# Overcoming the fear of development on Blockchain
Jirka Chadima, @jirkachadima
---
## Why Blockchain?

Block: hash of a previous block, timestamp and transaction data
---
## Where do the blocks come from
- Miners and incentives
- Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, ...
- Consensus
---
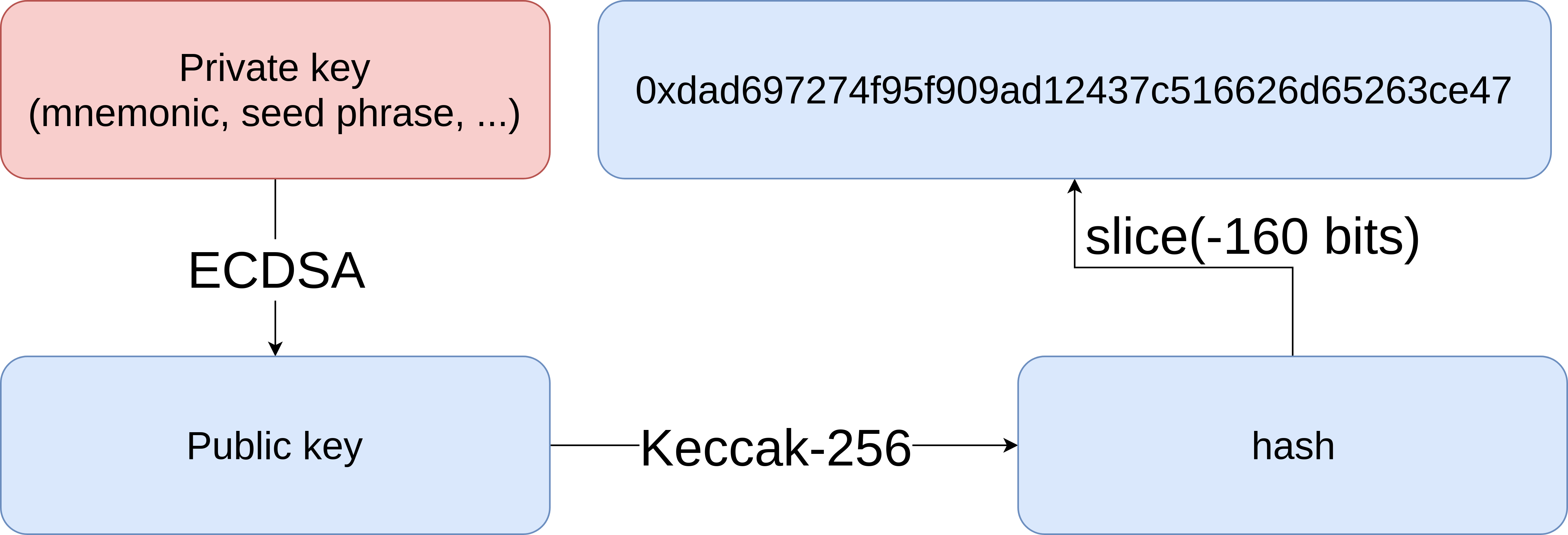
## Ethereum address
For a given private key, `pr`, the Ethereum address `A(pr)` (a 160-bit value) to which it corresponds is defined as the right most 160-bits of the Keccak hash of the corresponding ECDSA public key.
---
---
## What is a transaction
- `from` - Ethereum address
- `to` - Ethereum address
- `nonce` - ordinal of a transaction of the `from` address
- `value` - amount of Ether
- `data` - arbitrary message, function call, ...
- `gasLimit` - Maximum gas that is allowed to be spent
- `gasPrice` - How much am I willing to pay for unit of gas
---
## What the hell is gas?
Every operation costs something. That cost is represented in gas units.
Every transaction does some operations. The gas required is the total amount of gas needed for all the operations in the transaction.
---
## EVM
## (Ethereum Virtual Machine)
---
## Why would I be a miner?
As a reward, I get the gas from the transactions from the blocks I mine!
---
## Transact Ether
Send a transaction with non-zero `value`, some `gas` and no `data`.
---
## Smart contracts
Code that is deployed to a network and can be run by the EVM in a transaction, thus changing the state of blockchain.
---
## ABI
## (Application Binary Interface)
A list of methods available on a smart contract. You need an ABI it to properly call a smart contract.
---
## Deployment
1. Compile
2. Get Bytecode and ABI
3. Send a deployment transaction with the bytecode
4. Use ABI to construct a transaction that uses the bytecode
---
```json=
...
{
"constant": false,
"inputs": [
{
"internalType": "address",
"name": "organization",
"type": "address"
},
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "value",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"name": "addDeposit",
"outputs": [],
"payable": false,
"stateMutability": "nonpayable",
"type": "function"
},
...
```
---
## Transaction on a smart contract
Encode method signature and its arguments (based on the ABI), and you end up with a transaction `data`.
---
## DEMO TIME
https://remix.ethereum.org/
---
## Want more?
- https://www.ethereum.org/developers/
- https://eth.build/
- https://remix.ethereum.org/
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-15T01:22:58.287Z","metaMigratedFrom":"YAML","title":"Overcoming the fear of development on Blockchain","breaks":true,"slideOptions":"{\"theme\":\"white\",\"spotlight\":{\"enabled\":true}}","contributors":"[{\"id\":\"c2fca17c-7625-421a-9759-954f6dce6bc7\",\"add\":3686,\"del\":901}]"}