# Notes on how to install Docker
Notes on how to proceeed to install Docker on local machines.
All the instructions reported below are simply a shorthand of what extensively reported on the excellent installation guide of the [Docker website](https://docs.docker.com/).
[toc]
## <summary>Linux (tested on Ubuntu 22.04)</summary>
Fully detailed instructions are provided in the Docker documentation at the [link](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/).
### 0. Start from a clean installation by removing all previous Docker installations
```bash
for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
```
If you don't have Docker already installed on your laptop this will result in a harmless error like:
`E: Unable to locate package docker-engine`
### 1. Set up the Docker repository
```bash
# Add Docker's official GPG key:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
# Add the repository to Apt sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
```
### 2. Install Docker Engine and Docker Compose
```bash
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
```
### 3. Verify that the Docker Engine is installed correctly
```bash
sudo docker run hello-world
```
This should result in a message like this:

> To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
> 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
> 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub online registry.
> 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
> executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
> 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
> to your terminal.
>
> To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with a bash shell as explained in class:
> `$ sudo docker run --rm -i -t -d --name myubuntu ubuntu:noble /bin/bash`
>
> Or try something else entirely from [dockerhub](https://hub.docker.com/)
>
**Please note that the installation is not finished just yet!**
### 4. Setup Docker as a non-root user
The Docker daemon always runs as the root user. As a consequence, all Docker related commands need to be run with `sudo`. If you want to avoid that, follow the [post-installation instructions](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/), creating the `docker` group and adding your user to it:
```bash
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
```
### 5. Verify that you can use Docker as a non-root user
Run the same command as before, but as a simple user (i.e. do not use `sudo`)
```bash
docker run hello-world
```
This should result in a message like this:

### 6. Enable Docker Engine to startup at boot
```bash
sudo systemctl enable docker.service
sudo systemctl enable containerd.service
```
### 7. Test the Docker Compose installation
```bash
docker compose version
```
This should result in an output like the following:

---
<!-- ## <summary>Linux (tested on Ubuntu 20.04)</summary>
Fully detailed instructions are provided in the Docker documentation at the [link](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/).
### 0. Start from a clean installation by removing all previous Docker installations
```bash
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
```
If you don't have Docker already installed on your laptop this will result in a harmless error like:
`E: Unable to locate package docker-engine`
### 1. Set up the Docker repository
```bash
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
```
```bash
sudo mkdir -m 0755 -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
```
```bash
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
```
### 2. Install Docker Engine and Docker Compose
```bash
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
```
### 3. Verify that the Docker Engine is installed correctly
```bash
sudo docker run hello-world
```
This should result in a message like this:

> To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
> 1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
> 2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub online registry.
> 3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
> executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
> 4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
> to your terminal.
>
> To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with a bash shell as explained in class:
> `$ sudo docker run --rm -i -t -d --name myubuntu ubuntu:jammy /bin/bash`
>
> Or try something else entirely from [dockerhub](https://hub.docker.com/)
>
**Please note that the installation is not finished just yet!**
### 4. Setup Docker as a non-root user
The Docker daemon always runs as the root user. As a consequence, all Docker related commands need to be run with `sudo`. If you want to avoid that, just create the `docker` group and add your user:
```bash
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
```
### 5. Verify that you can use Docker as a non-root user
Run the same command as before, but as a simple user (i.e. do not use `sudo`)
```bash
docker run hello-world
```
This should result in a message like this:

### 6. Enable Docker Engine to startup at boot
```bash
sudo systemctl enable docker.service
sudo systemctl enable containerd.service
```
### 7. Test the Docker Compose installation
```bash
docker compose --version
```
This should result in an output like the following:
```bash
Docker Compose version v2.16.0
```
--- -->
## Windows (tested on Windows 10 & 11)
Refer to the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/features/wsl/) for more information.
### 0. Start from a clean system
- Remove any previous installation of Docker Desktop and WSL from your system
- just search for *Ubuntu* in the installed programmes to unistall WSL

### 1. Install Ubuntu on WSL
- Verify you are on Windows 10 21H2 (build 19044 or greater) or Windows 11. To do so `SuperKey + R` and type `winver`. If the build number is lower (!) please go ahead and update your system.


- Open the Windows PowerShell with Administrator privileges

- Set v2 as the default version for future installations:
```bash
wsl.exe --set-default-version 2
```
- Install Ubuntu
```bash
wsl --install -d ubuntu
```
- Wait for the download and installation.
After that, reboot your machine to complete the process.
- Now you should have an application called *Ubuntu*.
If you launch it, you have a complete functional Linux OS on Windows.
- **The first time you launch it, it asks you to insert a _username_ and a _password_**.
- On the bash shell, update all the Ubuntu packages:
```bash
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
```

- Please read the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/) if additional information is needed.
### 2. Install Docker Desktop
- Download and install Docker Desktop from the [Docker Website](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/windows/install/). As per default, the options *Install required Windows components for WSL 2* is already ticked on: **do not change it**.

- Start Docker Desktop.
Check that `Use the WSL 2 based engine` is checked in the settings.

- And under `Resources --> WSL Integration` enable the integration with the Ubuntu distro you previously installed (remember to `Apply & restart`).

### 3. Run Docker from WSL
- Open a WSL instance and type in `docker info`. Try also the the basic example: `docker run hello-world`. Everything should work fine.

- Just launch all **git and docker related commands from WSL**. Don't use the Windows Shell and PowerShell for this.
<!-- ### 4. Extra
- WSL is a great feature even outside the scope of this course if you need to program in Windows, as it provides a full Unix environment. Our suggestion is to explore it. For example, it is possible to install `conda` and `python` inside it.
- In addition, it can be a good mean to learn some bash and linux terminal, which is essential if you want to work with Big Data, do Machine Learning or just manage and analyze data in your life.
- There are editors such as [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) which automatically interface with it, offering great opportunities (do not be stuck just with Jupyter, there is more and better beyond it).
-->
---
## Mac
Until last year there was a list of known issues with the new M1/M2/... family Apple Silicon chip Mac and Docker.
If interested, you can find further informatiom [here](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/troubleshoot/known-issues/).
To install Docker for Mac, check which processor version is installed in your machine, which is going to be either:
- Intel
- Apple Silicon (M1/M2/... families)

Then, refer to the installation instructions related to your own processor at the [link](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/install/mac-install/).
### 0. Install `rosetta` ***--For Apple Silicon (M1, M2, ...) chip only--***
- From a terminal, run:
```bash
softwareupdate --install-rosetta
```
### 1. Download and install Docker Desktop
- Download the right version from the Docker installation [page](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/mac/install/), depending on the processor version installed in your machine
- Double-click `Docker.dmg` to open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.
- Double-click Docker.app in the Applications folder to start Docker
<!-- ### 2. Use a different GitHub branch ***--For Apple Silicon (M1) chip only--***
A dedicated github branch `2022-M1` for Mac M1 users with a workaround tweak can be found at the link:
[https://github.com/jpazzini/MAPD-B/tree/2022-M1](https://github.com/jpazzini/MAPD-B/tree/2022-M1)
Use this one instead of the standard `2022` branch.
*(Thanks to Nicolo' Lai for investigating the issue)*
-->
---
## Troubleshooting
### Linux
- ***What if the output of step 3. does not look as expected***
If you are getting an error at this stage, check that the Docker deamon is up and running:
```bash
sudo systemctl status docker.service | grep "Active"
```
If the output of this command looks like the following:
```bash
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Wed 2022-03-23 14:37:07 CET; 1min 15s ago
```
Then proceed to start and enable the Docker engine service:
```bash
sudo systemctl start docker.service
sudo systemctl enable docker.service
```
The output of the previous command should now signal that the service is `active` and `running` on your computer
```bash
$ systemctl status docker.service | grep "Active"
Active: active (running) since Wed 2022-03-23 14:38:35 CET; 5min ago
```
Then, test once again the installation with the command of Section 3. :
```bash
sudo docker run hello-world
```
If there are still errors, just reboot your machine: on Debian and Ubuntu, Docker service is configured to start on boot by default.
### Windows 10
- ***In step 1 I get an error at the beginning of the installation of Ubuntu***

You need to update from WSL to WSL2. To do so, follow the instructions:
- Download and install (double-click) the Linux kernel update package: [here](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-manual#step-4---download-the-linux-kernel-update-package)
- Set WSL 2 as your default version by running the follwing command in the Windows PowerShell with Administrative privileges, as explained [here](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-manual#step-5---set-wsl-2-as-your-default-version).
```bash
wsl --set-default-version 2
```
- ***I have both Docker and WSL but when I type `docker info` I get errors***
As default, Docker Desktop is only active on the default WSL Linux distribution (e.g. Ubuntu, Fedora, ...).
Open a PowerShell with Administrator privileges and type
```bash
wsl --list
```
You get a list of installed distributions with the indication of the default one.

If *Ubuntu* is not the default, type:
```
wsl --setdefault Ubuntu
```
Otherwise, you can go in Docker Desktop settings and enable it for a specific WSL distro.
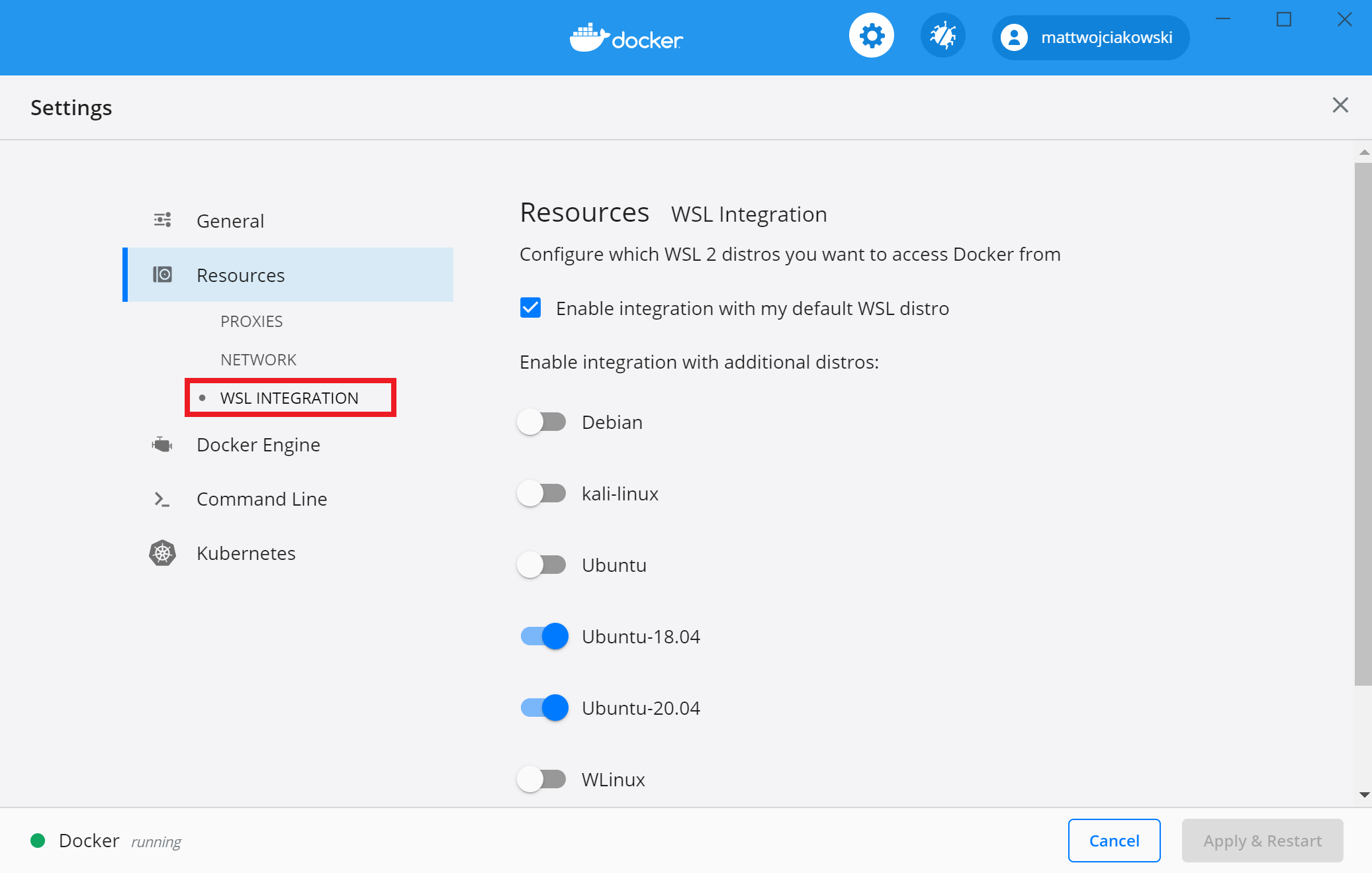
- ***How can I reach one of my Windows folders from WSL?***
Windows drives (e.g. `C:`) are mounted under the `/mnt` folder inside the WSL distribution.
For instance, you can reach a folder with something similar to:
```bash
cd /mnt/c/Users/<YOUR_USERNAME>/.../
```
<!-- Otherwise, open the folder using Windows File Explorer, click on the folder path in the top of the window and type `wsl` + Enter. An instance of WSL will open in the given folder.
-->
<!-- ### Mac
#### Apple Silicon (M1) chip
There is a list of known issues with the new M1 family Apple Silicon chip Mac, some of them specifically concerning MySQL.
You can find the full list [here](https://docs.docker.com/desktop/mac/apple-silicon/#known-issues).
A dedicated github branch `2022-M1` for Mac M1 users with a workaround tweak can be found at the link:
[https://github.com/jpazzini/MAPD-B/tree/2022-M1](https://github.com/jpazzini/MAPD-B/tree/2022-M1)
Use this one instead of the standard `2022` branch.
-->