current directory.
// It will be created if it doesn't exist.
db, err := bolt.Open("my.db", 0600, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer db.Close()
// Start a writable transaction.
tx, err := db.Begin(true)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer tx.Rollback()
// Use the transaction...
bucket, err := tx.CreateBucket([]byte("MyBucket"))
if err != nil {
return err
}
bucket.Put([]byte("foo"), []byte("bar"))
// Commit the transaction and check for error.
if err := tx.Commit(); err != nil {
return err
}
```
## Storage
In summary, boltdbthe storage has the following characteristics:
- Each dbcorresponds to one file, the files page size(usually 4096 Bytes) is divided into page:
- Before the two pagesaved metadata;
- Special pagepreservation freelist, storage free pageof id;
- The remaining pageconstitute a B+tree structure.
- Each Bucketis a complete B+tree;
- B+Each node of the tree corresponds to one or more continuous ones page;
- Because less memory than the disk, usually achieve page cachethe Cache section page, such as the use of LRUalgorithms. boltdbIt did not materialize, but the use of mmap()creating a shared, read-only file mapping and invoked madvise(MADV_RANDOM)by the operating system management page cache;
- No WALtransaction in all operations are done in memory, only committime will be written to disk;
- commitWhen will dirty pagewrite the new page, so as to ensure simultaneous read transactions are not affected.
boltdbTypical B+tree structure is as follows:
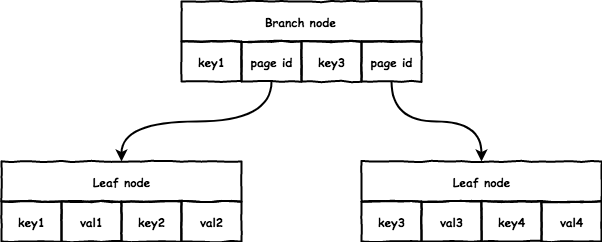
Its implementation and usual sense of the B+tree is somewhat different, the nodes keyand the valnumber is the same, and the general B+tree valthan keyone more:
- branch: Each pair of key/valpoints to a child node keyis the initiator node range, valstorage of the child node page id;
- leaf: For each key/valstored data, there is no pointer to sibiling node; conventional B+tree extra points to a pointer sibiling node.
boltdbThere are three structures and B+trees are closely related:
- page: Size generally 4096 bytescorresponding to each file page, the file is read in pageunits.
- node: B+Single node of the tree, the first access node pagecontent into memory node, each nodecorresponding to one or more continuous page.
- Bucket: Each Bucketis a complete B+tree, all operations are directed Bucket.
A typical search process is as follows:
1. First, find Bucketthe root node, which is the B+root of the tree page id;
2. Read the corresponding pageand convert it into the memory node;
3. If branch node, according to the keyfind the right child nodes page id;
4. 3 is repeated until it finds leaf nodeand returns nodethe corresponding val.
### Page
File is organized as page size(4096 bytes)the pagecorresponding structure is as follows: