> ( •̀ ω •́ )✧ 이 글은 논문과 코드를 맵핑하여 이해하기 위해 작성했습니다. 보완이 필요한 내용은 댓글 부탁드립니다.
>
> 📖 **Reference**
> - [논문 : Variational Autoencoders for Collaborative Filtering
](https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05814)
> - https://github.com/dawenl/vae_cf
> - https://github.com/younggyoseo/vae-cf-pytorch
> - [이성범님 Paper-Code-Review-2018-WWW-Variational-Autoencoders-for-Collaborative-Filtering](https://velog.io/@2712qwer/Paper-Code-Review-2018-WWW-Variational-Autoencoders-for-Collaborative-Filtering)
> - [Alfredo Canziani - 생산적 모델 - 변이형 오토인코더](https://atcold.github.io/pytorch-Deep-Learning/ko/week08/08-3/)
## 00. 사전 지식
### 1 ) 다항 분포 ( Multinomial distribution )
각각의 <span style="background-color: skyblue" ><strong> 독립적인 시행 </strong></span> 에서 나올 수 있는 값이 ${k}$ 가지 이고,
<span style="background-color: skyblue" ><strong> 각 값이 나타날 확률 </strong></span>은 ${p_i, p_2, ..., p_k}$ 일 때,
${n}$ 번의 시행에서 ${i}$ 번째 값이 <span style="background-color: skyblue" ><strong> 특정 횟수 </strong></span> ${x_i}$번 <span style="background-color: skyblue" ><strong> 만큼 나타날 확률 </strong></span> ( ${x_i+x_2+...+x_k = n )}$
### 2 ) VAE ( Variational Auto-Encoder )
> `참고` Auto Encoder 는 input 에서 feature 를 뽑고 output 을 만드는 모델이지만, VAE 는 ${p_{\theta}(x)}$ 를 최대화하는 generative model 이다. ( ${x}$는 ${P_{data}}$ 에서 샘플링됨 )
<img src="https://velog.velcdn.com/images/hobbang2/post/11906d6d-4fc7-46a0-9645-1b225fe228a3/image.png" width="60%" height="30%">
Posterior distribution : 주어진 데이터로 학습할 때 parameters 의 확률 분포 ${\rightarrow}$ 모델링이 어렵다.
${\Rightarrow}$ true posterior 사이의 KL divergence 를 최소화하는 variatoinal distribution 을 찾는 것
## 01. ABSTRACT
> VAE 를 implicit feedback 에 대한 collaborative filtering 으로 확장한다.
- Non-linear probabilistic model 사용으로 성능 개선
- Multinomial likelihood 사용
- Parameter estimation 에서 bayesian inference 사용
- maximum entropy discrimination 과 information bottleneck principle 사용
- maximum entropy discrimination : 주어진 입력에 대해 가장 가능성이 높은 클래스를 결정하기 위해 maximum entropy theory 를 사용하는 분류 방법
- information bottleneck principle : Noise 를 최소화하면서 data set 과 가장 연관성이 높은 정보를 추출하는 방법
## 02. Introduction
> 추천 시스템에서 다루는 데이터 셋은 user 와 아주 적은 item 간의 상호 작용만 있기 때문에, small data set problem 이라고 주장한다.
- VAE 는 linear-factor model 을 생성하고 non-linear probabilistic latent-variable model 을 제안한다.
- User 로 부터 sparse 한 signal 들 만 사용하고 overfitting 을 피하기 위해 user 와 item 사이의 통계적 강점을 공유하는 probabilistic latent-variable model 을 사용한다.
- principled-bayesian approach 를 사용하여 data 의 scarcity 와 관계없이 robust 한 성능을 보인다.
## 03. Model
> 해당 논문에서 generative process 는 deep latent Gaussian model 과 유사하다.
- 각각의 사용자 ${u}$ 에 대해, 표준 Gaussian prior 로 부터 K 차원 latent representation ${z_u}$ 를 sampling 함으로써 시작한다.
- Sampling 된 ${z_u}$ 는 non-linear function ( ${f_{\theta}(\cdot) \in \R^I}$ ) 에 의해 변형된다.
- non-linear function ${f_{\theta}(\cdot)}$ 은 parameter ${\theta}$ 를 가지는 multilayer perceptron 이다.
- ${z_u}$ 에 non-linear functoin 을 적용한 결과는 확률 vector ${\pi(z_u) \in S^{I-1}}$ 이다.
${\rightarrow}$ 해당 generative model 은 latent-factor model 을 일반화한다.
`참고` ${f_{\theta}(\cdot)}$ 를 linear 한 함수로 두고 Gaussian likelihood 를 사용하면 classical matrix factorization 을 recover 할 수 있다.
---
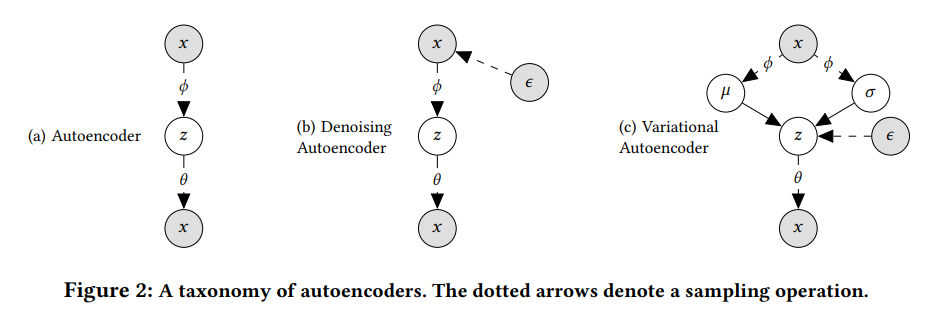
( b ) DAE : ${x}$ 에 noise ${\epsilon}$ 을 추가하여 복원
( c ) VAE : ${x}$ 를 encoder ${g_{\phi}(\cdot)}$ 를 이용해 평균 ${\mu}$ 와 분산 ${\sigma}$ 를 구한다. 구해진 평균과 분산으로 K-차원 latent representation ${z}$ 를 샘플링한다. ${z}$ 를 다시 decoder ${f_{\theta}}$ 로 복원한다.
---
## 04. Experimental setup
- training / validation / test sets 로 나누어 학습한다.
- training user 에 대한 전체 click history 를 사용한다.
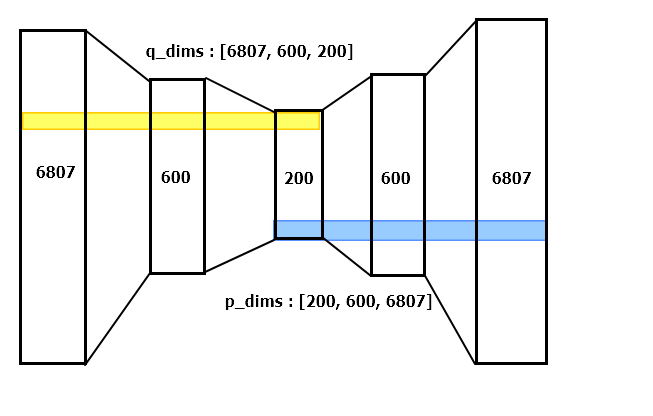
- 1 ( 또는 0 ) 개의 hidden layer 를 가지는 Multi-VAE / Multi-DAE 구조가 가장 좋은 성능을 냈다. ${( [ I \rightarrow 600 \rightarrow 200\rightarrow 600 \rightarrow I ] ) }$
- layer 간의 activation function 으로 tanh 을 사용했다.
- Mult-VAE 에서 ${g_\phi(\cdot)}$ 의 결과는 Gaussian random variable 의 평균 ( mean ) ${\mu}$ 와 분산 ( variance ) ${\sigma}$ 로 사용되기 때문에 activation function 을 사용하지 않는다.
- hidden layter 가 0 개 인 경우 log-linear model 이다.
- anneal KL term 으로 성능 향상 ( 찾아보기 ! )
- Drop out 은 input layer 에 대해 모두 0.5
- VAE model 에는 weight decay 사용하지 않는다.
- mult-VAE 와 Mult-DAE 모두 500 명의 user 를 가지는 batch 에서 Adam optimizer 사용
> 🐬 `checkpoint`
> - ${P_{data}}$ 에서 smapling 된 ${x}$
> - <span style="background-color: rgba(242,179,188,0.5)" ><strong> Input ${x}$ 의 평균 ${\mu}$ 와 분산 ${\sigma}$ 로 부터 ${z}$ 를 sampling 한다. </strong></span>
> - ${\mu}$ 에 따라서 distribution 의 어디에 위치하는지 등에 대한 정보가 결정된다.
> - ${\rightarrow}$ linear layer 는 ${\mu}$ 와 ${logvar}$ 에 대한 확률적인 값을 뽑기 위한 것
> - ${\mu}$ 와 ${logvar}$ 가 고정되면 값이 고정된다. ${\rightarrow}$ 항상 동일한 분포에서 sampling 된다.
> - 따라서, ${\mu}$ 와 ${logvar}$ 에 대한 linear layer 로 input 에 따른 ${\mu}$ 와 ${variance}$ 값을 뱉는다.
>
> ${\Rightarrow}$sampling function 에 들어가는 mu 와 variance 의 값이 됨
## 05. Code
### 1 ) MultiDAE
```python
class MultiDAE(nn.Module):
"""
Container module for Multi-DAE.
Multi-DAE : Denoising Autoencoder with Multinomial Likelihood
See Variational Autoencoders for Collaborative Filtering
https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05814
"""
def __init__(self, p_dims, q_dims=None, dropout=0.5):
super(MultiDAE, self).__init__()
self.p_dims = p_dims # [200, 600, 6807]
if q_dims:
assert q_dims[0] == p_dims[-1], "In and Out dimensions must equal to each other"
assert q_dims[-1] == p_dims[0], "Latent dimension for p- and q- network mismatches."
self.q_dims = q_dims
else:
self.q_dims = p_dims[::-1] # [6807, 600, 200]
self.dims = self.q_dims + self.p_dims[1:] # [6807, 600, 200] + [600, 6807]
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(d_in, d_out) for
d_in, d_out in zip(self.dims[:-1], self.dims[1:])]) # ( [6807, 600, 200, 600] , [600, 200, 600, 6807] )
self.drop = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.init_weights()
def forward(self, input):
# normal distribution 을 따르지 않은 input 에 대해 편향을 줄여줌
# 예 ) 평점을 대체로 높게 주는 사용자와 낮게 주는 사용자의 편향을 줄임
h = F.normalize(input)
h = self.drop(h)
for i, layer in enumerate(self.layers):
h = layer(h)
if i != len(self.weights) - 1:
h = F.tanh(h)
return h
def init_weights(self):
for layer in self.layers:
# Xavier Initialization for weights
size = layer.weight.size()
fan_out = size[0]
fan_in = size[1]
std = np.sqrt(2.0/(fan_in + fan_out))
layer.weight.data.normal_(0.0, std)
# Normal Initialization for Biases
layer.bias.data.normal_(0.0, 0.001)
```
### 2 ) MultiVAE
```python
class MultiVAE(nn.Module):
"""
Container module for Multi-VAE.
Multi-VAE : Variational Autoencoder with Multinomial Likelihood
See Variational Autoencoders for Collaborative Filtering
https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05814
"""
def __init__(self, p_dims, q_dims=None, dropout=0.5):
super(MultiVAE, self).__init__()
self.p_dims = p_dims
if q_dims:
assert q_dims[0] == p_dims[-1], "In and Out dimensions must equal to each other"
assert q_dims[-1] == p_dims[0], "Latent dimension for p- and q- network mismatches."
self.q_dims = q_dims
else:
self.q_dims = p_dims[::-1]
# Last dimension of q- network is for mean and variance
temp_q_dims = self.q_dims[:-1] + [self.q_dims[-1] * 2]
self.q_layers = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(d_in, d_out) for
d_in, d_out in zip(temp_q_dims[:-1], temp_q_dims[1:])])
self.p_layers = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(d_in, d_out) for
d_in, d_out in zip(self.p_dims[:-1], self.p_dims[1:])])
self.drop = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.init_weights()
# Gaussian Distribution
def forward(self, input):
mu, logvar = self.encode(input)
z = self.reparameterize(mu, logvar)
return self.decode(z), mu, logvar
def encode(self, input):
# normal distribution 을 따르지 않은 input 에 대해 편향을 줄여줌
# 예 ) 평점을 대체로 높게 주는 사용자와 낮게 주는 사용자의 편향을 줄임
h = F.normalize(input)
h = self.drop(h)
for i, layer in enumerate(self.q_layers):
h = layer(h)
if i != len(self.q_layers) - 1:
h = F.tanh(h)
else:
# z 값을 sampling 할 multinomial distributio 의 평균과 logvar
mu = h[:, :self.q_dims[-1]]
logvar = h[:, self.q_dims[-1]:]
return mu, logvar
def reparameterize(self, mu, logvar):
if self.training:
# Gaussian 분포의 표준 편차를 구하는 식 ( 분산의 제곱근 )
std = torch.exp(0.5 * logvar)
eps = torch.randn_like(std)
return eps.mul(std).add_(mu)
else:
return mu
def decode(self, z):
h = z
for i, layer in enumerate(self.p_layers):
h = layer(h)
if i != len(self.p_layers) - 1:
h = F.tanh(h)
return h
def init_weights(self):
for layer in self.q_layers:
# Xavier Initialization for weights
size = layer.weight.size()
fan_out = size[0]
fan_in = size[1]
std = np.sqrt(2.0/(fan_in + fan_out))
layer.weight.data.normal_(0.0, std)
# Normal Initialization for Biases
layer.bias.data.normal_(0.0, 0.001)
for layer in self.p_layers:
# Xavier Initialization for weights
size = layer.weight.size()
fan_out = size[0]
fan_in = size[1]
std = np.sqrt(2.0/(fan_in + fan_out))
layer.weight.data.normal_(0.0, std)
# Normal Initialization for Biases
layer.bias.data.normal_(0.0, 0.001)
def loss_function(recon_x, x, mu, logvar, anneal=1.0):
# BCE = F.binary_cross_entropy(recon_x, x)
BCE = -torch.mean(torch.sum(F.log_softmax(recon_x, 1) * x, -1))
KLD = -0.5 * torch.mean(torch.sum(1 + logvar - mu.pow(2) - logvar.exp(), dim=1))
return BCE + anneal * KLD
```