# AICSIR --- CV
###### tags: `AICSIR`
[TOC]
::: info
**Goal :**
- [x] detect the green object. (tennis)
- [x] calculate the object's 3D coordinate with reference to camera.
- [x] publish the object's position to specific topic.
- [x] improve position estimation accuracy.
:::
## basic
### camera specs
* Logitech, Inc. Webcam C310.
* video resolution support:
```
* 640x480 * 752x416 * 1280x960
* 160x120 * 800x448
* 176x144 * 800x600
* 320x176 * 864x480
* 320x240 * 960x544
* 352x288 * 960x720
* 432x240 * 1024x576
* 544x288 * 1184x656
* 640x360 * 1280x720
```
### pinhole model
* The pinhole camera model describes the mathematical relationship between the coordinates of a point in three-dimensional space and its projection onto the image plane of an ideal pinhole camera. [Pinhole camera model wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinhole_camera_model)
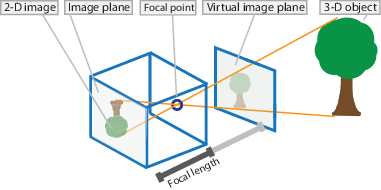
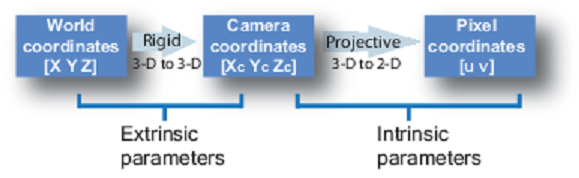
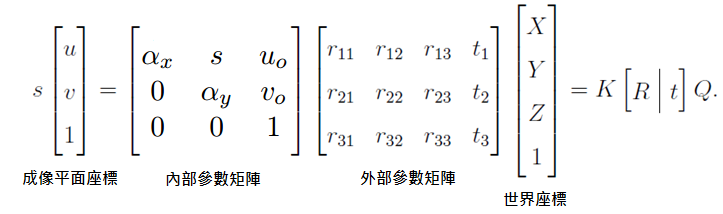
* In our case, we don't need to find out the extrinsic parameters because we just need the camera coordinate. World coordinate can be calculated by other ROS node.
* So we only concern about the intrinsic parameters
* $u_0$ means the center point along X-axis in a photo. in 640 x 480 case, $u_0\ = \frac{640}{2} = 320$. Another representation sign is $c_x$.
* $v_0$ means the center point along Y-axis in a photo. in 640 x 480 case, $v_0\ = \frac{480}{2} = 240$. Another representation sign is $c_y$.
* $s$ is skew parameter, to adjust pixels in a photo under a situation that u-axis doesn't perpendicular to v-axis. Usually $s$ is 0.
* $\sigma_x$ is focal length which camera project a point to X-axis of an image plane. Another representation sign is $f_x$. Unit is pixel.
* $\sigma_y$ is focal length which camera project a point to Y-axis of an image plane. Another representation sign is $f_y$. Unit is pixel
## computer vision
### camera calibration
* **method 1** :
1. measure the object's real width $W$(or height $H$) and the length between camera and object *D*.
2. take a picture of object and measure the object's pixels $P_x$(or $P_y$) in that photo.
3. use **triangle similarity therom** to calculate the camera intrinsic parameter $f_x$ and $f_y$.
4. formula : $\dfrac{f_x}{D} = \dfrac{P_x}{W}$ , $\dfrac{f_y}{D} = \dfrac{P_y}{H}$.

* **method 2** :
[NCRL相機校正筆記](https://sites.google.com/a/g2.nctu.edu.tw/ncrl-nctu/svo/攝影機校正?authuser=0)
### color tracking
1. take each frame of the video.
2. convert from BGR to HSV color-space. **In HSV, it is more easier to represent a color than RGB color-space**.
3. for example, we threshold the HSV image for a range of blue color.e
4. now extract the blue object alone, we can do whatever on that image we want.
* example :
```python3=1
import cv2
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while(1):
# Take each frame
_, frame = cap.read()
# Convert BGR to HSV
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# define range of blue color in HSV
lower_blue = np.array([110,50,50])
upper_blue = np.array([130,255,255])
# Threshold the HSV image to get only blue colors
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, lower_blue, upper_blue)
# Bitwise-AND mask and original image
res = cv2.bitwise_and(frame,frame, mask= mask)
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
cv2.imshow('mask',mask)
cv2.imshow('res',res)
k = cv2.waitKey(5) & 0xFF
if k == 27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
* example result :

* Q : How to find HSV values to track?
A : using function cv2.cvtColor(). Instead of passing an image, you just pass the ==BGR== values you want. For example :
```python3
>>> green = np.uint8([[[0,255,0 ]]])
>>> hsv_green = cv2.cvtColor(green,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
>>> print(hsv_green)
[[[ 60 255 255]]]
```
then you can take ==[H-10, 100,100] and [H+10, 255, 255]== as lower bound and upper bound respectively.
### position estimation
* leverage the formula above in camera calibration $\dfrac{f_x}{D} = \dfrac{P_x}{W}$ and $\dfrac{f_y}{D} = \dfrac{P_y}{H}$.
* first, assume that you have detected the object and got its pixels in image. Then from the formula $D = \dfrac{f_x \cdot{W}}{P_x}$, we can estimate the Z-axis value.
* therefore, we slighly change the definition of $P_x$ and $W$ to the `object's offset against the Y-axis in image` and `object's offset against the Y-axis in real world (camera coordinate)`.
* then we can estimate the X-axis value by formula $W = \dfrac{P_x\cdot{D}}{f_x}$.
* we also change the definition of $P_y$ and $H$ to the `object's offset against the X-axis in image` and `object's offset against the X-axis in real world (camera coordinate)`.
* and so on, we can estimate the Y-axis value by formula $H = \dfrac{P_y\cdot{D}}{f_y}$.
## progress
* 2/3~2/7: use one webcam c310 to detect the blue object, and return its 3D relative coordinate with reference to camera.
* 2/10~2/14: corrected the intrinsic parameter of camera, returned at least 80% accuracy of object Z-axis position. Also, wrote a publisher to publish Point msg to "camara coordinate" topic.
* 2/17~2/21: corrected the X-axis and Y-axis position estimation method. And the new method yield position estimation difference less than 1cm in each axis.
## reference
* [demo參考影片](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idSvJ-RXhq0)
* [辨識參考影片](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hQ-bpfdWQh8)
* [台中一中-機器手臂與電腦視覺結合](https://activity.ntsec.gov.tw/activity/race-1/59/pdf/NPHSF2019-052311.pdf)
* OpenNI
* [OpenCV + OpenNi](https://docs.opencv.org/master/d7/d6f/tutorial_kinect_openni.html)
* [OpenNI 2.x 教學文章](https://kheresy.wordpress.com/index_of_openni_and_kinect/documents-of-openni-2-x/)
* [OpenNI2 header](https://github.com/OpenNI/OpenNI2/blob/master/Include/OpenNI.h)
* openCV
* [openCV tutorial](https://opencv-python-tutroals.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html)
* [openCV API document](https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/modules/highgui/doc/reading_and_writing_images_and_video.html?highlight=read#cv2.VideoCapture.read)
* [openCV contour教學](https://chtseng.wordpress.com/2016/12/05/opencv-contour%E8%BC%AA%E5%BB%93/)
* [openCV denoise教學](https://opencv-python-tutroals.readthedocs.io/en/latest/py_tutorials/py_imgproc/py_morphological_ops/py_morphological_ops.html)
* 座標轉換
* [pinhole model](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinhole_camera_model)
* [針孔相機座標成像原理](http://silverwind1982.pixnet.net/blog/post/134551091-pinhole-camera%3A-%E7%9B%B8%E6%A9%9F%E5%BA%A7%E6%A8%99%E6%88%90%E5%83%8F%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86)
* 相機校正
* [pinhole 相機校正](http://silverwind1982.pixnet.net/blog/post/153218861)
* [利用ros校正相機](http://wiki.ros.org/camera_calibration/Tutorials/MonocularCalibration)
* [NCRL相機校正筆記](https://sites.google.com/a/g2.nctu.edu.tw/ncrl-nctu/svo/she-ying-ji-xiao-zheng?fbclid=IwAR3RDtt_0bXg-6Bb-WV6wUsa1RQYbAtl9l0o-23asJLhQQaU_3qgNZE6ooY)