# Time and Space complexity
---
## A few definitions
----
### Algorithm
----
A list of instructions to follow in order to solve a problem.
"Code" is a practical implementation of an algorithm.
----
Not just a silicon valley marketing term to make things sound cooler.
- Every single codewars kata solution you've written is an algorithm.
- The ternaries you write to tell react what to render are algorithms.
----
### Time Complexity
The time it takes to run an algorithm,
in relation to the size of the input.
----
### Space Complexity
The amount of memory it takes to run an algorithm,
in relation to the size of the input.
---
## Big O
----
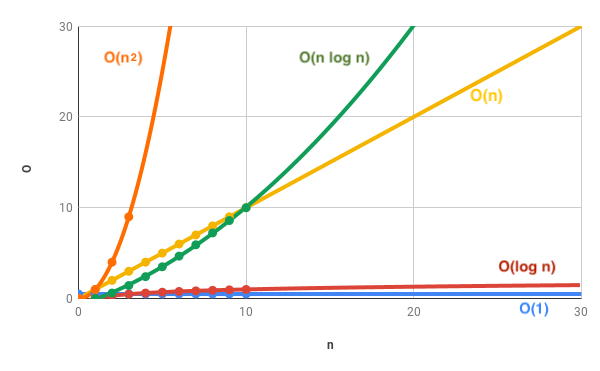
Big O describes the maximum number of "steps" it could take to complete the task, relative to the size of the input.
----
Big O is denoted in terms of n,
where n describes the size of the input.
----
Because it's a ratio, it tells us how the execution time of the algorithm will increase when the input size increases.
----
A lower value is better..
----
| Big O value | Steps taken if input size is 8 |
|-------------|---------------------------------------|
|O(1)|1|
|O(log n)|3 because log 8 == 3|
|O(n)|8|
|O(n log n)|24|
|O(n^2^)|64|
|O(2^n^)|256|
----
- see how the difference in time between two successive values gets bigger and bigger?
- the larger the input size, the more drastic these jumps are.
----
----
### Tasks
1. Can you find(or create?) an example algorithm in javascript for each of these? Try and understand why it has that big O value.
2. Do we care about the BEST possible performance(least number of steps)? Is there a measure of this? Are there situations where this matters?
3. (use a calculator) Pick a large number(>3 digits) for your input size, and make a similar table of the different big O values.
---
## Why do some sorting or search algorithms take longer than others?
----
- Sorting and searching data can be done in a variety of different ways, and thus are very commonly used as examples for time complexity.
- The following are two different approaches to searching for an element in an array, and we'll see why one is faster than the other.
----
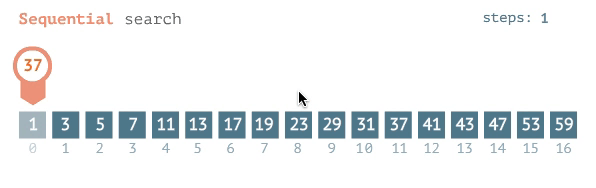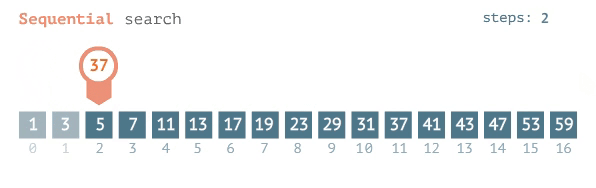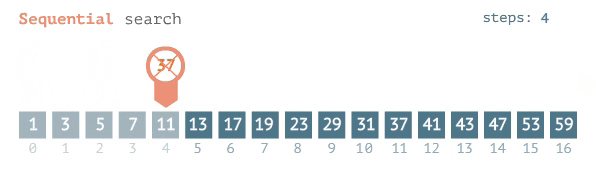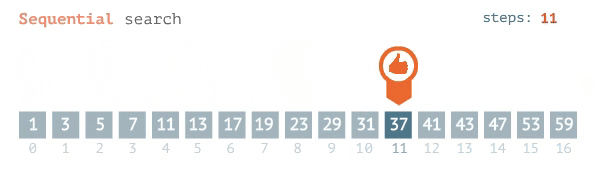
### Linear Search
- go from left to right one by one
- stop when the target element is found
----
### O(n)
- because if it is the last element you need to look through every single other element to get there.
### Ω(1)
- because if it is the first element the algorithm stops immediately.
----
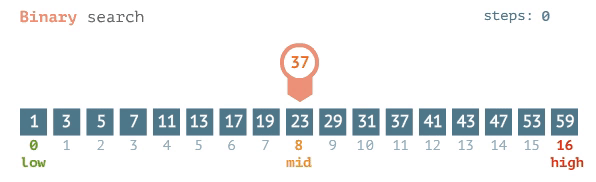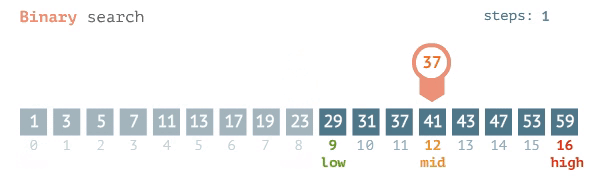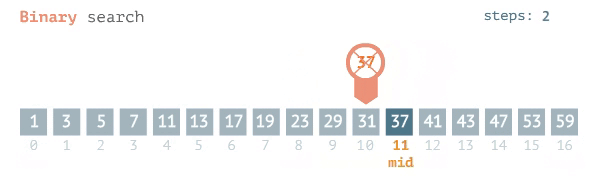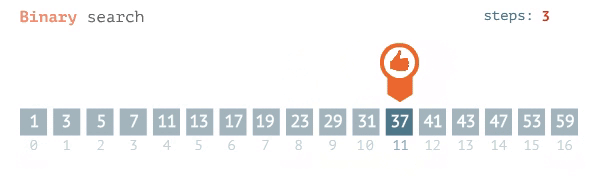
### Binary Search
- Requires that the data is SORTED in ascending order beforehand
- Involves repeatedly cutting the data in half
----
- compare the target element to the midpoint of the dataset.
- if target<midpoint, repeat the process on the left half
- else repeat the process on the right half
- eventually this process will land at one element(when target==midpoint)
----
### O(log n)
- since we're dividing by 2 each time, the max number of steps is the power of 2 where 2^x is the number of elements.
- so if there's 16 elements, 2^4=16, so no. of steps is 4.
- you can only halve 16 elements 4 times
----
### Ω(1)
- because best case scenario is only halving once.. i.e, the element is exactly in the middle of the dataset
----
### Comparing the two
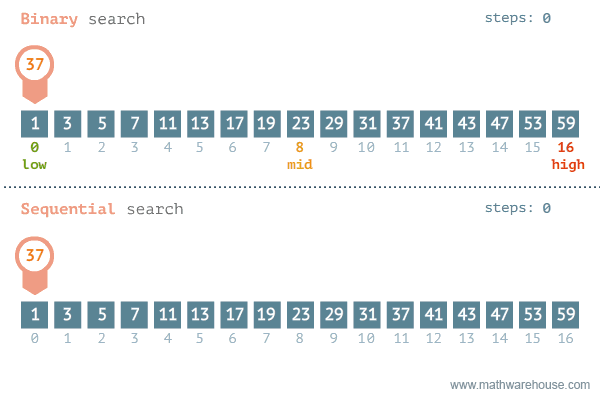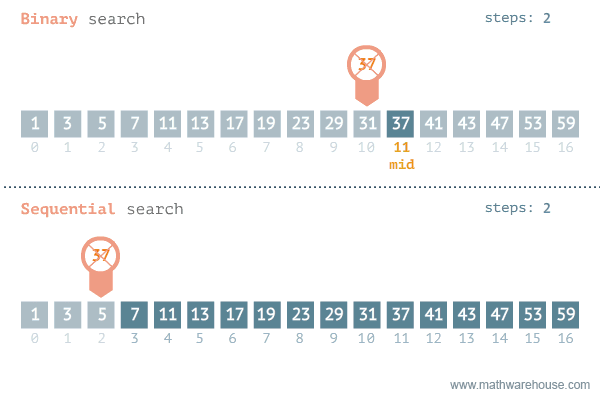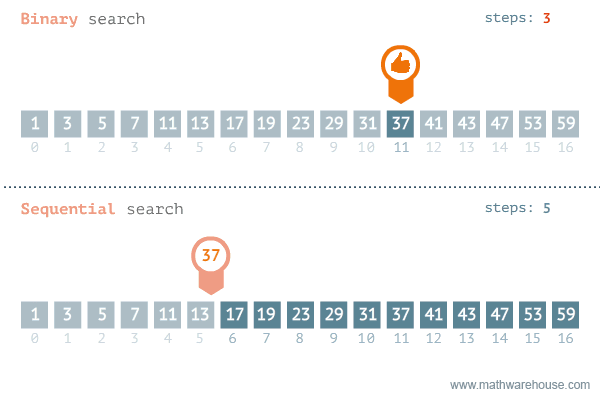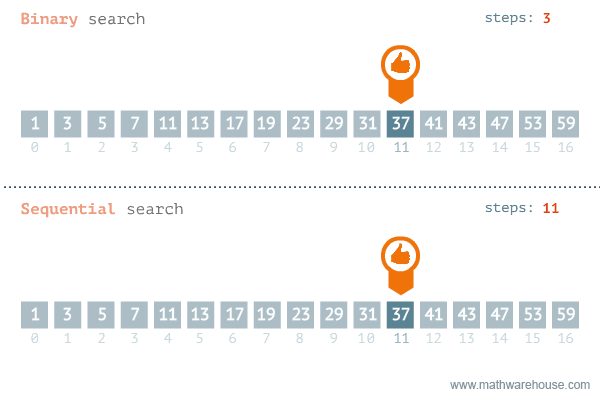
---
## Some questions for you
----
Why does any of this matter?
----
Where do data structures fit into this discussion?
----
How might we address these issues in our code? Find some common bottlenecks (hint: loopdeloop) that increase execution time, and some alternatives.
----
Does time or space matter more than the other?
---
Some resources
[great video on big o](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oJ5s2hs_cKk)
[an example for time/space complexity that doesn't involve sorting or searching algorithms, but does involve cats](https://medium.com/quick-code/considering-optimization-and-time-complexity-with-js-algorithms-4c8915086518)
[another example of improving time and space complexity](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DOsGPDHvea4&list=PLn2ipk-jqgZiAHiA70hOxAj8RMUeqYNK3&index=41)
[cs50 - great online course that'll give you more insight](cs50.harvard.edu/x/2020)
[a great, to the point introduction to data structures](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sVxBVvlnJsM)
[graph search algorithms implemented in javascript](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cWNEl4HE2OE)
----
[The Ultimate Big O Notation Tutorial (Time & Space Complexity For Algorithms) - quite a long video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=waPQP2TDOGE)
[A quora thread on time vs space complexity and what matters more](https://www.quora.com/What-matters-a-lot-space-complexity-or-time-complexity-Is-it-good-thing-that-minimizing-time-complexity-by-increasing-space-complexity)
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-15T09:43:13.707Z","metaMigratedFrom":"Content","title":"Time and Space complexity","breaks":true,"contributors":"[{\"id\":\"fe34a90e-d4b7-4af4-aa2e-64bfeaf42064\",\"add\":6521,\"del\":2450},{\"id\":\"2967aacf-1990-431e-b963-91e79ce4a2bf\",\"add\":1090,\"del\":9}]"}