So far in this program, you have been working in Google Colab which provides a cloud-based coding environment. We will be transitioning to using a Python environment stored on your local machine. You will be working in Jupyter Notebook, which is very common in the data industry. In addition, these instructions will include the installation of Github Desktop and Visual Studio Code (VS Code).
- In the Advanced Machine Learning course, you will need to submit a CORE ASSIGNMENT containing the error-free test notebook that is included within these instructions. This will ensure that you have the tools you will need to be successful.
- We recommend you begin the step-by-step installation AS SOON AS POSSIBLE to ensure you have time to troubleshoot any difficulties you may encounter.
- If you run into issues during installation, post your questions/issues on the [ds-python-installation](https://discord.com/channels/738494436467539968/999108307627294770) Discord channel, and tag your instructor in your question (e.g. @dojo_Instructor_name).
- These steps should take ~30-90 minutes, depending on the speed of your machine and internet connection.
- The [dojo-env-setup repository](https://github.com/coding-dojo-data-science/dojo-env-setup), which you will clone in Step 2.1, contains a backup copy of the entire set of instructions on the README, for convenience.
------
> Note: if you previously installed the dojo-env and are upgrading to the current version, please see the "Updating to New dojo-env" at the end of this chapter (after the Final Notes lesson)
By the end of this chapter, you will:
1. Install GitHub Desktop,
2. Install Python via Anaconda (or via miniforge - if on a Mac with an Apple Chip)
3. Create a special Python environment (dojo-env)
4. Supercharge Jupyter Notebooks with Extensions
5. Install Visual Studio Code.
## If you encounter an error during installation:
- First, read a little further down in the instructions to make sure we do not already address the error message that you ran into.
- Second, please check the "Troubleshooting" chapter for a lesson about the problem you are running into.
(The Troubleshooting section is the 3rd chapter in this course - see the screenshot below)

- Third, reach out on the #ds-python-installation Discord channel (Link) with:
- What step you are on (e.g. Step 2.3 Creating the dojo-env)
- What OS you are using (e.g. Windows 10, Windows 11, Mac with an Apple Processor, etc)
- Screenshots of the error/issue you are running into, whenever possible.
- Finally, if you have been able to run the test notebook in Step 2.4: Testing the Env, please upload these files with your question.
- Fourth, if you do not receive a response by the end of the day on Discord, please email your instructor.
------
## OS-Specific Steps/Commands
For several steps (e.g. Step 1), there are multiple versions of the instructions, depending on what operating system you are using.
For step 1, please make sure you are on the correct instruction page for your OS.
### Currently Supported Operating Systems
- We have prepared environment files (.yml files) for 4 different OS configurations:
- Windows (10 & 11)
- Mac (with Intel processors)*
- Mac (Apple Chips)*
- Linux**
#### **Note to Linux Users:
- Our Linux installation instructions are still in beta. While they have successfully been installed on students' Linux machines, we currently do not have a Linux machine available for troubleshooting.
- The beta Linux instructions are located [here](https://login.codingdojo.com/m/213/13909/99742) and all steps are combined into 1 lesson.
------
Regardless of OS, you will be using tools that serve the following purposes:
- Your "Terminal"/"Shell":
- The primary application you will use to execute coding-related commands.
- A Python Distribution:
- The fundamental infrastructure for installing Python.
- GitHub Desktop:
- App for working with and managing git repositories.
- Our custom Python Environment (dojo-env)
- A bundle of packages required for stacks 1-5+
- Jupyter Notebooks / Jupyter Lab
- The primary editor we will use (instead of Colab).
- Visual Studio Code
- A special text editor designed for code. It has many extensions and languages available.
- We will use it to edit special files, but it can also run notebooks too!
------
# 1. Downloading and Installing Required Apps
> Before we install our python environment, we need to take care of a couple requirements.
In step 1, we will install:
- Your "Terminal"/"Shell":
- The primary application you will use to execute coding-related commands.
- A Python Distribution (Anaconda/miniforge):
- The fundamental infrastructure that will allow us to install Python.
- GitHub Desktop:
- The way we will work with git repositories and the starting point for our local workflows.
# Step 1 - Windows
## Overview
In step 1, you will install 3 critical tools:
- Tool #1: A Linux-based bash terminal (Windows Terminal + GitBash)
- Tool #2: GitHub Desktop
- Tool #3: Anaconda
------
# Tool #1: A Linux-based bash Terminal:
- Windows users will use a combination of GitBash and Windows Terminal. Windows Terminal comes pre-installed with Windows 11, but can be added to Windows 10.
- You should not use the
windows command prompt because the commands for working with your terminal will not match the curriculum and other cloud-based platforms (like Amazon Web Services).
- Note: for a list of the equivalent commands for Windows command prompt see [this cheat sheet](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/linux-vs-windows-commands/).
### Tool 1, Step 0: (Windows 10 Only) Install Windows Terminal via the Microsoft Store
NOTE: Windows 11 comes with Windows Terminal pre-installed. If you are running Windows 11, you can skip Step 0 and start with Step 1.
- For Windows 10 users, open your start menu using your Windows key or clicking on the Start Menu in the bottom left corner.

- Type "Store" with the start menu open and it will automatically start searching. You should see "Microsoft Store" appear.

- Click on the Microsoft Store app on the left or click "Open" on the right sidebar to open the Microsoft store.
- Once the Microsoft store opens, click on the Search box on the top of app.

- Enter "Windows Terminal" in the search box and you should see the Windows Terminal result appear with a blue "Get" button like in the screenshot below:

- Click on the blue "Get" button to start downloading the app.

- Once its done downloading, the blue "Get" button will become an "Open" button. Click on "Open" to confirm that Windows Terminal is properly installed.
- A new "Windows Terminal" window running Powershell should appear, like in the screenshot below:

- After confirming windows terminal is installed, click on the X in the top right corner to close the app. You are all set to move on to the next step!
------
### Tool 1, Step 1: Install Git for Windows
- Download the Git for Windows installer (https://gitforwindows.org/) and open it.
#### Select the same options as you see in the screenshots below:
- On the first page, make sure to UNCHECK "Only show new options" like in the screenshot below:

- Make sure to select the option pictured below "Add Git Bash Profile to Windows Terminal"!!

- Then select the default options for the remaining options (unless noted otherwise below):








- One non-default option that you may want to select is to "Enable symbolic links" in the screenshot below.
- This option will be helpful if you ever need to access data stored on a network drive. This will *not* be required for the program.


- TROUBLESHOOTING NOTE:
- If you see the following "Replacing in-use files" screen (screenshot below) about closing open instances of gitbash: close all other windows of GitBash.
- If it still shows items that are running that you cannot find, the easiest solution is to cancel the installation, restart your computer, and then open the installer again before opening any gitbash windows.

- Click install and wait for the process to finish. Next, move on to Tool #2: GitHub Desktop.
### Tool 1, Step 2: Make GitBash the Default Profile in Windows Terminal
- From your Windows Start menu, search for "Terminal" and open a new Windows Terminal window.
- It will open using the default shell "Powershell", pictured below:

- Click on the drop down arrow to reveal the menu.
- Select Settings

- The settings tab will open and should look like the screenshot below:

- Click on the drop down menu for the first option "Default Profile" and select GitBash

- Click the blue Save button in the bottom right corner.
### Tool 1, Step 3: Confirm that your default shell is set to GitBash
- To test if the default shell is now set to GitBash, open a new Terminal window.
- If you see a window like the one below that has the GitBash icon (the multicolored 4-squares in the top left corner), then you are all set!

- You're all set up with Windows Terminal and GitBash!
------
# Tool #2: GitHub Desktop
### Tool 2, Step 1: Install GitHub Desktop and Log Into GitHub Account
- Download the installer from this link: [GitHub Desktop](https://desktop.github.com/)
- Once installation is complete, open the application.
- Log into the same GitHub account you have been using for your projects.
### Tool 2, Step 2: Make Windows Terminal the Default Shell in GitHub Desktop
- Once you have logged into the app, open the Options menu.
- Click on `File` in the menu bar and then select `Options`

- Select the "Integrations" tab on the left sidebar of the Options window.

- Click on the drop-down menu for Shell and select Windows Terminal. (Windows 10 users, if you do not see this option, make sure you have followed Step 0 of these instructions. If you still do not see Windows Terminal as an option, please restart your computer and try again.)

- Click Save and the window will close.
- Click Save. You may close Github Desktop for now.
------
# Tool #3: Python Distribution - Anaconda
- Anaconda is a data-science-focused python distributable that comes with a convenient GUI program for working with our python environments.
### Tool #3, Step 1: Download and Install Anaconda
- Download and run the installer from the following link:
Anaconda Individual Edition
- Use the default options, EXCEPT when you see the "Advanced Installation Options" window (like in the screenshot below).
- Select "Add Anaconda3 to my Path environment variable". Disregard the warning message will appear in red text.
- BOTH options should be checked, like in the screenshot below:

### Tool 3, Step 2: Verifying that Terminal/GitBash Knows "conda"
1. Windows users may need to take an additional step to get anaconda and Terminal working together.
2. Open a new Terminal window from your start menu. It MUST be a new window
3. Enter the command `conda` and press enter.
1. If you see a list of available conda commands, great!
1. You are all set to move on to Step 2: "Setting Up Your `dojo-env`"
2. Disregard the final section below that says "Adding Conda to GitBash"
2. If you see a message that says: "bash: conda: command not found", then follow the instructions below under "Adding Conda to GitBash"
### Tool 3, Step 3 (if needed) Adding Conda to GitBash:
If a NEW terminal window recognized the conda command in Tool 3, Step 2 then you may skip this step!
Note: the instructions below are adapted from this [Blog Post](https://fmorenovr.medium.com/how-to-add-conda-to-git-bash-windows-21f5e5987f3d)
- Once you have installed anaconda, use File Explorer to Open Your User folder. (Windows key +E is shortcut for File Explorer)
- This is the folder that contains your Desktop, Downloads, My Documents, and other user-specific files.
- Example: `Users/your_name/`
- If you're having trouble finding your user folder:
- Go to This PC in File Explorer, and then double click on your C drive.
- Then double click the Users folder and then click on the folder that corresponds to your windows username.
- Inside your user folder, you should see a folder named "`anaconda3`" (note: not the hidden folder called `.anaconda` that starts with a `.`). Double-click the folder to open it.
- You should see a folder named `etc` inside the `anaconda3` folder. Open it.
- You should see a folder called `profile.d` folder inside the `etc`. Open it.
- You should see a `conda.sh` file in this folder (it may just say conda if your File Explorer is set to not show names for known extensions).
- (Note: depending on your setting in File Explorer, it may not show the .sh and may just show "conda", which is fine!)
- Right-click somewhere in the "profile.d" folder and select "Git Bash Here".
- Note for Windows 11 Users: "GitBash here" is going to appear in the "Show more options" sub-menu when you right-click
. 
- From the GitBash window that opens:
- Enter the command
```
pwd
```
and hit enter and examine the file path that's displayed
- If the file path displayed ends with `profile.d` then are in the right folder!
- If not, restart the "Adding Conda to GitBash" instructions again and make sure you can find your profile.d folder.
- Reach out to your instructor or a TA if you are still having issues.
- Next, Enter the following command and hit enter:
```bash
echo ". '${PWD}'/conda.sh" >> ~/.bashrc
```
- Open a new GitBash window and enter `conda` again.
- You should no longer get the "bash: conda: command not found" error message!
- Reach out to your instructor or a TA if you are still having issues.
> You are all set to move on to the next lesson "2. Setting Up Your dojo-env Environment"
# 2. Setting Up Your dojo-env Environment
## Step 2 Overview:
- In Step 1, we installed the foundational tools needed for our local python installation.
- While we did install a Python distribution with a basic copy of Python (Anaconda or miniforge), we have not installed all of the packages and tools that we need as data scientists.
- In Step 2, you will be creating a custom python environment called "dojo-env".
- An "environment" is a bundle of specific python packages that are used together. Importantly, an environment specifies specific version #'s of the packages to ensure that all of the versions installed are mutually compatible.
- You can install many environments on your computer and switch between them as needed for different projects.
- We have designed the dojo-env to include everything you'd need for our program, so you may not have a reason to add additional environments.
- The environment files (and a backup of these instructions) are in the [dojo-env-setup repository](https://github.com/coding-dojo-data-science/dojo-env-setup)
- The Detailed Instructions below will guide you through how to clone and use the environment setup repository.
## Brief Summary of the Following Steps:
- Step 2.1: Clone the dojo-env-setup repository
- Step 2.2: Open the repo in your terminal/GitBash
- Step 2.3: Create the dojo-env environment
- Step 2.4: Setting dojo-env as your default.
# Step 2.1 Clone the dojo-env-setup repository
1. Open the dojo-env-setup repository on GitHub.com:
1. https://github.com/coding-dojo-data-science/dojo-env-setup
2. Make sure that :
1. you are logged in to your account on GitHub.com
2. and you are logged into the SAME account in the GitHub Desktop app (that you installed in step 1.)
3. Click on the green `Code` button and then click `Open in GitHub desktop.`
1. GitHub desktop should open automatically and ask you what folder you would like to store your repository in.

**Troubleshooting Note: if you are brought to the Download GitHub Desktop web page instead:**
1. It means you were not logged into the same account on GitHub.com and GitHub Desktop when you clicked Open in GitHub Desktop.
1. Make sure you see your user profile pic in the top right of GitHub.com
2. and check your Account in GitHub Desktop's Preferences/Options menu.
3. and then try again.
1. By default, GitHub Desktop will use a new "GitHub" folder in your Documents folder
1. GitHub Desktop will create a NEW folder with the same name as the repository INSIDE of whichever folder you select.
2. If you use the default options, then this will create a "dojo-env-setup/" folder inside of "Documents/GitHub/"
3. Note: it is strongly recommended that you use the Documents/GitHub folder for this repository.
1. But if you'd rather save the folder somewhere else:
1. Use the "Choose" button (the button name may be "Browse" on Windows).
2. A window should pop up for you to find and click on the folder where you want to create the "dojo-env-setup" folder.
3. Once you have selected a new folder using the Browse button, you should see the full folder path displayed.
4. IMPORTANT STEP: Make sure to remember the full file path of the folder you selected!
(See the screenshot below. )
1. 
# Step 2.2: Open the Repo in Terminal(GitBash)
## Open the Repo in Terminal
Once you have cloned the repository, you will need to open a terminal/gitbash window in the same folder as the repository.
- Open a new terminal in the dojo-env-setup folder
- First, in GitHub Desktop: make sure the left sidebar says "dojo-env-setup" in the top-left corner under Current Repository.
- Click on the Repository menu and select "`Open in terminal`" or "`Open in gitbash`"
- Windows Users: the menu will be at the top of GitHub Desktop's window.
- Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut to do the same thing. The command for both Mac and Windows is:
- Control + ` (the key above tab that also has the tilde symbol ~)
- In the terminal window that appears, type the "pwd" command (stands for print working directory) and press Enter.
- It will display the folder name of the folder your terminal is currently located.
- The folder path should end in "dojo-env-setup/"
- If you used the default GitHub folder when you cloned dojo-env, the full filepath would be something similar to "/Users/yourname/Documents/GitHub/dojo-env-setup/"
### Troubleshooting (Windows):
If you are having trouble getting GitHub desktop to open GitBash in the correct folder there are 2 solutions for getting your gitbash window in the dojo-env-setup folder.
#### Solution #1: Using File Explorer + Right Click
If you followed the instructions in step 1 and used the default options when installing Git for Windows/GitBash, you should have a new option in your Right-Click menu that says "GitBash here".
- In GitHub Desktop click the Repository menu again and select "Show in File Explorer".
- Once file explorer opens, right-click anywhere inside the folder (right-click on empty space, not on a file) and select GitBash here.
- A GitBash window should open in the correct folder.
- Type pwd to confirm that you are indeed in the dojo-env-setup folder.
#### Solution #2: Open a new GitBash and navigate to the right folder.
If you do not have the option to "GitBash here", you can manually navigate there in GitBash.
- Open the windows start menu, find and click on GitBash to open a new window.
- Important Note: You must know the full file path for the repo for the next step. We will refer to as <repo_filepath> in the instructions below.
- if you used the suggested default folder
when cloning the repo, your repo_filepath should be:
- " /Users/<your name>/Documents/GitHub/dojo-env-setup"
- But instead of <your name> it will be your actual user name for your computer
- If you are not sure what your username is, run the "whoami" command in your GitBash to see your user name.
- If you did NOT use the suggested default folder,
- Your repo_filepath will be the path displayed in the window that appeared when you cloned the repo.
- You should have taken note of the file path you selected, as indicated in the screenshot.
- Once you know what your repo_filepath is navigate to that folder using the change directory command (cd)
- "cd <repo_filepath>".
- See the examples below:
```
## Examples are assuming your username is "codingdojo"
# Example if you used default folder:
cd /Users/codingdojo/Documents/GitHub/dojo-env-setup/
# Example if you used a different folder. e.g. you made a Boot Camp Stuff folder in your Documents folder.
cd /Users/codingdojo/Documents/Boot Camp Stuff/
```
## Verify Step 2.2
Run one last command to verify that you are indeed in the correct folder.
Run the "ls -a" command to see a detailed list of all files in the repo.
```
ls -a
```
You should see a list of all the files in the current folder.
If you are in the right folder, you should see 3 files that start with "environment" and end with ".yml" like in the screenshot below.

If so, you are all set for the next step: create the dojo-env environment!
2. # Step 2.3 Create the dojo-env environment
### 1) Create the dojo-env using the correct "conda create" command for your OS
- Run the conda env create command below in your Terminal
#### Windows
```
conda env create -f environment-ds_windows.yml
```
### Wait (patiently) for the dojo-env to be created.
- It can take anywhere from 3-45 minutes to finish creating the environment, depending on your computer and internet connection.
- You will see several progress bars during the process. Once it has been completed you should see a message that says
```
# To activate this environment use:
conda activate dojo-env
# To deactivate this environment use:
conda deactivate
# If conda deactivate doesn't work, activate the "base" env
conda activate base
```
- Confirm your environment was installed and activate it.
- Enter the following command to display the list of your locally installed environments.
```
conda env list
```
- You should see 2 environments, including dojo-env:
- `base`
- `dojo-env`
- If you see dojo-env in the list:
- Success! dojo-env was successfully created! But we aren't using it yet just yet. We must first "activate" an environment to determine which version of python & packages are currently being used.
- ### 2) Activate the dojo-env and Install the Env in Jupyter
- The first line in the code block below will switch to dojo-env.
- The second line will install dojo-env as an option in Juyter Notebook/Lab, which you will use instead of Google Colab when working locally.
```
conda activate dojo-env
python -m ipykernel install --user --name dojo-env --display-name "Python (dojo-env)"
```
## ✅ TO DO: ADD BETTER TIPS ON HANDLING CONDA ACTIVATE (the t.s. lesson)
**Troubleshooting:**
- If you see a message that says "your terminal is not set up for conda activate":
- [Recommended Solution] you should navigate to the Troubleshooting section on the course sidebar and follow the instructions on the "[Enable Conda Activate for GitBash](https://login.codingdojo.com/m/213/13547/107855)" page.
- [Alternative/Older Solution] Alternatively, you could use a slightly different command to activate your environment. Replace the word "conda" with "source"
```
source activate dojo-env
python -m ipykernel install --user --name dojo-env --display-name "Python (dojo-env)"
```
# Step 2.4: Setting dojo-env as the default + alias commands
- This section will require you to enter several commands in your Terminal (on Mac) or GitBash (on Windows).
- Make sure that your terminal is not running jupyter notebook (you can press "`Cntrl`+`C`" to force quit the server from your terminal).
- Alternatively, you can open a new terminal/GitBash. (You can perform these steps from any folder.)
------
# Part 1) Commands for Windows
### Determine if your PC Can Run "conda activate" or "source activate"
For windows computers, we need to determine if your computer uses the word "conda" or "source" to activate an environment.
You've already run this command before, but if you don't remember which command you ran:
- In a new GitBash window, enter the "conda activate base" or "conda activate dojo-env" command.
- If you see a message about your shell not being set up to run conda activate,
- You need to use the "1B) if your PC has to run source activate" section below
- If the conda activate command worked,
- Follow the "1A) If your PC ran conda activate" section below.
------
## 1A) If your PC can run "conda activate":
- Run the following commands to automatically activate dojo-env and to add shortcuts for Jupyter:
```
touch ~/.bash_profile
echo "conda activate dojo-env" >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'alias jnb="jupyter notebook"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'alias lab="jupyter lab"' >> ~/.bash_profile
```
- Finally, activate the new settings:
- - Run `source ~/.bash_profile` or open a new GitBash window to activate the changes you just made
- *Scroll down to the "Part 2) Final Verification Steps (Mac & Windows)" step.*
------
## 1B) If your PC has to "source activate":
- Run the following commands to automatically activate dojo-env and to add shortcuts for Jupyter:
```
touch ~/.bash_profile
echo "source activate dojo-env" >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'alias jnb="jupyter notebook"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'alias lab="jupyter lab"' >> ~/.bash_profile
```
- Finally, activate the new settings:
- - Run `source ~/.bash_profile` or open a new GitBash window to activate the changes you just made
- *Scroll down to the "Part 2) Final Verification Steps (Mac & Windows)" step.*
------
# Part 2) Final Verification Steps (Mac & Windows)
### Confirm `dojo-env` is your default
- To confirm that dojo-env is now your default environment:
- You should see `(dojo-env)` appear next to your prompt.

### Confirm the shortcut aliases work
- Try running the command "lab" in your terminal/kitbash.
- If jupyter lab launches, you're all set!
- If not, contact your instructor or a TA for assistance.
- Shut down jupyter from the terminal
- Return to your Terminal window that you used to start jupyter.
- Press Control+C to shut down the server.
- Respond "y" when asked to confirm.
## Note: you can still move on to the next step even if you could not successfully complete this step.
## The moment of truth...
You are all set for the next step: Testing Your New Environment!
# Step 2.5: Testing the Environment
To test that your installation and packages are working properly. We are going to run a specific Environment Testing notebook that is also located in the "dojo-env-setup" folder.
## Running the environment tester notebook with jupyter notebook
- Next, you will close all of your previous Terminal/GitBash windows BUT before you do:
- if your terminal is still running jupyter notebook and you do not see the prompt waiting for a command:
- You must press "Control +C" to force-quit jupyter.
- Make sure to reply "y" if asked for confirmation.
- If the cursor appears waiting for a new command, you are all set.
- Now, return to GitHub desktop and click on the "Open in Terminal/GitBash" to open a terminal in the dojo-env-setup folder.
- - Type pwd to confirm it says dojo-env-setup.
- Note: if you do not see the button for Open in Terminal:
- - Click on the menu for "Repository" at the very top of the window (if using Windows) or at the very top of your screen on your menu bar (if using a Mac).
- You should see the word "Repository" next to the FIle, Edit, View menus.
- - From the Repository menu: click on Open in Terminal/GitBash
- In the new window that opens, start jupyter notebook by entering the `jupyter lab` command in your terminal (or the "lab" shortcut!)
A new tab should open in your web browser that shows the File view for jupyter notebook.
You should see all of the files that were in the dojo-env-folder.

- There are 2 "EnvironmentTester" notebooks:
- "EnvironmentTester-mac.ipynb" for macs (both Intel and Apple Chip macs)
- "EnvironmentTester-windows.ipynb" for Windows.
- Click on the EnvironmentTester-mac.ipynb notebook to open it.
Once the notebook interface has loaded, you should see a toolbar with several menu choices.
## ✅ TO DO: NEW SCREENSHOTS

- We want to run all of the cells in this notebook and confirm it can make it to the end without errors.
- To Run the Entire Notebook:
- Select the "Kernel" Menu > "Restart and Run All"
- Wait patiently.
The testing notebook is going to run through several modeling and EDA steps to confirm that the packages are working correctly.
- This could take anywhere from 2-10 minutes to run.
- You will see the web browser tab icon turn to an hourglass when the notebook is running and back to an orange notebook icon when it is done.
- Scroll down to the bottom of the notebook and confirm the cells have run:
- Check if the very last cell printed the success message.

- If the entire notebook ran successfully
- Congrats! Your dojo-env is fully functional and you can move on to the next step/lesson!
- If your notebook did not run the entire notebook successfully:
- You need to contact your instructor or a TA for assistance.
- Before contacting them, please follow the instructions below to prepare the troubleshooting files to give to your instructor.
### To Get Help Troubleshooting Your Environment.
- There are 2 files that you should share with your instructor/TA
1. A copy of your Environment Tester notebook that error'd.
2. A copy of "FINAL_REPORT.txt" file that is in the Troubleshooting folder of the repo.
1. To share your notebook with an instructor/TA for help:
- Click File > Save & Checkpoint.
- Click File > Download As > Notebook (.ipynb)
- Your web browser should save a copy of the notebook to your normal "Downloads" folder.

2. To share a copy of your FINAL_REPORT.txt:
- In the first Files tab that opened when you started jupyter notebook you should see a folder called "Troubleshooting"
- Click on the Troubleshooting folder.
- Inside the folder you should have a file called "FINAL_REPORT.txt".
- Check the checkbox next to the file and click on the "Download" button that appears at the top of the list of files.
- Your web browser will also save this file to your Downloads folder.

- Send an email to your instructor
- Attach the 2 files listed above. They are located in your Downloads folder.
- Add any additional details or info you think may be helpful for us to know.
- For example:
- "my computer is really old and I think that may be part of the problem."
- "I share this computer with someone else who also uses python"
- An instructor or TA will get back to you within 1 business day with the next steps for you to try.
- You will most likely need to set up a Zoom call and share your screen for us to help.
# Step 3: Install a Code Text Editor
## Visual Studio Code
- The final tool to install is a text editor that is designed for programmers.
- There are several text editors available, but we will be using Visual Studio Code.
- Visual Studio Code (A.K.A "VS Code")
is a free editor that is highly customizable and supports many languages.
- It is maintained by Microsoft and has a robust community of extensions and add-ons.
- It is very popular and is used by many companies (e.g. Facebook/Meta)
- How will we use VS Code?
- We could technically run all of our jupyter notebooks using VS Code, but this is not recommended at this point in your education.
- While VS Code is convenient for quickly opening and working with a repository or viewing a notebook, it has some limitations in how notebooks look and some quirks to the interface for notebooks.
- Instead, we will focus on using
jupyter notebook or jupyter lab in the lessons and live class.
- You are welcome to try VS Code for notebooks, but it is recommended you become comfortable with jupyter first.
- We will use VS Code for editing simple code files or hidden files.
- We can open and edit the settings file for your terminal (e.g.: "`~/.bash_profile"`.or "~/.zshrc"
- We will use it to create and store credentials for APIs (Stack 4)
- We can use VS Code to edit your projects' README files while previewing them in real time!
- Finally, while beyond the scope of the standard curriculum, we can also use VS Code to store functions in external files that we can use just like pandas, matplotlib,
## Install Visual Studio Code
- Go to https://code.visualstudio.com/
- It should auto-recognize your OS and have a blue Download button with a version for your OS.
- Click Download to download the installer.
- Click on the installer to run it.
- Select the default options.
- Once Visual Studio Code installation is completed, open it!
- Check your Start Menu to find Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
## Install Python Extensions
- On the left sidebar, there are several icons for different menus.
- Click on the Extensions sidebar icon (5th down, looks like 4 squares).
- On the Extension sidebar, there will be several sections (INSTALLED/POPULAR/RECOMMENDED).
- Right now you should have nothing under the INSTALLED menu.
- You should see "Python" listed under POPULAR.
- If not, you can enter "Python" in the search box at the top of the sidebar
- OR you can click on [this link to the extension ](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-python.python)on the extension marketplace website.
- Click on the "Install" button for the Python extension.

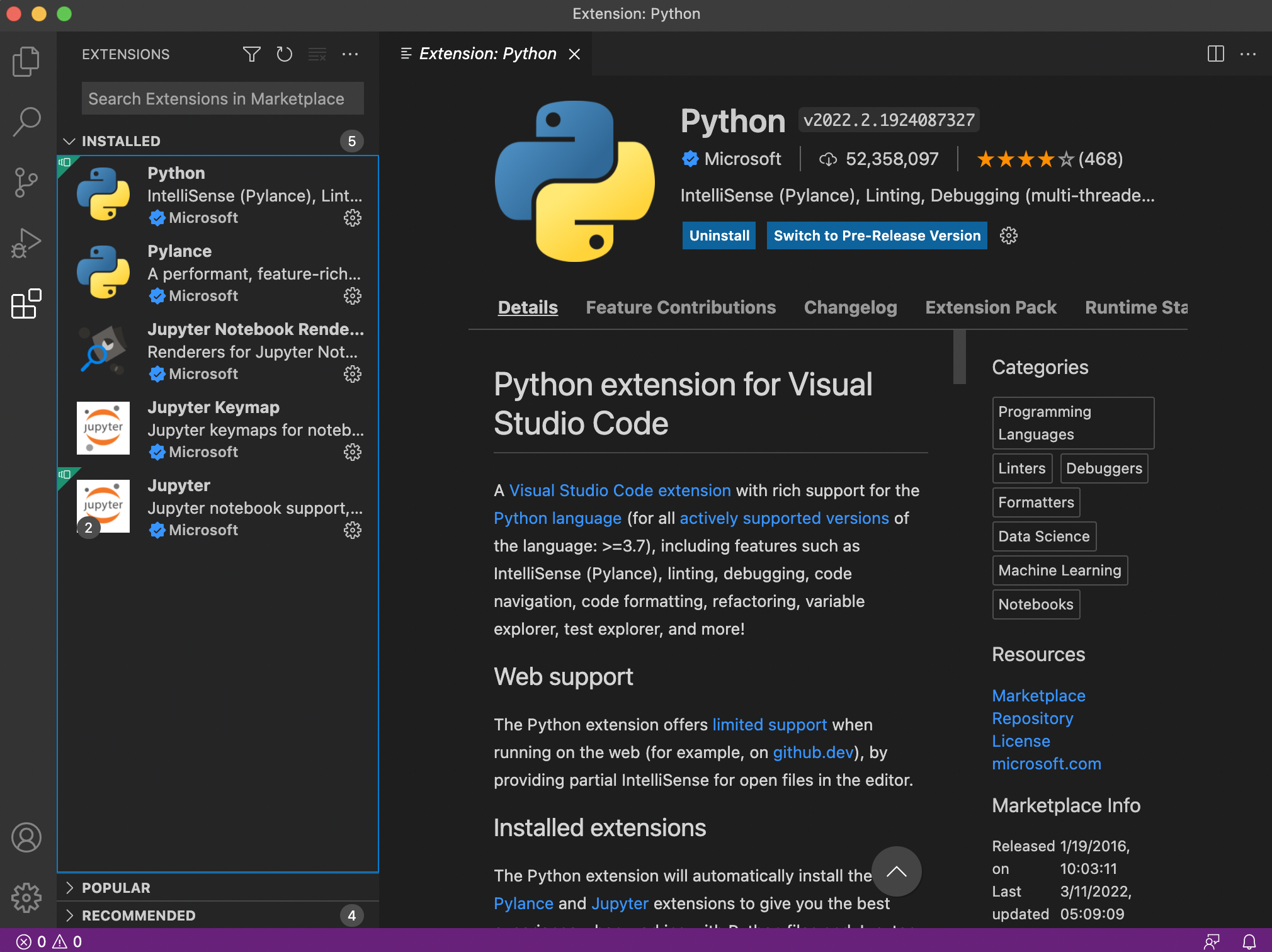
- Note: the Python extension will also install several required extensions. When installation is complete, you should see the following under the "INSTALLED" section:
- Python, Pylance, Jupyter Notebook renderer, Jupyter, and Jupyter Keymap
## Setting VS Code to use your `dojo-env` as the default Python installation
- We must teach the Python extension where to find our `dojo-env`'s version of Python.
- On the extension sidebar, click on the Gear icon for the Python extension and select "Extension Settings" 
- You should see a new "Settings" pane open in the main window.
- Take note of the "Default Interpreter Path".
- It is currently set to just "python".
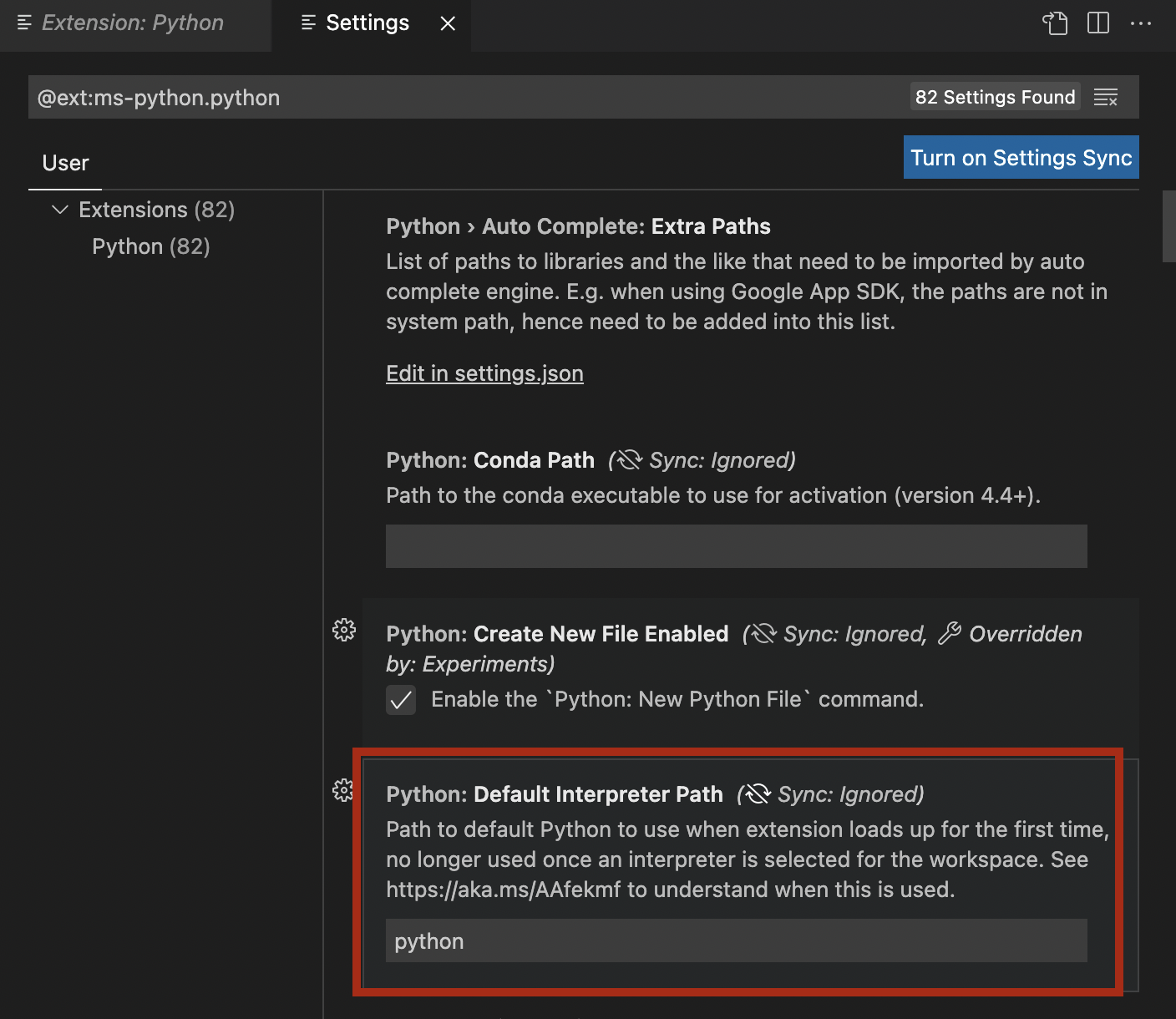
- We need to change this setting to match the exact filepath for our `dojo-env`'s python.
- In your terminal or GitBash:
- Make sure your dojo-env is activated
- Run the command:
```
which python
```
- It will print out a filepath to your dojo-env.
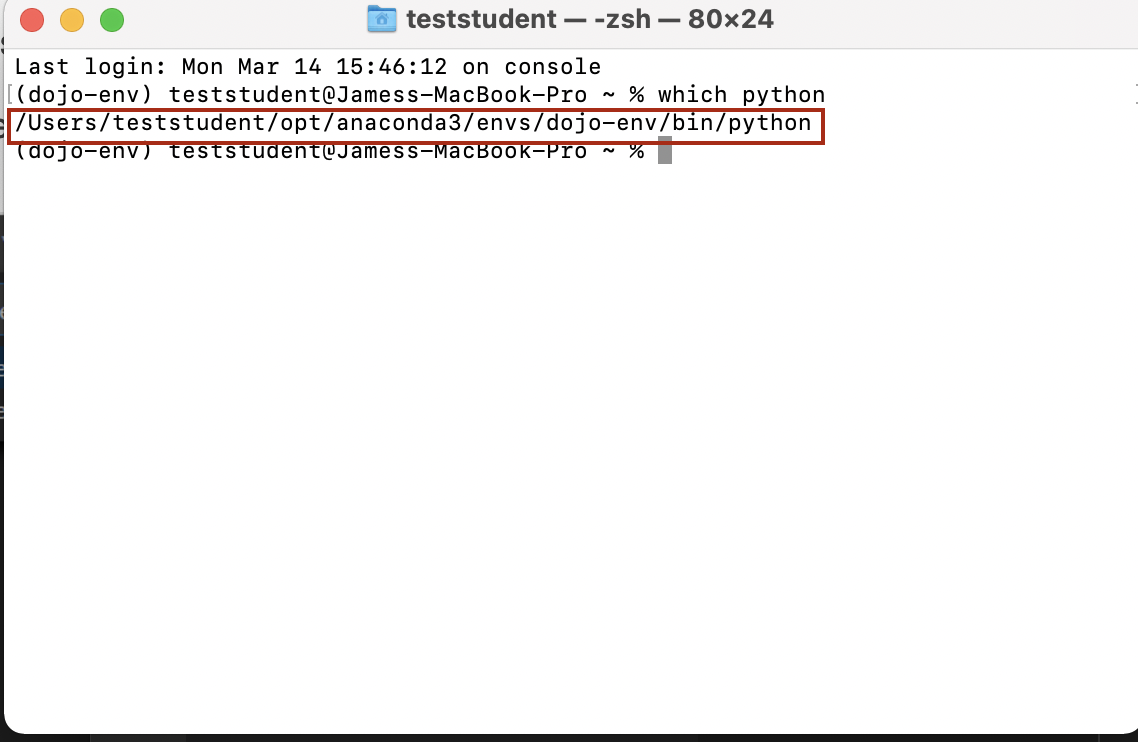
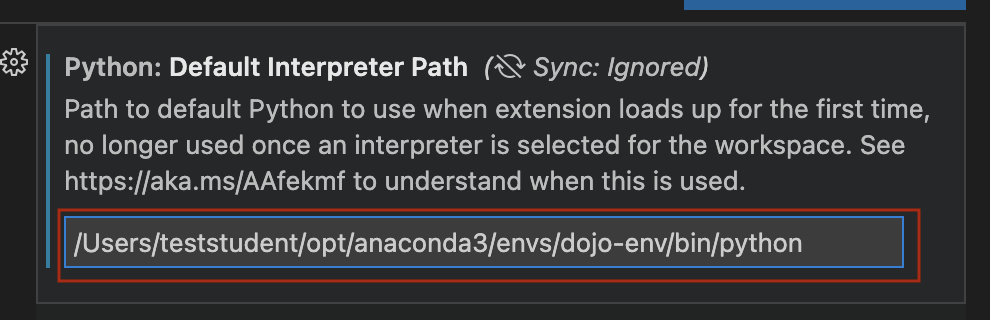
- Copy and paste that exact file path into the "Default Interpreter Path" field in the Python extension settings.
### Test the `code` command
- Open a new terminal or GitBash window.
- Run the command `code` to verify that VS Code opens.
- Note: You can add a specific folder or filename to open, after the word code.
- To open the current folder `code .`
- If it opens, great!
- If not, make sure you've opened a new terminal window AFTER installing the code command.
> Congratulations! You are all set up with your local python environment!
> You may want to read the Final Notes + Appendix lesson so that you are aware of the contents, in case you need them.
# Final Notes
##
Congrats! You've got a fully functional professional data science environment on your local machine!
- Please see the next chapter "Working Locally" for:
- a walkthrough of how to use your new local installation and tools together
- a summary of terminal commands
- jupyter notebook chgeat sheets
- how to install additional packages
- & more!
- Please see the "Troubleshooting" chapter for commonly encountered errors and any known solutions. including:
- Reinstalling your dojo-env
- "code" command not working
- GitBash "Could not fork child process" error
**Updating to New dojo-env**
- If you have already installed your dojo-env and wish to update to the new version, you must first remove the current dojo-env from your computer.
- Note: the new version of dojo-env was released in July 2022. If you installed your environment in July or later you already have the updated dojo-env.
- The benefits of upgrading to the new dojo-env:
- New sklearn v1.1 with simplified column transformer feature names!
- Jupyter Lab added
- - New Packages and Tools Included:
- - nbdime: Version control for jupyter notebooks.
- Model Explainer Packages (SHAP, Lime, Yellowbrick)
- Stack 2 & 3 Packages Previously Not Included:
- Tensorflow
- xgboost
- lightbgm
- Pandas Profiling (incredibly powerful all-in-one EDA report)
- Time Series Modeling:
- pmdarima
- prohpet
- sktime (though still some issues to resolve)
- And more!
#### IMPORTANT NOTE FOR MAC USERS WITH AN APPLE CHIP (M1, M1Pro, M2, etc)!
The original v1 of dojo-env did not fully support Apple processors, but the new dojo-env does. HOWEVER, in order to do so, Mac users with an Apple chip need to UNINSTALL ANACONDA and switch to using Miniforge.
Please see "Step 1 - MacOS (Apple Chip)" and scroll to the bottom for the UNINSTALLING ANACONDA instructions.
IT IS CRITICAL THAT YOU DO THIS OR IT MAY PERMANENTLY BREAK YOUR ENVIRONMENT!
> NOTE: there is an abbreviated summary of commands for this process at the bottom of this page for convenience.
## Step 1: Remove Your Old dojo-env
- 1. Open your terminal/GitBash
2. Deactivate
```
dojo-env
```
:
1. Type
```
conda activate base
```
(or source activate base if you are on older versions of windows)
1. Your terminal should now say `(base)` next to your prompt instead of `(dojo-env)`.
3. Remove the old `dojo-env` using the command:
```
conda remove --name dojo-env --all
```
Enter `y` to approve the removal of the environment and hit enter.
4. Wait for the env to be removed.
This will delete all of the files associated with JUST our `dojo-env`.
Anaconda & GitBash will still be installed. We will just need to re-install our `dojo-env`
## Step 2: Clone the updated dojo-env-setup repo
1. To avoid merge conflicts when pulling the updated repository,
you should remove your old clone of the dojo-env-setup repo
and then clone it again.
1. In GitHubDesktop, switch to the dojo-env-setup repository in the Current Repo drop down menu (top left). Once you're in dojo-env-setup, click on the "Repository" menu and select "Remove" > check Move to Trash/Recycle Bin.
2. Navigate to the dojo-env-setup repo: https://github.com/coding-dojo-data-science/dojo-env-setup
3. Clone the Repository to Your Computer:
1. Click the green Code button and select "Open in GitHub Desktop. "
2. If you still have your previously cloned copy, GitHub Desktop should show a # and down arrow on the top right corner where it should say "Fetch Origin".
1. Press the button to "Fetch Origin", which will download the updated environment files.
2. You may need to press it again if it changes to "Pull Origin"
3. If you've updated the repo successfully there should be no remaining #'s or arrows on the top right corner.
1. If so, click on the Repository menu > Open in Terminal (or Open in GitBash).
## Step 3: (Re)Create Your dojo-env using the updated repo
1. Run the same commands from the original step "2. Setting Up Your
```
dojo-env
```
Environment" (summarized below).
1. If you are unsure about which version of the summary instructions below to use, please go to the original Step 2 lesson for your specific OS and follow those steps again.
2. "Step 2: Setting Up Your Dojo-Env" Summary:
1. Depending on your OS and processor, you will use a different environment file in the conda env create command.
1. In the table below find the environment yml file name that is correct for your computer/OS.
Note: Whenever the instructions below refer to your <ENV_FILE> below, it means the filename from the following list (without < >).
| Computer/OS Type | Environment File Name |
| -------------------------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| Windows | environment_windows.yml |
| MacOS with an Intel Processor | environment_mac_intel.yml |
| MacOS with an Apple Chip (m1, m1pro, m2,etc) | environment_mac_mchip.yml |
- Make sure you are still using a terminal inside the folder for the dojo-env-setup (pwd)
- Run the following command (replace <ENV_FILE> with your filename from the table above)
```
conda env create -f <env_file>
## Env Creation Commands by OS
# Windows
conda env create -f environment_windows.yml
# Mac - Intel Processor
conda env create -f environment_mac_intel.yml
# Mac - Apple Chip
conda env create -f environment_mac_mchip.yml
```
- Wait (patiently) for the dojo-env to be created.
- Note: the new environment includes many additional tools and can take anywhere from 3-20 minutes to finish downloading and installing the packages for the new environment.
- Once its complete, run the following "conda activate dojo-env" command:
```
conda activate dojo-env
```
- Note for Windows users:
- if you see a message that says "your terminal is not set up for conda activate", change the command to "source activate"
```
source activate dojo-env
```
- You should now see "(dojo-env)" next to your prompt in your terminal (may be above the prompt, on the left, or on the right depending on your OS)

- After confirming you now see (dojo-env) displayed next to your prompt:
- Run the following command to make sure Jupyter Notebook/Lab knows your new environment.
```
python -m ipykernel install --user --name dojo-env --display-name "Python (dojo-env)"
```
##
## Testing Your New Environment
- From the same terminal window, start jupyter notebook (run `jupyter notebook` in your terminal)
- Open the test notebook for your OS (windows vs mac).
- EnvironmentTester-Mac.ipynb or EnvironmentTester-Windows.ipynb
- Select the Kernel Menu > Restart and Run All.
- The notebook should run all the way to the end.
- If it doesn't, contact your instructor for assistance.
## Bonus: Jupyter Lab
Your new dojo-env also includes jupyter lab. It is very similar to jupyter notebook, but has a more fleshed out user interface that is more similar to Colab than jupyter notebook.
To start jupyter lab run the following command:
```
jupyter lab
```
#
# Cheat Sheet/Summary Steps
1. Clone repo or Fetch & Pull: [https://github.com/coding-dojo-data-science/dojo-env-setup
](https://github.com/coding-dojo-data-science/dojo-env-setup)
2. Open in Terminal/GitBash.
Execute the following commands:
```
## 1. Deactivate dojo-env
conda activate base
# Windows users may need to use "source activate base"
## 2. Remove dojo-env
conda remove --name dojo-env --all
# press y to confirm
## 3. Create new environment
# run ONE of the following (depending on you computer)
conda env create -f environment_mac_mchip.yml
conda env create -f environment_mac_intel.yml
conda env create -f environment_windows.yml
## Wait patiently, once completed, activate new env
conda activate dojo-env
# windows users may need "source activate dojo-env"
## Add dojo-env kernel to jupyter
python -m ipykernel install --user --name dojo-env --display-name "Python (dojo-env)"
## Boot up jupyter notebook
jupyter notebook
# OR If you previously follwed "3. Setting dojo-env as your default"
jnb
## Read Final step below code cell
```
- Final step:
Open and run the appropriate environment testing notebook for your OS:
- "EnvironmentTester-mac.ipynb"
- "EnvironmentTester-windows.ipynb"
- Notify a TA or instructor if the notebook does not successfully run ALL cells.
## Enjoy your new dojo-env!
#