[TOC]
# RNN model and NLP summary
## Data processing
1. one-hot encoding
### Processing Text Data
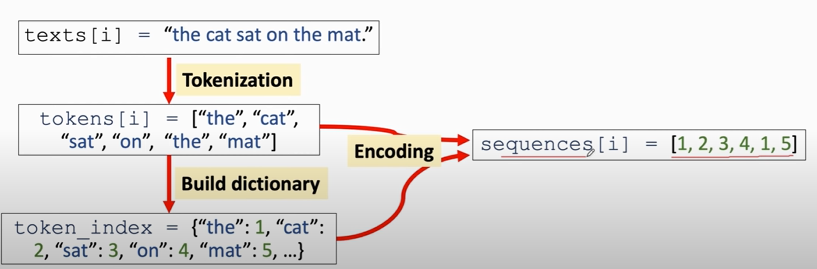
1. Tokenization (text to words)
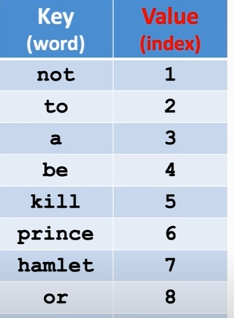
2. count word frequencies
- stored in a hash table:

- Sort the table so that the frequency is in the descending order.
- Replace "frequency" by "index" (starting from 1.)
- The number of unique words is called "vocabulary".
## Text Processing and Word Embedding
### Text processing
1. tokenization
Considerations in tokenization:
- Upper case to lower case. ("Apple" to "apple"?)
- Remove stop words, e.g., "the", "a", "of", etc.
- Typo correction. ("goood" to "good".)
2. build the dictionary
3. align sequences (使每个sequence长度一样)
### Word embedding
1. One-hot encoding
- First, represent words using one-hot vectors.
- Suppose the dictionary contains $v$ unique words (vocabulary $=v)$.
- Then the one-hot vectors $\mathbf{e}_{1}, \mathbf{e}_{2}, \mathbf{e}_{3}, \cdots, \mathbf{e}_{v}$ are $v$ -dimensional.
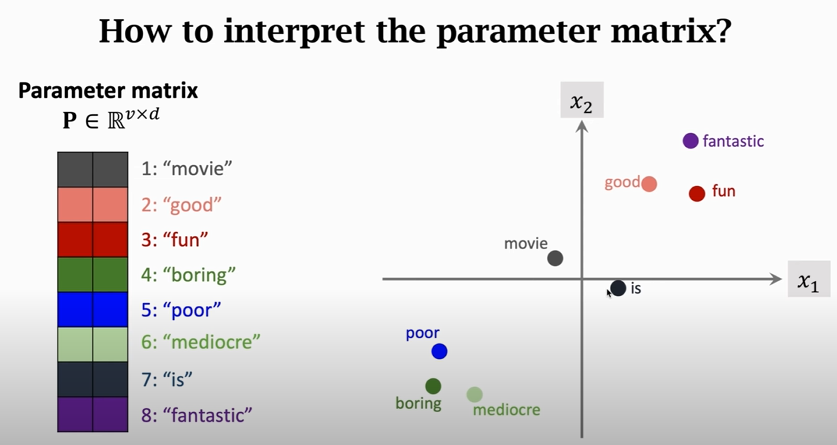
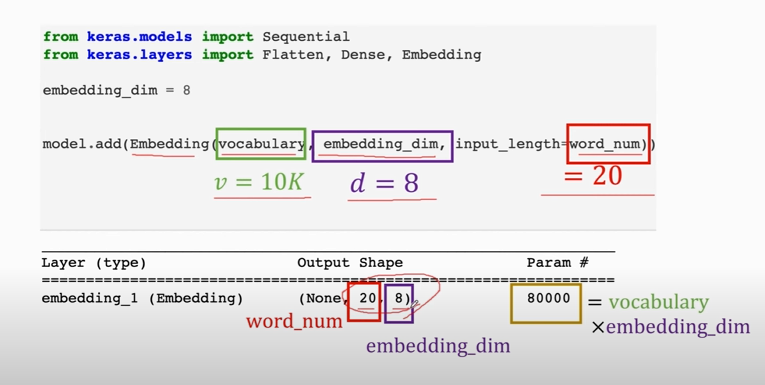
2. word embedding
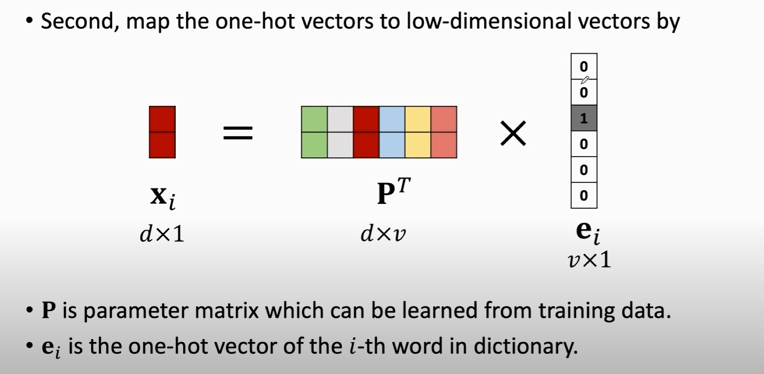
**`d` 由用户决定**
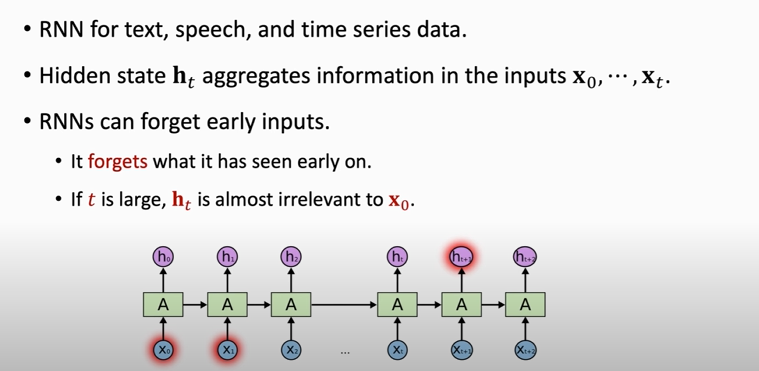
## Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
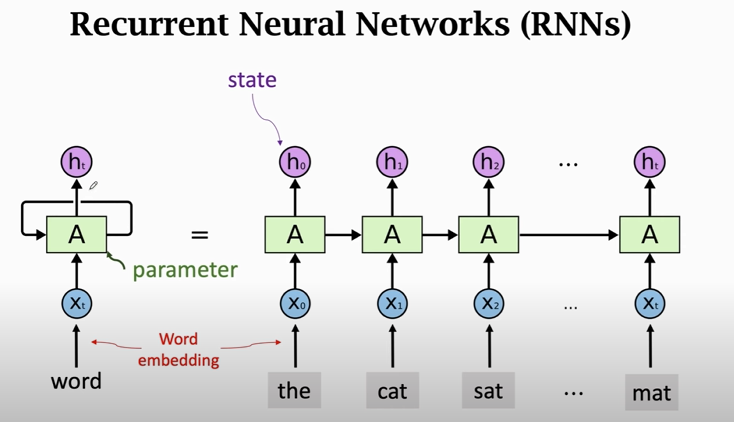
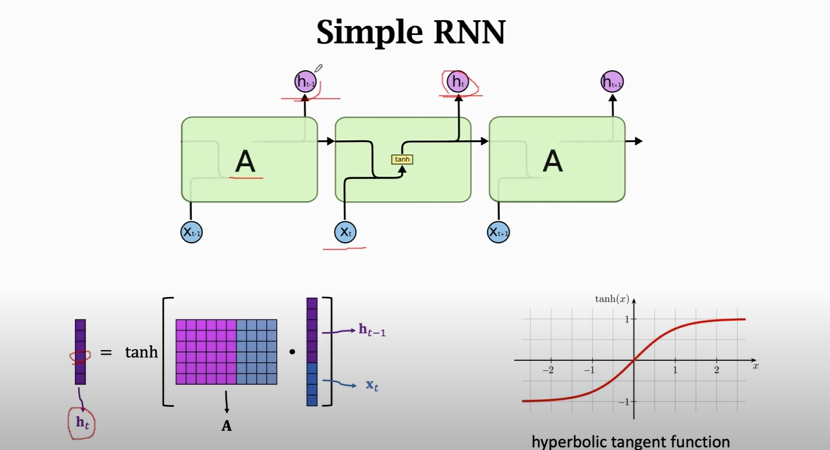
1. `ho`包含了 *the* 的信息
`h1`包含了 *the cat* 的信息
`h2`包含了 *the cat sat* 的信息
...
`ht`包含了整句话的信息
2. 整个RNN只有一个参数`A`, 无论这条链有多长
### Simple RNN
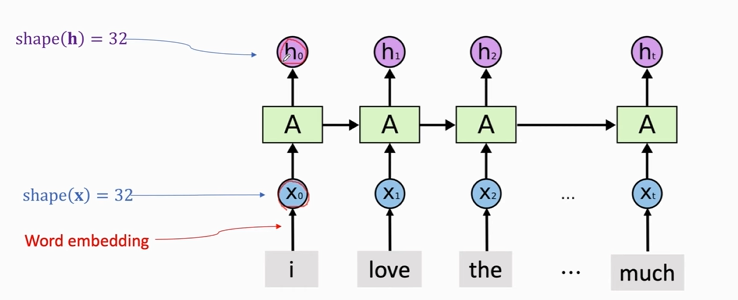
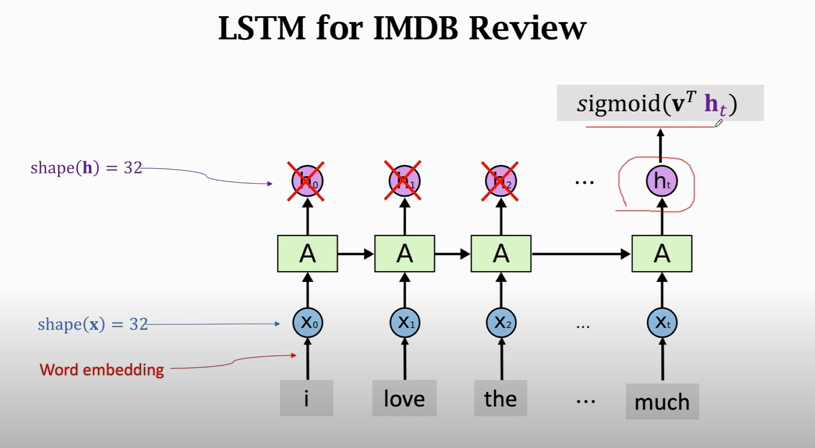
### Simple RNN for IMDB Review
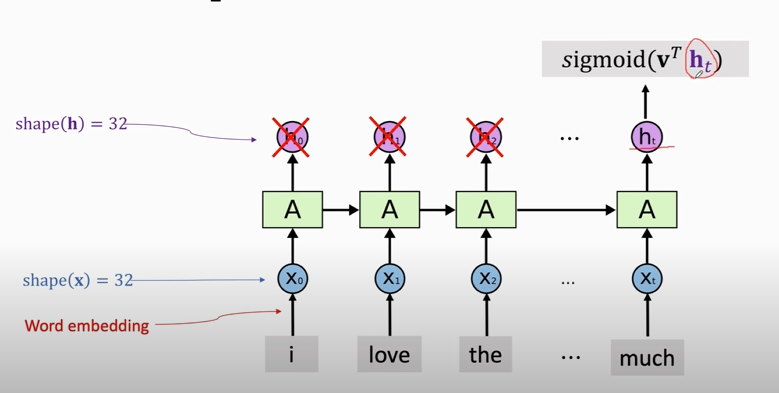

`return_sequences = False`: RNN只返回最后一个state `ht`

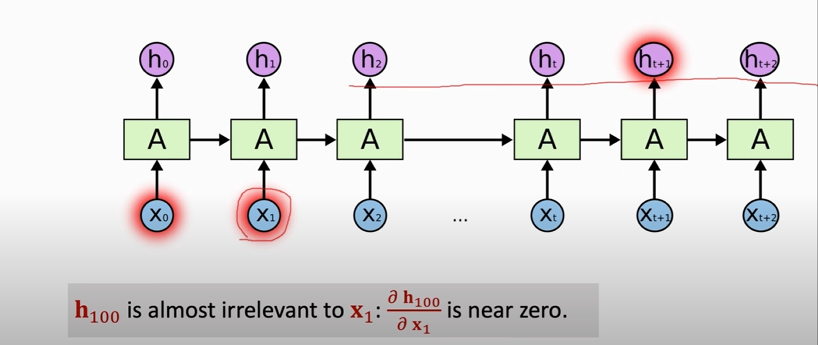
### shortcomings of simple RNN
1. simple RNN is good at short-term dependence
2. simple RNN is bad at long-term dependence
### Summary

## Long Short Term Memory (LSTM)
### LSTM Model
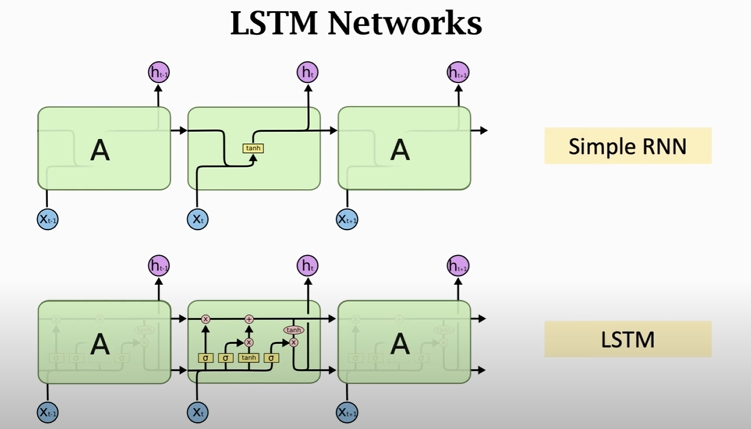
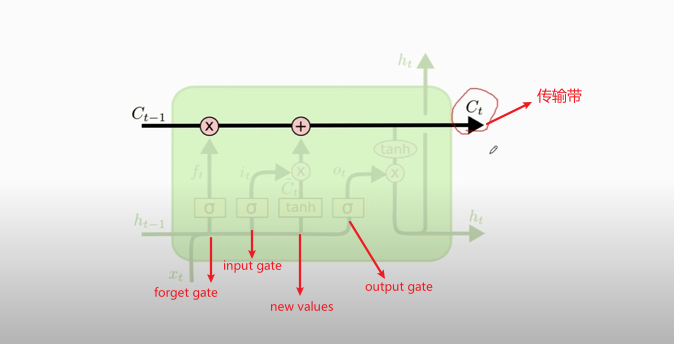
- Conveyor belt: the past information directly flows to the future
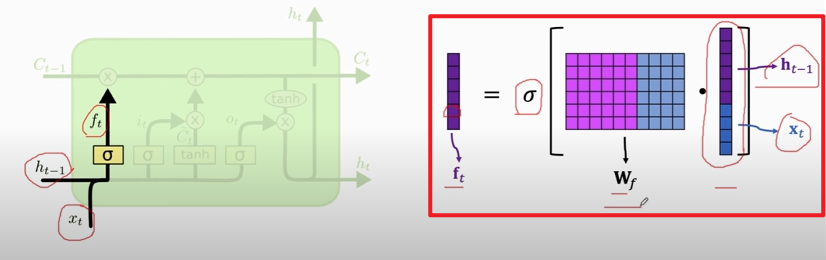
#### Forget gate
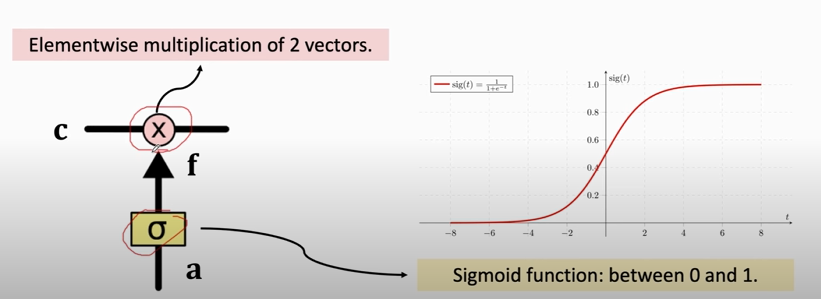
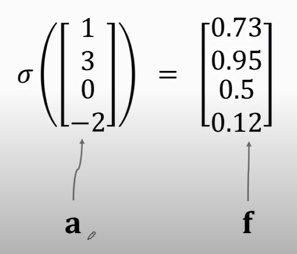
- Forget gate (`f`): a vector (the same shape as $\mathbf{c}$ and $\mathbf{h}$ ).
- A value of **zero** means "let nothing through".
- A value of **one** means "let everything through!"
- 作用于$C_{t-1}$
- `f`的计算过程:
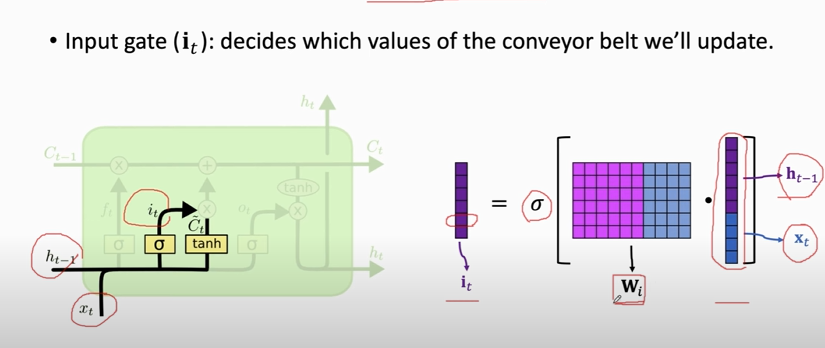
#### Input gate
#### New value
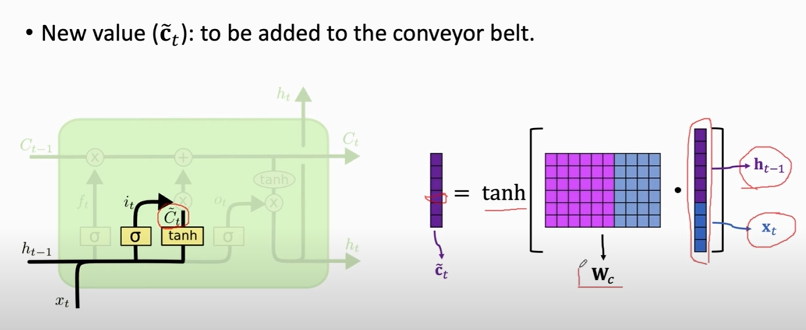
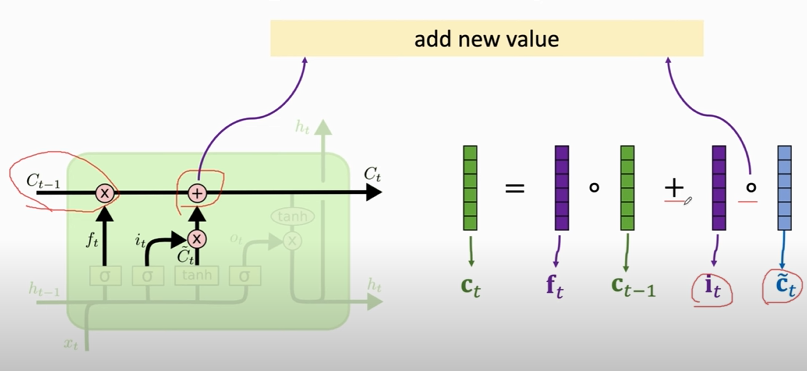
#### $C_{t}$
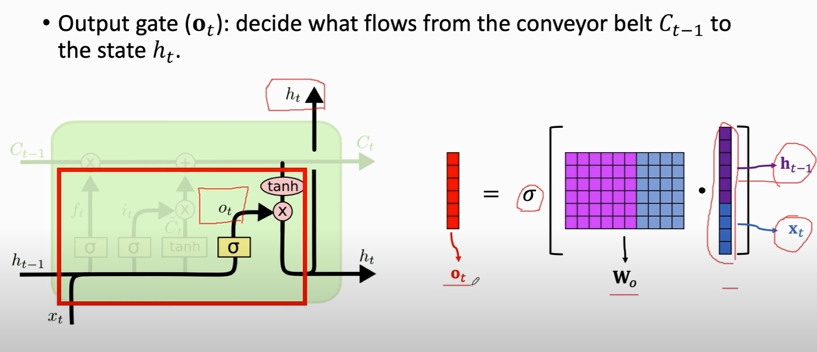
#### Output gate
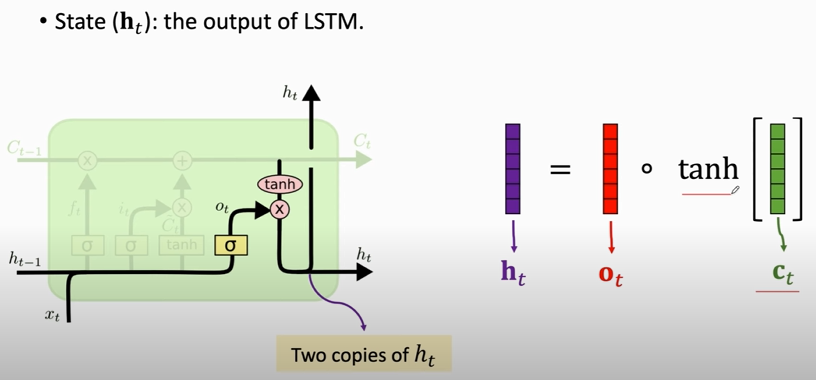
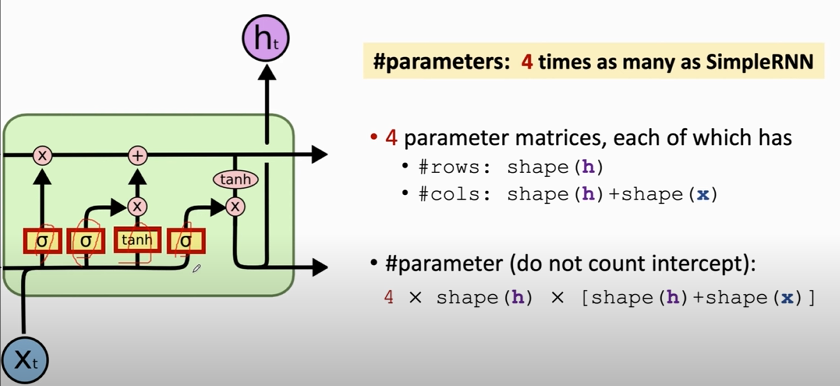
#### LSTM: Number of parameters
### LSTM Using Keras

### Summary

## Making RNNs More Effective
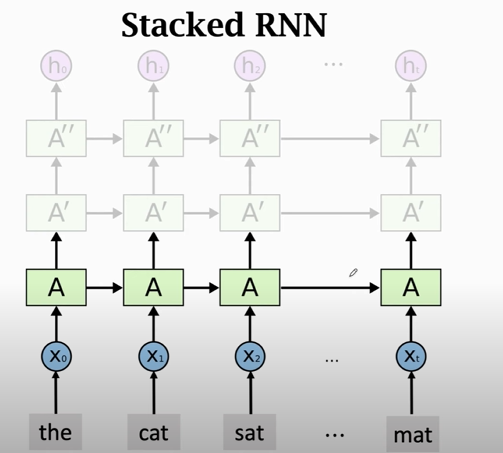
### Stacked RNN
### Stacked LSTM
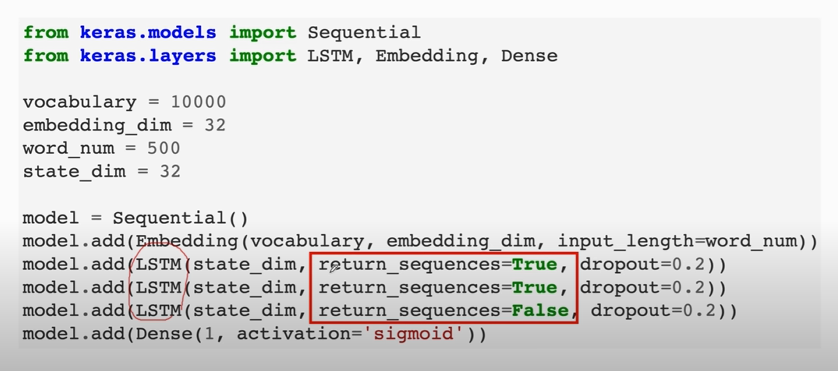
最后一层LSTM的 `return_sequences = True`
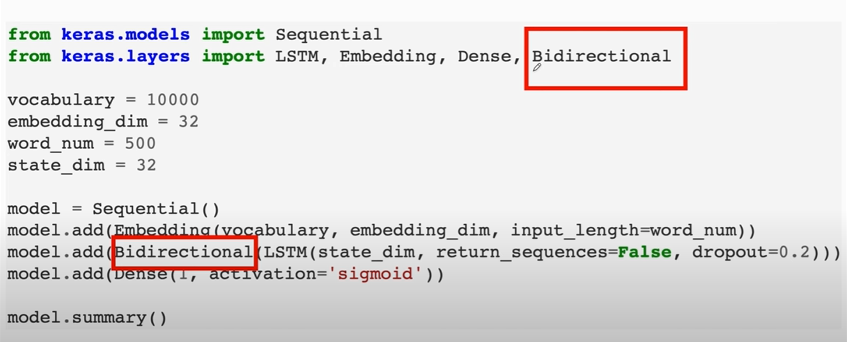
### Bidirectional RNN
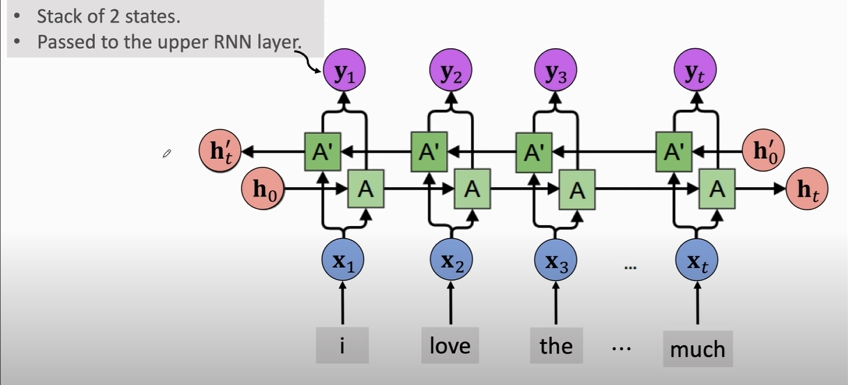
If there is no upper RNN layer, then return $\left[\mathbf{h}_{t}, \mathbf{h}_{t}^{\prime}\right]$
### Pretraining
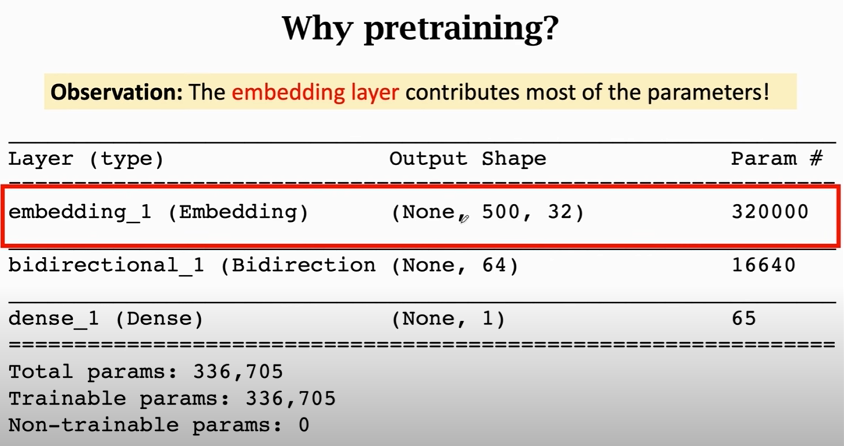
**Step 1:** Train a model on large dataset.
- Perhaps different problem
- Perhaps different model.
**Step 2:** keep only the embedding layer
**Step 3:** 
### Summary
- SimpleRNN and LSTM are two kinds of RNNs; always use LSTM instead of SimpleRNN.
- Use Bi-RNN instead of RNN whenever possible.
- Stacked RNN may be better than a single RNN layer (if $n$ is big).
- Pretrain the embedding layer (if $n$ is small).
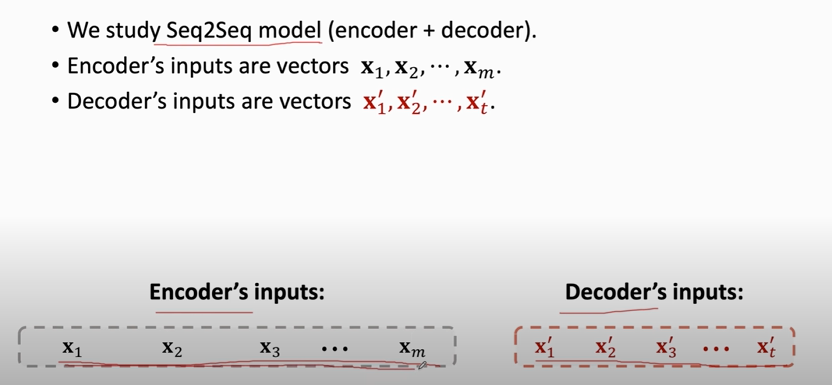
## Machine Translation and Seq2Seq Model
### Sequence-to-Sequence Model (Seq2Seq)
1. Tokenization \& Build Dictionary
- Use 2 different tokenizers for the 2 languages.
- Then build 2 different dictionaries.

2. One-Hot encoding
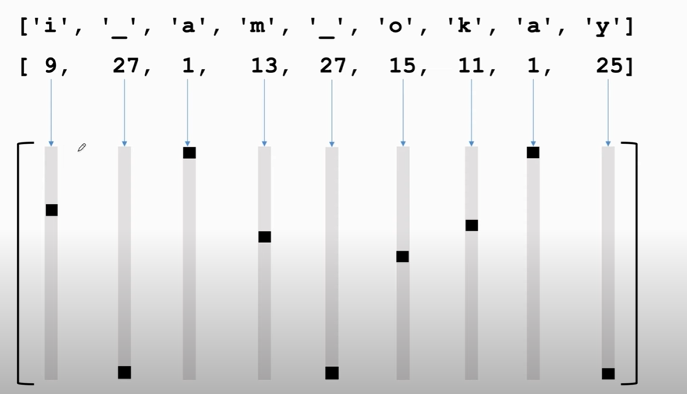
3. training the Seq2Seq model
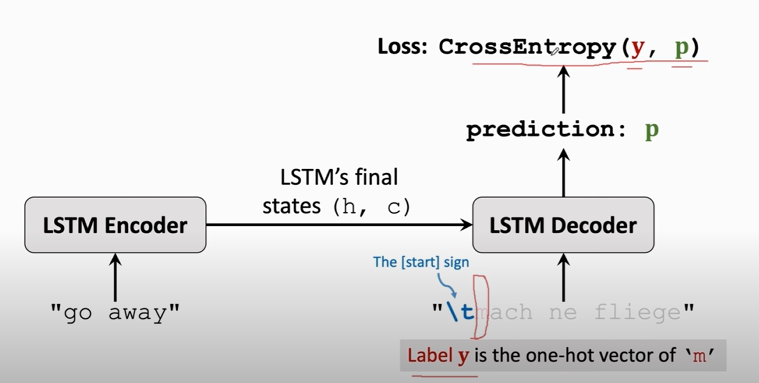
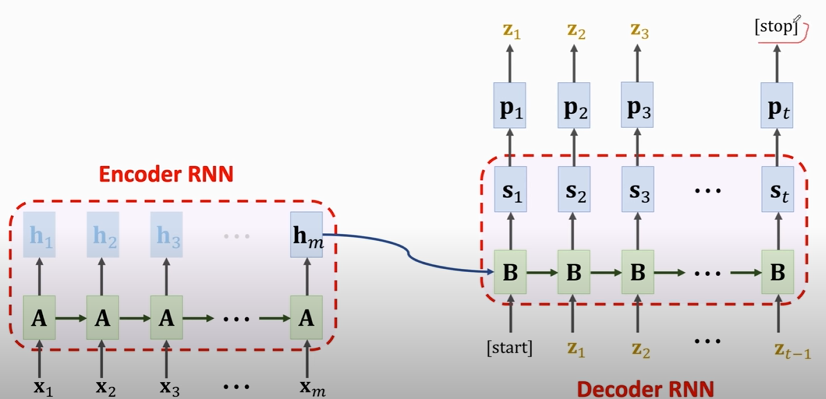
### Improvements
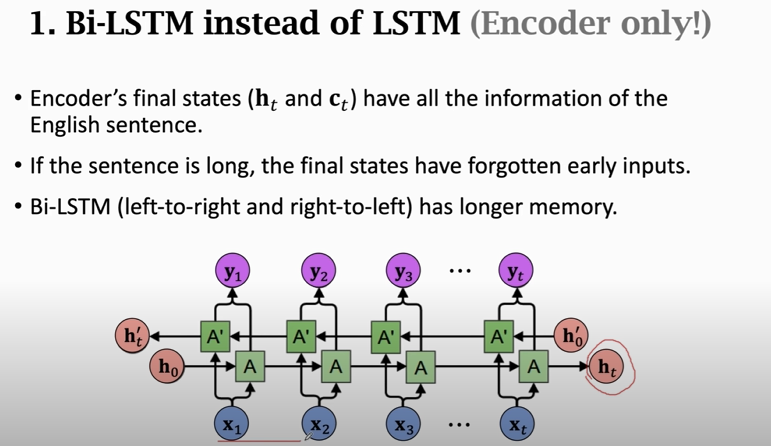
Use Bi-LSTM in the encoder;
use unidirectional LSTM in the decoder.
## Attention
**Shortcoming** of Seq2Seq model: The final state is incapable of remembering a **long** sequence.
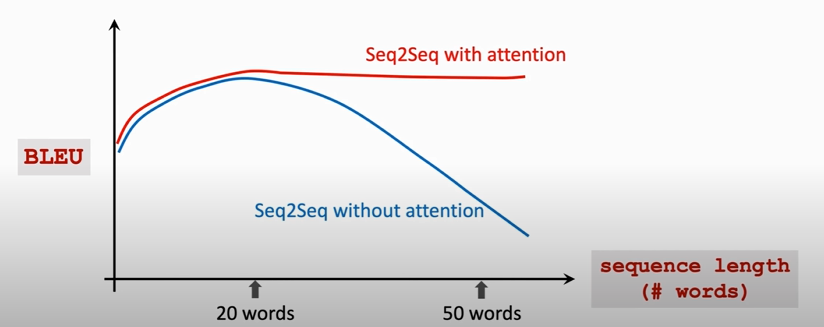
### Seq2Seq model with attention

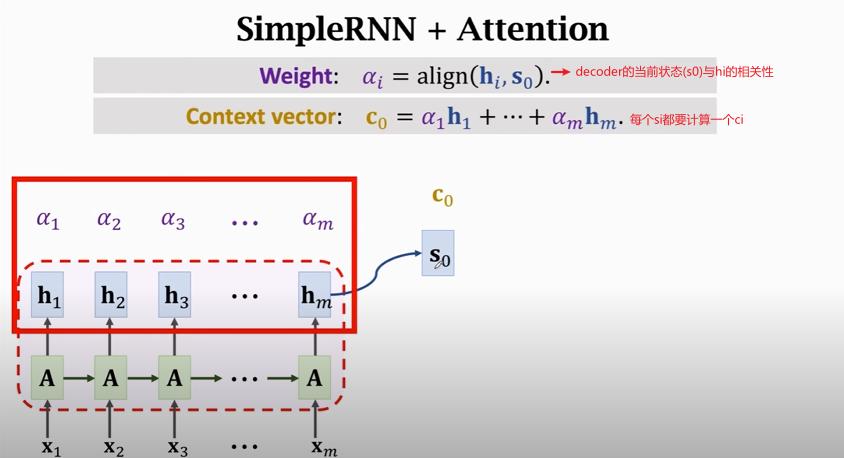
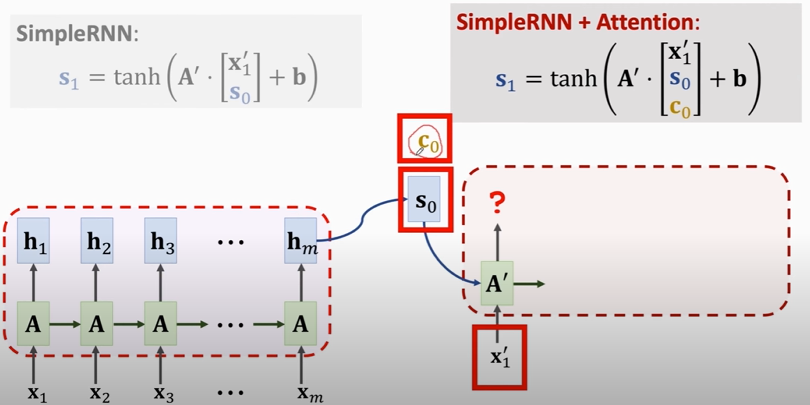
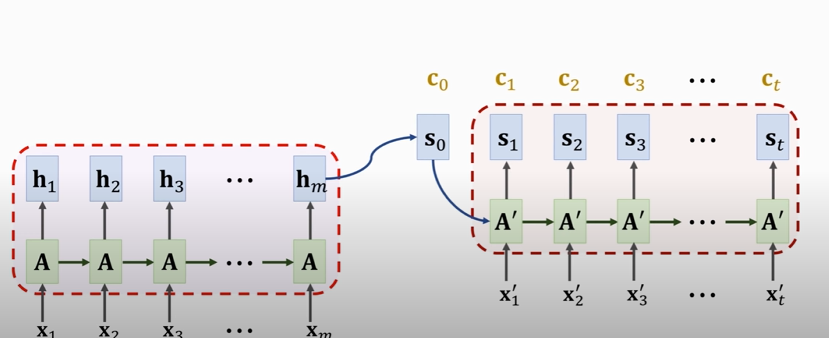
### Summary

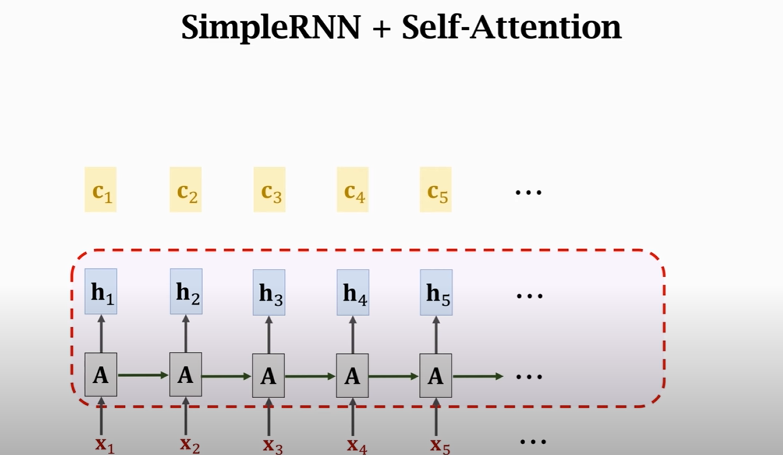
## Self-Attention

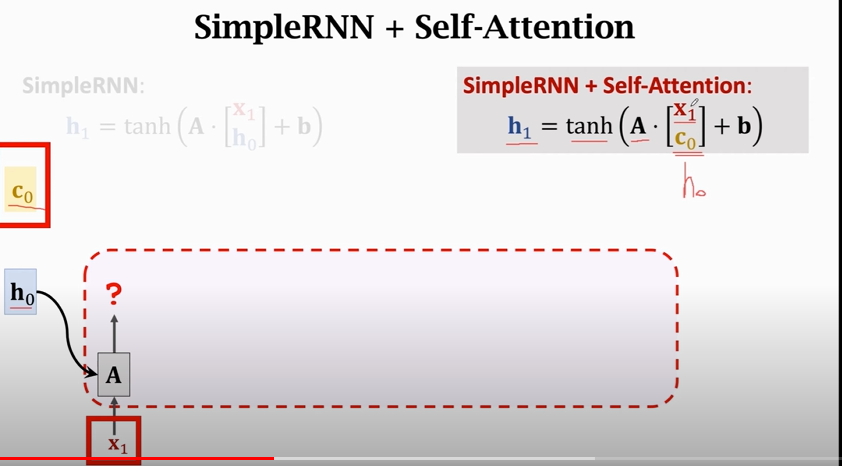
# Transformer Model
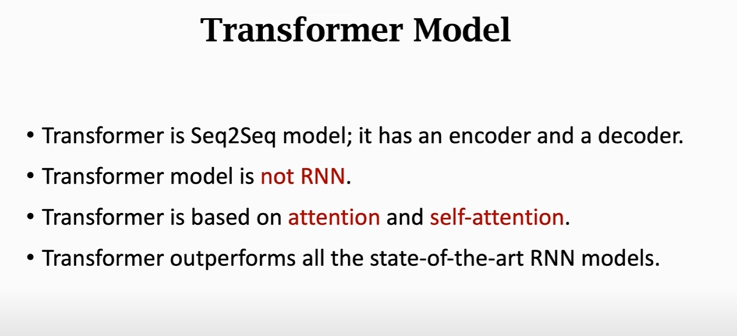
- Transformer is a Seq2Seq model.
- Transformer is not RNN.
- Purely based attention and dense layers.
- Higher accuracy than RNNs on large datasets.
## Attention for Seq2Seq Model
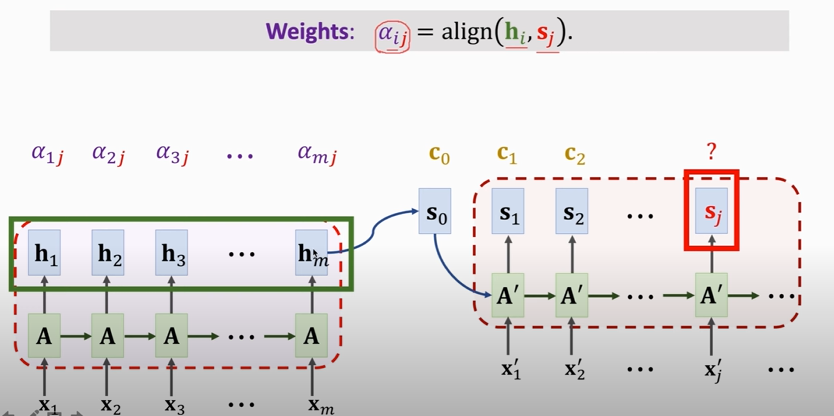
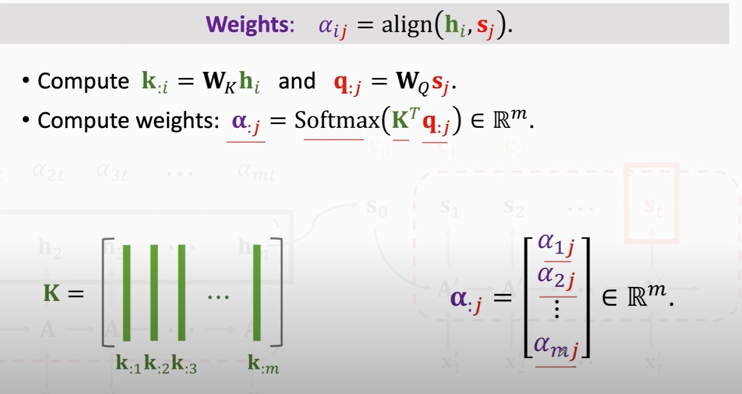

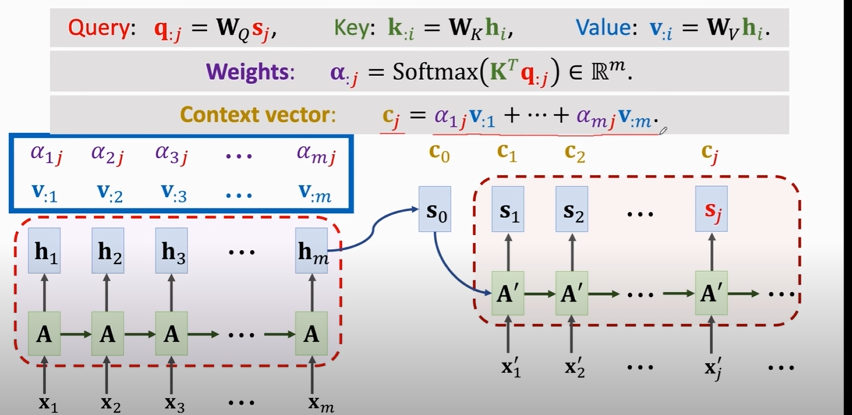
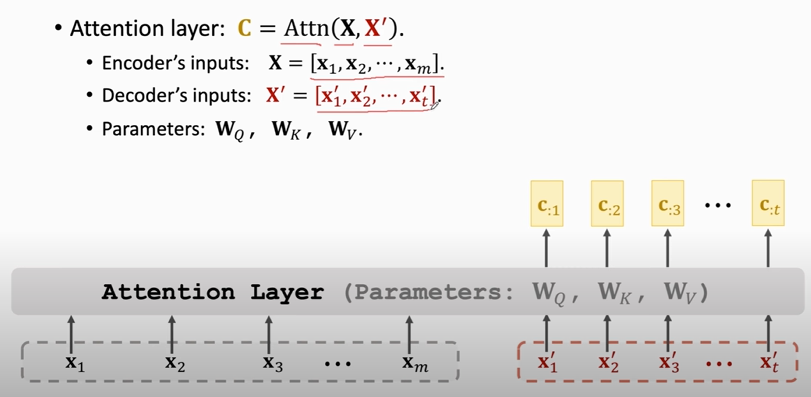
### Attention without RNN
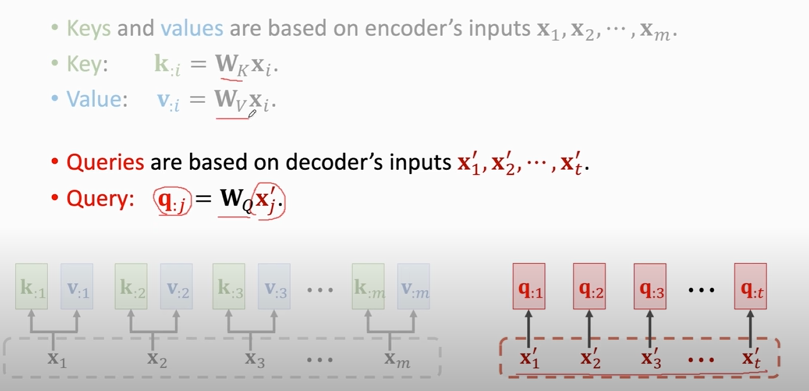
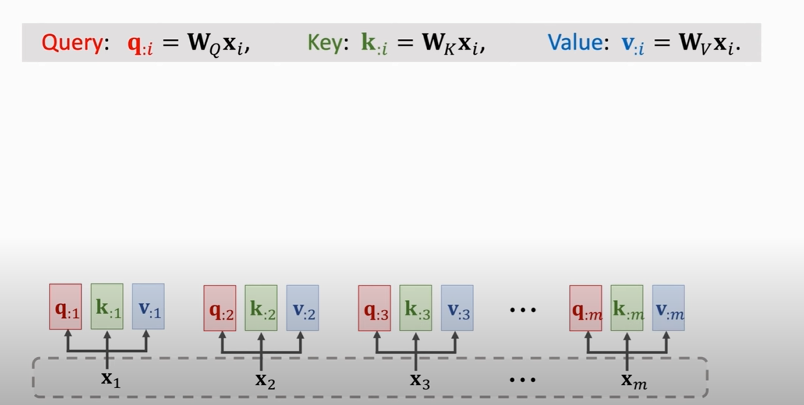
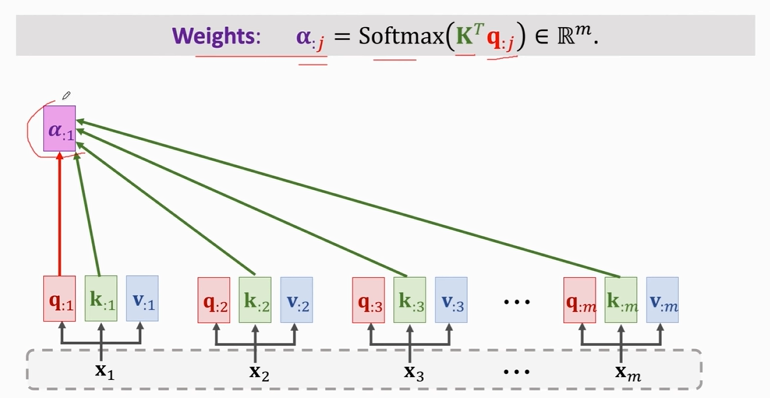
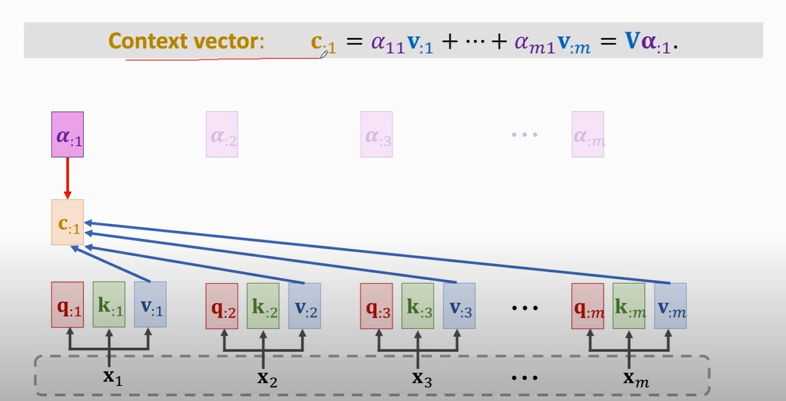
1. compute weights: 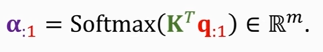
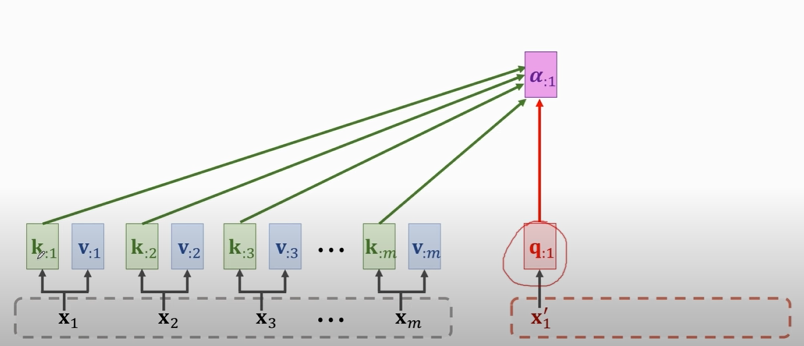
2. compute context vector: 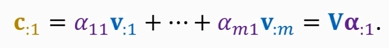
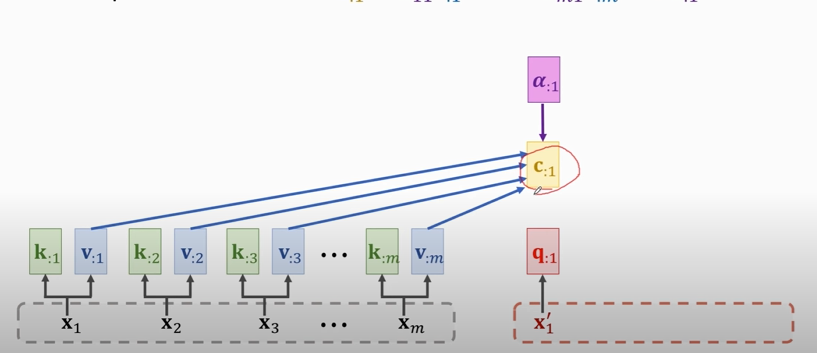
3. repeat this process
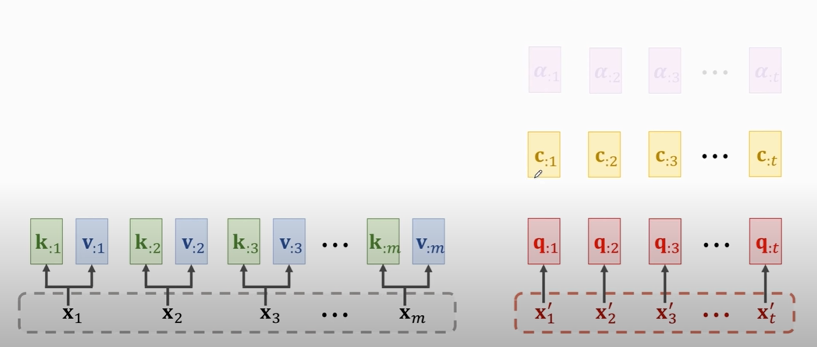
#### Output of attention layer
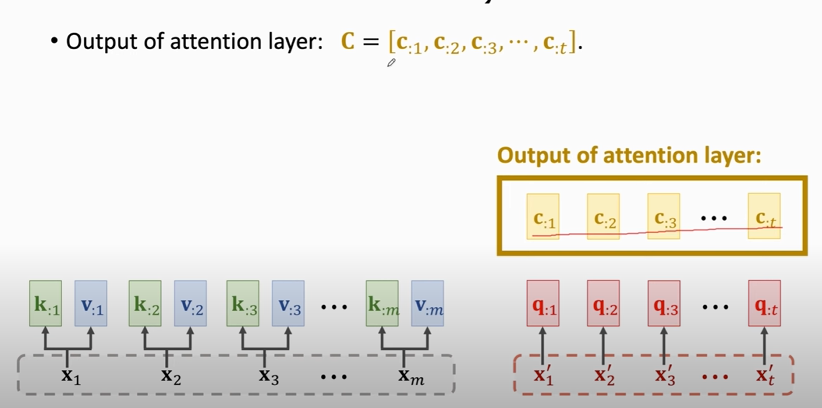
### Attention Layer for Machine Translation
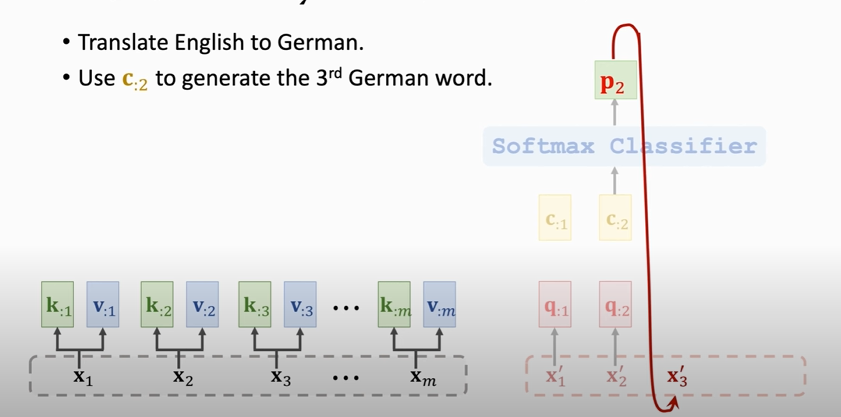
RNN for machine translation: 状态 `h` 作为特征向量
Attention layer for ... : context vector `c` 作为特征向量
### Summary
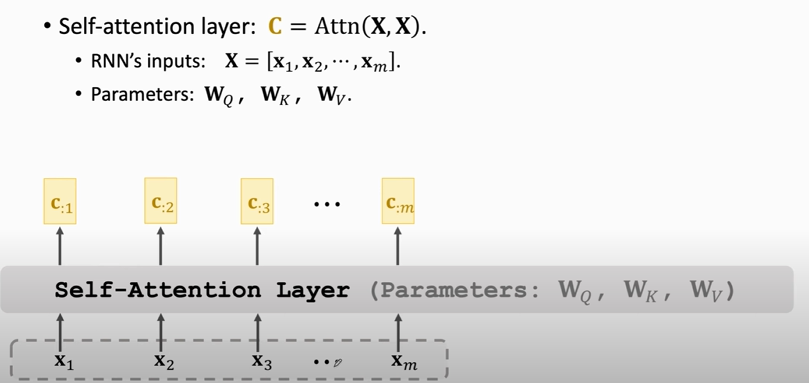
## Self-Attention without RNN
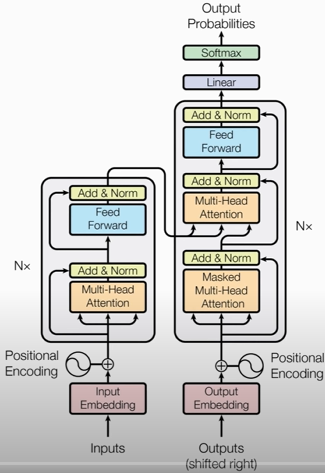
## Transformer model
### Word Embedding + Positinal Encoding

- `PE` 向量和 embedding后的词向量维度一样
- `PE` 由该词在句中的位置决定, 从而解释输入序列中的单词顺序
- `PE` 的计算公式:
$$
\begin{array}{c}
P E(\text { pos }, 2 i)=\sin \left(\text { pos } / 10000^{2 i} / d_{m} \text { odel }\right) \\
P E(\text { pos }, 2 i+1)=\cos \left(\text { pos } / 10000^{2 i} / d_{m} \text { odel }\right)
\end{array}
$$
- `pos` 为当前词在句中的位置
- `i` 为词向量中entry的index
- 偶数位置,使用正弦编码; 奇数位置,使用余弦编码
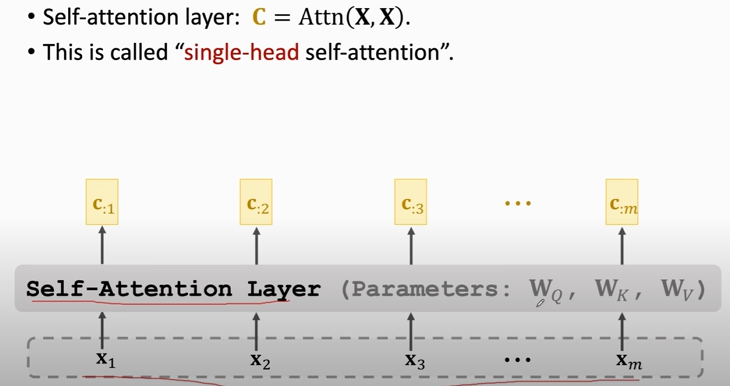
### Single-Head Self-Attention
### Multi-Head Self-Attention
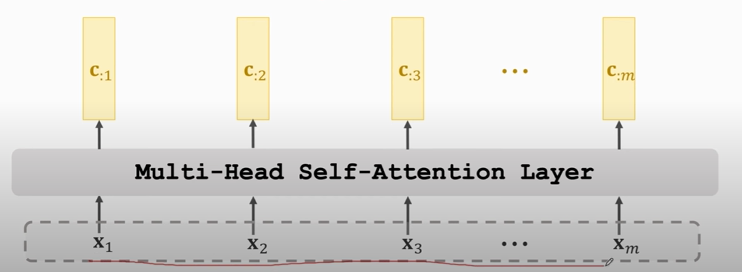
- Using $l$ single-head self-attentions (which do not share parameters.)
- A single-head self-attention has 3 parameter matrices: $\mathrm{W}_{Q}, \mathrm{~W}_{K}, \mathrm{~W}_{V}$
- Totally $3 l$ parameters matrices
- Concatenating outputs of single-head self-attentions.
- Suppose single-head self-attentions' outputs are $d \times m$ matrices.
- Multi-head's output shape: $(l d) \times m$.
### Self-Attention Layer + Dense Layer
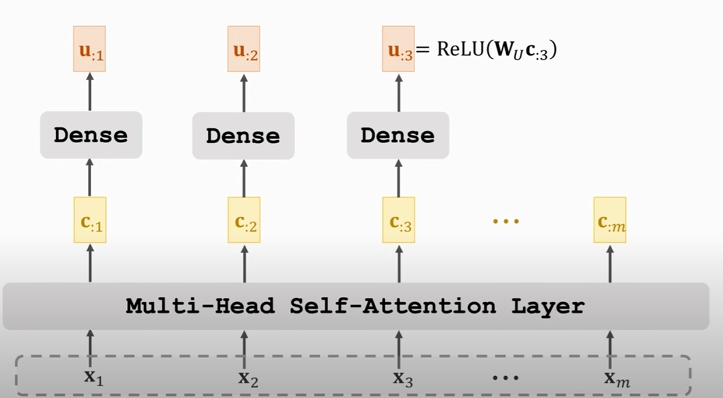
这些全连接层完全一样 (same $W_{U}$)
### Stacked Self-Attention Layers
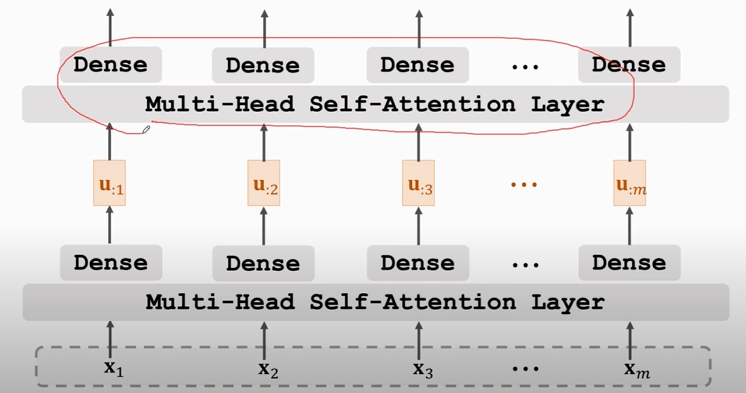
### Transformer's Encoder
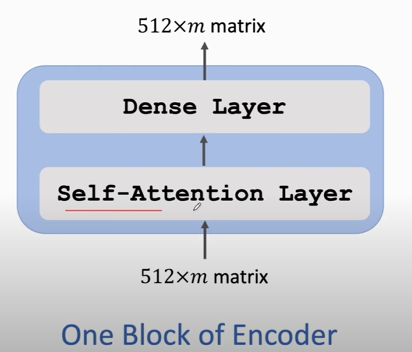
- 输入和输出一样, 所以可以用 resnet的残差结构, 把输入加到输出上
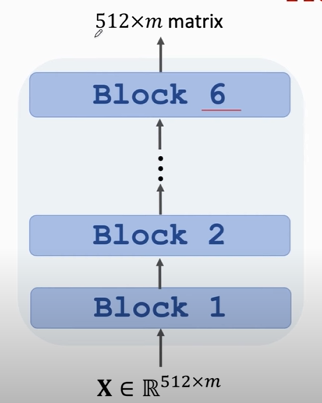
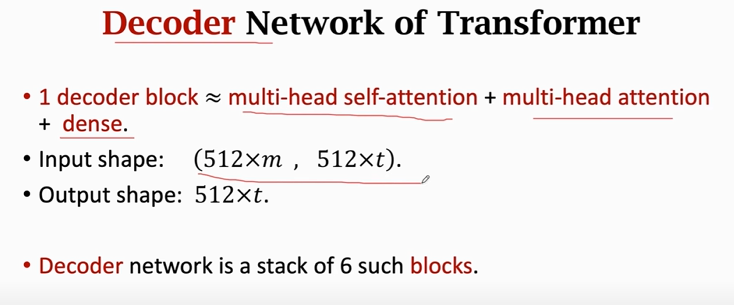
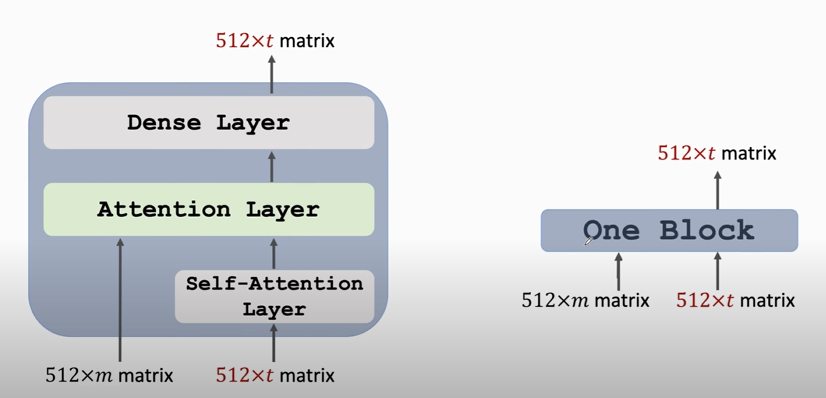
### Transformer's Decoder: One Block
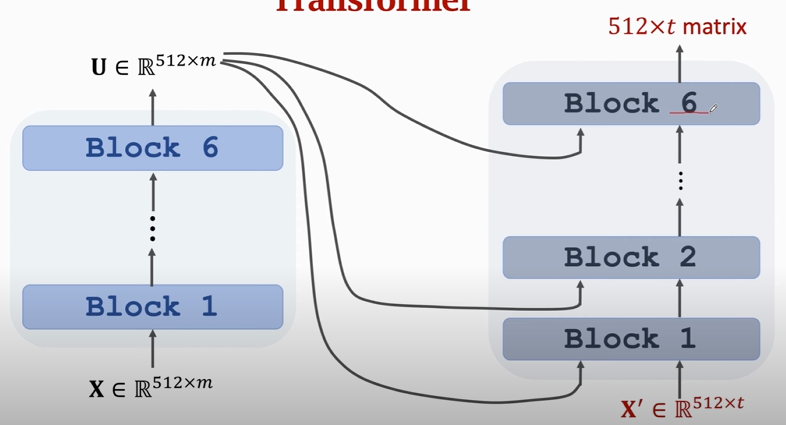
### Transformer
### Summary