# kernel study -- list_head
1. [内核基础设施——list_head结构解析](http://linux.laoqinren.net/kernel/list/)
2. [Linux鏈結串列struct list_head 研究](https://myao0730.blogspot.com/2016/12/linux.html)
因為在任意的sturct中加入singly或是doubly linked list是個很常見的架構。但是每個struct結構都不同,很難有同一的API。
==kernel定義了一個list_head,可以放在任意的struct裡面。定義了一些API來操作list_head。重點就是針對list_head做操作。==
## list_head
struct list_head為doubly linked-list。
```c=
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
```
==必須使用一個list_head來當dummy head,因為list_for_each才會work。==
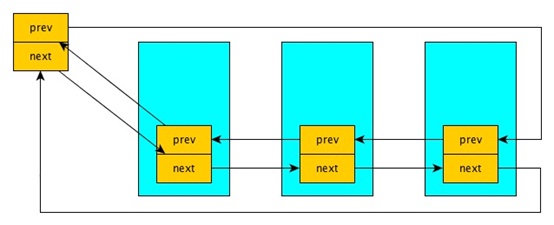
### Declare and initialize
```c=
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
```
## list_add/list_add_tail
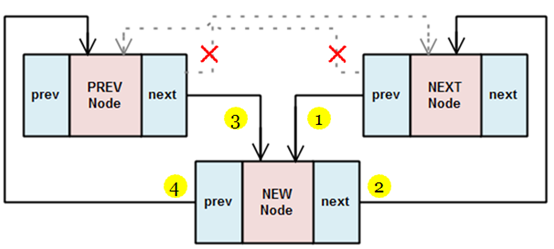
+ list_add(new, head) : 把new加到head的後面,因為head常常為dummy head所以等於是把new加到list的開頭。
+ list_add_tail(new, head) : 把new加到head的前面,因為head常常為dummy head所以等於是把new加到list的最後。
```c
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head);
```
==這個圖表示執行__list_add的結果。把new插在prev和next的中間。==
## list_del/list_del_init
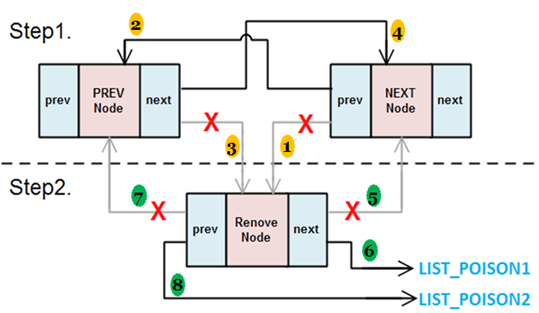
把這個節點entry從list中拿掉。但是只是鏈結斷開,如果有allocate記憶體必須自己free。list_del_init是斷開後,連entry的鏈結也斷開。
```c
void list_del(struct list_head *entry);
void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
```
其中斷開的node的prev和next會被指向LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2。這兩個定義如下。==以往都是指向NULL但是這邊是指向一個non-NULL但是存取它會發生page faults.==
```c=
/*
* These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults
* under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses
* non-initialized list entries.
*/
#define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100)
#define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200)
```
## list_move/list_move_tail
把list從原本的鏈結串上面搬到另一個頭或是尾。
```c
void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head);
void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
```
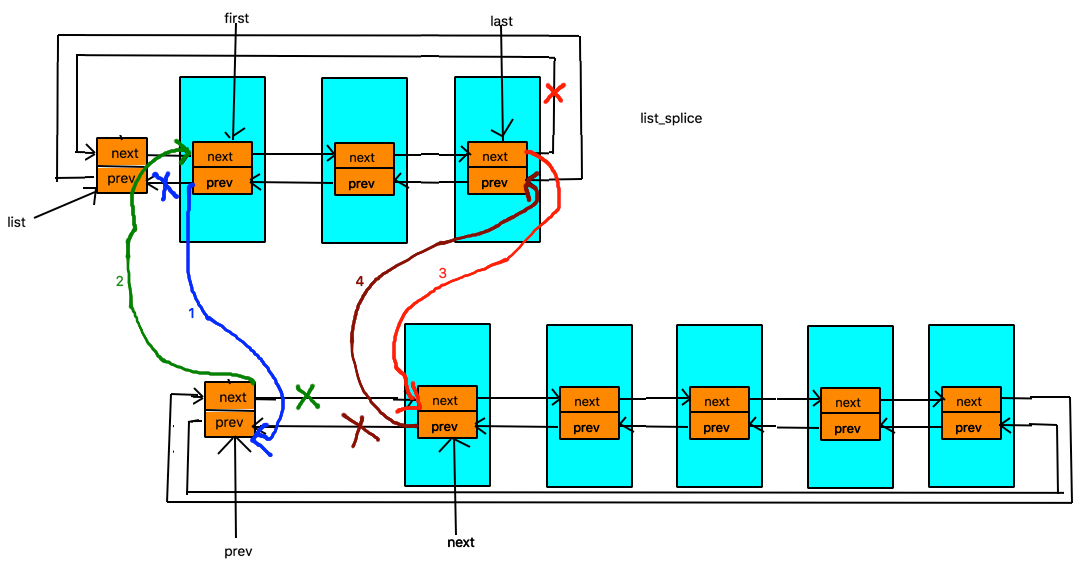
## list_splice/list_splice_init
把list的內容全部接到head的前面,init版再把list初始化。
```c
void list_splice(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head);
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
```
## list_entry
從struct list_head轉換到存放這個list_head的struct。
```c=
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t)&((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
```
## list_for_each/list_for_each_prev/list_for_each_safe
順著或逆著走訪這個linked list。
其中pos為目前走到entry,head為list的dummy head。
**由程式碼可以看出必須要有一個dummy head不然會少走一個entry。**
```c
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->prev; prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head); pos = pos->prev)
```
如果使用list_for_each或是list_for_each_prev來del或是move節點會產生問題,因為pos的關係會被你切斷,導致pos = pos->next會找不到下一個節點。所以必須使用list_for_each_safe來刪除或是移動節點。
```c
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->next)
```
==這邊會先把下一個節點存在n,for loop之後再把下一個node指向n。==
## list_for_each_entry/list_for_each_entry_safe
## list_for_each_entry_reverse/list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse
走訪整個linked list但是取出list_head所在的struct(entry)來使用。
pos : 每次取出type \*的pointer。
head : 指向list_head的dummy header。
member : entry中list_head的名稱。
```c
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop counter.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member)
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member)
```
## list_for_each_entry_continue/list_for_each_entry_safe_continue
從給定的entry pos的下一個開始,繼續走訪這個linked list。
```c=
/**
* list_for_each_entry_continue - iterate over list of given type
* continuing after existing point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop counter.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
```
###### tags: `linux2021`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet