---
tags: 機器學習基石上:數學篇
---
Ch5 Training vs Testing
===
## Content
[TOC]
## [Slides & Videos](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~htlin/mooc/)
參考筆記: [林軒田教授機器學習基石 第五講學習筆記](http://blog.fukuball.com/lin-xuan-tian-jiao-shou-ji-qi-xue-xi-ji-shi-machine-learning-foundations-di-wu-jiang-xue-xi-bi-ji/)
## [Recap and Preview](https://www.coursera.org/learn/ntumlone-mathematicalfoundations/lecture/uvlPc/recap-and-preview)
learning的兩個核心問題
1. 能不能讓 $E_{out}(g)$ 和 $E_{in}(g)$ 非常接近?
2. 能不能讓 $E_{in}(g)$ 非常小?
### Trade-off on $M$
<!--  -->

最後題目
- $2\cdot 100\cdot exp(-2\cdot0.1^2\cdot N) = 0.05$
- $N = \frac{ln(0.05/200)}{-0.02} \approx 414.702$
## [Effective Number of Lines](https://www.coursera.org/learn/ntumlone-mathematicalfoundations/lecture/Bv6Sg/effective-number-of-lines)
### 當 $M$ 是無限大的時候,前面說的 union bound 就會出問題

- $\mathbb P[\mathcal B_m]$:壞事情發生在 $h_m$ 上的機率
### 那麼 union bound 有什麼問題呢

- 我們之前用相加的方式 (union bound) 其實只是在計算 worst case
- worst case 發生代表我們的 bad events 幾乎不重疊
- 然而實際上,hypothesis $h_1,h_2$ 很接近的時候 (例如 perceptron 的兩條線很接近)
1. $E_{out}(h_1),E_{out}(h_2)$ 也會很接近
2. 對多數的 $D$ 來說,$E_{in}(h_1)$ 也會等於 $E_{in}(h_2)$
3. 因此,$\mathcal B_1,\mathcal B_2$ 會有很大的重疊
4. 這就導致了我們的 union bound 是 over-estimating 的
- 那麼我們能不能把無限多個的 hypothesis 分成有限多類? 這樣就可以知道哪些部分有重疊。
- 可以回顧一下 week 4 的最後一題 Fun Time
### 對 1 個 datapoint 而言,有 2 種 line

### 對 2 個 datapoint 而言,有 4 種 line

### 對 3 個 datapoint 而言,有 8 種 line (1/2)

### 對 3 個 datapoint 而言,總是有 8 種 line 嗎? (2/2)

### 對 4 個 datapoint 而言,最多只有 14 種 line

### Effective Number of Lines

Effective Number of Lines: 對這n個資料點來說的 分隔線種類
- 我們可以發現,在 $N$ 大到一定程度時,$\text{effective}(N)$ 會小於 $2^N$
- 我們希望它可以用來取代無限大的 $M$
- **_不懂為啥可以取代, 這樣不就只看 in-sample的表現了嗎_**
- 後面 Growth Function 的部分就會講
- 希望它在 $N$ 夠大的時候,會遠小於 $2^N$,這樣 $N$ 越大,右邊那項就會越小
- **_如果只是等於 $2^N$ 似乎不夠 ?_**
### Fun Time: Effective Number of Lines

- 先把 5 個點擺在圓上
- 取相鄰點的所有組合?
- 22 是目前可以試出來的最大數字
- 之後會給更正式的證明
## [Effective Number of Hypothesis](https://www.coursera.org/learn/ntumlone-mathematicalfoundations/lecture/lOFVM/effective-number-of-hypotheses)
### Dichotomies: Mini-hypotheses

- dichotomy
- 字面意思是「二分」
- 把手上的資料分成兩堆,圈圈的一堆,叉叉的一堆
- 一個 dichotomy 就是一種分類組合,在二元分類裡這樣組合的上界就是 2 的 N 次方,我們可以用這個數字來取代無限大的 M。
- $\{x,o\}^N$
- $N$ 維向量,每個 element 不是 x 就是 o,所有這些向量組成的集合
- $h(x_1,...,x_N)$
- 一個 hypothesis $h$ 在 $x_1,...,x_N$ 所產生的一個 dichotomy
- $\mathcal H(x_1,...,x_N)$
- hypothesis set $\mathcal H$ 在 $x_1,...,x_N$ 所能產生的所有 dichotomies
- $|\mathcal H(x_1,...,x_N)|$
- hypothesis set $\mathcal H$ 在 $x_1,...,x_N$ 所能產生的**所有 dichotomies 的數量**
- 這個數字可能可以用來替換 $M$
### Growth Function

- 但是用 dichotomy 有個不好的地方是,dichotomy 取決於我們「預先」選好的 data points,這樣在未來理論推導會有麻煩的地方。
- 為了移除掉對 $X$ 的依賴, 我們要計算「最多」會有多少種 dichotomy $m_H$(**Growth Function**) , 即對於這個Hypothesis Set 來說最大的 dichotomy set 的大小, 用來取代 $M$
- $m_H(N)$ (Growth Function)
- 以這個 Hypothesis set 能切出最多有多少種的 dichotomy
- 它是一個函數,輸入是 $N$
### Growth Function for Positive Rays

- $m_H(N)=N+1$
### Growth Function for Positive Intervals

- $m_H(N)=\frac 1 2 N^2 + \frac 1 2 N + 1$
### Growth Function for Convex Sets

- 左邊是一個 convex 的 hypothesis;右邊不是。
### Growth Function for Convex Sets - Shatter

- those $N$ inputs **shattered** by $H$
- 「這 $n$ 個點」可以被 $H$ 給 shatter
- 這個 hypothesis set 可以找出 $x_1$ 到 $x_n$ 的所有 dichotomy, 即 $2^N$ 種
- $m_H(N)=2^N \leftrightarrow$ 「存在」 $N$ 個 inputs 可以被 $\mathcal H$ 給 shatter
## [Break Point](https://www.coursera.org/learn/ntumlone-mathematicalfoundations/lecture/TpVTX/break-point)
<!-- 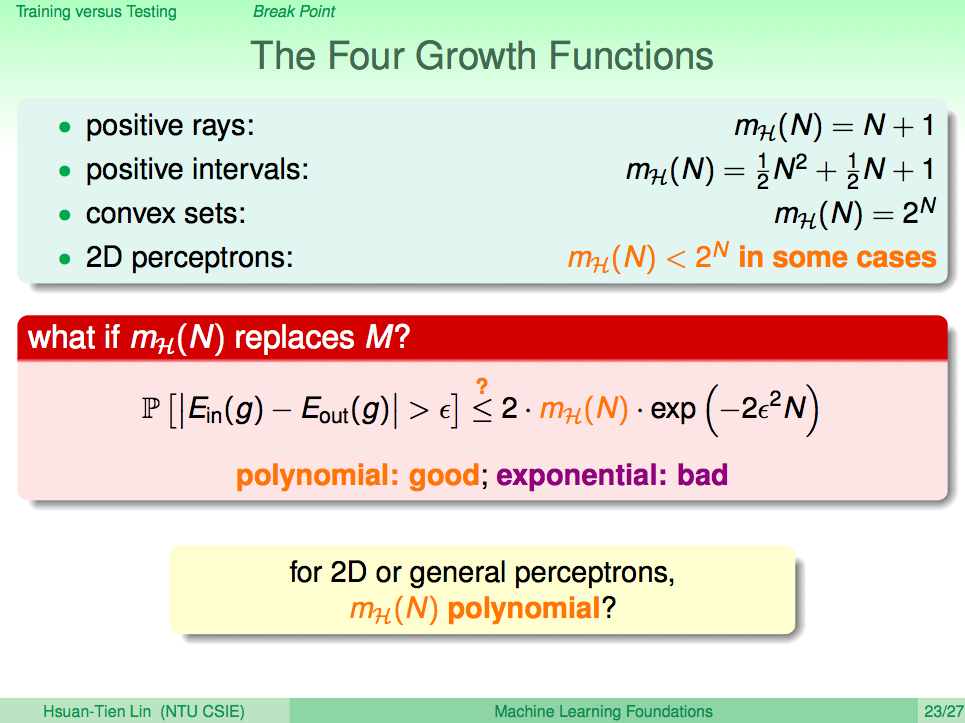 -->

- 我們可以用 $m_H(N)$ 來取代 $M$
- 如果這個 Hypothesis Set 的 Growth Function 是 N 的多項式, 則在N很大的時候, $2\cdot m_H(N)\cdot exp(-2\epsilon^2N)$ 會變得很小。反之, 若 Growth Function 是 N 的指數成長(或稱 exponentially 成長),就無法確保 $E_{in}$ 跟 $E_{out}$ 非常接近。
### Break Point
<!-- 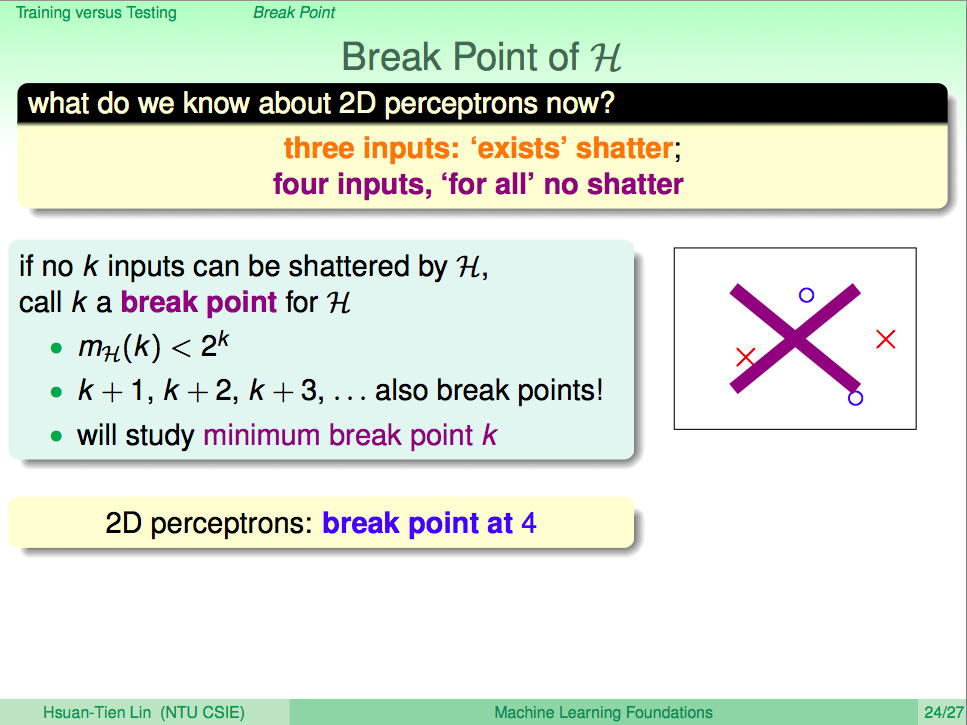 -->

- 給 k 筆inputs, 導致 $m_H(k)$ 比 $2^k$ 小, 則k就是 break point, 同樣大於 k 的也都是 break point
- 也就是「任何 k 筆資料」都沒辦法被 $\mathcal H$ 給 shatter
- 我們比較在乎「最小的」break point $k$
- 就像是從哪邊開始,出現一線曙光 (使得我們的 $m_H(N)$ 不是 exponentially 成長的)
<!-- 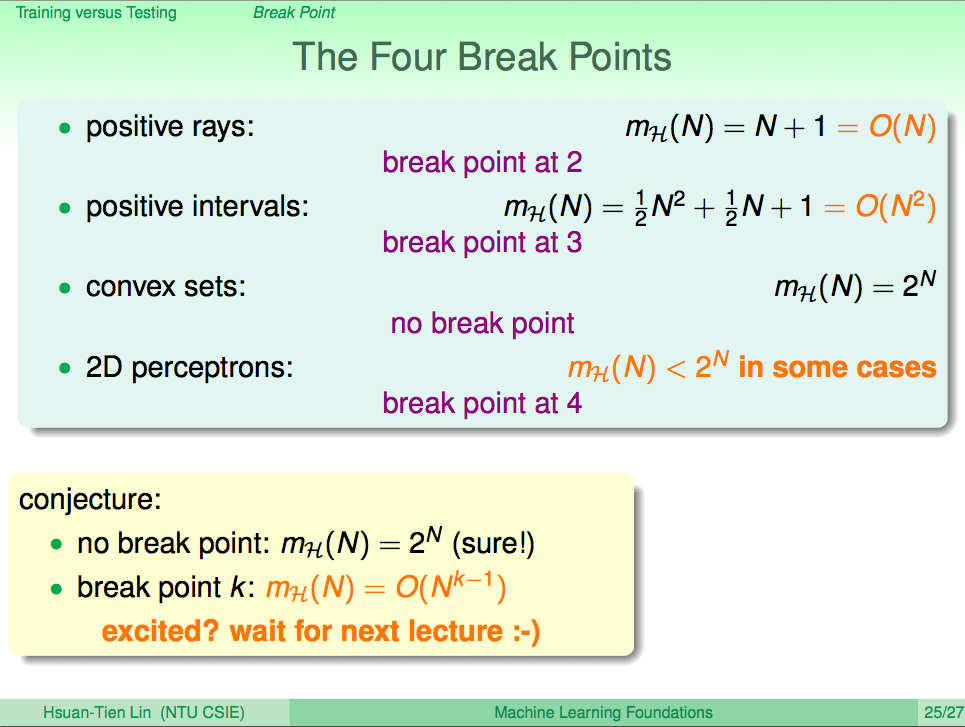 -->

- 由上面 growth function $m_H(N)$ 和 minimum break point $k$ 之間的關係,我們可以推測出一個猜想:
- 在 minimum break point 為 k 時, $m_H(N) = O(N^{k-1})$
- 若 $m_H(N)$ 成長速度真的只跟多項式一樣慢的話那就太好ㄌ
### Fun Time: Minimum Break Point

- ***雖然照 break point 定義的確是 3 沒錯,可是這不就跟上面的猜想牴觸了嗎***
- 其實也沒有,$m_H(N)=O(N^{k-1})$ 代表 $m_H(N)$ 「最多」就是 $cN^{k-1}$
- 本題 $m_H(N)=2N < cN^{3-1}$,故沒有牴觸
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet