###### tags: `OCE_SQL`
# 資料庫結構化查詢語言 - 補充資料
## Concept Map

## 參考資料
[Oracle SQL Language Reference 12c Release 2 (12.2)](https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/12.2/sqlrf/)
[SQL Fundamentals Learning Path, Oracle Learning Library](https://apexapps.oracle.com/pls/apex/f?p=44785:50:5931274687897:::50:P50_COURSE_ID,P50_EVENT_ID:466,6365)
[Sample databases and schema diagrams](https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/21/comsc/schema-diagrams.html#GUID-D268A4DE-BA8D-428E-B47F-80519DC6EE6E)
## WS1 - L3 Restricting and Sorting Data
### Row Limiting Clause
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/SQLRF/statements_10002.htm#BABBADDD
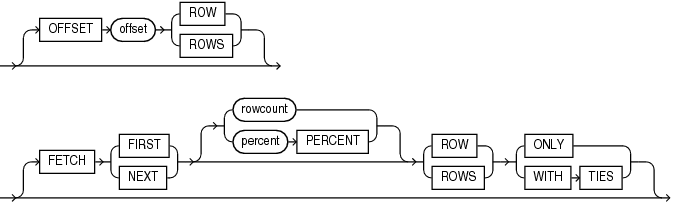
```sql=
create table demo_grades (grade number);
-- populate the data
begin
for i in 1..100 loop
INSERT into demo_grades(grade) values(i);
end loop;
for int in 1..3 loop
insert into demo_grades(grade) values(80);
end loop;
end;
/
commit;
select * from demo_grades
order by grade desc
offset 11 ROWS
FETCH FIRST 10 rows WITH ties;
```
執行結果 13 rows
```
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
80
80
80
```
### P3-33 Single Ampersand (&)
替代變數,若不存在(先前沒有 define),會要求使用者輸入,用完後即丟棄。
### P3-33 Double Ampersand (&&)
Using a double ampersand in front of a substitution variable to define that variable for the duration of the session.
This is useful when you need to reference a variable several times in one script, because you don’t usually want to prompt the user separately for each occurrence.
### P3-41 `define` and `undefine` sqlplus commands
用 define 去定義一個替代變數及初始值。
每當執行 script ,SQLPlus 或 SQLDeveloper 都會使用先前用 define 命令建立的替代變數(格式為&variable或&& variable)的值,不會再要求使用者輸入。
Example:
```sql=
define tgt_salary = 10000
select employee_id, salary from employees
where salary > &tgt_salary;
undefine tgt_salary
```
## WS1 - L4 Using single-row functions to customize outputs
### Concepts

### change the data type by the single-row function
Use single-row function to change the data type of the input variable.
```sql=
select
case when salary >= 10000 then 'High'
when salary < 10000 then 'Low' end salary_grade
from employees;
```
Parts of the Outputs

### Comparing RR and YY formats
```sql=
-- Comparing RR and YY formats
select to_char(to_date('01-01-90', 'dd-mm-rr'), 'dd-mm-yyyy') "RR format",
to_char(to_date('01-01-90', 'dd-mm-yy'), 'dd-mm-yyyy') "YY format"
from dual;
```

### Date and timestamp for the client and server
Date and timestamp functions:
date/timestamp | Server | client |
--|--|--|
date | sysdate | current_date
timestamp | systimestamp | current_timestamp
```sql=
-- https://database.guide/how-to-return-a-list-of-valid-time-zones-in-oracle-database/
-- V$TIMEZONE_NAMES displays valid time zone names.
SELECT * FROM V$TIMEZONE_NAMES
where tzname like '%Taipei%' or tzname like '%Japan';
-- Asia/Taipei
select SESSIONTIMEZONE FROM DUAL;
-- Change to Japan
alter session set TIME_ZONE = 'Japan';
select systimestamp "Server timestamp",
current_timestamp "Client timestamp" from dual;
```

### Use ROUND and TRUNC on DATE
ROUND API ref: https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/12.2/sqlrf/ROUND-date.html#GUID-C6D342D0-6068-4986-A759-70EF4599EC41
TRUNC API ref: https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/12.2/sqlrf/TRUNC-date.html#GUID-BC82227A-2698-4EC8-8C1A-ABECC64B0E79
### Use NEXT_DAY function
P4-35
API Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/12.2/sqlrf/NEXT_DAY.html#GUID-01B2CC7A-1A64-4A74-918E-26158C9096F6
```sql=
select add_months('20-Feb-22', 3) "Eval Anchor Day",
next_day(add_months('20-Feb-22', 3), 'Friday') "Eval Day"
from dual;
```
### 回顧練習
找出薪水前 20% 的員工,顯示他們的員工編號, 薪水及工作年資。工作年資欄位以月為單位,個位數4捨5入。
### 挑戰練習
員工自到職日後每滿 6 年的最近一次星期五要被 review, 請 report 每個員工最近一次的 review 的日期。
第一個欄位: 使用 months_between 計自兩個日期間的月份數
第二個欄位: 算出員工應 review 的週期(6年(72月) 的倍數)
第三個欄位: 算出員工下一次 review 的日期
第四個欄位: 算出員工下一次 review 的星期五日期
```sql=
select hire_date,
months_between(sysdate, hire_date)/72 "Years",
ceil(months_between(sysdate, hire_date)/72) "Review Cycle",
add_months(hire_date, 72 * ceil(months_between(sysdate, hire_date)/72)) "The next 6 years",
next_day(add_months(hire_date, 72 * ceil(months_between(sysdate, hire_date)/72)), 'Fri') "Review Date"
from employees;
-- 使用 with clause 重構上面的查詢
with work_year as (
select hire_date, months_between(sysdate, hire_date)/72 work_year
from employees
), review_cycle as (
select hire_date, work_year, ceil(work_year) review_cycle
from work_year
), next_6_years as (
select hire_date, review_cycle, add_months(hire_date, 72 * review_cycle) next_6_years
from review_cycle
), review_date as (
select hire_date, review_cycle, next_6_years, next_day(next_6_years, 'Fri') review_date
from next_6_years
) select * from review_date;
```
### 挑戰練習
員工每滿 2 年的所在月份的最後一天要交評估報告
列出每位員工的最近下一次的評估報告日期
```sql=
select employee_id,
hire_date,
ceil(months_between(sysdate,hire_date)/12/2) "Next Cycle",
add_months(hire_date, ceil(months_between(sysdate,hire_date)/12/2) * 24) "Next Evaluate Date",
last_day(add_months(hire_date, ceil(months_between(sysdate,hire_date)/12/2) * 24)) "Report date"
from employees;
```
## WS1 - L5
### P5-11 `to_char()` 參數的 auto type conversion
```sql=
select to_char('12a3', '999.00') from dual;
```
第一個參數的文字被嘗試轉換到數字, 但轉換失敗:
```
ORA-01722: invalid number
01722. 00000 - "invalid number"
*Cause: The specified number was invalid.
*Action: Specify a valid number.
```
### P5-11 格式化輸出時,日期及周天格式長度固定,內容靠右,左邊補白
```sql=
select to_char(hire_date, 'Month-Day') "Month-Day",
length(to_char(hire_date, 'Month-Day')) "Length"
from employees
order by 1 desc;
```
### P5-11 `fm` modifier 的使用
```sql
alter session set nls_language = 'American';
select first_name, to_char(salary, '$000,999.00') salary
from employees;
-- Oracle uses trailing blank characters and leading zeroes to fill format elements to a constant width.
-- For example, the largest lengh in month elements is SEPTEMBER.
-- The FM modifier toggles the padding in the return value of the TO_CHAR function.
-- FM = Fill Mode (Remove padded blanks or supress leading zeros
-- Use the fm modifier to toggle the fill mode. The default to the fill mode is on.
select first_name, to_char(hire_date, 'YYYY-Month-DD') "Date without fm modifier"
, to_char(hire_date, 'YYYY-fmMonth-fmDD') "Date with fm modifier"
, to_char(salary, '999,999') "Salary without fm modifier"
, to_char(salary, 'fm999,999') "Salary with fm modifier "
from employees;
```

See: [Format Model Modifiers | Format Models](https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28286/sql_elements004.htm#SQLRF00216)
### P5-17 數字格式化練習
```sql=
-- P5-17 數字格式化練習
select to_char(salary, 'L99,999') "Salary",
to_char(commission_pct, 'B9.00') "Commision",
to_char(salary * (1+commission_pct), 'L09,999.00') "Salary with Comm"
from employees;
select nvl(commission_pct, 'No Value')
from employees;
```
[Number format model](https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/sql_elements004.htm#i34570)
### P5-24 The return data type of the `NVL` function
底下有兩個 NVL 的使用例子, 為何第一個例子成功, 第二個失敗呢?
```sql=
select employee_id, first_name, nvl(commission_pct, '0')
from employees;
```
Reports:

```sql=
select employee_id, first_name, nvl(commission_pct, 'Empty')
from employees;
```
Reports:
```
ORA-01722: invalid number
01722. 00000 - "invalid number"
*Cause: The specified number was invalid.
*Action: Specify a valid number.
```
### P5-27 練習: the use of NULLIF function
Selects those employees from the sample schema hr who have changed jobs since they were hired, as indicated by a job_id in the job_history table different from the current job_id in the employees table:
Ref: [ NULLIF @ SQL Language Reference](https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/12.2/sqlrf/NULLIF.html#GUID-445FC268-7FFA-4850-98C9-D53D88AB2405)
```sql=
SELECT e.last_name, NULLIF(j.job_id, e.job_id) "Old Job ID"
FROM employees e, job_history j
WHERE e.employee_id = j.employee_id
ORDER BY last_name, "Old Job ID";
```
Reports:
```
LAST_NAME Old Job ID
------------------------- ----------
De Haan IT_PROG
Hartstein MK_REP
Kaufling ST_CLERK
Kochhar AC_ACCOUNT
Kochhar AC_MGR
Raphaely ST_CLERK
Taylor SA_MAN
Taylor
Whalen AC_ACCOUNT
Whalen
```
or
```sql
select employee_id, nullif(j.job_id, e.job_id) "Old Job", j.start_date "Job Start Date"
from employees e join job_history j using (employee_id)
order by 1;
```
### P5-29 Coalesce
The following example uses the sample oe.product_information table to organize a clearance sale of products.
It gives a 10% discount to all products with a list price. If there is no list price, then the sale price is the minimum price. If there is no minimum price, then the sale price is "5.
(Src: https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/23/sqlrf/COALESCE.html)
```sql=
SELECT product_id, list_price, min_price,
COALESCE(0.9*list_price, min_price, 5) "Sale"
FROM product_information
WHERE supplier_id = 102050
ORDER BY product_id;
PRODUCT_ID LIST_PRICE MIN_PRICE Sale
---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1769 48 43.2
1770 73 73
2378 305 247 274.5
2382 850 731 765
3355 5
```
### P5-33 Inconsistent data types in the Case Expression
Inconsistent data type in the `WHEN` clause:
```sql=
-- Trap: Inconsistent data between the expr and comparison_expr
-- ORA-00932: inconsistent datatypes: expected CHAR got NUMBER
-- No implicit conversion in the CASE express
select last_name, job_id, salary,
( case job_id
when 'IT_PROG' then salary * 1.1
when 'ST_CLERK' then salary * 1.05
when 100 then salary * 1.05
ELSE salary * 1.01
end
) "Revised Salary"
from employees;
```
Inconsistent data type in the `THEN` clause:
```sql=
-- Trap: Inconsistent data types in return expression
-- ORA-00932: inconsistent datatypes: expected CHAR got NUMBER
select last_name, salary,
( case when salary < 5000 then 'Low'
when salary < 10000 then 'Medium'
when salary < 20000 then 2
else 'Excellent'
end
) qualified_salary
from employees;
-- Another example
-- The first return expr is the data type to return
-- ORA-00932: inconsistent datatypes: expected NUMBER got CHAR
select last_name, salary,
( case when salary < 5000 then 100
when salary < 10000 then 200
when salary < 20000 then 300
else 'Excellent'
end
) qualified_salary
from employees;
```
Return nulls in the `THEN` and `ELSE` clauses:
```sql=
-- Q: Is the following statement correct?
-- The statement is ok.
select last_name, job_id, salary,
( case job_id when 'IT_PROG' then null
when 'ST_CLERK' then null
when 'SA_REP' then null
else null
end
) qualified_salary
from employees;
```
### P5-36 練習 Case Expression
```sql=
-- P5-26 Case example
create or replace function seniority(p_hire_date date) return number
as
begin
return round(months_between(sysdate, p_hire_date)/12, 0);
end;
/
select employee_id "Emp_id", salary "Salary",
seniority(hire_date) "Seniority",
case when seniority(hire_date) <= 5 then 1000
when seniority(hire_date) <= 10 then 3000
when seniority(hire_date) <= 15 then 6000
else 9000
end "Subsidy"
from employees
order by 3 desc;
```
### P5-37 Inconsistent return types in the DECODE function
Feature of the DECODE function
1. Only equal comparisons
2. Returned data types have to be consistent.
The following query is OK:
```sql=
select last_name, job_id, salary,
( decode( job_id, 'IT_PROG', salary * 1.2,
'ST_CLERK', salary * 1.1,
1.05
)
) revised_salary
from employees;
```
The following codes are OK.
`decode` 回傳的資料型態為 `char`, 由第一個回傳值決定.
第二及第三個回傳值的資料型態雖不一致, 但自動型態轉換可以成功.
Number and date can be converted to char:
```sql=
select last_name, job_id, salary,
( decode( job_id, 'IT_PROG', 'A',
'ST_CLERK', salary * 1.1,
to_date('01-01-2019', 'DD-MM-YYYY')
)
) revised_salary
from employees;
```
The following codes are NOT OK.
'A' and date cannot convert to number
```sql=
select last_name, job_id, salary,
( decode( job_id, 'IT_PROG', salary * 1.1,
'ST_CLERK', 'A',
to_date('01-01-2019', 'DD-MM-YYYY')
)
) revised_salary
from employees;
```
## WS1-L6 Reporting Aggregated Data Using the Group Functions

### P6-6 LISTAGG 群函數的使用範例
製作每個部門的員工清單, 員工以 hire date 排序
```sql=
select department_id,
Listagg(first_name, ', ') within group (order by hire_date) as "Emp_List"
from employees
group by department_id;
```

語法:

### P6-15 在 Group By 子句中使用 expression
Group By 子句內可使用 column 或者 expression.
```sql=
select case when salary between 0 and 4999 then 'C'
when salary between 5000 and 9999 then 'B'
when salary >= 10000 then 'A' end "Salary Grade",
count(employee_id) "# of Emp"
from employees
group by case when salary between 0 and 4999 then 'C'
when salary between 5000 and 9999 then 'B'
when salary >= 10000 then 'A' end
order by 1;
```

注意:
1. Group By 中使用的 express 的回傳值要和 select list 中的 expression (group expression) 要一致。否則產生錯誤:
`ORA-00979: not a GROUP BY expression`.
2. Group By 子句中不接受 column alias 或者 column numeric position:
```sql=
-- Cannot use the column alias in the GROUP BY clause
-- ORA-00904: "GROUP_ID": invalid identifier
select floor(emp.salary/1000) group_id, round(avg(emp.salary), 2) avg, count(round(emp.salary/1000, 0)) n
from employees emp
-- group by 子句錯誤
group by group_id
order by 1;
```
### P6-23 在 Having 子句使用非 group column 或 group measure 時產生的錯誤
`salary` 欄位不是 group column, 所以不能出現在 HAVING 子句中:
```sql=
select department_id, avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
having salary > 10000;
```

## WS1-L7 Display data from multiple tables using joins

### Inner 及 Outer join 的差異
Emp table join Dept table:

### P7-10 Natural Join 找兩個表格中名稱相同的欄位做表格串接

### P7-10 What happens when the columns are different data types when natural join? ( Natural Join 時,串接的欄位資料型態不一致時,發生什麼事情?)
Ans: Oracle tries to convert the data type.(Oracle 嘗試自動轉型)
- 若轉換失敗會報錯
```sql=
create table p7_10_1 (c1 varchar2(20), c2 number);
create table p7_10_2 (c1 number, c3 number);
insert into p7_10_1 values ('1', 1);
insert into p7_10_1 values ('2', 2);
insert into p7_10_1 values ('a', 3);
insert into p7_10_2 values (1, 1);
insert into p7_10_2 values (2, 2);
commit;
-- Auto converting varchar2 to number when execut the natural join
-- Error occurs when the converions fail.
select *
from p7_10_1 natural join p7_10_2;
drop table p7_10_1;
drop table p7_10_2;
```

### P7-12
[inner_corss_join_clause](https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/19/sqlrf/SELECT.html#GUID-CFA006CA-6FF1-4972-821E-6996142A51C6__BABCGEDH)
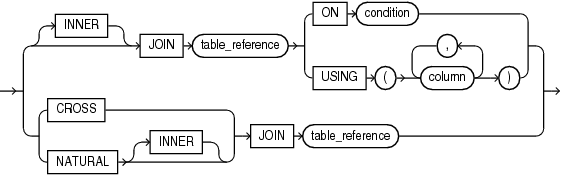
### P7-16 Column ambiguity when querying from joined tables
- `departments` 及 `employees` 表格中皆有 `manager_id` 欄位.
- 兩個表格 join 時要對`manager_id` 欄位修飾表格名稱, 必免 Column ambiguity error, 例 `dept.manager_id`。
```sql=
-- MANAGER_ID column appears in the EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS tables
-- DEPARTMENTS MANAGER_ID
-- EMPLOYEES MANAGER_ID
select table_name, COLUMN_NAME from user_tab_columns where column_name = 'MANAGER_ID';
-- Find the first name of employees and the department namd and manager id in department id = 50
-- ORA-00918: column ambiguously defined
select first_name, department_name, manager_id
from employees emp join departments dept using (department_id)
where department_id = 50;
-- Quality the columns except ones in the NATURE JOIN or USING clause
select emp.first_name, dept.department_name, dept.manager_id
from employees emp join departments dept using (department_id)
where department_id = 50;
```
### P7-17使用 non-FK column 做 join
```sql=
-- join use non-FK
create table tab1(c1 number, c2 varchar2(2));
create table tab2(c1 varchar2(2), c2 varchar2(2));
insert into tab1 values(1, 'a');
insert into tab1 values(2, 'b');
insert into tab1 values(3, 'c');
insert into tab2 values('a', 'a1');
insert into tab2 values('a', 'a2');
insert into tab2 values('b', 'b1');
insert into tab2 values('b', 'b2');
insert into tab2 values('c', 'c1');
insert into tab2 values('c', 'c2');
commit;
select * from tab1 t1 join tab2 t2
on t1.c2 = t2.c1;
```
Join results:

### P7-22 Self Join 練習
找出和員工 123 有相同 manager 的員工
(此題也可使用 subquery 建立報表.)
```sql=
select c.last_name "c_last_name",
e.employee_id "e_employee_id",
e.manager_id "e_manager_id",
c.employee_id "c_employee_id",
c.manager_id "c_manager_id"
from employees e join employees c
on (e.manager_id = c.manager_id)
where e.employee_id = 123 and c.employee_id <> 123;
```

### P7-26 Non-Equal Joins
建立 `job_grade` 表格及其資料
```sql=
create table job_grades(
grade_level varchar2(2),
lowest_salary number,
highest_salary number);
insert into job_grades values ('A', 1000, 2999);
insert into job_grades values ('B', 3000, 5999);
insert into job_grades values ('C', 6000, 9999);
insert into job_grades values ('D', 10000, 14999);
insert into job_grades values ('E', 15000, 24999);
insert into job_grades values ('F', 25000, 40000);
commit;
```
P7-26 Nonequal join, 顯示員工薪水的等級:

### P7-30
列出 city 及設置在該城市的 department name, 要包含那些沒有設置部門的城市。
```sql=
select l.city "City", d.department_name "Dept Name"
from locations l left outer join departments d using (location_id);
```

## WS1-L8 Using subqueries to solve queries
### P8-16 課堂練習
找出員工 107 在同個部門工作的同事。列出這些同事的 employee_id, last_name 及 first_name.
使用 Subquery
```sql=
-- subquery
select c.employee_id, c.last_name, c.first_name
from employees c
where c.department_id = (select department_id
from employees where employee_id = 107);
```
使用 self-join
```sql=
-- join
select c.employee_id, c.last_name, c.first_name
from employees w join employees c on (w.department_id = c.department_id)
where w.employee_id = 107;
```

### P8-19 Summary for the multiple-row comparison operators:
多列比較運算子間的對等性:
- `NOT IN` <=> `<>ALL`
- `IN` <=> `=ANY`
- `>ANY` <=> `>Minimum`
- `<ANY` <=> `<Maximum`
- `>ALL` <=> `>Maximum`
- `<ALL` <=> `<Minimum`
Any: at least one elemnet in the set.
All: All elements in the set.
### P8-21 Pairwise and Non-pairwise comparisons
Multiple-Column comparisons: Pairwise and Non-pairwise comparisons
Pairwise: 兩個集合中的元素間的關係為 One-To-One
Non-Pairwise: 兩個集合中的元素間的關係為 Many-To-Many

**non-pairwise comparison**
建立以下的表格:
```sql=
create table emp05 ( id number, mgr_id number, dept number, name varchar2(20));
insert into emp05 values (1, 2, 10, 'John');
insert into emp05 values (2, 3, 20, 'John');
insert into emp05 values (3, 2, 20, 'Fred');
insert into emp05 values (4, 3, 10, 'Bill');
commit;
```
管理者編號符合 john 的, 以及部門編號符合 john 的 row:
```sql=
SELECT id, mgr_id, dept, name
FROM emp05
WHERE mgr_id IN (SELECT mgr_id FROM emp
WHERE name = 'John') AND
dept IN (SELECT dept FROM emp
WHERE name = 'John') AND
name != 'John';
```
Codes from: https://community.oracle.com/tech/developers/discussion/988143/pairwise-e-non-pairwise-comparison
Result:
```
ID MGR_ID DEPT NAME
---------- ---------- ---------- ----
3 2 20 Fred
4 3 10 Bill
```
**Pairwise comparison**
管理者編號程部門編號的組合要和 John 的相同.
```sql=
SELECT id, mgr_id, dept, name
FROM emp
WHERE (mgr_id, dept) IN (SELECT mgr_id, dept
FROM emp
WHERE name = 'John') AND
name != 'John';
```
Codes from: https://community.oracle.com/tech/developers/discussion/988143/pairwise-e-non-pairwise-comparison
Result
```
no rows selected
```
### 課堂練習: Pairwise comparison
請先執行以下 DML 產生需要的測試資料
```sql=
create table emp06 as
select * from employees;
update emp06
set department_id = 80
where employee_id in (125, 126);
commit;
```
接著, 請撰寫 Query 完成以下的 reporting 要求:
Display the details of the employees who are managed by the same manager and work in the same department as the employees with `EMPLOYEE_ID` 180 or 176 (公司內 last name 為 Taylor 的兩位員工).
這兩名員工的 manager_id 及 department_id 如下:
```
employee_id manager_id department_id
-------------------------
176 149 80
180 120 50
```
```sql=
-- Pairwise comparison
select employee_id, manager_id, department_id
from emp06
where (department_id, manager_id)
in (select department_id, manager_id
from emp06
where employee_id in (180, 176));
```
The report contains the columns of `EMPLOYEE_ID`, `MANAGER_ID` and `DEPARTMENT_ID`.
### 課堂練習: Non-Pairwise comparison
Display the details of the employees who are managed by the same manager as the employees with `EMPLOYEE_ID` 180 or 176 and work in the same departments as the employees with `EMPLOYEE_ID` 180 or 176.
The report contains the columns of `EMPLOYEE_ID`, `MANAGER_ID` and `DEPARTMENT_ID`.
```sql=
-- Non-pairwise comparison
select employee_id, manager_id, department_id
from emp06
where department_id in (select department_id
from emp06
where employee_id in (180, 176))
and
manager_id in (select manager_id
from emp06
where employee_id in (180, 176))
```
所找出的員工有可能是員工 180 的 department_id, 配上 員工 176 的 manager_id。
### P8-28
練習 1
Subquery
```sql=
select employee_id, last_name
from employees
where salary < (select max(salary) from employees);
```
Join
```sql=
select e.salary, c.avg_salary
from employees e
join (select round(avg(salary)) avg_salary from employees) c
on (1=1)
where e.salary > c.avg_salary;
```
## WS1-L9 Using Set Operators
### 需要的 Tables
[本章需要的 employees 及 retired_employees 表格 @ gist.github.com](https://gist.github.com/hychen39/5b4c0f1300ec2d6dac18f01a1f35412c)
### 課堂練習
找出員工, 他們曾經在公司內擔任過 `ST_CLERK`, 的職位. 顯示的欄位包括:
employee_id, last_name, hire_date, start_date, 及 end_date.
結果請依 employee_id 排序.
員工的現職在 `employees` 表格中.
員工的職位歷史資料可在 `job_history` 表格中找到.
參考輸出如下:

## WS2-L6 Retriving data using subqueries
### With Clause 的補充例子(多個 subquery blocks)
找出部門, 其部門成本大於部門平均成本.
- `dept_costs` subquery: 找出各部門的成本結果暫時存放在 user's temporary tablespace
- `avg_cost` subquery: 計算部門平均成本
- main query: 列出部門成本大於部門平均成本的部門資料
- 使用先前的 subquery 做為資料來源.
```sql=
WITH
dept_costs AS (
SELECT department_name, SUM(salary) dept_total
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE e.department_id = d.department_id
GROUP BY department_name),
avg_cost AS (
SELECT AVG(dept_total) avg
FROM dept_costs)
SELECT * FROM dept_costs
WHERE dept_total >
(SELECT avg FROM avg_cost)
ORDER BY department_name;
```
執行結果
```
DEPARTMENT_NAME DEPT_TOTAL
------------------------------ ----------
Sales 304500
Shipping 156400
```
### Recursive Query (遞迴查詢)
遞迴的方向為向前遞迴.
Recursive Query 執行的過程:
1. Anchor member 先執行, 得到一組資料列.
2. 執行第一次的 Recursive member query block, 其資料來源為 Anchor Member 的資料, 產生新的資料列
3. 執行第二次的 Recursive member query block. From clause 的資料來源表示上一次的 Recursive member query block 的執行結果, Select clause 的 column 運算用於產生新的資料列.
4. 重複執行 Recursive member query block, 直到沒有產生任何資料列(停止條件)
5. 將所有的 query block 結果 union all 在一起.
注意: WITH clause 必須要有 column alias list 否則會報錯 `ORA-32039: recursive WITH clause must have column alias list`
以下是會報錯, 因為 `subordinate` 之後要加 column alias list
```sql=
with subordinate as (
select employee_id, last_name , first_name , manager_id , 1 as sub_level
from employees
where employee_id = 100
union all
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.first_name, e.manager_id, s.sub_level+1
from subordinate s join employees e on (s.employee_id = e.manager_id)
where sub_level + 1 <=3
)
select * from subordinate;
```
#### Ex. 產生 1~100 的數字
產生 1~100 的數字, 毎個數字一個 row:
```sql=
with acc_sum(total) AS (
-- base query (起始查詢)
-- Start from this query
-- Total is set to 1.
select 1 from dual
union all
-- Recursive query (遞迴查詢)
-- 在 acc_sum table 中的 row 代表上一次計算的結果
select total + 1
from acc_sum -- 於 recursive part 中的資料來源中再次使用自己(subquery)
where total < 100
)
select * from acc_sum;
```
其中 `total` 是 column alias, Base query l 欄位的 alias name.

遞迴時, 前後資料列可視為是父、子的階層關係:
```mermaid
graph TD
1 -- +1 --> 2
2 -- +1 --> 3
```
### Recursive Query (遞迴查詢): 產生公司的人事階層圖
找出自員工 100 以降的員工及其管理者
#### 使用 Hierarchical Query
```sql=
select employee_id, last_name, first_name, manager_id, LEVEL
from employees
start with employee_id = 100
CONNECT by PRIOR employee_id = manager_id;
```
其中:
- LEVEL 為 Pseudocolumn, 表示層級, 最高層級為 1.
- PRIOR 運算子代表父資料列(parent row)
- CONNECT BY 子句代表 parent 及 child row 在階層中串接的關係。
- START WITH 子句代表階層的起始點資料
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/queries003.htm

#### 使用 With Recursive
因為 Hierarchical Query 也是一種遞迴關係, 上述程式可用 With Recursive 形式改寫:
```sql=
-- rewrite using the recursive
-- query name 後的括號為 base query 的 column alias
with org_chart (employee_id, last_name, first_name, manager_id) as (
-- base query ( Start with clause)
select employee_id, last_name, first_name, manager_id
from employees where employee_id = 100
union all
-- recursive query
-- 欄位的資料來源來自於 child row
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.first_name, e.manager_id
-- Connect By clause, 指定 parent & child row 串接的關係
-- Rows in the org_char 代表 parent row
-- Rows in the Employees 代表 child row
from org_chart oc
join employees e on (oc.employee_id = e. manager_id)
)
select * from org_chart;
```
### P6-28 飛機航班製作
建立需要的 table
```sql=
create table flights (source varchar2(20), dest varchar2(20), flight_time number);
truncate TABLE flights;
-- Prepare the flight data
-- See P6-28, workshop II
insert into flights values ('San Jose', 'Los Angeles', 1.3);
insert into flights values ('New York', 'Boston', 1.1);
insert into flights values ('Los Angeles', 'New York', 5.8);
commit;
select * from flights;
```
航班路線:
```mermaid
graph LR;
A[San Jose] -->|1.3 hours| B[Los Angeles];
C[New York] -->|1.1 hours| D[Boston];
B[Los Angeles] -->|5.8 hours| C[New York];
```
飛機航班製作
```sql=
with reachable_from (source, dest, total_time, level_count, path) as (
-- anchor part
select source, dest, flight_time, 1, source || ' - ' || dest from flights
union all
select incoming.source,
outgoing.dest,
incoming.total_time + outgoing.flight_time,
incoming.level_count+1,
incoming.path || ' > ' || outgoing.source || ' - ' || outgoing.dest
from reachable_from incoming join flights outgoing on (incoming.dest = outgoing.source)
)
-- main query
select source,
dest,
total_time,
rpad('*', (level_count), '*') as tree,
path
from reachable_from;
```
執行結果:

飛機轉機表產生過程:

### 練習
使用 Recursive query, 計算以下算式的總合:
$ 1 + 2^2 + 3^2 + ... + 10^2 $
產生的報表如下:

參考答案:
```sql=
with squared_sum(n, total) as (
select 1, 1 from dual
union all
select n+1, total + power((n+1),2)
from squared_sum
where n+1 <= 10
)
select * from squared_sum;
```
## WS1-L10 Managing tables using DMLs
### 課堂練習 1
建立以下表格 sales_rep
```sql
create table sales_rep (
emp_id number,
full_name varchar2(100),
salary number,
department_name varchar2(100)
);
```
要求:
1. 將 job_id 為 SA_REP 的員工的 employee_id 增加至 sales_rep 表格。
2. 使用 correlated subquery,以 sales_rep 中的 emp_id 更新 sales_rep 內的其它欄位。
### Columns in v$locked_object
[v$locked_object](https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/REFRN/GUID-3F9F26AA-197F-4D36-939E-FAF1EFD8C0DD.htm#REFRN30125)
##### Modes of table locks
0 - NONE: lock requested but not yet obtained
1 - NULL
2 - ROWS_S (SS): Row Share Lock
3 - ROW_X (SX): Row Exclusive Table Lock (or Subexclusive (SX) table lock)
4 - SHARE (S): Share Table Lock
5 - S/ROW-X (SSX): Share Row Exclusive Table Lock
6 - Exclusive (X): Exclusive Table Lock
[Lock modes 說明 @ Oracle](https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/CNCPT/consist.htm#CNCPT1342)
[Overview of the Oracle Database Locking Mechanism 22.1](https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/21/cncpt/data-concurrency-and-consistency.html#GUID-AD0CEE83-2F33-4906-94E1-3D1022924C63)
執行 DML 時需要:
1. 先取得 Subexclusive (SX) table lock.
2. 再取得 Exclusive row lock (TX)

Reference: [Oracle Database - Row Locks (TX)](https://datacadamia.com/db/oracle/row_lock)
### Ready Consistency

Key concepts:
- System Change Number (SCN): the system change number (SCN) is Oracle's clock - every time we commit, the clock increments. The SCN just marks a consistent point in time in the database.
- Undo segment: 執行 DML 前, data block 的舊版本會被儲存到 Undo Segment 保存。
- Consistent Read (CR) Clones: 針對某個 SCN 開始的 Query, Oracle 會使用現有的 data block 及 Undo Segment 中的 data block 建構 Query 可以看到的內容。此過程稱為 CR Clones. 只有那些在 Query 開始後遭到其他 session 修改的 data block (SCN 大於 Query 的 SCN) 會被 Oracle 從 Undo Segment 中取得其相對應的舊版本。
- 上圖中黑色帶箭頭的線便是 CR Clone 的動作。
Reference: [Data Concurrency and Consistency](https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/CNCPT/consist.htm#CNCPT020)
## WS1-L11
[WS1-L11 Introduction to DDL](/VvhJtpoBRY-L9xEJ7r70yw)
## WS2-L7
### What is key-preserved table
"Key preserved means the row from the base table will appear AT MOST ONCE in the output view on that table."
換具話說,該 table 的 PK column 在 Join 後的 View,仍保有 Primary Key 的特性 (unique, not null)
在 1-1 的關係下做出來的 View, Parent(被別人參考的) 及 Child (參考別人的) table,皆能保有 PK 的特性。
但是,在 1-M 的關係下做出來的 View, 只有 Child (參考別人的) table 的 PK column 保有其特性;在 Parent table 中的 PK column 無法保有 unique 的特性。
Example:
建立 demo 及 demo_chile tables:
```sql=
drop table demo;
drop table demo_child;
create table demo (t1 number primary key, t2 varchar2(20), t3 date, t4 number);
create table demo_child(s1 number, s2_t1 number REFERENCES demo(t1));
set AUTOCOMMIT off
insert into demo values (1, 'R1', SYSDATE, 1);
insert into demo values (2, 'R2', SYSDATE, 2);
insert into demo_child values (1, 1);
insert into demo_child values (2, 1);
commit;
```
demo 及 demo_chile tables 的 Join View
```sql=
select d.t1, d.t2, d.t3, d.t4, c.s1, c.s2_t1
from demo d join demo_child c on (d.t1 = c.s2_t1);
```

demo.t1 欄位在 Join view 中失敗 PK column 的特性。所以 demo table 在 join view 中稱為 non key-preserved table.
Ref: [Key-preserved table concept in join view](https://asktom.oracle.com/pls/apex/f?p=100:11:0::::P11_QUESTION_ID:548422757486)
### 使用 Subquery 替代 Values 子句
```sql=
-- Copy rows to a table using the Insert statement
create table emp_temp(emp_id number, fname varchar2(50));
-- Into single table
insert into emp_temp
(select employee_id, first_name from employees
where employee_id < 200);
```
### P7-16 程式改寫
員工輪調時,只保留最近 4 次的工作記錄。
```sql=
drop table demo_jbh;
create table demo_jbh as
select * from job_history;
insert into demo_jbh values(200, '18-Jun-01', '18-Jun-02', 'SA_MAN', 80);
insert into demo_jbh values(200, '18-Jun-03', '18-Jun-04', 'AC_MGR', 80);
commit;
select * from demo_jbh order by 1, 2 ;
delete from demo_jbh dj
where
-- make sure current employee
employee_id = (select employee_id from employees where employee_id = dj.employee_id)
-- find the min start date in the job history
and start_date = (
select min(start_date) from demo_jbh where employee_id = dj.employee_id)
-- at least 3 job rotations.
and 3 <= (select count(*) from demo_jbh where employee_id = dj.employee_id);
```
以下這筆資料應被刪除:
```
200 17-SEP-95 17-JUN-01 AD_ASST 90
```
## WS2-9 Retriving data using advanced subqueries
### Merge statement
- Use the MERGE statement to select rows from one or more sources for **update** or **insertion** into a table or view. You can specify conditions to determine whether to update or insert into the target table or view.
- You cannot update the same row of the target table multiple times in the same MERGE statement.
Syntax

merge_update_clause

merge_insert_clause (update 後, 可判斷是否刪除)

### Example

使用以下的程式合併 `monthly_orders` 內的資料列到 `order_master` 表格, 結果為何?
```sql=
CREATE TABLE ORDER_MASTER (ORDER_ID NUMBER, ORDER_TOTAL NUMBER);
CREATE TABLE MONTHLY_ORDERS (ORDER_ID NUMBER, ORDER_TOTAL NUMBER);
INSERT INTO ORDER_MASTER VALUES(1, 1000);
INSERT INTO ORDER_MASTER VALUES(2, 2000);
INSERT INTO ORDER_MASTER VALUES(3, 3000);
INSERT INTO ORDER_MASTER VALUES(4, NULL);
COMMIT;
INSERT INTO MONTHLY_ORDERS VALUES(2, 2500);
INSERT INTO MONTHLY_ORDERS VALUES(3, NULL);
COMMIT;
SELECT * FROM ORDER_MASTER;
SELECT * FROM MONTHLY_ORDERS;
MERGE INTO ORDER_MASTER O
USING MONTHLY_ORDERS M ON (O.ORDER_ID = M.ORDER_ID)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET O.ORDER_TOTAL = M.ORDER_TOTAL
DELETE WHERE (M.ORDER_TOTAL IS NULL)
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT VALUES (M.ORDER_ID, M.ORDER_TOTAL);
SELECT * FROM ORDER_MASTER;
ROLLBACK;
DROP TABLE ORDER_MASTER;
DROP TABLE MONTHLY_ORDERS;
```
### Example of Flashback table
```sql=
-- WS2-L9
-- Flashback table
create table dept_test as
select * from departments;
create restore POINT before_delete;
select * from dept_test;
delete dept_test where department_id between 10 and 50;
commit;
alter table dept_test enable row movement;
flashback TABLE dept_test to RESTORE point before_delete;
```
## 階層式查詢 (Hierarchical Query)
Example
將 '104,105,106' 的字串轉成 3 個 rows:
```sql=
SELECT regexp_substr('104,105,106','[^,]+',1,level)
FROM dual CONNECT BY
regexp_substr('104,105,106','[^,]+',1,level) IS NOT NULL
```
也可以使用 [apex_string.split](https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/apex/22.1/aeapi/SPLIT-Function-Signature-1.html#GUID-3BE7FF37-E54F-4503-91B8-94F374E243E6) function 轉成 table of varchar2.
## 其他
[解決 SQLDeveloper 常常自動斷線的問題的 SQLDeveloper Plugin](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/oracle-sql-developer-did-your-connection-break-again-saransh-bansal/)