# Survey of Data Synchronization Tools
## Requirements
* Data synchronisation
* AAA
* Messaging / Notifications
## Necessary Steps for Comparison of Tools and Frameworks
* Requirementsanalysis
* proper Interface-Definition
Easy way to go is to search for surveys!
* Tutorials / Intros / Documentation
* Who is using it?
* **Community / Help** How many hits do you find on this topic? Look for Google Analytics and the trend also e.g. StackOverflow Questions. Is there an active community to ask for help?
* Changelogs / Development
* Learning to use the tool
* Init and Prerequisites
* Documentation and research
* Coding
* Testing
* Deployment
First search for tools or frameworks which will compare to firebase [firestore]. Form teams of at least three participants and check the steps and describe the chosen tool.
## Couchbase
_"Couchbase is the modern database for enterprise applications.
Couchbase is a distributed document database with a powerful search engine and in-built operational and analytical capabilities. It brings the power of NoSQL to the edge and provides fast, efficient bidirectional synchronization of data between the edge and the cloud.
Find the documentation, samples, and references to help you use Couchbase and build applications."_ [couchbase-doc]
**Team:** Klara Hermann, _Caroline Jethan_, Anne Kreppenhofer, Felix Koch
Couchbase offers severals services and delevoper tools, for example [couchbase-doc]:
+ _Couchbase Capella (DBaaS)_: a fully-managed database as a service offering
+ _Couchbase Server_: distributed document database with all the desired capabilities of a relational database and more; scale-out, key-value store with managed cache for sub-millisecond data operations, purpose-built indexers for efficient queries, and a powerful query engine for executing SQL-like queries
+ _Couchbase Lite_: an embedded, NoSQL JSON Document Style database for mobile apps (able to sync with Couchbase Server)
+ _SDK and Connectors_: SDKs allow applications to access a Couchbase cluster, Connectors enable data exchange with other platforms
+ _CLI and REST APIs_: manage and monitor Couchbase deployment
+ _Couchbase Shell_: interact with Couchbase Server and Cloud
### Tutorials / Intros / Documentation (Felix)
_"The Couchbase Autonomous Operator provides native integration of Couchbase Server with open source Kubernetes and Red Hat OpenShift. It enables you to automate the management of common Couchbase tasks such as the configuration, creation, scaling, and recovery of Couchbase clusters. By reducing the complexity of running a Couchbase cluster, it lets you focus on the desired configuration and not worry about the details of manual deployment and life-cycle management."_ [couchbase-intro]
Documentation contains a Tutorial Section with:
* a _short_ Getting Started with instructions to set up a Couchbase Server ([couchbase-quickinstall]).
* a scripted exploration for the webinterface
* an explanation of the query language
A big *Research* section([couchbase-overview]), that explains in detail how Couchbase works.
The documentation has a feature to warn you, if you are accessing older versions of the documentation and links you to the current version of the page.
### Who is using it? (Anne)
Companies, which are using Chouchbase:
* Sky
* Tesco
* Cisco
* Linkedin
* Tommy Hilfiger
* PayPal
* ComCast
### Community / Help (Anne)
#### Stackoverflow
On Stackoverflow people have asked over 3,500 question and last question is from 21st of January. Of these question there are 1,169 question which do not have a upvoted or accepted answer. [couchbase-stackoverflow]
#### Google Trends

In this graphic we see that ChouchDB was the most popular 2016. But there is still a high demand if we look at the end of the graph.
#### Community
On the Community site of the Couchbase website you will find many links about developer groups (like on github).
##### Github [couchbase-github]
On Github
### Changelogs / Development (Felix)
You can look at the issue tracker on [issues.couchbase.com](https://issues.couchbase.com/secure/Dashboard.jspa)
### Init and Prerequisites (Klara)
#### Couchbase Capella (DBaaS)
_"Capella delivers industry-leading flexibility and performance at scale for enterprise applications, with the best price-performance of any fully managed document database. It’s the easiest and fastest way to begin with Couchbase and eliminate your database management efforts."_ [couchbase-capella]
There is a 30-day free trial for Couchbase Capella [couchbase-trial]. After logging in, you can choose between:
* Couchbase's cloud account with AWS as provider, or
* Your cloud account with AWS or Azure as provider

For this test, Couchbase's cloud account is the better option. The status of my environment can be checkes in "Clusters". There is a beginner tutorial for getting started with Couchbase Capella. [couchbase-getting-started]
After deploying, there is one project with one cluster in it. The cluster has metrics, with will be initialised by a template to show the status of the cluster. Sample data can be imported through the cl
uster at "Tools" > "Import". JSON or CSV ist allowed as import data type. In this test, the Beer sample is used.
The configuration tab shows settings like services, nodes, compute, and disk type. This makes it easy to scale horizontally and vertically.
A bucket is a database within Couchbase. Every data sample is a bucket. By clicking on one, the memory can be changed to allow faster queries.
On the Connection tab, an external connection to the Couchbase cluster can be established.

To use the cluster from the host system, the IP address has to be linked. SDK examples can also be accessed. [couchbase-sdk-examples]
In order to connect an external application to Capella, at least one set of credentials must be defined. For this test, the user can access all Buckets with Read/Write access.
Initalisation and Prerequisites took about 40 minutes, inlucing waiting 5 minutes for the confirmation mail.
There is an option to run the Couchbase Server CE container and WebUI via Docker [couchbase-docker]
### Documentation and Research (Caro)
The documentation [couchbase-doc] can be accessed via a link on the Couchbase website. It is structured by the different services Couchbase offeres. For the Couchbase services Capella and Server, the documentation is structured the same way. Therefore, once you get used to the documentation for one service, you can easily use the documentation of both.
The API documentation can be found under 'Reference'.
With the API of Capella you can
* onboard and offboard users
* manage the lifecycle of a cluster:
* Clouds: List clouds and obtain detailed information about them
* Projects: List, Create and Delete projects
* Clusters: List, Create and Delete clusters (and its buckets and users) and manage access using the Allow List
* get monitoring information for a cluster
How to use the API is explained step by step with pictures.
There is an openapi.yaml file and by importing it into Postman or a similar program, you are provided with exact details of each API.
In the online API documentation is explained what the parameters and return types are, alongside with a brief description.
However, there are no exaples of usage, but they can be found easily in the openapi.yaml.
In general, the documentation is structured very well, providing the user with an overview all the time.
### Coding (Klara)
There are SDKs for the following programming languages:
* Java
* C
* Go
* .NET
* Node.js
* PHP
* Python
Couchbase Capella provides an interactive query tool called the Query Workbench. Using the Query Workbench, you can conveniently explore data, create, edit, run, and save query results. You can also explore the document structures in a bucket — all in a single window. It is accessible under the cluster's Tools > Query workbench menu. [couchbase-queries]
Couchbase allows SQL queries.
The login platform is here [couchbase-sign-in].
This documentation says, that you can only connect to the cloud if you have a supported cloud provider account, which the test trial does not have. [couchbase-cloud-connect].
So the next step is to initialise a docker image and try to connect to it. Therefore this documentation is used. [couchbase-docker]
After over one hour of trying, it was not possible to connect to either of the buckets, cloud-based or docker-based with Java.
### Testing (Caro)
#### Integration Test
Integration Tests are useful to verify that all units work together right.
Couchbase can be tested with Java by using TestContainers. While creating a Couchbase Container, various options can be specified. The program waits until the Container is up and ready.
"*TestContainers is a Java library that supports JUnit tests, providing lightweight, throwaway instances of common databases, Selenium web browsers, or anything else that can run in a Docker container.*" [couchbase-testing]
After that additional back- and frontends can be started. Then the Docker Containers can be linked by creating a LinkedContainer. After this setup, it can be tested with Selenium for example.
#### Unit Test
As for the integation tests, the database has to be started and stopped, for example by the build scripts.
The actual test method defines a new Couchbase Environment. After connecting the cluster and environment, the actual test takes place. For that the usual "assertTrue" or similar methods are used.
For other languages than Java, the procedure is the same, although there is way less information about that.
### Deployment
## CouchDB
_"Apache CouchDB is one of a new breed of database management systems. This topic explains why there’s a need for new systems as well as the motivations behind building CouchDB.
As CouchDB developers, we’re naturally very excited to be using CouchDB. In this topic we’ll share with you the reasons for our enthusiasm. We’ll show you how CouchDB’s schema-free document model is a better fit for common applications, how the built-in query engine is a powerful way to use and process your data, and how CouchDB’s design lends itself to modularization and scalability."_ [couchdb-doc]
**Team:** Christian Proschek, Jonas Trebicki, _Lilly Elgebaly_, Alexander Hristov
__here comes also an overview__ (Lilly)
Before anything, its important to note that Couchdb is an open Source Project. [couchdb-introduction] meaning that anyone can use, and add to Couchdb. This enabled the development of other Frameworks, like pouchdb (which also has an offline-first stance)[pouchdb]
Couchdb is a database, comprised of multiple Documents, couchdb also provides a RESTful HTTP API for editing said Documents, (A document contains Metadata and Fields of variying Datatypes). Ths optimistic (meaning that no fields are stuck in place as edits are happening.)
In case of 2 Clients editing the same Field, the first one (whether actually first, or first processed by the server), is the one being enforced, while the second Client has to look into the now updated Document, and edit that.
Every Client also receives a Snapshot of the Database as they are editing it, so that problems can only arrive in the afformentioned Situation.
Couchdb is also specifically designed to work in bad Situations (which it advertises in its homepage), stating their "offline-first" Viewpoint. A user would be able to (after at least accessing the DB once of course) edit the DB whilst being offline, and even after several hours could sync up with the DB, without many problems.
To get data inside of Documents, Couchdb has a "View model" this allows users to access documents in specific formats (say you want to only select documents where a field is a certain value).
For security, Couchdb has a native "reader access and update validation model" one can expand on. [couchdb-overview]
### Tutorials / Intros / Documentation (Lilly)
First I'd have to say, that the Couchdb Doc, at least at first glance, does a good job explaining the general Architecture of the [couchdb-overview].
Looking up "How to use Couchdb" on google lead to 4000 results, this doesnt say anything about how good those results are, but at least some work is being done in introducing this framework.
The first page I found gave a quick explanation to couchdb, and tells you how to deploy the framework. [couchdb-tutorial], it also gives a quick tutorial on how to use couchdb as a Database. This is a pattern that was followed by
other tutorials, it was often used as a Database and not as a Messaging App.
### Who is using it? (Lilly)
According to hgdata, Couchdb is being used by really big companies like Apple and Samsung. [hgdata-couchdb], however, the Site never mentiones to what extent these Companies use the framework, and also doesnt cite their Sources. Npm does use Couchdb for their npm-registry, though this has been archived. [npm-github]. Overall it seems that Couchdb may have been popular (though even of that I'm unsure) but its popularity is waning.
### Community / Help (Trebicki)
Auf dieser Seite [couchdb-main](https://couchdb.apache.org/) findet man zwei interessante Punkte: "Documentation" und "Guidance"; hier findet man höchst wahrscheinliche Hilfe
#### Dokumentation
Unter Documentation findet man das CouchDB Wiki; bei diesem findet man die Doku verlinkt ([couchdb-doku](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/)); ebenso gibt es ein eigenes GitHub Repo mit der Doku ([couchdb-dokurepo](https://github.com/apache/couchdb-documentation))(die gerendete Version ist auf der vorhin erwähnten Doku Page)
Die Dokumentation behinhaltet zuerst, was neu in CouchDB ist, warum man es verwenden sollte, einen "Technical Overview" und wie CouchDBs Synchronisation funktioniert.
Danach finden sich einige Getting Started Tutorials und dann noch komplette/kompliziertere Referenzdokumente.
#### Community
Unter Guidance findet man einige Links, unter denen man Hilfe finden kann; einen Chat ([couchdb-chat](https://web.libera.chat/#couchdb)), einen StackOverflow Link mit Fragen mit Tag "CouchDB" ([couchdb-stackow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/couchdb)) und die Issue Site des CouchDB Repos ([couchdb-issues](https://github.com/apache/couchdb/issues)).
Als ich dem Chat zum Test beitrat, waren 32 User:Innen online; eine schnelle Antwort auf eine Frage zu bekommen scheint hier nicht unwahrscheinlich. StackOverflow und die Issue Seite auf GitHub sind auch generell nicht schlecht.
Außerdem probierte ich noch Dinge, die vermutlich jeder einmal probiert hat: Auf Google und auf YouTube nach einem Tutorial zu suchen; man findet das offizielle Tutorial mit dem Getting Started, sowie Anleitungen von unseren alten Bekannten Tutorialspoint und javatpoint. Auf YouTube findet man auch einige Erklärungen zu CouchDB.
##### Experience
Das hier war ziemlich unkompliziert; die Möglichkeit zur Hilfe durch einen eigenen Chat war eine positive Überraschung, das sieht man nicht so oft.
### Changelogs / Development (Alex)
Die [Releasenotes](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/whatsnew/index.html) beinhalten eine Liste mit den CouchDB Versionen.
### Init and Prerequisites (Alex)
In der [Apache CouchDB Release 3.2.0](https://buildmedia.readthedocs.org/media/pdf/couchdb/latest/couchdb.pdf#page=621&zoom=100,96,284) Dokumentation werden die einzelne Installationsschritte im fünten Kapitel genau beschrieben.
Hier findet man die [CouchDB System Resource Requirments](https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/install/pre-install.html)
### Documentation and Research (Christian) [couchdb-docs-api]
If we need to get information about the API, we can go to the official documentation. Under [API Reference](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/api/index.html) we can find all the endpoints of the database and their description and usage.
#### API Basics
CouchDB uses HTTP Requests to Communicate between the database and its clients. All in all it makes use of a large variety of HTTP Status codes and HTTP Headers. This way it is ensured, that we can catch an error and see what exactly went wrong.
There is a web interface at `/_utils`!!
#### Server
Getting the information of a server or node is very easy! When a HTTP GET is sent to `/`, you get the information of the server that receives the request and if you want to talk to a specific node `/_node/{node-name}`. To get info of the current connected node, use `_local` for `{node-name}`.
To get all the databases, there is `/_all_dbs`.
#### Databases
With `/{db}/_all_docs` all the documents in a database can be retreived. If a specific document is needed, use `/{db}/{docid}`
#### Other things in the doc
There are many more enpoints that can be used. They can be found in the [API Reference](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/api/index.html) of the documentation.
#### Using the built in Web Interface
If the webinterface at `/_utils` is being user, theres always a button called `{}JSON` on the top right corner. That button shows the content of the current page as a JSON using the *normal* method of retrieving data through the normal endpoints.

##### Experience
The web interface is way, way easier to use. My suggestion is to use the interface and the click the `{}JSON` button to convert the view into the url needed.
#### Getting help from the outside
A quick look at StackOverflow reveils that the tag `couchdb` has 6,023 questions. In comparison, `mysql` has *640,718*, `couchbase` has *3,750*, or `AWS-Datasync` has *22* questions (thats **VERY** low). That statistics shows that it might be a niche DBMS, but is a very popular software in that afformentioned niche. [stackoverflow]
A look at [Google Trends](https://trends.google.at/trends) reveils that fact as well. It seems to be a very popular option compared to its competition. [google-trends]

##### Experience
In my experienc, its relatively easy to get help. There are quite a few StackOverflow questions that might help. On the Stackoverflow website it is also very apparent, that the questions get read and answered. There are questions being posted/answered as recently as yesterday (27.01.2022).
### Coding (Trebicki)
Laut [CouchDBs GitHub Repo](https://github.com/apache/couchdb) ist CouchDB größtenteils in Erlang geschrieben.
In CouchDB selbst schreibt man mit curls bzw. über das Webinterface. (REST Schnittstelle)
Ein paar Beispiele:
- Eine Datenbank erstellen: `curl -X PUT http://admin:password@127.0.0.1:5984/baseball`
- Alle DBs abrufen: `curl -X GET http://admin:password@127.0.0.1:5984/_all_dbs`
Über `http://<Server>:5984/_utils/` kommt man auf Fauxton. Dort kann man mit Clicken und Textfelder befüllen dieselben Dinge tun.
Dokumente in CouchDB haben folgende Struktur:
```
{
"_id": "00a271787f89c0ef2e10e88a0c0001f4",
"type": "movie",
"title": "My Neighbour Totoro",
"year": 1988,
"director": "miyazaki",
"rating": 8.2
}
```
Dieses Dokument habe ich in Fauxton erstellt. In Fauxton hat man auch die Möglichkeit, Queries durchzuführen. Diese haben folgende Form:
```
{
"selector": {
"year": {
"$eq": 1988
}
}
}
```

##### Experience
Ich hoffe, ich habe den Punkt Coding richtig verstanden, sonst war das eigentlich aber auch relativ angenommen. Docker Befehl zusammengesucht, Doku bisschen angesehen und schon konnte man damit arbeiten; das Webinterface ist sehr angenehm zum Arbeiten und man kann schnell Objekte/Dokumente erstellen und Queries machen.
### Testing (Trebicki)
Beim Suchen habe ich dieses NPM Modul gefunden [couchdb-mockcouch](https://chris-l.github.io/mock-couch/). Damit kann man einen CouchDB Server "mocken", also ein Imitat erstellen .
> Ein Mock-Objekt (auch Attrappe, von englisch to mock ‚etwas vortäuschen‘) ist in der Softwareentwicklung ein Programmteil, der zur Durchführung von Modultests als Platzhalter für echte Objekte verwendet wird. Solche Hilfsmittel werden umgangssprachlich auch Mocks genannt
MockCouch kann man für Unit-Tests verwenden.
> Mock Couch is not attempting to fully implement CouchDB, but only the features necessary for unit testing CouchDB based apps.
> Mock Couch will emit events, so you can listen to them to see the result of your test.
Alte Versionen: In der (veralteten) Doku ([couchdb-tutorialexcerpt](https://guide.couchdb.org/draft/tour.html)) fand ich, dass CouchDB ein eingebautes administratives Interface namens Futon hat. Dieses hat eine eingebaute Test Suite:
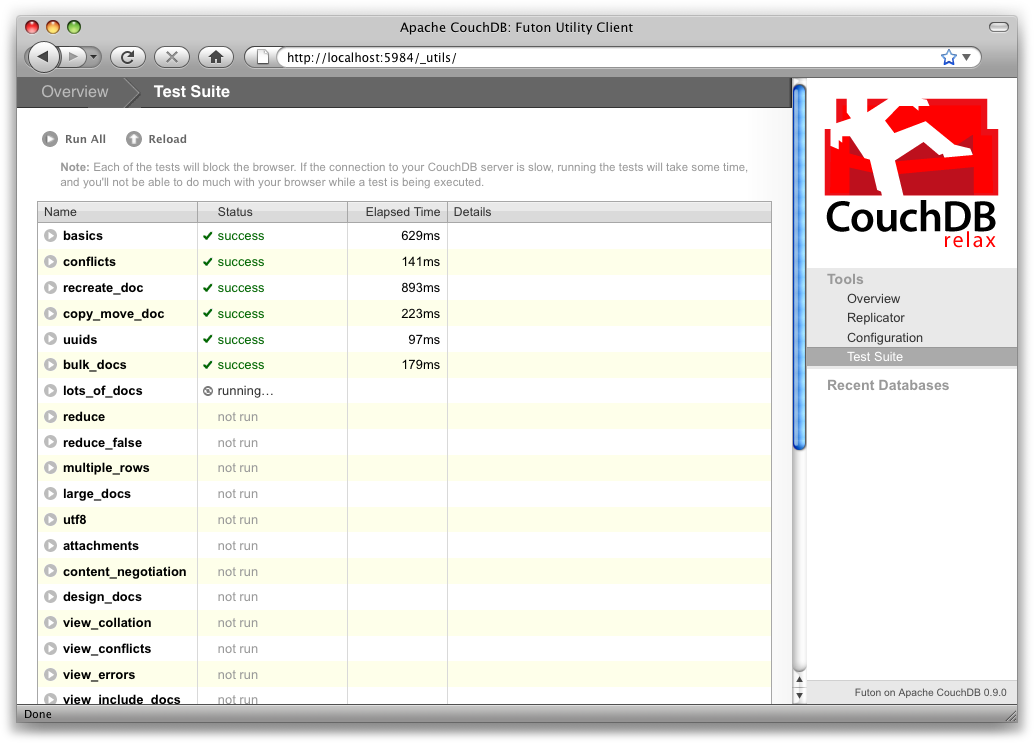
Weil die Test Suite im Browser läuft, testet sie nicht nur die Funktionalität von CouchDB, sondern auch dass die Verbindung vom Browser zu Datenbank richtig funktioniert, was sehr nett zum Diagnostizieren von falsch verhaltenden Proxies oder anderen Middleware ist.
Neue Versionen: CouchDB hat in der neuesten Version ein neues Interface, namens Fauxton. [couchdb-fauxton](https://couchdb.apache.org/fauxton-visual-guide).
Im [Fauxton Repository](https://github.com/apache/couchdb-fauxton/blob/main/tests.md) finden wir eine Tests.md, in welcher die Tests beschrieben werden; Fauxton hat Unit Tests und End-to-End Tests.
##### Experience
Hier war es schon ein bisschen schwerer, Dinge herauszusuchen, ich musste auch von meiner Main Search Engine DuckDuckGo weggehen, um einige dieser Dinge zu finden.
### Deployment (Christian) [couchdb-dockerhub]
CouchDB has an official Image on Dockerhub. The [Dockerhub Image](https://hub.docker.com/_/couchdb/) has over 100 Million Downloads, which suggests the Image is very heavily used. The prerequesits of this trend is that it is very easy to use.

To create an image you can set the username and password with the environmental variables `COUCHDB_USER` and `COUCHDB_PASSWORD`.
Example:
```shell
docker run -p 5984:5984 -e COUCHDB_USER=admin -e COUCHDB_PASSWORD=password --name couchdb -v couchdb:/opt/couchdb/data couchdb:latest
```
#### Experience
War sehr einfach. Kann jedes Kind machen!
## AWS Datasync
*AWS DataSync is a secure, online service that automates and accelerates moving data between on premises and AWS storage services. DataSync can copy data between Network File System (NFS) shares, Server Message Block (SMB) shares, Hadoop Distributed File Systems (HDFS), self-managed object storage, AWS Snowcone, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets, Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file systems, Amazon FSx for Windows File Server file systems, and Amazon FSx for Lustre file systems.* - [aws-doc]
**Team:** Ahmed Öztürk, Moriz Schaffer, Lukas Moser, Matteo Marincek, _Sina Meth_
__here comes also an overview__ (Schaffer)
_"AWS DataSync is a secure online data transfer service that simplifies, automates, and accelerates copying terabytes of data to and from AWS storage services. Easily migrate or replicate large data sets without having to build custom solutions or oversee repetitive tasks. DataSync can copy data between Network File System (NFS) shares, or Server Message Block (SMB) shares, Hadoop Distributed File Systems (HDFS), self-managed object storage, AWS Snowcone, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets, Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file systems, Amazon FSx for Windows File Server file systems, and Amazon FSx for Lustre file systems."_ [aws-features]
These are some of the main use cases for AWS DataSync [aws_user-guide]:
* __Data migration__: _Move active datasets rapidly over the network into Amazon S3, Amazon EFS, FSx for Windows File Server, or FSx for Lustre. DataSync includes automatic encryption and data integrity validation to help make sure that your data arrives securely, intact, and ready to use._
* __Archiving cold data__: _Move cold data stored in on-premises storage directly to durable and secure long-term storage classes such as S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval or S3 Glacier Deep Archive. Doing so can free up on-premises storage capacity and shut down legacy systems._
* __Data protection__: _Move data into any Amazon S3 storage class, choosing the most cost-effective storage class for your needs. You can also send data to Amazon EFS, FSx for Windows File Server, or FSx for Lustre for a standby file system._
* __Data movement for timely in-cloud-processing__: Move data in to or out of AWS for processing when working with systems that generate data on-premises. This approach can speed up critical hybrid cloud workflows across many industries. These include machine learning in the life-sciences industry, video production in media and entertainment, big-data analytics in financial services, and seismic research in the oil and gas industry.
### Tutorials / Intros / Documentation (Schaffer)
_"Getting started with DataSync is easy: Deploy the DataSync agent on premises, specify a file system or storage array using the NFS or SMB protocols, specify the API endpoint for your self-managed object storage, or specify a configuration to connect to HDFS on your Hadoop cluster. Then, select Amazon S3, Amazon EFS, Amazon FSx for Windows File Server, or Amazon FSx for Lustre as your AWS Storage, and start moving data."_[aws-doc]
AWS Datasync offers a large amount of documentation. This includes "getting started" examples as well as complete documentation on the requirements and features of Datasync. Furthermore, topics like security or the AWS CLI are covered. [aws-user-guide]
### Who is using it? (Marincek)
Plenty of companies are using AWS, due to being the first cloud solution on the market. The following companies are listed on AWS' website to use their DataSync subsystem:
- Chan Zuckerberg Biohub
- Formel 1
- Autodesk
### Community / Help (Öztürk)
There is a discussion forum hosted by AWS itself for its users to participate. There are about 68 Threads and 258 messages related to Datasync as of 2022-01-21.
Here is a link to the forum:
* https://forums.aws.amazon.com/forum.jspa?forumID=316
There are also questions regarding Datasync at 'repost.aws'. The frequency of questions being asked is roughly about 7-10 times a year. The views per question are 3-4 on average. So we can't really say it's actively being used.
Here is a link to it:
* https://repost.aws/tags/TAwgolRKhDTKGPCIHXy1zrHA/aws-data-sync
On Stackoverflow we can see, that there are only 22 questions tagged as 'aws-datasync'. The majority of them don't have a single answer nor a single view. So we can conclude that there is no big aws-datasync community.
Here is a link to the questions regarding aws-datasync on stackoverflow:
* https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/aws-datasync
### Changelogs / Development (Marincek)
Updates are logged in the documentation, which itself is updated in their history. [aws-doc-history]
### Init and Prerequisites (Moser)
Prerequisites:
* AWS account needed (billing information required)
Init:
* follow [this tutorial](https://console.aws.amazon.com/datasync/)
* choose a support plan
* log in to the [management console](https://console.aws.amazon.com/console/home?region=us-east-1)
* select the service AWS DataSync
* choose the task "between on-premises storage and AWS"
* download the deploy agent VM(I selected "VMware ESXi")
* I chose the standard public service point because it sounded like I don't have any specific needs for encryption or so on
* now I wait for my VM to set up
* I fail to type in login credentials on the VM. I haven't set up any on this virtual device and using the AWS login does't really seem to make sense
### Documentation and Research (Schaffer)
The documentation can be accessed via the following link:
* [aws-documentation]
After opening the user guide in the documentation, you can open the API reference tab, among others:
_"In addition to using the console, you can use the AWS DataSync API to programmatically configure and manage DataSync and its resources. This section describes the AWS DataSync operations and data types and contains the API Reference documentation for AWS DataSync."_[aws-api-ref]
### Coding (Marincek)
The offical UserGuide for AWS DataSync [aws-userguide] and the documentation both contain a lot of information on how to programm with and for an application using AWS DataSync.
### Testing (Schaffer)
Under the link [aws-testing] two subtopics explaining local testing before connections can be found:
* Testing your agent connection to DataSync endpoints
* Testing connectivity to self-managed storage
The subtopics explain step by step how to set up testing locally.
AWS also offers a form of troubleshooting. This can be found at the link [aws-troubleshooting]. Several errors and their solutions are linked here, as well as further testing options within the documentation.
### Deployment (Öztürk)
In the official aws-documentation to DataSync we can find a variety of methods for deploying a datasync agent.
Here are the listed ones: [aws-deploy-agentseploymenteploymenteploymenteploymenteployment]
* Deployment on VMware
* Deployment on KVM
* Deployment on Hyper-V
* Deploy as an Amazon EC2 instance to access in-cloud file systems
* Deployment on a Snow Family Devices
* Deployment on AWS Outposts
## Resources
* [couchbase-doc] "Couchbase Documentation" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/home/index.html)
* [couchdb-doc] "Why CouchDB?" [online](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/intro/why.html)
* [firestore] "Cloud Firestore" [online](https://firebase.google.com/docs/firestore)
* [aws-doc] "AWS Datasync" [online](https://aws.amazon.com/datasync/)
* [google-trens] "Google Trens | CouchBase vs CouchDB vs DataSync" [online](https://trends.google.at/trends/explore?q=%2Fm%2F03c4_2p,%2Fm%2F0crh5qh,datasync)
* [stackoverflow] "StackOverflow" [online](https://stackoverflow.com/)
### Couchbase
* [couchbase-quickinstall] "Couchbase: Do a Quick Install" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/getting-started/do-a-quick-install.html)
* [couchbase-capella] "Couchbase Capella (DBaaS)" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/cloud/index.html)
* [coubase-stackoverflow] "Questions tagged \[couchbase]" [online] (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/couchbase?tab=Newest)
* [couchbase-getting-started] "Beginning with your Couchbase Capella Free Trial" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/tutorials/dbaas-self-service/index.html)
* [couchbase-overview] "Learn: Overview" [online] (https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/learn/architecture-overview.html)
* [couchbase-sdk-examples] "SDK Examples" [online](https://github.com/couchbaselabs/sdk-examples)
* [couchbase-queries] "Run Your First Queries" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/tutorials/dbaas-self-service/run-first-queries.html)
* [couchbase-github] "Couchbase" [online](https://github.com/couchbase)
* [couchbase-docker] "Couchbase Server CE Docker Container - Example Manual Configuration" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/tutorials/quick-start/quickstart-docker-image-manual-cb65.html)
* [couchbase-sign-in] "Couchbase Capella - Sign In" [online](https://cloud.couchbase.com/login)
* [couchbase-testing] "Unit and Integration Tests with Couchbase and Docker Containers" [online](https://blog.couchbase.com/unit-integration-tests-couchbase-docker-container/)
* [couchbase-cloud-connect] "Connect and Manage Clouds
- Connect a Cloud" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/cloud/clouds/manage-clouds.html#connect-cloud)
### Couchdb
* [couchdb-dockerhub] "CouchDB Docker Hub Page" [online](https://hub.docker.com/_/couchdb)
* [couchdb-docs-api] "CouchDB Documentation | API Reference" [online](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/api/index.html)
* https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/whatsnew/index.html
* [couchdb-main] "CouchDB Main Page" [online] (https://couchdb.apache.org/)
* [couchdb-doku] "CouchDB Documentation" [online] (https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/)
* [couchdb-dokurepo] "DouchDB Documentation Repository" [online] (https://github.com/apache/couchdb-documentation)
* [couchdb-chat] "CouchDB Chat" [online] (https://web.libera.chat/#couchdb)
* [couchdb-stackow] "StackOverflow Questions tagged with CouchDB" [online] (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/couchdb)
* [couchdb-issues] "CouchDB Repo Issues Page" [online] (https://github.com/apache/couchdb/issues)
* [coudchdb-overview] "Technical Overview" https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/intro/overview.html
* [couchdb-mockcouch] "MockCouch for Testing CouchDB" [online] (https://chris-l.github.io/mock-couch/)
* [hgdata-couchdb] "Companies Currently Using CouchDB" https://discovery.hgdata.com/product/couchdb
* [mocking] "Wikipedia Artikel zu Mocking" [online] (https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mock-Objekt)
* [npm-github] "npm-registry-couchapp" [online](https://github.com/npm/npm-registry-couchapp)
* [couchdb-introduction] "Couchdb Homepage" [online](https://couchdb.apache.org/)
* [couchdb-tutorialexcerpt] "CouchDB Tutorial/Tour" [online] (https://guide.couchdb.org/draft/tour.html)
* [couchdb-changelogs] "Couchdb Release Notes" [online](https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/whatsnew/index.html)
* [couchdb-init] "Apache CouchDB Release 3.2.0" [online](https://buildmedia.readthedocs.org/media/pdf/couchdb/latest/couchdb.pdf#page=621&zoom=100,96,284)
* [couchdb-prerequisites] "CouchDB System Resource Requirments" [online](https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/install/pre-install.html)
* [couchdb-fauxton] "CouchDB Fauxton Interface" [online] (https://couchdb.apache.org/fauxton-visual-guide)
* [pouchdb] "homepage of pouchdb" [online](https://pouchdb.com/)
* [couchdb-tutorial] "First page introducing couchdb" [online](https://hyperledger-fabric.readthedocs.io/en/release-2.2/couchdb_tutorial.html)
* [couchdb-fauxton-testing] "Tests.md in the couchdb-fauxton Repo" [online] (https://github.com/apache/couchdb-fauxton/blob/main/tests.md)
* [couchdb-github] "CouchDB Main Github Repo" [online] (https://github.com/apache/couchdb)
### AWS Datasync
* [aws-user-guide] "AWS UserGuide" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/what-is-datasync.html)
* [aws-features] "AWS DataSync features" [online](https://aws.amazon.com/datasync/features/)
* [aws-doc-history] "AWS Update History" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/doc-history.html)
* [aws-documentation] "AWS DataSync Documentation" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/?id=docs_gateway)
* [aws-api-ref] "API Reference" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/API_Reference.html)
* [aws-testing] "Working with your agent on the local console" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/local-console-vm.html#self-managed-storage-connectivity)
* [aws-deploy-agents] "Deploy an AWS DataSync agent - AWS DataSync" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/deploy-agents.html)
* [aws-userguide] "AWS UserGuide" - [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/what-is-datasync.html)
* [aws-troubleshooting] "Troubleshooting AWS DataSync issues" [online](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/troubleshooting-datasync.html)