# Collective Communication
- 作用於一整個 communicator,一次讓多個 process 進行傳輸的 API
- Communicator 中 **所有 processes** 都會參與傳輸
- 一對多
- 其中一個 process 是溝通過程的 **root**
- **一發送、多接收** - root 負責發送資料給其他 processes
- **多發送、一發送** - 所有 processes 發送資料給 root
- **多發送,多接收**
- 溝通過程中沒有 root,所有 process 都做相同的事情
- 通常一個 function 就包含 **接收** 和 **發送**
- 可以用來同步或分配資料
- 發送、接收資料的同時進行某些運算 (reduction)
- 用來統整運算結果
## Reduce
- 用來 **統整** 每個 processes 上的 **計算結果**
- 在 **傳輸的同時對資料進行運算**,透過該運算對計算結果做統整
- E.g.: 加總、取最大值、取最小值
- 運算的結果可以儲存在某一個 process 中,也可以同時儲存在所有 processes 中
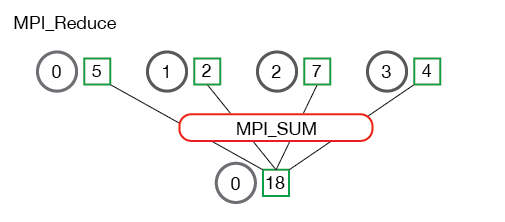
- 每個 process 分別傳送一筆資料給 root
- 但是這些資料會經過運算,所以最終 root 上只會有一筆統整過的資料
- **Example**: 計算總合
- 可以把一個陣列分為多個等長的子陣列
- 每個 process 計算一個子陣列的總和
- 最後透過 reduce,加總每個 process 的運算結果 (子陣列總和)
- 結果就是整個陣列的加總
### `MPI_Reduce(sendbuf, recvbuf, count, datatype, op, root, comm)`
- `sendbuf` - `void*`: 指向要送出的資料,通常是單一 process 運算的結果,即整個運算中的部分結果
- `recvbuf` - `void*`: 指向 reduce 的結果,表示整個運算的結果
- `count` - `int`: 要傳輸的資料個數
- `datatype` - `MPI_Datatype`: 傳輸資料的 type
- `op` - `MPI_Op`: 過程中要進行的運算
- MPI 已有定義一些 [**常用的運算**](https://www.mpi-forum.org/docs/mpi-1.1/mpi-11-html/node78.html)
- 加總: `MPI_SUM`
- 最大值: `MPI_MAX`
- 最小值: `MPI_MIN`
- 可以自定義運算,運算必須是一種 **二元運算**
- 即運算只能有兩個輸入
- 使用方式之後筆記會補上
- `root` - `MPI_Rank`: 儲存結果的 process 的 rank
- `comm` - `MPI_Comm`: 進行傳輸的 communicator
**描述**
- 執行 `MPI_Reduce()` 時
- 若目前的 rank 等於 `root`
- 目前的 process 會接收來自其他 processes 的資料
- 最終經過 `op` 處理的資料,儲存在該 process 的 `recvbuf` 中
- 其他 processes 則會把 `sendbuf` 中的資料發送給 rank 為 `root` 的 process
- `MPI_Reduce()` 屬於 **blocking communication**
- 任何 process,執行到 `MPI_Reduce()` 時會 **暫停執行**
- 直到所有 processes 都執行 `MPI_Reduce()`,**完成所有資料複製和運算後**,才會 **恢復執行**
:::info
```cpp
#include <mpi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
int rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
// 所有 process 將 rank 的數值送出並加總
// 加總結果會儲存在 rank 0 的 process 的 sum_rank
int sum_rank = 0;
MPI_Reduce(&rank, &sum_rank, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("rank %d: %d\n", rank, sum_rank);
MPI_Finalize();
}
```
- **Compile & Execute**
```bash
mpic++ demo.cc -o demo
mpirun -np 4 demo
```
- **Output**
```
rank 2: 0
rank 3: 0
rank 1: 0
rank 0: 6
```
> 順序僅供參考
:::
:::success
**實際應用** 陣列加總
- 用 command-line arguments 當作輸入
- 每個 process 負責加總陣列的一小部分
```cpp
// demo.cc
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cmath> // ceil() - 無條件進位到整數
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib> // atoi() - string to int
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
int rank, comm_size;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_size);
// 計算一個 process 要計算的子陣列大小
int n = argc - 1;
float chunk_size = n;
chunk_size = ceil(chunk_size / comm_size);
// 計算子陣列的起始和終止位置
int start = chunk_size * rank;
int end = start + chunk_size;
// 加總子陣列 結果存在 sum_local
int sum_local = 0;
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (i < n) {
int num = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
sum_local += num;
}
}
// 加總 sum_local
int sum = 0;
MPI_Reduce(&sum_local, &sum, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if (rank == 0) {
printf("Sum of %d numbers: %d\n", n, sum);
}
MPI_Finalize();
}
```
- **Compile & Execute**
```bash
mpic++ demo.cc -o demo
mpirun -np 4 demo 1 2 3 4 5
```
- **Output**
```
Sum of 5 numbers: 15
```
:::
### `MPI_Allreduce(sendbuf, recvbuf, count, datatype, op, comm)`
- 使用方式和 `MPI_Reduce()` 類似,但是沒有 `root`
- 所有 processes 都會拿到 reduce 的結果
:::info
```c
#include <mpi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
int rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
// 所有 process 將 rank 的數值送出並取出最大值
// 結果會儲存在所有 process 的 sum_rank
int sum_rank = 0;
MPI_Allreduce(&rank, &sum_rank, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_MAX, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("rank %d: %d\n", rank, sum_rank);
MPI_Finalize();
}
```
- **Compile & Execute**
```bash
mpic++ demo.cc -o demo
mpirun -np 4 demo
```
- **Output**
```
rank 1: 3
rank 2: 3
rank 3: 3
rank 0: 3
```
> 順序僅供參考
:::
## Gather
- 把每個 process 上的結果,分別傳送到同一個或所有 process 上
- 可以分別拿到每一個 process 上、**原始的運算的結果**
- 使用 reduce 沒辦法知道,資料在原本的 process 中的數值
- 可以分別對每個運算結果做處理
- Gather 的結果,會依照 rank 排序
- rank 0 的 process,送出的資料會被排在第一個
- rank 1 的 process,送出的資料會被排在第二個
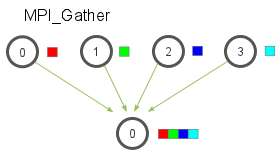
### `MPI_Gather(sendbuf, sendcnt, sendtype, recvbuf, recvcount, recvtype, root, comm)`
- `sendbuf` - `void*`: 指向要送出的資料
- `sendcnt` - `int`: 送出的資料個數
- `sendtype`- `MPI_Datatype`: 送出資料的型別
- `recvbuf` - `void*`: 指向要儲存資料的記憶體空間
- **注意**: 該空間要可以容納所有資料
- 例如有 4 個 processes、發送 2 個 int,則此 buffer 至少要有 8 個 int 的空間
- `sendcnt` - `int`: 接收到的 ***資料個數***
- 這邊指的是 "會 **從一個 process** 收到多少資料"
- `sendtype` - `MPI_Datatype`: 接收資料的型別
- `root` - `MPI_Rank`: 進行發送的 process 的 rank
- `comm` - `MPI_Comm`: 進行傳輸的 communicator
:::info
```c
#include <mpi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
int rank, size;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
// 為了節省記憶體 可以只在 root process 配置陣列
// 所以通常用動態配置的方法實作
int* res;
if (rank == 0) {
res = new int[size];
}
int val = rank * rank + 3 * rank - 5;
printf("Rank %d: %d\n", rank, val);
// 發送 val 給 rank 0 的 process 並儲存在 res 中
// 每個 process 送出的 val 會依照 rank 的順序排列在 res 中
MPI_Gather(&val, 1, MPI_INT, res, 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if (rank == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", res[i]);
}
// 因為只在 root process 配置
// 所以只需要在 root process 釋放
delete res;
}
MPI_Finalize();
}
```
- **Compile & Execute**
```bash
mpic++ demo.cc -o demo
mpirun -np 4 demo
```
- **Output**
```
Rank 0: -5
Rank 2: 5
Rank 1: -1
Rank 3: 13
-5 -1 5 13
```
> 前幾行的順序僅供參考
:::
### `MPI_Allgather(sendbuf, sendcnt, sendtype, recvbuf, recvcount, recvtype, comm)`
- 和 `MPI_Gather()` 類似,但是沒有 root
- 所有 process 都會收到 Gather 的結果
:::info
```c
```
- **Compile & Execute**
```bash
mpic++ demo.cc -o demo
mpirun -np 4 demo
```
- **Output**
```
Rank 0: -5
Rank 1: -1
Rank 2: 5
Rank 3: 13
```
:::
## Broadcast
- 一個 process 發送資料
- 其他 processes 接收資料
- 所有 processes **收到一樣的資料**
- 可以用來 **同步** 所有 process 的資料
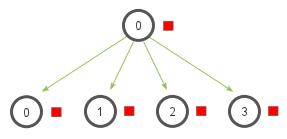
### `MPI_Bcast(buffer, count, datatype, root, comm)`
- `buffer` - `void*`: 指向用於傳輸的 buffer
- 對 **送出資料的 process** 來說,指向要 **送出的資料**
- 對 **接收資料的 process** 來說,指向要 **存放資料的位置**
- `count` - `int`: 要傳輸的資料個數
- `datatype` - `MPI_Datatype`: 傳輸資料的 type
- `root` - `MPI_Rank`: 進行發送的 process 的 rank
- `comm` - `MPI_Comm`: 進行傳輸的 communicator
**描述**
- 執行 `MPI_Bcast()` 時
- 若目前的 rank 等於 `root`,該 process 的 `buffer` 中的內容會被發送給其他 process
- 其他 process 則會把收到的資料儲存於 `buffer` 中
- `MPI_Bcast()` 屬於 **blocking communication**
- 任何 process,執行到 `MPI_Bcast()` 時會 **暫停執行**
- 直到所有 processes 都執行 `MPI_Bcast()`,**完成所有資料複製後**,所有 processes 才會 **恢復執行**
- 可用在 **同步資料和執行順序**
- 運算的輸入來自外界
- E.g.: **stdin**, **file**, ...
- 由其中一個 process 執行輸入
- 完成輸入後再透過 `MPI_Bcast()` 將輸入資料發送給其他 process
:::warning
若輸入來自 command-line argument,則不一定要用 broadcast (或其他傳輸)
- 所有 processes 都可以直接存取 command-line argument,用 broadcast 反而更加耗時
- 除非處理 command-line argument 的過程更加耗時,且不能平行執行
- 先由其中一個 process 處理 command-line argument
- 在把結果發送給其他 process
:::
:::success
用 C++ 計算質數數量
- 輸入一整數 $n$
- 計算 $1$ ~ $n$ 共有多少質數
```cpp
// demo.cc
#include <mpi.h>
#include <cstdio>
// 判斷是不是質數
bool is_prime(int num) {
if (num <= 1)
return false;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= num; i++) {
if (num % i == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int rank, comm_size;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_size);
int n;
if (rank == 0) {
// 如果 rank 是 0
// 呼叫 scanf() 讀取使用者輸入的 n
scanf("%d", &n);
}
// rank 是 0 的 process 把使用者輸入的 n 發給其他 process
// 因為 MPI_Bcast() 是 blocking 的 function
// rank 非 0 的 process 會停在這行等待 直到收到資料
// 這保證了計算會在使用者完成輸入後才執行
MPI_Bcast(&n, 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 計數質數的數量
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += comm_size) {
int m = i + rank;
// 如果是質數 count 遞增 1
if (m <= n && is_prime(m)) {
count++;
}
}
int result = 0;
MPI_Reduce(&count, &result, 1, MPI_INT, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if (rank == 0) {
printf("There are %d prime numbers between 1 and %d\n", result, n);
}
MPI_Finalize();
}
```
- **Compile & Execute**
```bash
mpic++ demo.cc -o demo
mpirun -np 4 demo
```
- **Input**
```
65535
```
- **Output**
```
There are 6542 prime numbers between 1 and 65535
```
:::
## Scatter
- 一個 process 發送資料,其他 processe 接收資料
- 每個 process 拿到 **不同的資料**
- 但每個 process 拿到的資料量需相同

- 可以一次把資料分成多個相同大小的區段,並把每個小區段分別發送給每個 processes
### `MPI_Scatter (sendbuf, sendcnt, sendtype, recvbuf, recvcnt, recvtype, root, comm)`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet