# Week 5
## Day 1 - Probability
### Weekly project presentation
- Presentation of Weekly Project
### Machine Learning Introduction
**What is Machine Learning?**
- Build a mathematical model based on sample data, known as "training data"
- Make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so
- Can spot patterns and make predictions about future events
--> Because this is prediction, machine learning not usually guardrantee 100$ accuracy but machine learning can be much more flexible than traddional programing (like english voice recognization of non-native english speakers)
**Applications of machine learning&**
- Voice Recognition
- Predicting stock market price, fraudulent transactions (e-commerce or banking)
- Recommendation System
- Computer Vision
**Type of Machine Learning**
<img src="https://i.imgur.com/U3SAhRi.png" width="1000px"/>
<br/>
- Supervissed Machine Learning:
-- ML model that work with labeled data
-- The learned model can make predictions about unseen data
-- “Supervised”: the label/output of your training data is already known
- Unsupervised Machine Learning
-- ML model that work with unlabeled data
-- Can work well with clustering problems
**Supervised Machine Learning**
The training data comes in pairs on $(x, y)$, where $x \in R^n$ is the input instance and y is label. The entire training data is:
$$
D = \{(x^{(1)}, y^{(1)}), \dots ,(x^{(m)}, y^{(m)})\} \subseteq R^n \times C
$$
where:
* $R^n$ is the n-dimensional feature space
* $x^{(i)}$ is the input vector of the $i^{th}$ sample
* $y^{(i)}$ is the label of the $i^{th}$ sample
* $C$ is the label space
* $m$ is the number of samples in $D$
**Machine Learning Process**
<img src="https://i.imgur.com/nHOsIXv.png" width="1000px"/>
### Hypothesis classes and No Free Lunch
Before you can find a function h , we must specify what type of function it is that we are looking for. It could be a neural network, a decision tree, or many other types of classifiers. The set of possible functions is called hypothesis class H
The **[No Free Lunch Theorem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/No_free_lunch_theorem)** states that every successful machine learning algorithm has to make assumptions about the dataset/distribution $P$. For example, Linear Regression has to make assumption that there is a linear relationship between dependent and independent variables. This also means that there is no perfect algorithm for all problems.
### Loss Function
A loss function evaluate the model on our training set to tells us how bad it is. The higher the loss, the worst it is. A loss of zero means it makes perfect predictions. By trying to minimize loss, we can get the best model.
### Overfitting and Underfitting
The central challenge in machine learning is that **the model must perform well on new, previously unseen input**.
To do this, when developing ML model, we usually split our dataset into 3 set: Train, Validation and Test
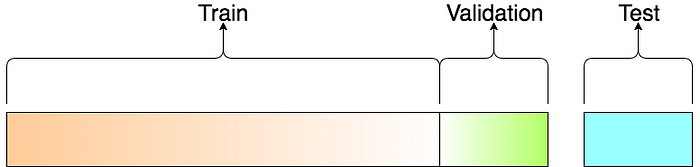
- Overfitting happen when model perform very well on training dataset but poorly on test set. It mean that our model tried to memorize the training dataset instead of making prediction.
- Underfitting happen when model can not perform well on training dataset.
### Basic Probability
Probability: **quantifying the uncertainty**.
**Probability distribution function:** Function that measures the probability that a particular outcome or set of outcomes will occur.
**The sample space** $\Omega$ is a fixed set of all possible outcomes. **The probability** $P(A)$ measures the probability that the event $A$ will occur. $P(A)$ should be > 0 and < 1.
**Random variable** X is a function that assigns a real number to each outcome in the probability space.
- Discrete random variable: X can only takes on a set of finite values
- Continuous random variable: X takes on a infinite number of possible values
**Expected value:** sum of probability * values
**Distributions**
Discrete distribution: Bernoulli and Binomial
Continuous distribution: Uniform and Normal
**Central limit theorem**
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) states that the sample mean of a sufficiently large number of independent random variables is approximately normally distributed. The larger the sample, the better the approximation.
## Day 2 - Linear Algebra
### Vector
A vector represents the magnitude and direction of potential change to a point.
### Vector Similarity
**Vector Operation:** Scalar multiplication and Addition
**Dot Product**
* Dot Product of Vectors --> Bigger Number, more similarity. Smaller number, less similarity. Can only determine similarity, cannot tell whether the similarity is big or small
**Cosin Similarity**
* Cosin Similarity, the value ranging from 1 (2 vector with exactly the same magnitude) and -1 (2 vector with opposit magnitude). Can be used to compare.
* Two vector with 90 degree angle will have cosin = 0
### Matrix
A matrix is a two-dimensional rectangular array of numbers
For a matrix with **m rows and n columns**, we describe the dimensions of a matrix as **m by n** (m x n), and it belongs to $R^{mxn}$
**Matrix Operation**
- **Broadcasting:** the matrix of the smaller shape is expanded to match the matrix of the bigger shape. It is nnly when shapes are **compatible** when trying to do an elementwise operation. (m1 x n) * (n x m2)
- Matrix and scalar: we can multiply a scalar number with matrix
- **Matrix multiplication**: In order to multiply, the number of columns in the first matrix must equal the number of rows in the second
--> The product of an M x N matrix and an N x K matrix is an M x K matrix.
For matrix multiplication, using '@' is prefered than np.dot
- Matrix transpose: We often need to change the dimensions of our matrix for operations like matrix multiplication. Just like in excel, to transpose a matrix there are two steps:
-- Rotate the matrix 90°
-- Reverse the order of elements in each row (e.g. [a b c] becomes [c b a
### Movie Recommendation
Matrix of Movie Genres and Movies represented by 2D vectors.
Each user has a rating represented by a constant number for each movies.
3 Dimension: Movie, User and Feature (Genre/Category):
* Movie-Feature Table: Listing which category a movie is belong to
* User-Movie Table: Listing rating of each user for a movie
* User-Feature Table: Listing Average Rating of Users to each Features (Genre). It is generated by doing dot product between 2 above tables.
Final movie recommendation for each user will be generated by dotproduct between User-Feature Table and Feature-Movie table
But this one is very old techniques, big company like Netflix are no longer use it anymore
**Collaborative Filtering** for further reading
### Gradient Descent
Minimizing the loss function automatically (training), while lower the loss function will make better algorithm
Learning rate: how fast you should take a step to update the x.
Big learning rate: updating a big jump for x -> overshoot the global minimum.
## Day 3 - Linear Regression
**Linear Regression:**
- Supervised machine learning algorithm --> need labeled input data
- solves a **regression** problem.
- The value that our model predicts y is called $\hat{y}$, which is defined as:
$$
\hat{y} = w^Tx + b
$$
--> Main goal is to find the best line (hyperplane) that can minimize the loss function between out dependent and independent variable ( **Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Linear Regression**)
### Loss Function
Mean Square Error will be used as loss function.
Ther main goal of linear regression is to minimize loss function. The loss function has its own curve and its own derivatives. So by observing the slope of this curve tells us the direction we should update our weights to make the model more accurate! --> Gradient Descent
### Gradient Descent
To minimize MSE we need to calculate the gradient of our loss function with respect to our weight and bias

Summary of Gradient Descent. Through the process of trail and error, machine continiously making iteration to update w, b to obtain optimal loss.

**Multiple linear regression example using sklearn and from scratch**
## Day 4 - Logistic Regression
**Introduction**
* Classification Problems - To determine whether a event is belong to category
* Regression Problems - Predict a number with unlimited range of value
--> Logistic Regression --> Solving classification problems
**The Hyperplane**
A hyperplane is a subspace of its ambient space, and defined as:
$$
H = \{x: w^Tx + b = 0 \}
$$
It is a vector that served as a decision boundary to classify X into 2 group of value.

**Confusion Matrix**
* Type 1 error is also known as False Positive, or FP (predict Positive, but actual label is Negative)
* Type 2 error is also known as False Negative, or FN (predict Negative, but actual label is Positive)

Accuray may not be good indicator for unbalanced dataset (like only 5% of dataset get negative value).
Example Application:
* High Recall/Sensitivity Rate: minimize Type 2 error, Covid detectection test.
* High Precision Rate: minimize Type 1 error, credit approval evaluation.
# Day 5 - Sentiment Analysis
## Twitter Sentiment Analysis with NLP
Preprocessing data:
- Bag of word: create a list of unique words
- CountVectorizer: construct a feature vector that contain the frequency of each word in a tweets
- TfidfVectorizer: term frequency-inverse document frequency --> penalize common word since they are not relevant
- Remove stop_words: word that common like (he, she, and, or, to, .etc)
- Remove special characters
- Stemming: grouping word by similarity (Ving vs past-tense, loved vs loving)
Train model:
- Fit in scikit learn
- Construct pipeline
Work on weekly project