# Leetcode刷題學習筆記 -- Time/Space Complexity
## Introduction
{%youtube D6xkbGLQesk %}

## [Input Sive V.S. Time Complexity](https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/sp/input-size-v-s-time-complexity/)
從input size來推測只少要用什麼演算法。
{%youtube eG99FDBeuJo %}
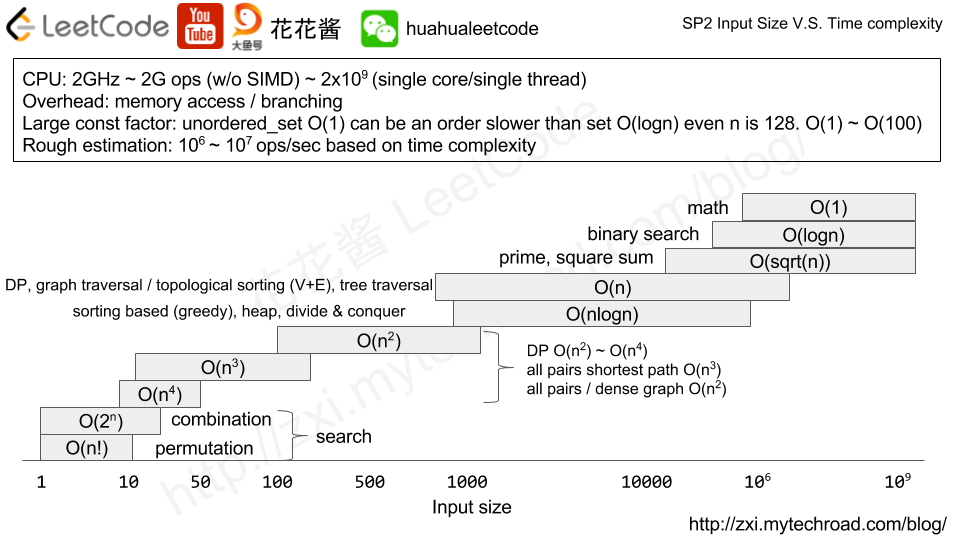
+ < 10: $O(n!)$ permutation
+ < 15: $O(2^n)$ combination
+ < 50: $O(n^4)$ DP
+ < 200: $O(n^3)$ DP, all pairs shortest path
+ < $10^3$: $O(n^2)$ DP, all pairs, dense graph
+ < $10^6$: $O(nlogn)$, sorting-based (greedy), heap, divide & conquer
+ < $10^6$: $O(n)$, DP, graph traversal / topological sorting (V+E), tree traversal
+ < INT_MAX: $O(sqrt(n))$, prime, square sum
+ < INT_MAX: $O(logn)$, binary search
+ < INT_MAX: $O(1)$ Math
## C++ STL
ref : https://alyssaq.github.io/stl-complexities/
ref : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/set-vs-map-c-stl/
ref : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/map-vs-unordered_map-c/
>set and map in STL are similar in the sense that they both use ==Red Black Tree (A self balancing BST).== Note that the time complexities of search, insert and delete are O(Log n) + Rebalance.
> unordered_map/unordered_map implmented by ==Hash Table==
> 因為是hash Table,所以time complexity皆為 $O(1)$, 但是考慮碰撞的問題所以worst cast為 $O(N)$ (全部數的hash值都為同一個)
N = Container中的element數量。
| Method | vector | deque | list | note |
| ---------------------------------- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------------------------------- |
| size()</br>empty()</br>capacity() | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | |
| resize() | $O(N)$ | $O(N)$ | $O(N)$ | 把舊的一個一個搬到新的空間 |
| front()</br>back()</br>operator[i] | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | map找出index i和find()一樣 |
| push_back()</br>pop_back() | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | |
| push_front()</br>pop_front() | | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | vector不能操作front |
| splice(iter, list &, inIter) | | | $O(1)$ | 對list來說iter等於知道了address |
| count()</br>find()</br> | | | | 因為是RB-tree所以是$O(logN)$ |
| insert(iter, val)</br>erase(iter) | $O(N)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | |
| Method | set | map | hash table</br>unordered_map</br>unordered_set | note |
| --------------------------------- | --------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------- |
| size()</br>empty()</br>capacity() | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | |
| count()</br>find()</br> | $O(logN)$ | $O(logN)$ | $O(1)$ | 因為是RB-tree所以是$O(logN)$ |
| insert(val)</br>erase(val) | $O(logN)$ | $O(logN)$ | $O(1)$ | |
| insert(iter, val)</br>erase(iter) | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | |
ref : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/analysis-of-time-and-space-complexity-of-stl-containers/
| Method | Stack | queue | priority_queue | note |
| ------ | ----- | ----- | -------------- | --- |
| size()</br>empty() | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | $O(1)$ | |
| top() | $O(1)$ | | $O(1)$||
| front()</br>back()| | $O(1)$| |
| push()</br>pop()|$O(1)$|$O(1)$|$O(logN)$||
| method | time complexity |
| ------ | --------------- |
| sort() | $O(NlogN)$ |
| lower_bound()</br>upper_bound()|$O(logN)$|
## Sorting Algorithm
ref : [Time Complexities of all Sorting Algorithms](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/time-complexities-of-all-sorting-algorithms/)
ref : [Sorting Algorithm Summary](https://leetcode.com/explore/learn/card/sorting/696/summary-and-conclusion/4440/)
| | Best | Average | Worst | Space | stability |
| -------------- | ---------- | ---------- | ------------ | --------- | --- |
| Selection Sort | $O(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(1)$ | non-stable |
| Bubble Sort | $O(N)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(1)$ | stable |
| Insertion Sort | $O(N)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(1)$ | stable |
| Heap Sort | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(1)$ |non-stable |
| Quick Sort | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(NlogN)$ | ==$O(N^2)$== | $O(logN)$ | |
| Merge Sort | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(NlogN)$ | $O(N)$ | |
| Bucket Sort | $O(N+K)$ | $O(N+K)$ | ==$O(N^2)$== | $O(N)$ | stable |
| Radix Sort | $O(W(N+K))$ | $O(W(N+K))$ | $O(W(N+K))$ | $O(N+K)$ | stable |
| Count Sort | $O(N+K)$ | $O(N+K)$ | $O(N+K)$ | $O(K)$ | stable |
###### tags: `leetcode` `刷題`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet