:::warning
# <center><i class="fa fa-edit"></i> RAN Intelligence Controller</center>
:::
###### tags: `Pre-Internship` `RIC` `Machine Learning` `Deep Learning`
:::success
**Learning Objective:**
The study objectives were to:
- Learn how disaggregation RAN controlled that run virtualized and/or physically
- Learn how models
- Learn how deploying machine learning and deep learning into RAN Controller
:::
[TOC]
# RAN Intelligence Controller
## I. Background and Definition
**Background**
Last week that we talk about O-RAN that disaggregation hardware and software to helps operators reduce deployment cost and complexity, O-RAN brings to communications networks centralizes network intelligence in a network element by disassociating data plane and control plane. O-RAN architecutre that split between DU and CU. Furthermore, CU has been split into CU-CP and CU-UP. For RIC, it's allowing operators to bring software-defined controllability to RAN to increase system performance.
New RAN require advanced RAN virtualization combined with SDN. NFV and SDN combination is necessary to enable configuration, optimization and control of RAN infrastructure before aggregation. RIC provides to enable gNB functionalities as xApps on northbound interfaces. It also provides advanced control functionality, which is increasing efficiency and radio resource management.
**Definition**
RIC is one of component O-RAN achitecture that's responsible for controlling and optimizing RAN. Because of O-RAN is disaggregation, it should run interoperability, intelligence, agility, and programmability to RAN. RIC helps mobile operators to reduce both infrasctructure and operational costs and improve network performance.
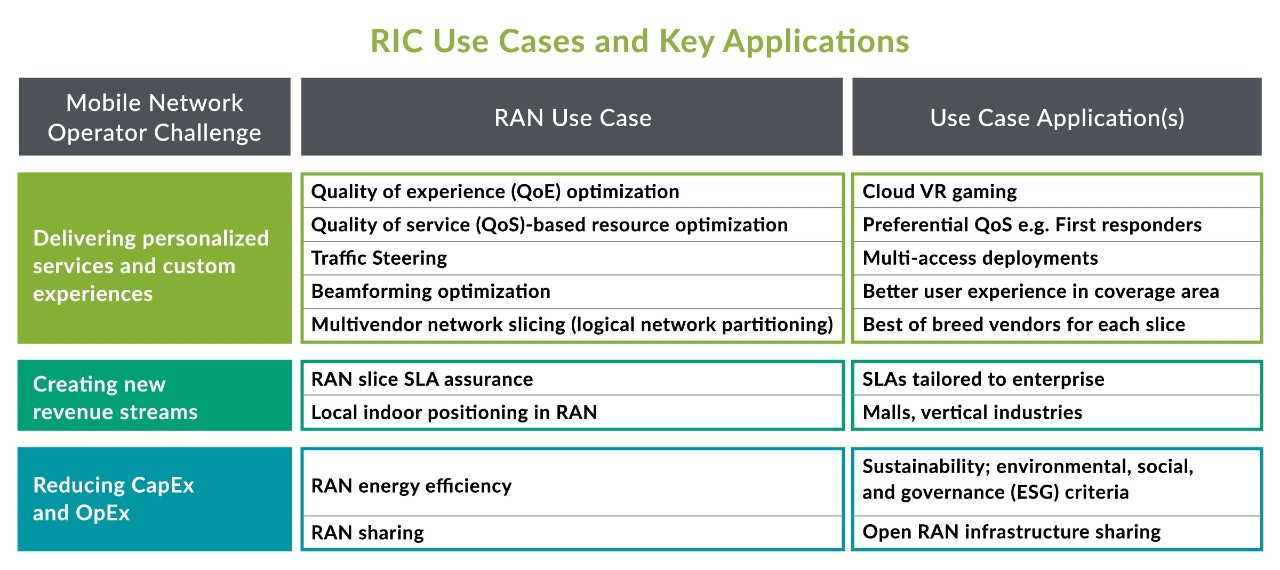
There are three objectives of the RIC
* Performance Data; RIC analyze from their elements and AI/ML engines to make RAN optimization. The data is from stream of RAN data (counters, KPIs, measurements)
* Resource Assurance; Ensure service attain required performance
* Balance and Harmony; Ensure RAN efficiency when many users are battling for scarce resource
## II. RIC Architecture
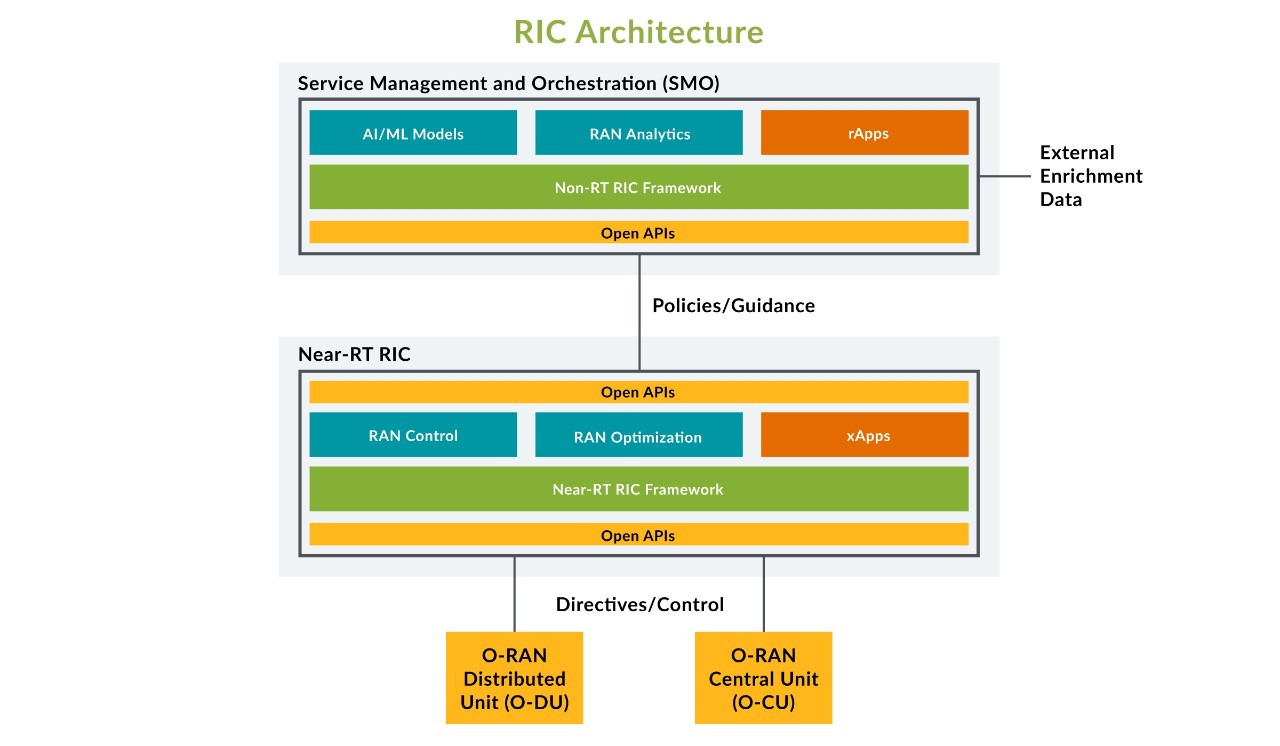
RIC is divided into non-real-time and near-real-time components.
* **Non-RT** is an elements of the operator to centralized SMO Framework. Using this specialized application called **rApps**. The Non-RT RIC should enables more than 1 second control RAN elements and their resources in the loop. It also provides network data, subscriber data, performance metrics, and AI-based recommendation for network optimization and policy guidance to xApps that running in Near-RT RIC.
* **Near-RT** resides within a telco edge cloud that's responsible for intelligent edge control of RAN nodes and resources. It should control RAN elemeents and resources from 10ms to 1s. It also receives policy guidance from Non-RT RIC and provides policy feedback to the Non-RT RIC through specialized applications called **xApps**.
## III. Near-RT RIC
The Near Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Near-RT RIC) is a software platform that hosts microservices-based applications called xApps. Near-RT RIC leverages a Radio-Network Information Base (R-NIB) database that captures near real-time state of the underlying network to provide unique Radio Resource Management (RRM) for distributed RAN infrastructure CUs and DU NE/NF via directional E2 protocols "southbound". This means that the RRMs that power the system, and which are usually embedded within the Base Band, can now be decoupled from the CU vendor software, with MNOs having the possibility to deploy their own or at best 3rd party xApps.
Near-RT RICs can be used in a centralized or distributed model, depending on the network topology. Given 5G use cases that require very low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, Near-RT RICs can be used at the 'edge', and indeed the Radio Network Information Service of Multi-Access Edge Compute (MEC).
Near-RT RIC shall:
* Provide database function to store data from E2 nodes, cells, bearers, flows, UEs and mapping between them;
* Provide ML tools for data pipelining
* Provide message infrastrucutre
* Provide logging, tracing, and metrics collection from near-RT RIC framework and xApps to SMO
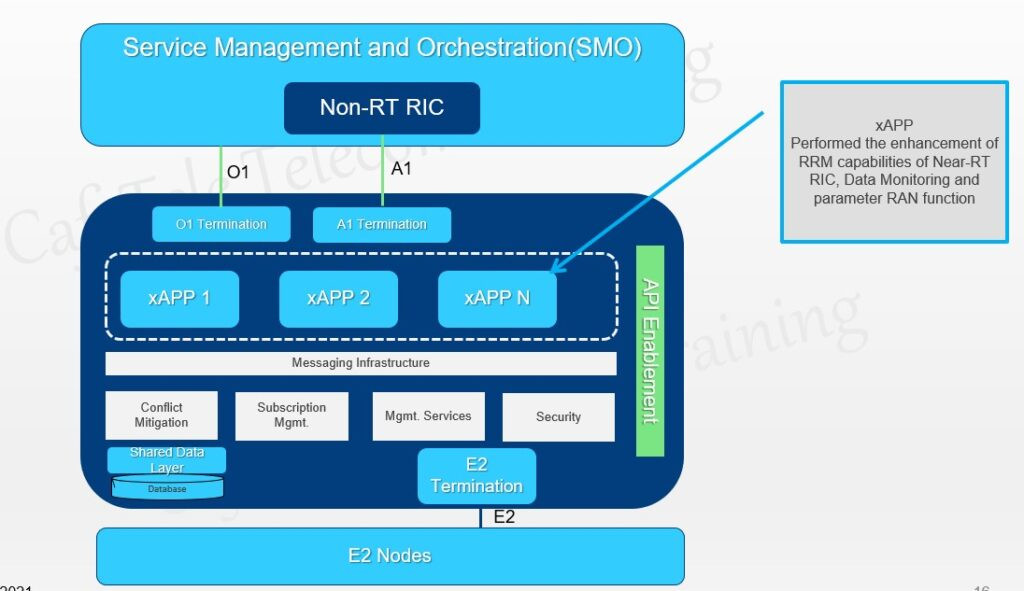
Function each element:
* **Database** allows reading and writing from UE information
* **Internal messaging infrastructure** support registration, discovery, and deletion of endpoints. It also provides APIs for sending and receiving message and routing to avoid internal loss.
* **xApp subscription management** merges subscription form different xApp and provides unified data to xApp
* **Conflicts mitigation** resolves potentially overlapping and conflic request from multiple xApp
* **Message infrastructure** enables message interaction among near-rtRIC internal
* **Security** provides security for xApp
* **xApp management** that helps near-RT to feature services and APIs for automated management fro onboardin to deployment. xApp management in the OSC RIC wrap on the **Kubernetes** infrascructure.
The main component of near-RT RIC are xApps. xApps implements custom logic for RAN data analysis and control. xApps send and receive data from E2 interface. xApps is defined by descriptor and software image. xApp descriptor (YAML or JSON) includes information on parameters need to manage xApp such as autoscaling policies, deployment, deletion and upgrade information. xApp is defined by a **Docker image** that can be deployed on **Kubernetes** infrastructure by applying the descriptor schema. The near-RT RIC platform needs to provides xApp
**Near-RT RIC API Requirements**
* Near-RT shall provide API enabling the hosting third part xApp and platform vendor.
* Near-RT shall provide API from specific implementation solution (incl. SDL).
* Near-RT shall provide an API repository for services provided by the near-RT RIC.
* Near-RT shall provide APIs aiming to simplify development of xApps.
* Near-RT shall provide Near-RT APIs supporting xApp development in mulitple programming languages (e.g. C, C++, python, Go).
* Near-RT APIs shall support xApp subscription maangement based on operators' policies.
## IV. Non-RT RIC and Orchestration
Key element of RIC is the SMO framework. SMO handles all orchestration, management and automation procedures to monitor and control RAN. SMO hosts non-RT RIC and provide a set of interface to support the interaction between the different network component as data collection capabiliites that facilitate network monitoring and control via AI/ML.
The non-RT RIC is one of the core component of RIC. Like near-RT, non-RTC supports the execution third-party application, i.e., rApps that provide value-added service to support RAN optimzation and operation. There is one internal interface in non-RT, i.e., R1 termination. This interface allows non-RT RIC to obtain access to data management and exposure services, AI/ML functionalities, as well as A1, O1, and O2 interface through internal messaging infrastructure.
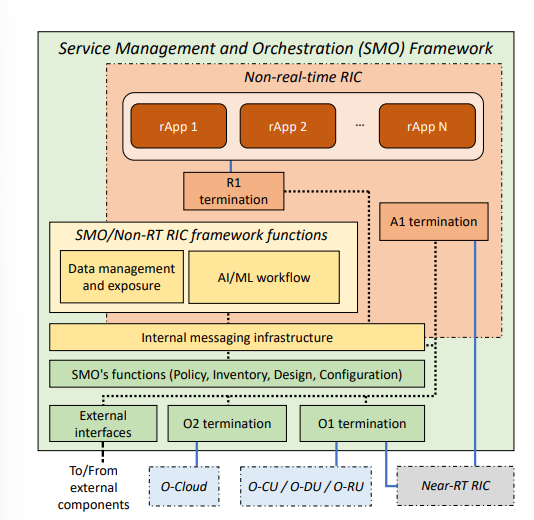
The non-RT RIC offers two high-level management and orchestration services to provide a flexible architecture.
* Intent-based network management allows operator to specify via high-level language through HMI. The activity from the operator will parsed by non-RT RIC that determines the policies and the set of applications such as rApps and xApps. This set of applications need to be deployed and executed to satisfy the operators (actually there HMI from OSC within the design of non-RT RIC).
* Intelligence Orchestration is coordinating and orchestrating these application to make sure that the applications well-suited to satisfy the operator, instantiated the appropriate RIC location, ensure the application does not produce conflicts due to the use of paralel applications and contros simultaneously (usually about the scheduling and non-RT must select only those xApps to able scheduling decision).
Other SMO/Non-RT RIC functionalitis:
* Internal messaging infrastructure allow all components within SMO to access and utilize interface, data and functionalities offered by both SMO and non-RT RIC.
* Data management and exposure services, this fumction allows O-RAN to follow cosumer protocol in which data consumers in the SMO can advertise and publish data. In other hand, consumers can discover, subscribe, receive and consume relevant data types form selected number of node in SMO. SMO/non-RT RIC can perform collection of all data being produced to support AI/ML.
* SMO/non-RT RIC offer AI/ML workflow by observe the entire AI life cycle and cover all the aspects of them (including data collection, training, validation, deployment and execution).
## V. Functional Architecture
There are key functional design principle of the RIC
**O-CU-CP Functional split and RIC processing over O2**
Compare to nondisaggregated RAN, CP only processing inside the CU-CP. In disaggregated RAN, there're serveral E2-based CP mechanism namely INSERT (notify the xApp about specific event in the E2 node), REPORT (report E2 RIC message contains from E2 node), CONTROL (control RIC request) and POLICY (event trigger E2 node should autonomously follow to perfrom RRM). The output from xApp ML algorithms is subsequently delivered in the form of closed-loop control action or policy back to the CU-CP for completing CP processing.
**NFV and RAN state informaation persistance**
R-NIB is an in-memory database inside RIC that stores RAN state information. RAN can send state information over E2 following the POLICY mechanism. Predicitive intelligence technique used in ML-based xApp can depend on RAN state information.
**xApp management via O1 interface**
This interface is responsibility the follow:
* Managing subscription to RAN data and KPIs from RAN nodes
* Controlling the access of xApp to R-NIB for main operations.
* Controling xAPP that can be service to perform complex RRM decisions
**Policy guidance via A1 interface**
RIC xApp is optimizing RRM decisions, subject to policy guidance from SMO to RIC over A1 interface. There're RAN policy guidance:
* Assignment optimization KPI and service objective
* Providing enrichment information from outside RAN ecosystem to RIC (e.g., weather information) for use ML-based xApp as input feature.
* Prioritizing or blacklisting of cells and bands of many loads.
# Machine Learning in the RIC
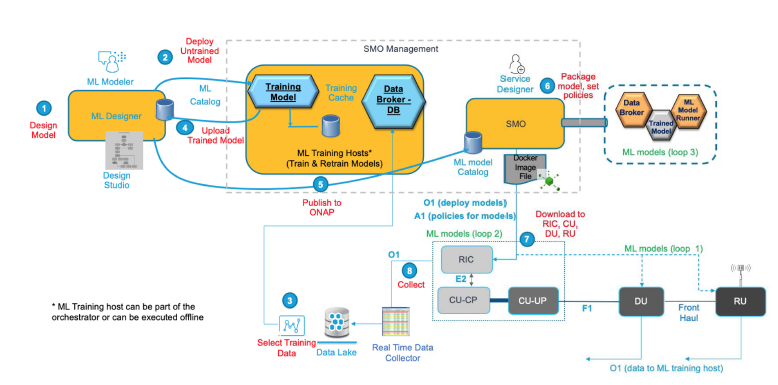
Take a look of picture above. This picture will be reference on this section. As mention before, ML in RIC enhanced RRM (optimized RRM decision). There will be 3 loops to control based in ML:
**Loop 3:** ML/AI analytics engine uses RAN KPI statistics reported from RAN to SMO over O1 interface as training dataset to build models. This ML model will make accurate decisions on policies and configuration of KPI objectives. Decision will communicated to Near-RT RIC over A1 interface.
**Loop 2:** As we know that machine learning have 2 models based on adaptive works i.e. offline and online ML. ML-based microservices the RIC use hybrid models to compare this models. Online ML models further in deep learning can achieve lower control loop latency since the processed on a single stream of incoming RAN data to the RIC (adaptive control). Online learning is used for generating optimized RRM decision, complementary offline ML are used leveraging historical information in R-NIB. When ML models in loop 2 misbehave performance, nonreal-time RIC may instruct loop 2 to terminate or switch to improved model.
**Loop 1:** Latency budget will be strict for loop 1 due to limit the DUs from adopting a request and response approach with the RIC. Asynchronous policy (scheduling algorithm) is the solution to directive from RIC to the DU. AI-based policy directive can be used by the DUs with the loop 1 online ML models to enhanced RRM in real time.
Besides of optimizing RRM, ML-based model help to DC optimization that key feature in 5G-NR. DC enables RAN to serve an IP traffic flow to a UE by splitting the packet of the flow betweeen eNB ad gNB. ML-based split the packet by 3 control loops
**Loop 3:** Offline ML models built from large historical RAN KPI that reported over O1. This models suggest a load imbalance across the pairs of base station. This suggest will generate threshold. Such threshold fractions are commmuicated as policy guidance over A1 or over O1 and updated over coarser time sclaes.
**Loop 2:** RIC splits DC traffic between eNB-gNB pair for optimize RAN utility function in near-RT RIC, policy set by SMO and service objective associated with traffic profile. To optimize split can be use hybrid models, offline models for take advantage of the limited persistence of RAN status information in the R-NIB and online models for instantaneous RAN data streams coming through E2.
**Loop 1:** DUs use online ML models to optimally schedule resource and manage buffers for the split fraction, based on policy directives from RIC over E2 and channel feedback form the UEs.
Lastly, ML can help massive MIMO to optimize beam generation and assignment at different time scales.
**Loop 3:** non-RT RIC can be trained to make inference about the temporal and geographic distribution of UEs. This provide guidance to specific gNBs to make adjustments antenna arrays.
**Loop 2:** using recent time-series information about UEs' channel condiiton, handover events, and buffer status, ML beam steering algorithm in near-RT RIC can clusters which UEs can be benefit from an MU-MIMO transmission mode.
**Loop 1:** DU can dynamically optimize the individual beams for the UEs of each group.
# Deep Learning Based Works for RIC
There're many research about deep learning in 5G networks controller. At least a minimum of 3 focuses used by deep learning on 5G networks since 2020.
**Resource management optimization**
* Predict traffic congestion and occupancy state of the eNBs. Thus, the network can predict uplink and downlink ratio by utilize deep tree model and LSTM. Deep tree model (using CNN that generated by UEs) to avoid traffic congestion, then LSTM to predict future traffic based on current and past traffic (as RNN should be).
* Resource scheduling with iRSS by exploit both DNN based on LSTM and reinforcement learning. DL is used to deal with large time-scale resource, while reinforcement learning provides an online resource scheduling to tackling small time-scale network (unexpected events). LSTM is divided into a set of prediciton windows that predict traffic volume to next prediciton windows
* Maximizing the downlink cell sum-rate by addressed of power allocation. It aims to implement a near-optimal power allocation policy. This methods use reinforcement learning in mostly appied. RL maximize the downlink network throughput while ensuring an optimal power allocation
All this works belongs to O-DU since O-DUs target the resource (radio and power). All these works also concern the MAC layers in term of resource assignment, scheduling, and High-PHY.
**Mobility management optimization**
* Handover is critical function in RAN. Handover consists of moving users connection from a cell to another to get better radio condition and better experience. DL will predict the suitable next base station to which users will migrate. Because of that, DL is an early preparation decisison of handover procedurs. As we know O-RAN architecture, the handover act at O-CU-CP module.
* Base station represent the main source of energy consumption in networks. Thus, BS should be maintained in order to networks save energy. Reinforcement learning is applied to decide BS mode by switching to sleeping or active mode. This energy will be implemented at O-CU-CP.
**Spectrum management optimization**
* In modulating utilize OFDM system, frequency selectivity and time variance of channels are challeging. DL is used in order to minimze difference between sent and receive signals. In addition, channel estimation that recover transmitted signal at receive side will ensure by PUCCH of the O-DU module.
* Beam direct communication will be. Thus, the best beam is necessary to ensuring accurate alignments between base stations and users. Beam selection function consits to selecting best beam. Reinforcement learning is applied to update the beam based on users feedback. Supervised learning such as DNN helps predict the best beam based on environment context susch as presence of obstacle. O-RU module is responsible this function.
* DNN can deal with signal classification, encoding and decoding. DNN encodes the transmitted signal then deliver it to DNN in receiver. For classification, DNN classifier the signal into suitable modulation type. This works in O-DU due to high-PHY's responsible to ensure the signal.
O1 interface is in charge to monitor targeted data types from O-DU module, for training models at Non-RT RIC. Learning models can be trained either offline or online at Non-RT RIC. Genereted model will be communicate to Near-RT RIC through A1 interface to be executed in real-time at Near-RT RIC. To compare the data, the result is collected to O1 interface to help detecting violations in real-time, such as latency or throughput violation. This make more adequate decision. Near-RT RIC can enforce decision on O-DU through E2 interface.