# Leetcode刷題學習筆記--Two Pointers
## Introduction
### 使用two pointers在sorted array
在sorted array中尋找兩個值的和。
```cpp
vector<int> nums{1, 2, 4, 5, 7};
// 所有可能認兩個element的和
// 2,3,4,5,6,6,7,8,8,9,9,10,11,12,14
// 從最左邊和最右邊開始
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
// {1}, 2, 4, 5, [7],就是選中所以組合的中間值
// 2,3,4,5,6,6,7,8,[8],9,9,10,11,12,14
// case 1如果left++,就是往比較大的值移動
// 2,3,4,5,6,6,7,8,8,[9],9,10,11,12,14
// case 2如果right--,就是往比較小的值移動
// 2,3,4,5,6,[6],7,8,8,9,9,10,11,12,14
// 所以靠移動left, right就可以快速找到任何想要的two sum
while(left <= right) // 因為left和right可以一樣,使用等於
{
int sum = nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == target) return true;
else if(sum > target) --right;
else ++left;
}
return false;
```
## Problems
### [977. Squares of a Sorted Array(Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/)
給一個遞增的array,輸出每個數字平方的遞增array。
使用兩個pointer,一個指向開頭,一個指向結尾,==因為這是一個遞增array,平方後的最大值只會出現在頭尾兩端==。
```cpp=
vector<int> sortedSquares(vector<int>& nums) {
auto n = nums.size();
int i = 0, j = n - 1, k = n - 1;
vector<int> ret(n);
while(j > i) {
if(abs(nums[i]) > abs(nums[j])) {
ret[k--] = nums[i] * nums[i];
i++;
} else {
ret[k--] = nums[j] * nums[j];
j--;
}
}
ret[0] = nums[i] * nums[i];
return ret;
}
```
### [922. Sort Array By Parity II(Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-array-by-parity-ii/)
將偶數的index放偶數,把奇數的index放奇數。
>一樣使用兩個pointers來排列。一個指向偶數index,一個指向奇數index,如果偶數index不是偶數,奇數index不是奇數就進行交換。
```cpp=
vector<int> sortArrayByParityII(vector<int>& nums) {
auto n = nums.size();
int i = 0, j = 1;
while(i < n && j < n) {
for(;i < n && nums[i] % 2 == 0; i+= 2);
for(;j < n && nums[j] % 2 == 1; j+= 2);
if(i >= n || j >= n) break;
else swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
return nums;
}
```
### [15. 3Sum(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum/)
這是一題經典題。給你一個int的array nums找出,nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]的和為零。其中i<j<k。也就是i,j,和k不相等。
解題思路:
> 1. 先把array排序。因為這樣使用two pointer來尋找會比較有效率。
> 2. 固定一個數字nums[i],則題目變為[two sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/),nums[j] + nums[k] = -nums[i]
> 3. 最後使用two pointer來找解答。
```cpp=
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
if(nums.empty() || nums.front() > 0 || nums.back() < 0) return {};
auto nsize = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> res;
for(int k = 0; k < nsize; ++k) {
if(nums[k] > 0) break; // 因為排序過,後面數值皆為正
int target = 0 - nums[k];
int i = k + 1; // 從k的下一個
int j = nsize - 1;// 和從最後面找起
while(i < j) {
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
res.push_back({nums[k], nums[i], nums[j]});
// 跳過重複的數值
while (i < j && nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) ++i;
while (i < j && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) --j;
++i;
--j;
} else if(nums[i] + nums[j] > target) {
// 因為和比較大,所以最大值減少
--j;
} else {
// 因為和比較小,所以最小值增加
++i;
}
}
}
return res;
}
```
### [18. 4Sum(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/4sum/)
和3sum類似,這次改成4sum,並且不可以有重複的答案。
> 1. 一樣用左右pointer分別來逼近答案。
> 2. 遇到一樣的數字則跳過.
```cpp=
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> rtn;
auto n = nums.size();
if(n < 3) return {};
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i = 0; i < n - 3; ++i) {
// i 為第二個以後,遇到一樣的則跳過
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
for(int j = i + 1; j < n - 2; ++j) {
// j為i + 2以後,遇到一樣的則跳過
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue;
int left = j + 1, right = n - 1;
while(left < right) {
long sum = (long)nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == target) {
rtn.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]});
// 跳過下一個一樣的數字
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
left++;
right--;
} else if(sum < target)
left++;
else
right--;
}
}
}
return rtn;
}
```
### [986. Interval List Intersections(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/interval-list-intersections/)
給定兩個數列vector<vector<int>> firstList和secondList,求出兩個數列的交集。
例如:
Input:
+ firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]],
+ secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output:
+ [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
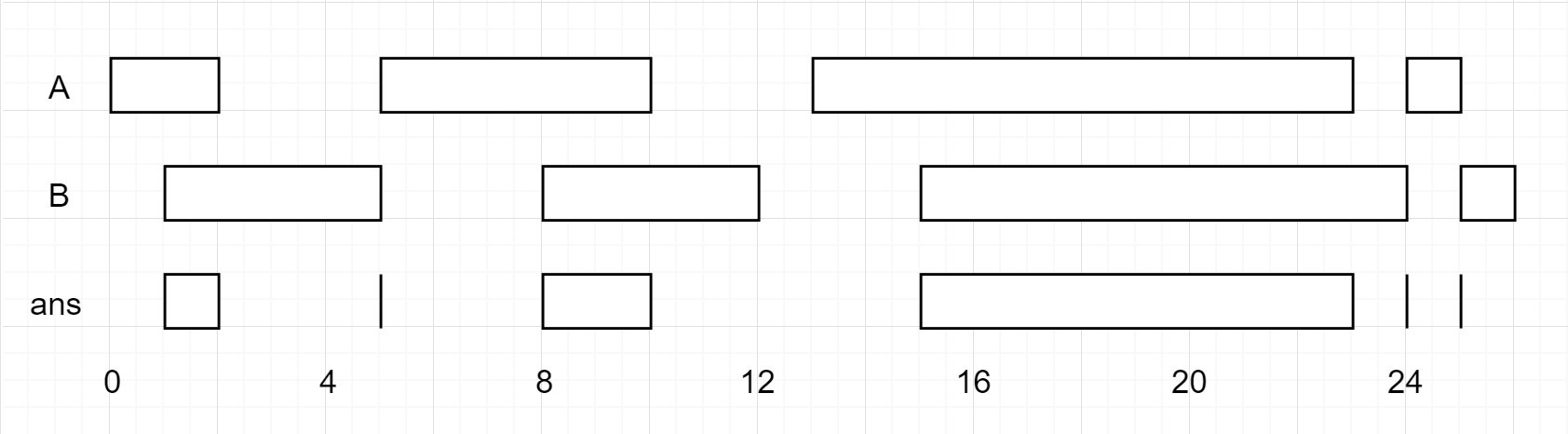
解題思路
> 1. 列出所有的關係。
> 2. case 1 : secondList[j][start] 都在 firstList[i][start] 前面。
> 3. case 2 : secondList[j][start] 都在 firstList[i]中間。
> 4. case 3 : secondList[j][start] 都在 firstList[i][end] 後面。
> 5. 交集 = {max(firstList[i][start], secondList[j][start]),
> min(firstList[i][end], secondList[j][end])}
case 1 :

case 2 :

case 3 :

```cpp=
class Solution {
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& firstList,
vector<vector<int>>& secondList) {
auto L1 = firstList.size();
auto L2 = secondList.size();
// special case
if(L1 == 0 || L2 == 0) return {};
vector<vector<int>> rtn;
int i{0}, j{0};
while(i < L1 && j < L2) {
// case 1-1
if(firstList[i][start] > secondList[j][end])
j++;
// case 3-1
else if(secondList[j][start] > firstList[i][end])
i++;
else {
rtn.push_back({max(firstList[i][start], secondList[j][start])
,min(firstList[i][end], secondList[j][end])});
// case 1-2, 1-3, 2-1
if(firstList[i][end] > secondList[j][end])
j++;
// case 1-5, 2-3
else if(secondList[j][end] > firstList[i][end])
i++;
// case 1-4, 2-2
else {
i++;
j++;
}
}
}
return rtn;
}
};
```
### [11. Container With Most Water(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/container-with-most-water/)
給你一個數列,求出任兩個值中間可以儲存的水是最大值。
> 1. 因為最大的寬(right - left)是最左和最右的點{height[0], height[n - 1]}。
> 2. 下一個寬(right - left -1)有兩個可能,{height[0], height[n - 2]}和{height[1], height[n - 1]}。
> 3. 短邊往中間前進,可以得到最好的結果。
```cpp=
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int rtn = -1;
int left = 0, right = height.size() - 1;
do{
rtn = max(rtn, min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left));
height[left] < height[right] ? left++ : right--;
} while(left < right);
return rtn;
}
```
### [75. Sort Colors(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-colors/)
給你一個vector<int> nums,其中數值只有0, 1, 2。照由小大到大排序。
> 1. 這一題可以有很多解法。最簡單就是統計0, 1, 2出現的次數,然後依序寫回nums。
> 2. 另一種使用two pointers,一個指向red(0)應該出現的位置,一個指向blue(2)應該出現的位置。另外使用另一個指標i來看是否需要交換位置。

```cpp=
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
auto n = nums.size();
if(n == 1) return;
int red = 0, blue = n - 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= blue;) {
if(nums[i] == 0)
swap(nums[i++], nums[red++]);
// i的位置不動,因為可能交換了0/1過來,需要重新判斷
else if(nums[i] == 2)
swap(nums[i], nums[blue--]);
else
i++;
}
}
```
### [941. Valid Mountain Array(Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-mountain-array/)
給你一個vector<int>,試問這個是不是moutain array。
moutain array的定義是指存在一個top(i),使得左邊的數和右邊的數都小於top。
> 1. 使用two pointer從左右邊前進。
> 2. 如果兩個pointer相遇在非開始結尾的地方,就是motain array。
```cpp=
bool validMountainArray(vector<int>& arr) {
auto n = arr.size();
if(n <= 2) return false;
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
while(left < n && arr[left] < arr[left + 1]) left++;
while(right > 0 && arr[right] < arr[right - 1]) right--;
if(left == 0 || left == n - 1)
return false;
else
return left == right;
}
```
### [556. Next Greater Element III](https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-iii/)
找出比n還大的下一個最小的排列數。
```cpp
class Solution {
// 沒有答案的數字為 54321 依序遞減的數字,因為這樣最大
// 例如 : (3)54321, 前面多了一個3
// 從後面尋找比3還大的數,就會找到4
// 把兩個數對調後, (4)53321
// 因為後面是遞增數列,必須改成遞減才是最小的數
// 所以變成 (4)12335
bool nextGreaterElement(string& s) {
int sz = s.length();
// 從後面開始尋找突然變小的數
int i = sz - 2;
while(i >= 0 && s[i] >= s[i + 1]) --i;
if(i < 0) return false; // 找不到變小的數
// 從後面找比這個數還大的數
int j = sz - 1;
while(j > i && s[j] <= s[i]) --j;
swap(s[i], s[j]); // 對調
reverse(s.begin() + i + 1, s.end()); // 後面的數改成遞增,這樣才是最小的
return true;
}
public:
int nextGreaterElement(int n) {
string s = to_string(n);
if(s.length() == 1) return -1;
if(nextGreaterElement(s)) {
long long val = stoll(s);
return val > INT_MAX || val == n ? -1 : val;
} else
return -1;
}
};
```
### [1695. Maximum Erasure Value(Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-erasure-value/)
找出subarray的和為最大,並且subarray中的element不重複。
> 1. 因為subarray為連續的所以使用two-pointer。
> 2. 使用一個vector來記錄是否有重複的element。
> 3. 當有重複的element(val[nums[right]] > 1),則把left往前推進直到條件式消失。
```cpp=
int maximumUniqueSubarray(vector<int>& nums) {
int sz = nums.size();
if(sz == 1) return nums[0];
vector<int> val(1e4 + 1);
int maxans = 0, sum = 0, left = 0, right = 0;
for(; right < sz; ++right) {
sum += nums[right];
val[nums[right]]++;
while(val[nums[right]] > 1) {
sum -= nums[left];
val[nums[left++]]--;
}
maxans = max(maxans, sum);
}
return maxans;
}
```
### [838. Push Dominoes](https://leetcode.com/problems/push-dominoes/)
給你一個dominoes,和同時會從幾個地方往左或是右邊推,求最後的狀態。
> 一開始想要用queue來統計狀態轉移,不過好像很麻煩
> 當沒什麼頭緒的時候,應該先分析有幾種狀況。
> 1. L...L 或是 R...R 也就是兩邊都是一樣,這樣中間也一定是一樣。
> 2. L...R 往兩邊倒,中間不會影響。
> 3. R...L 往中間倒,則需知道中間'.'的個數是否為奇數,因為奇數的話中間還是'.',兩邊各為R和L。
> **前後加上'L' 和 'R'可以讓程式不用判斷邊界條件**。
```cpp
string pushDominoes(string dominoes) {
string rtn{""};
string d = 'L' + dominoes + 'R';
for(int i = 0, j = 1; j < d.size(); ++j) {
if(d[j] == '.') continue;
if(i > 0) rtn += d[i];
int len = j - i - 1;
// case 1
if(d[i] == d[j]) rtn += string(len, d[i]);
// case 2
else if(d[i] == 'L' && d[j] == 'R') rtn += string(len, '.');
// case 3
else rtn += string(len / 2, 'R') + string(len % 2, '.') + string(len / 2, 'L');
i = j;
}
return oss.str();
}
```
### [1574. Shortest Subarray to be Removed to Make Array Sorted](https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-subarray-to-be-removed-to-make-array-sorted/)
```cpp
class Solution {
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 index
// [1, 2, 3, 10], 4, [2, 3, 5], sz = 8
// r step1 : 找出r的位置,如果r == 0 就是不需要刪任何element
// L --> step2 : L從0開始找,每找到一個就檢查是否可以和r接起來
// step3 : 接不起來就把r倒退,直到條件成立,儲存L~R之間長度的最小值
public:
int findLengthOfShortestSubarray(vector<int>& nums) {
int sz = nums.size(), right = sz - 1;
// step1 : find out the right position
while(right > 0 && nums[right] >= nums[right - 1]) --right;
if(right == 0) return 0;
int ans = right;
// step2 : search left from index 0 to sz - 1
for(int left = 0; left < sz; ++left) {
if(left > 0 && nums[left] < nums[left - 1]) break;
// step3 : find a left then check if nums[left] <= nums[right]
// if not back the right
while(right < sz && nums[left] > nums[right]) ++right;
ans = min(ans, right - left - 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
### [1498. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-subsequences-that-satisfy-the-given-sum-condition/)
找出所有subsequences的個數,符合最大值+最小值 <= target。
> 1. 因為是subsequence,所以可以先對nums做排序,不影響結果。
> 2. 因為只需知道最大值+最小值<=target,所以使用two pointer
> 3. 最大最小值決定了,subsequence的個數就是中間值選或不選的個數。pow(2, right - left);
```cpp
class Solution {
// two sum, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// 2, 3, 4, 5, [6], 7, 8, 9, 10
// 1 + 5就是中間值,right--就是往下,left++就是往上
public:
int numSubseq(vector<int>& A, int target) {
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
int res = 0, n = A.size(), l = 0, r = n - 1, mod = 1e9 + 7;
// 因為pow(2, N) 會有int overflow
// 所以先存在vector中
vector<int> pows(n, 1);
for (int i = 1 ; i < n ; ++i)
pows[i] = pows[i - 1] * 2 % mod;
while (l <= r) {
if (A[l] + A[r] > target) {
r--;
} else {
res = (res + pows[r - l]) % mod;
l++;
}
}
return res;
}
};
```
###### tags: `leetcode` `刷題`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet