# Lab #2 - Type System and Collections
###### tags: `scala` `scala-innopolis` `lab`
### Links
- https://docs.scala-lang.org/overviews/collections-2.13/seqs.html
- https://www.baeldung.com/scala/collections
### Type Hierarchy
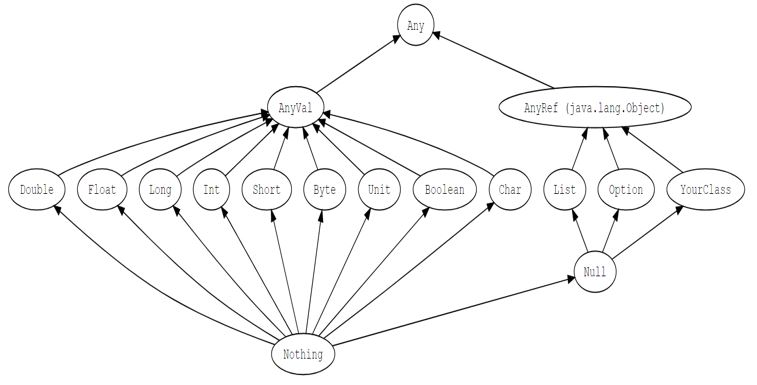
### Immutable collections

### Seq
- trait representing sequences. Sequence - is a kind of iterable that has a length and whose elements have fixed index positions, starting from 0.
- apply - get element at index
```scala=
val seq = Seq(1,2,3)
seq(1) // 2
```
- head/headOption - get first element
- tail - get seq without first element
- last - get last element
```scala=
val seq = Seq(1,2,3,4)
seq.head // 1
seq.tail // Seq(2,3,4)
```
- addition ops: prepend, append, prependAll, appendAll
```scala=
val seq = Seq(1,2,3)
seq.append(4) // Seq(1,2,3,4)
seq :+ 4 // Seq(1,2,3,4) - syntax for append
seq.prepend(0) // Seq(0,1,2,3)
0 +: seq // Seq(0,1,2,3) - syntax for prepend
```
- update ops: updated
```scala=
val seq = Seq(1,2,3)
val seqUpd = seq.updated(0, 4) // seqUpd = Seq(4,2,3)
```
- comparisons, search, sorting
```scala=
val seq = Seq(2,1,3)
seq.contains(1)
seq.sorted // Seq(1,2,3)
seq.sortBy(f) // sorted seq using comparison function f
```
### List
- linked list
- has two implementations: scala.::
```scala=
case class ::[A](head: A, tail: List[A]) extends List[A]
case object Nil[Nothing] // represents empty list
```
- O(1) prepend, head and tail operations
- LIFO - best choice for a stack-like access patterns
- haskell like pattern matching: we can use pattern matching on list to branch out program execution
```scala=
val list = List(1,2,3)
list match {
case List(1,2,3) => println("found list")
case list @ List(1,2,3) => println(s"found list $list")
case 1 :: tail => println("head equals to 1")
case head :: List(2,3) => println(head)
case head :: Nil => println(s"list has the only element $head")
case List(a, _*) if a == 1 => println("pattern matching with guard")
}
```
- `::` constructor and syntax: we can construct/deconstuct list using the same `::` operator
```scala=
val l = 1 :: 2 :: Nil
val l2 = 3 :: Nil
val l3 = l ::: l2 // List(1, 2, 3)
val l4 = l3 ++ l // List(1, 2, 3, 1, 2)
val x :: xs = l3 // x = 1, xs = List(2, 3)
```
- special constructors (fill, apply, ...)
```scala=
List.fill(3)(1) // List(1,1,1)
List.fill(2,3)(1) // List(List(1,1,1), List(1,1,1))
List.empty // Nil
List.range(0,10) // List(0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
List.range(0, 10, 2) // List(0,2,4,6,8)
List.tabulate(5)(n => n*n) // List(0,1,4,9,16)
```
### Vector
- vector is an indexed immutable sequence
- rapid acces by index
- speed of append and prepend is similar
- has iterable like operations: head, tail
- syntax
```scala=
val v = Vector(1,2,3)
v(2) // 3
4 +: v // Vector(4,1,2,3)
v :+ 4 // Vector(1,2,3,4)
v ++ Vector(0) // Vector(1,2,3,0)
```
- pattern matching
```scala=
val v = Vector(1,2,3)
v match {
case x +: xs => ...
case Vector(1, _*) => ...
case _ => ...
}
```
- has same special constructors as List
### Array
- java array: Array[T] in scala is a representation for java's T[] with scala's syntactic sugar
- mutable
- apply to access index
```scala=
val array = Array(1,2,3)
array(0) // 1
array(0) = 4 // array = Array(4,2,3)
```
### Map
- Dictionary
```scala=
val states = Map("AL" -> "Alabama", "AK" -> "Alaska")
states += ("AZ" -> "Arizona")
states -= ("AZ" -> "Arizona")
states.keys // Seq("AL", "AK")
states.values // Seq("Alabama", "Alaska")
states("US") // not safe, throws NoSuchElementException
states.get("US") // safe, returns Option, in this case None
```
### Set
- iterable that does not contain duplicates
```scala=
Set(1,1,2,3,5,1) // Set(1,2,3,5)
```
- diff
- union
- intersect
```scala=
val s1 = Set("CA", "NY", "AL")
val s2 = Set("CA", "WA")
s1 diff s2 // Set("NY", "AL")
s1 union s2 // Set("CA", "NY", "AL", "WA")
s1 intersect s2 // Set("CA")
```
### Iteration
- To iterate over a collection one can use either coll.foreach function, or a for ... yield ... structure
```scala=
val seq = Seq(1,2,3)
seq.foreach(i => println(i)) // applies function to each element and returns Unit
for i <- seq yield i*i // returns new seq of squares
```
### Combinators
- filter: filter collection using predicate, removing elements that dont satisfy it
```scala=
val seq = Seq(1,2,3,4,5)
val onlyEven = seq.filter(_ % 2 == 0) // Seq(2, 4)
```
- find: finds first element using predicate, or returns None
```scala=
val seq = Seq("CA", "NY")
seq.find(_ == "CA") // Some("CA") find
```
- collect: builds a new collection by applying a partial function to all elements of this one on which the function is defined.
```scala=
val states = Map("AL" -> "Alabama", "AK" -> "Alaska", "CA" -> "California")
states.collect {
case (key -> value) if key.startsWith("A") => value
}
```
- count: count number of elements satisfying predicate
```scala=
val states = Map("AL" -> "Alabama", "AK" -> "Alaska", "CA" -> "California")
states.count {
case (key, value) => key.startsWith("A")
}
```
- zip: merges two collections combining their elements in pairs. length = min(coll1.length, coll2.length)
```scala=
val seq1 = Seq(1,2,3)
val seq2 = Seq(4,5,6)
seq1 zip seq2 // Seq((1,4), (2,5), (3, 6))
```
- map: builds a new collection applying user function to each element
```scala=
val seq1 = Seq(1,2,3)
seq1.map(i => i*i) // squares
```
- flatMap: builds a new collection applying function that takes element and returns a collection of the same type
```scala=
val numbers = Seq(0,2,4)
def f(x: Int) = Seq(x-1, x, x+1)
numbers.flatMap(f(_)) // Seq(-1,0,1,1,2,3,3,4,5)
```
- take: select first n elements, takeRight, takeWhile
- drop: select all elements except first n, dropRight, dropWhile
- sliding: Groups elements in fixed size blocks by passing a "sliding window" over them
```scala=
// sliding(windowSize, step)
val seq = Seq("CA", "NY", "WA")
seq.sliding(2, 1) // Iterator(Seq("CA", "NY"), Seq("NY", "WA"))
```
- foldLeft/right: Applies a binary operator to a start value and all elements of this map, going left to right.
```scala=
Iterable[A].foldLeft[B](startElement: B)((B, A) => B): B
val seq = Seq(1,2,3)
seq.foldLeft(0)(_ + _) // 6
```
- reduceLeft/Right: Same as foldLeft/Right, but assumes that iterable is not empty and starts from its first element on either side
- scanLeft/Rigth: takes an associative binary operator function as parameter and will use it to collapse elements from the collection to create a running total(collection)
```scala=
val numbers: Seq[Int] = Seq(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
numbers.scanLeft(0)(_ + _) // Seq(0, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15)
```
### Exercises
#### Practice 1
```scala=
/*
In a sorted list find two numbers which have a gap between
None for List(1, 2, 3, 4)
Some((2, 8)) for List(1, 2, 8)
*/
def findGap(l: List[Int]): Option[(Int, Int)] = {
???
}
// try to implement min different ways (fold, reduce, recursion)
def minFold(map: Map[String, Int]): Option[String -> Int] = {
???
}
def minReduce(map: Map[String, Int]): Option[String -> Int] = {
???
}
def minRecursion(map: Map[String, Int]): Option[String -> Int]
// Implement scanLeft (not using scans ofc)
def scanLeft[T](zero: T)(list: List[T])(f: (T, T) => T): List[T] = {
???
}
```

```scala=
// pass the interview
def count(s: String): List[(Char, Int)] = {
???
}
```
#### Practice 2