---
tags: java_se
---
# Java SE Notes
## Learning resources
[Java SE 8 Tutorials | Oracle](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/)
## Java raw String literals and Text Box
- https://www.vojtechruzicka.com/raw-strings/
- https://www.vojtechruzicka.com/java-text-blocks/
- https://www.jrebel.com/blog/using-text-blocks-in-java-13
## Scanner Class
`java.util.Scanner`
`Scanner` class 是一個簡單的 text scanner 可以讀取並 parse 具 `Readable` interface 物件的內的文字串流, 之後轉換成不同的 primitive types.
讀取過程中若發生 `IOException`, 則認為已至輸入結尾.
若該物件類別具有 `Closeable` interface, `Scanner` 物件類別也可代為執行關閉動作.
分隔字元預設為空白, 但也可使用 regular expression.
有實作 `Readable` interface 的物件類別:
使用上, 可從:
- `String`
- `InputStream`
- `Path`
- `File`
- `Readable`
等物件讀取文字內容。
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Scanner.html
## System class
The System class contains several useful class fields and methods. It cannot be instantiated.
Among the facilities provided by the System class are:
- standard input, standard output, and error output streams;
- access to externally defined properties and environment variables;
- a means of loading files and libraries; and
- a utility method for quickly copying a portion of an array.
[`System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length):void`](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/System.html#arraycopy-java.lang.Object-int-java.lang.Object-int-int-)
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/System.html
## Nested Classes
Nested classes are divided into two categories: static and non-static. Nested classes that are declared static are called static nested classes. Non-static nested classes are called inner classes.
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/javaOO/nested.html
## Java Variables
The Java programming language defines the following kinds of variables:
* Instance Variables (Non-Static Fields)
* Class Variables (Static Fields)
* Local Variables
* Parameters
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/variables.html
## Local Variable 的宣告
A local variable declaration statement declares one or more local variable names.
```
int a, b, c=0;
```
Declare three variables: `a`, `b`, and `c`. The `c` has been initialized to value 0.
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se8/html/jls-14.html#jls-LocalVariableDeclaration
## Constructor Chain
Constructor 可以呼叫其它的 constructor. 呼叫時必須符合以下規則:
1. 所有建構子必須明確宣告, 無法呼叫 default construct.
2. 使用 `this` 呼叫建構子
3. 多個建構子中, 至少有一個建構子沒有再呼叫其它的建構子, 做為 constructor chain 中的 base case.
4. 建構子的執行順序由呼叫的順序決定, 和建構子在程式碼中的位置無關。
Ref: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/constructor-chaining-java-examples/
Example:
底下程式碼在 n1 及 n2 的地方產生編譯錯誤.
```java=
public class Ch11_q14 {
String name;
int age = 25;
public Ch11_q14(String name) {
this(); // line n1
setName(name);
}
public Ch11_q14(String name, int age) {
Ch11_q14(name); // line n2
setAge(age);
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public String show(){
return name + " " + age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ch11_q14 p1 = new Ch11_q14("Duke");
Ch11_q14 p2 = new Ch11_q14("Jim", 52);
System.out.println(p1.show());
System.out.println(p2.show());
}
}
```
## UnannType
What is the "UnannType"?
UnannType is unannotated type. For example, `int`, `String` etc.
See: https://www.reddit.com/r/java/comments/2mf2jq/what_is_an_unanntype_exactly/
## Benefits of the Java exception handling mechanism
- Advantage 1: Separating Error-Handling Code from "Regular" Code
- Advantage 2: Propagating Errors Up the Call Stack
- Advantage 3: Grouping and Differentiating Error Types
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/exceptions/advantages.html
## How many objects have been created?
How many objects have been created when the line / / do complex stuff is reached?
```java=
class Duke {
Duke () {
try {
throw new Exception("Exception in Duke constructor");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
/**
* Ch13_q16
*/
public class Ch13_q16 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Duke d1 = new Duke();
Duke d2 = new Duke();
Duke d3 = d2;
System.out.printf("%s %s %s", d1, d2, d3);
}
}
```
共有 4 個 objects 被建立, 2 個 `Duke`, 2 個 `Exception`. 注意程式中 `new` 出現的位置.
Ref: http://www.briefmenow.org/oracle/how-many-objects-have-been-created-when-the-line-do-complex-stuff-is-reached-2/
## Java time api (java.time)
### 下星期二是幾月幾號?
```java=
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate nextTue = now.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.TUESDAY));
System.out.println("Next Tue is " + nextTue.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE));
```
Try in [jShell](https://tryjshell.org/)
### 給一個 time zone offset, 找出該時區中的所有 Zone ID
找出 UTC+08:00 下的所有 Zone ID:
```java=
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.time.Instant;
public class TimeZone {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneOffset taipeiOffset = ZoneOffset.of("+8");
ZoneId taipeiZoneId = ZoneId.ofOffset("UTC", taipeiOffset);
System.out.println(taipeiZoneId);
//Ref: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/51045064/how-to-get-timezone-by-utc-offset
// 由 Zone offset 找出該時區中的所有 Zone ID
final List<ZoneId> timeZoneByUtc = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds().stream().map(ZoneId::of)
.filter(z -> z.getRules().getOffset(Instant.now()).equals(taipeiOffset))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
timeZoneByUtc.stream().forEach(zid -> System.out.println(zid));
}
}
```
### 某個地方的 Daylight Saving Time 的轉換時間
夏令時間 Daylight Saving Time 簡稱為:DST,基本上都開始於春季,並於同年的秋季結束。
北半球的夏令時間每年開始於年初,也就是春季的 2~4 月之間。結束於年底,也就是秋季的 9~11月之間。
因南半球的春秋兩季正好與北半球相反,所以南半球的夏令時間於當年的年底 ( 南半球的春季 ) 開始,再於次年的年初 ( 南半球的秋季 ) 結束。
夏令時間開始實施,必須將當地的時間撥快一個小時,也就是以當地的 GMT 標準時間 + 1小時,直到夏令時間結束就恢復到當地原來的標準時間。
澳洲(南半球) 2020年夏令時間 DST
- 開始: 10月4日(日)02:00上午
- 結束: 4月5日(日) 03:00上午
Ref: https://time.artjoey.com/australia.htm
```java=
import java.time.zone.*;
import java.time.*;
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Australia/Sydney");
ZoneRules rules = zoneId.getRules();
ZoneOffsetTransition nextTransition = rules.nextTransition(Instant.now());
System.out.println("Next transition at: " +
nextTransition.getInstant().atZone(zoneId));
ZoneOffsetTransition nextNextTransition =
rules.nextTransition(nextTransition.getInstant());
System.out.println("Next transition after that at: " +
nextNextTransition.getInstant().atZone(zoneId));
```
Output
```
nextTransition ==> Transition[Overlap at 2020-04-05T03:00+11:00 to +10:00]
Next transition at: 2020-04-05T02:00+10:00[Australia/Sydney]
nextNextTransition ==> Transition[Gap at 2020-10-04T02:00+10:00 to +11:00]
Next transition after that at: 2020-10-04T03:00+11:00[Australia/Sydney]
```
Ref: https://stackoverflow.com/a/38737097
### offsetDateTime.atZoneSimilarLocal() 的使用
Ref:
- https://www.logicbig.com/how-to/code-snippets/jcode-java-8-date-time-api-offsetdatetime-atzonesimilarlocal.html
- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/time/OffsetDateTime.html#atZoneSameInstant-java.time.ZoneId-
### 由 LocalDateTime 取得 Instant
取得 `LocalDateTime` 後, 再提供 Zone 資訊, 以取得 time Instant.
```java=
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Taipei")).toInstant();
```
Ref: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44569202/java-8-create-instant-from-localdatetime-with-timezone
## java.nio
[nio2 file attributes | dzone.com](https://dzone.com/articles/java-nio2-file-attributes)
[Walking the File Tree | Java SE 8 Tutorial](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/io/walk.html)
[Watching a Directory for Changes | The Java Tutorials](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/io/notification.html)
# Java Virtual Machine
## JVM Run-Time Data Areas
[Java JVM Run-time Data Areas @ javapapers.com](https://javapapers.com/core-java/java-jvm-run-time-data-areas/)
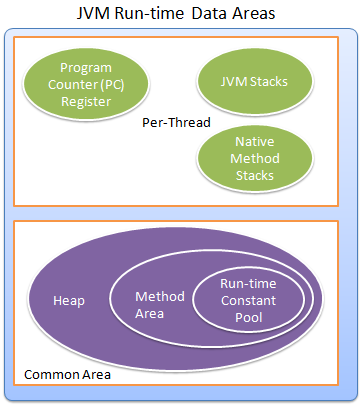
- program counter (PC) register keeps track of the current instruction executing at any moment
## Class.forName() 的用途
> The big difference with the traditional `new` is that `newInstance()` allows to instantiate a class that you don't know until runtime, making your code more dynamic.
[What is the difference between `Class.forName()` and `Class.forName().newInstance()`?](https://stackoverflow.com/a/2093100)
[`Class` object | Java SE 8 Document](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Class.html)
## Java Memory Model

[Java (JVM) Memory Model – Memory Management in Java 7](https://www.journaldev.com/2856/java-jvm-memory-model-memory-management-in-java)
## Java 8 standard and advanced options
[Java Synopsis and options](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/tools/windows/java.html#BABDJJFI)
## Garbage Collection
Anatomy of a Garbage Collection Log Statement

[Garbage Collection log](https://dzone.com/articles/understanding-garbage-collection-log)