# **Java Note**
- Resource:
- [openhome.cc](https://openhome.cc/Gossip/Java/index.html)
- [package/import](itread01.com/content/1542859869.html)
- JetBrains
## 概念 (Concept)
- Java has a mechanism that `cleans memory automatically.`
- Java follows the "write once, run anywhere" (or WORA) principle. The same program can be run on multiple platforms without any changes.
- compile java program: javac
- 執行`javac xxx.java`後, 會將`xxx.java`編譯成`xxx.class`,其中.class檔是可以運行在JVM的bytecode格式
- execute java program:`java xxx`
## 資料型態 (Data Type)

### Primitive
- `mutable`
- 包含有: boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, double
- boolean: `true`, `false` (特別注意是==全小寫==)
- ==1不等於true, 0不等於false==
- NOT: !
- AND: && (跟false做AND都會是false)
- OR: || (跟true做OR都會是true)
- XOR: ^ (兩值不同則true)
- NOR: !(a||b) 或 (!a&&!b)
- char: 'x' ==單引號==, 且最多只能放一個字元)
- int: 1000000 (可以寫成1_000_000)
- long: 1000000L (可以寫成1_000_000L)
- float: 2.71828f
- double: 5e-3, 0.01e2
- ==double d1 = 5 / 4 = 1==
- ==double d1 = 5.0 / 4 = 1.25==
- var: Java 10 support (e.g., var s='x', var i=10)
| name | bits | range |
| ------ | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| char | 16 | 0 ~ 65536 |
| short | 16 | -2^15^ ~ (2^15^-1) |
| int | 32 | -2^31^ ~ (2^31^-) |
| long | 64 | -2^63^ ~ (2^63^-1) |
| float | 32 | 1.40239846 x 10^-45^ ~ 3.40282347 x 10^38^ |
| double | 64 | 4.9406564584124654 x 10^-324^ ~ 1.7976931348623157 x 10^308^ |
| byte | 8 | -128 ~ 127 |
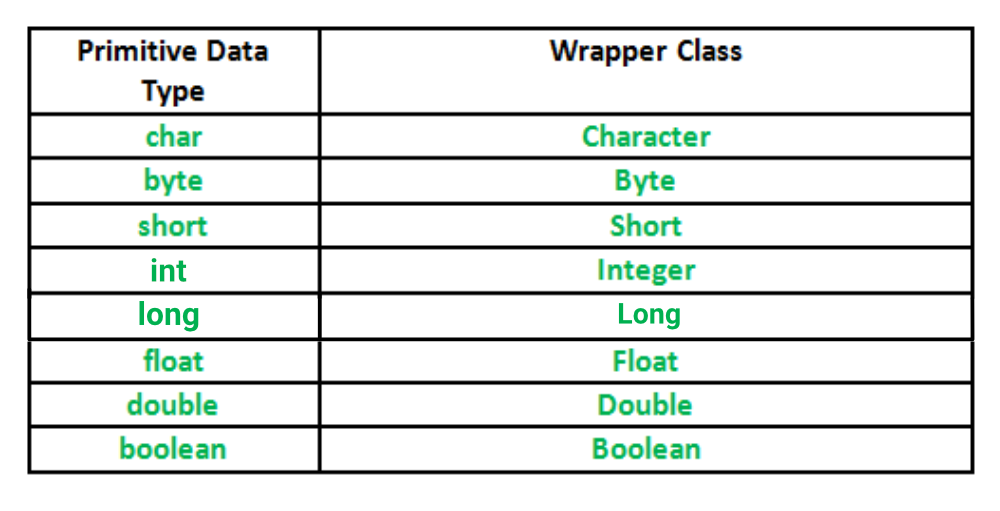
### Non-Primitive
- `immutable` (參見 [wrapper_class_example](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/primitive-wrapper-classes-are-immutable-in-java/))
- 包含有: wrapper class, string, array, ...
- string: "x" (用==雙引號==, 放一個字元仍視為字串)
- wrapper class: Boolean, Byte, Character, Double, Float, Integer, Long, Short
### Final
- `final` [[Ref]](http://blog.kenyang.net/2011/03/09/java-staticfinal)
- 用來宣告在類別時, 該類別就不能被繼承
- 用來宣告在函數時, 繼承他的子類別不能覆寫
- 用來宣告在變數時, 其值不能被修改(即常數)
### Static
- `static`
- 只佔一組記憶體位置, 所有new出來的都共享同一個值 (只有唯一值)
- 可以直接透過類別存取使用
```java=
class test{
static int value = 0;
...
}
//直接透過類別access value
System.out.print(test.value);
//new object後去access value
test t = new test();
System.out.print(t.value);
```
### Initialization Block
- static initialization block
- 用來初始化static fields與constants
```java=
static{
...
}
```
- 例如
```java=
class example{
private static String str;
private static final String strConst;
static{
str = "initialization";
strConst = "a string constant";
}
}
```
- 當static field (第二與三行)與static block都做assignment時, 會先做static field再做static block裡的assignment
- instance initialization block
- 在所有的constructor之前執行, 但在superclass的constructor之後執行
- 語法
```java=
{
...
}
```
- 例如
```java=
class example{
private int value;
{
value = 10;
}
}
```
- 當然也可以寫成`private int value = 10;`, 但當你有很複雜的assignment時, 且又想在constructor之前做, 就可以善加利用它
- 有趣的是, 下方的output順序為block A -> block B -> constructor
```java=
class A {
{
System.out.println("block A");
}
public A() {
System.out.println("constructor");
}
{
System.out.println("block B");
}
}
```
- 再看一個例子, 下方的output出來的field (即InitBlock.field) 其值為40
```java=
class InitBlock {
static int field = 20;
static {
field = 30;
}
static {
field = 40;
}
}
```
### Boxing
- primitve → object
```java=
//boxing
int primitiveInt = 10;
Integer boxInt = Integer.valueOf(primitiveInt);
//auto-boxing
Integer boxInt = primitiveInt;
```
### Unboxing
- object → primitive
```java=
//unoxing
int unboxInt = boxInt.intValue();
//auto-unboxing
int unboxInt = boxInt;
```
### 補充資料
- [變數放stack或是heap?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3646632/do-java-primitives-go-on-the-stack-or-the-heap)
- [RefCopy](https://hyperskill.org/learn/step/5035)
- [wrapper class是reference type?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27283104/arprimitive-wrapper-classes-in-java-treated-as-reference-types)
## Enum (Enumeration)
- 例如
```java=
enum Season {
SPRING, SUMMER, AUTUMN, WINTER // four instances
}
```
- 宣告(有兩種):
- `Season s = Season.AUTUMN`
- `Season s = Season.valueOf("AUTUMN")`
- 看enum value的名字: `s.name()`
- load所有元素: `Season [] sTable = Season.values()`
- 在enum中相對應位置(數值化): `int idx = s.ordinal()` 以AUTUMN為例, idx=2
- 可以搭配用在switch-case
```java=
switch(s){
case SPRING:
...
break;
case SUMMER:
...
break;
case AUTUMN:
...
break;
case WINTER:
...
break;
default:
...
}
```
```java=
public enum Dir{
top("T_Y"), bottom("B_Y"), left("L_X"), right("R_X");
private String dir;
Dir(String){
this.dir = dir;
}
private String getValue(){
return dir;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.getValue();
}
}
String intputDir = "top";
String transformedDir = Dir.valueOf(inputDir).toString(); //"T_Y"
```
## Object
==對物件(包含常見使用到的array)之操作要小心==
- 比較兩物件內實際的值, 不要用`==` 去判斷, 應該要用==obj1.equals(obj2)==, 因為使用在物件上的意思是去判斷兩個物件是否歸屬同一個物件
- ==只有當比較對象為primitive如int, 才能使用`==`做值的判斷==
```java=
//ref:https://openhome.cc/Gossip/Java/Reference.html
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal c = a;
System.out.println(a == b); //false
System.out.println(a == c); //true
System.out.println(a.equals(b)); //true
```
- 再看一個例子, 因為array是object, 而在程式碼第二行將Arr1參考的物件也給Arr2參考, 所以Arr2更動的其實就是Arr1參考的物件
- 其中第二行的assign叫做==參考之複製(shallow copy)==, 而非==物件之複製(deep copy)==, 在Java中, 對於所有非non-primitive資料型態(如object, arraylist), 的`=`符號之assign方法都是參考
- 而在C++的概念中, 第二行程式碼代表Arr1這個物件的內容複製一份給Arr2
```java=
int[] Arr1 = {88, 81, 74, 68, 78, 76, 77, 85, 95, 93};
int[] Arr2 = Arr1;
Arr2[0] = 99;
System.out.println(Arr1[0]); //99
```
- 再多看幾個例子
```java=
//ref: https://openhome.cc/Gossip/Java/InsideString.html
char[] name = {'J', 'u', 's', 't', 'i', 'n'};
String name1 = new String(name);
String name2 = new String(name);
System.out.println(name1 == name2); //false
```
```java=
String name1 = "Justin";
String name2 = "Justin";
System.out.println(name1 == name2); //true
```
- 陣列複製: `System.arraycopy(sourceArr, startIndex, targetArr, startIndex, copyLen)`
- `System.arraycopy(Arr1, 0, Arr2, 0, Arr1.length)`
- 陣列複製(JDK6以上): `Array.copyOf(sourceArr, sourceArrLen)`
- import java.util.Arrays;
int[] Arr2 = Arrays.copyOf(Arr1, Arr1.length)
## Array
### 固定長度
- 語法: `dataType [] name = new dataType[x];`
- 指定: `name[position]=xxx;`
- 元素個數: `name.length;`
- 陣列視覺化(包含陣列的`[]`符號):
```java=
import java.util.Arrays;
byte[] name = {4, 8, 0, 1, 2};
String VisArr = Arrays.toString(name);
(output) >>> [4, 8, 0, 1, 2]
```
- 排序:
```java=
Arrays.sort(name);
>>> [0, 1, 2, 4, 8]
```
- 比對: `Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2)` 如相對應的值都相同則true, 否則false
- 二維陣列: `dataType[][] name = new int[x][]` 跟c++不一樣的是, ==java允許每列可以存不同數量的元素值==
```java=
int[][] twoDArr = new int[3][];
twoDArr[0] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
twoDArr[1] = new int[] { 5, 7, 3};
twoDArr[2] = new int[] { 8 };
```
- 拜訪元素:
- for-loop:
```java=
for(int r=0; r<twoDArr.length; r++)
for(int c=0; c<twoDArr[r].length; c++)
```
- ==foreach-loop:==
`for(int [][] element : twoDArr)`
### 變動長度(ArrayList)
- 必須要先`import java.util.ArrayList;`
- 可以是`mutable`或是`immutable`
- 可以利用for-loop或是foreach-loop去access資料
- 跟c++ vector很像 (java也有vectorㄚ)
- ==不能使用primitive data type (e.g., int, double, ...)==, 但可以使用object(e.g., String)與wrapper class type (e.g., Double, Integer, Boolean, ...)
- 語法: `ArrayList <dataType> name = new ArrayList <dataType>();`
- 讀取: `name.get(index)`, ==不允許name[index]的用法==
- 元素個數: `name.size()`
- 新增: `name.add(dataValue)`
- 新增(指定位置): `name.add(index, dataValue)`
- 移除(指定位置): `name.remove(index)`
- 移除(指定值): `name.remove(new dataType (dataValue))`
- 例如: name: [1, 2, 3, 4], 當要移除元素值2(即name.get(1)), 則用`name.remove(new Integer(2))`
- 移除(特定條件): `name.removeIf(i -> condition)`
- 例如: name: [1, 2, 3, 4], 我想要移除小於3的所有元素, 則用`name.removeIf(i -> (i<3))`
- 全部清空: `name.clear()`
- 取代: `name.set(index, newValue)`
- 新增另一個arrayList(如叫anotherArrList)中所有元素: `name.addAll(anotherArrList)`
- 第一個出現元素E的位置: `name.indexOf(E)`, 回傳-1代表沒有該元素
- 最後一個出現元素E的位置: `name.lastIndexOf(E)`, 回傳-1代表沒有該元素
- 是否存在元素E: `name.contain(E)` 回傳true/false
- 排序: 必須要先`import java.util.Collection`
- 升序: `Collections.sort(name)`
- 降序: `Collections.sort(name,Collections.reverseOrder())`
- ==複製物件: Collections.copy(destinationList, sourceList);==
## String
[[null V.S. 空字串](https://www.itread01.com/content/1547523036.html)]
### 字串反轉
```java=
String str = "xyz";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(str);
String strRev = sb.reverse(); //strRev = "zyx"
```
### 擷取字串
- `str.substring(beginIndex, endIndexExclude);`
- str = "qazxcv", str.substring(1, 3) = "az"
### 字串長度
- `str.length()`
- str.length() = 6
### 提取特定位置之字元
- `str.charAt(index)`
- str.charAt(1) = 'a'
### 判斷空字串
- `str.isEmpty()`
- str.isEmpty() = false
### 轉大寫
- `str.toUpperCase()`
- str.toUpperCase() = "QAZXCV"
### 轉小寫
- `str.toLowerCase()`
- str.toLowerCase() = "qazxcv"
### 取代特定字元/字串
- `str.replace(old, new)`
- str.replace("az", "") = "qxcv"
- str.replace('a', 'b') = "qbzxcv"
### 移除字串前後空白(包含\n與\t)
- `str.trim()`
- str = "\t A B C \n \t", str.trim() = "A B C"
### 字串串聯
- `str1+str2` 或 `str.concat(str2)`
- str1 = "A", str2 = " B"
- str1+str2 = "A B"
- str.concat(str2) = "A B"
### 字串比較
- `str.eqauls(str2)`
- str1 = "a", str2 = "a"
- str1.equals(str2) = true
### 字串比較(忽略大小寫)
- `str.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)`
- str1 = "aB", str2 = "Ab"
- str.equalsIgnoreCase(str2) = true
### 前綴比對
- `str.startsWith(str)`
- str = "apple", prefix = "ap", prefix2 = "pp"
- str.startsWith(prefix) = true
- str.startsWith(prefix2) = false
### 前綴比對(指定起始位置)
- `str.startsWith(str, pos)`
- str.startsWith(prefix, 1) = true
### 後綴比對
- `str.endsWith(str)`
- str = "apple", suffix = "ple"
- str.endsWith(suffix) = true
### 字串切割
- `str.split(delimiter)`
- str = "apple-pen"
- String [] s = str.split("-")
- s[0] = "apple", s[1] = "pen"
### 正規表達式比對
- 字串只包含數字: `str.matches("\\d+")` 或 `str.matches("[0-9]+")`
- 字串只包含字母: `str.matches("[a-zA-Z]+")`
```java=
str1 = '114554', str2 = '115?239'
str1.matches("\\d+") => true
str2.matches("\\d+") => false
```
## Int to String
```java=
int n;
String s = String.valueOf(n);
//toString(): the string representatation of the object
String s = Integer.toString(n);
String s = "" + n;
```
## Read Input from Stdin
### 必要
- 透過Scanner讀入
```java=
import java.util.Scanner;
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
```
### 判斷是否有無輸入
- `s.hasNext()`
- 有則回傳true, 否則false
### 讀一行
- `s.nextLine()`
- 讀到\n之前
- 如input: "abc ab"
s.nextLine() = "abc ab"
### 讀一個word
- `s.next()`
- 如input: "abc ab"
s.next() = "abc"
s.next() = "ab"
- 讀一個資料型態 (long, double, ...等8種dataType):
- int:`s.nextInt()`
- long: `s.nextLong()`
- double: `s.nextDouble()`
- ==當遇到小數點(如3.14)時scanner會只讀到整數部分(不確定,還沒測試過), 因此在call scanner時應該要==
`Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in).useLocale(Locale.US)`
- 將字串轉成其他型態 (8種dataType): `dataType.parsedataType(s.nextLine())`
- int: int i = Integer.parseInt(s.nextLine())
- long: parseLong
- double: parseDouble
## Print
### 無換行
- `System.out.print('XXX')`
### 有輸出格式
- `System.out.printf('INT = %d', i)`
- %d: int; %o: 8進位int; %x: 16進位int;
%f: float; %s: string
```java=
String s1 = s.next();
int x = s.nextInt();
// %: formatter
// -: left-justified (預設right-justified)
// 15s: (string+空格)佔15格
// 03d: int佔三格,不足的補零
// %n: 換行 (\n也行)
System.out.printf("%-15s%03d%n", s1, x);
```
### 有換行
- `System.out.println('XXX')`
## If-else/for-loop
- syntax is the same as C++
## Get Day
```java=
//s的結果為:MONDAY
int year=2020, month=12, day=21;
String s = LocalDate.of(year, month, day).getDayOfWeek().name();
```
## File
使用時記得要`import java.io.File;`
### 檔案屬性相關的function
- 路徑分隔符號`/` 或是 `\`: `File.separator`
- 檔案絕對路徑: `String getPath()`
- 檔案名稱: `String getName()`
- 檢查路徑名稱的文件是否為目錄: `boolean isDirectory()`
- 檢查路徑名稱的文件是否為檔案: `boolean isFile()`
- 檢查路徑名稱的文件或目錄是否存在: `boolean exists()`
- 父目錄: `String getParent()`
- 使用範例
```java=
File file = new File("/home/username/Documents/javamaterials.pdf");
System.out.println("File name: " + file.getName());
System.out.println("File path: " + file.getPath());
System.out.println("Is file: " + file.isFile());
System.out.println("Is directory: " + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("Exists: " + file.exists());
System.out.println("Parent path:" + file.getParent());
(output)
File name: javamaterials.pdf
File path: /home/username/Documents/javamaterials.pdf
Is file: true
Is directory: false
Exists: true
Parent path: /home/username/Documents
```
### 建立/移除/改名/移動相關的function
- 建立檔案: `boolean creatNewFile()`
- File file = new File("/home/username/Documents/file.txt");
- boolean createdNew = file.createNewFile();
- 建立目錄(父目錄需存在): `boolean mkdir()`
- File file = new File("/home/art/Documents/dir");
- boolean createdNewDirectory = file.mkdir();
- 建立多集目錄: `boolean mkdirs()`
- File file = new File("/home/art/Documents/dir/dir/dir");
- boolean createdNewDirectory = file.mkdirs();
- 移除檔案: `boolean delete()`
- File file = new File("/home/art/Documents/dir/dir/dir");
- boolean removedFile = file.delete();
- 更改/移動檔案名稱: `booolean renameTo()`
- File file = new File("/home/art/Documents/dir/filename.txt");
- boolean renamed = file.renameTo(new File("/home/art/Documents/dir/newname.txt"));
- boolean moved = file.renameTo(new File("/home/art/Documents/another/file.txt"));
以上function執行成功時, 會回傳true, 但可能因為權限問題return false
### 寫檔案
必須要先`import java.io.FileWriter` 或是 `import.java.io.PrintWriter`
- step 1: 建立空檔案
`File f = new File("path/to/your/file.txt");`
- step 2.0: 寫檔案(覆蓋原始檔案)
```java=
FileWriter w = new FileWriter(f);
w.write("xxxx");
PrintWriter p = new PrintWriter(f);
p.print("xxx"); //無換行
p.println("xxx"); //有換行
String str = "xxx"
p.printf("String is %s", str); //輸出格式
```
- step 2.1: 寫檔案(新增文字在原始檔案後)
```java=
FileWriter w = new FileWriter(f, true);
w.write("xxx");
```
- step 3: 關檔案
```java=
w.close();
```
## Output Stream
[[OutputStram V.S. PrintWriter]](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10212682)
### Character Stream
- 可以output `char` 或是 `String`
- 必須要先`import java.io.StringWriter` 或是 `import Java.io.CharArrayWriter`
- 用`StringWriter`建立String; 用`CharArrayWriter`建立char[]
- 將CharArrayWriter轉成char[]: `.toCharArray()`
```java=
CharArrayWriter caw = new CharArrayWriter();
...
char [] charArr = caw.toCharArray();
```
- 將char[]寫入檔案:
```java=
CharArrayWriter c = new CharArrayWriter();
File f = new File("path/to/your/file.txt");
FileWriter w = new FileWriter(f, true);
//寫入char[]
c.write("xxx; yyy, zzz; qqq");
c.writeTo(f);
f.close();
c.close();
```
- per char讀檔案:
- 必須要`import java.io.FileReader`
- 讀char: 用`.read()`, 會回傳int, 當回傳`-1`==代表已經讀到檔案最後==
```java=
FileReader r = new FileReader("xxx.txt");
int charAsNumber = r.read();
while(charAsNumber != -1) {
char character = (char) charAsNumber;
charAsNumber = r.read();
}
r.close();
```
### Byte Stream
- 寫入的內容0,1 序列 (即寫binary檔案)
- 必須要先`import FileOutputStream` 與`import OutputStream`
- 可以利用`.getBytes()`將String轉成byte[]
- String str = "hby";
- byte[] strByte = str.getBytes();
- 將byte[]寫入檔案:
```java=
byte[] data = new byte[] {'s', 't', 'r', 'e', 'a', 'm'};
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("sample.txt", false);
outputStream.write(data);
outputStream.close();
```
- per byte/multiple bytes讀檔案:
- 必須要`import java.io.FileInputStream`
- 讀byte: 用`read()`, 會回傳int, 當回傳`-1`==代表已經讀到檔案最後==
- 目前剩餘可讀取的byte數量: `.available()`
```java=
//per byte
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("xxx.txt");
byte b =(byte) fis.read();
//multiple bytes (例如10bytes)
byte [] mb = new byte[10];
fis.read(mb);
```
## Class
### 語法
```java=
class className{
modifier dataType varName;
...
//constructor
public className(dataType varName){
this.varName = varName;
...
}
//instance method (public/private/protected/default)
public dataType funName(parameter){
...
}
}
```
- 四種可access的modifiers
|modifier|同class|同package|不同package<br>有繼承|不同package<br>無繼承|
|---------|:-:|:-:|:-:|:-:|
|private | V | | | |
|default | V | V | | |
|protected| V | V | V | |
|public | V | V | V | V |
- 舉例來說
```java=
//Bird/Cat/Dog/Mammal are in different packages
package birds;
public class Bird{
public void fly(){...}
protected void sing(){...}
}
public class Cat extends Mammal{
public void meow(){...}
}
public class Dog extends Mammal{...}
package mammals;
public class Mammal{
protected void motherChild(){...}
void yell(){...}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Cat cat = new Cat();
}
}
```
- 可以看到Cat繼承Mannal, 其中Mammal中有`protected`的motherChild與`default`的yell, 因此當呼叫cat.motherChild()是沒問題的, 但cat.yell()則會出錯
- 當要建立subclass object時有兩種方法
(延續上述例子, Cat與Dog都繼承Mammal)
- subclass reference
```java=
//reference與object皆是Cat
Cat c = new Cat();
//reference與object皆是Dog
Dog d = new Dog();
//reference與object皆是Mammal
Mammal m = new Mammal();
//相互(Cat <-> Dog)沒繼承, 不能assign
Cat c = new Dog(); //wrong!
Dog d = new Cat(); //wrong!
```
- superclass reference
```java=
//reference是Mammal, object是Cat
Mammal c = new Cat();
//Mammal沒有meow(), 不能透過superclass reference去呼叫
//c.meow() //compile-time error!
//reference是Mammal, object是Dog
Mammal d = new Dog();
//不能將parent的object assign給subclass
Cat c = new Mammal(); //wrong!
Dog d = new Mammal(); //wrong!
```
### Nullability
- `className c1 = null`
### 繼承 (Inheritance)
- `class subClass extends superClass { ... }`
- 利用`super`可以access superclass的fields, 或呼叫 methods, constructor
```java=
class A {
protected int a;
protected int b;
public A(int a, int b){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
class B extends A {
protected int c;
//constructor
public B(int a, int b, int c) {
//呼叫superclass的constructor
super(a, b);
//super(a, b)的寫法可以改成第24,25行
super.a = a;
super.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public void printSuperClass(){
super.print();
//第30行可以改寫成
print();
}
}
```
### Interface
- 一個class可以實作(implements)多個interface, 卻只能繼承(extends)一個superclass
### Polymorphism
```java=
class Alphabet{}
class A extends Alphabet{}
class B extends Alphabet{}
```
- 在宣告成array時
```java=
Alphabet [] AlphabetList = {A, B}
```
### Overload (重載)
- 在compile time
- 根據參數型態或個數不同, 會呼叫相對應的constructor
```java=
public example{
public void example(){...}
public void example(int i){...}
public void exmaple(float j){...}
public void example(int i, float j){...}
...
}
```
### Override (覆寫)
- 在runtime
- `@Override`
## Method
### 語法
- `modifiers` `return_type` `method_name` `(list_of_parameters)` `{ body }`
- 例如: public static int sum2int (int a, int b) { return a + b; }
- modifiers: public static
- return_type: int
- method_name: sum2int
- list_of_parameters: int a, int b
- body: return a + b
### 修飾詞 (modifier)
- 分成access跟non-access
- access: public, protected, default, private
- non-access: static, final, abstract, synchronized, volatile [[Ref]](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_nonaccess_modifiers.htm)
### 參數 (list_of_parameters)
- 允許可變動個數之參數量`varargs (即variable-length arguments)`, ==當參數是一個以上時, `varargs`就要放在最後==
- 語法1: `(dataType... xxx)`
- 例如: public static void show`(int... num)`{}
- 語法2(以三個參數為例): `(dataType1 xxx, dataType2 yyy, dataType3... zzz)`
- 例如: public static void show`(double fstPara, long secPara, int... num)`{}
## Exception
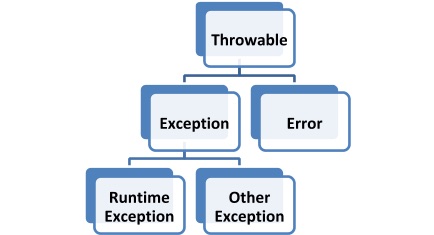
Base class 是 `java.lang.Throwable`
### Classes
- Trowable
- Exception
- compile-time exception
- 例如: RuntimeException, IOException,...
- RuntimeException
- unchecked exception (在compile-time不會檢查)
- 例如: ArithmeticException, NumberFormatException, NullPointerException (NPE), ...
```java=
String str = null;
String str2 = null;
//no NPE
if(str == null) ....
//no NPE
if(Object.equals(str, str2)) ....
//no NPE
if("xxx".equals(str)) ....
//throws NPE
if(str.equals("xxx")) ....
```
- Error
- unchecked exception (really?) [Ref](https://hyperskill.org/learn/step/3570)
- 例如: OutOfMemoryError, StackOverflowError, ...
### Exception Handling
- `try-catch-finally` 或 `try-finally`
- 跟python的語法有異曲同工之妙 [[Ref](https://hackmd.io/YX_ji6AZToalWsQh3SSYoA?view#IfForWhileTryRaise)]
- 當進入到catch時並執行完此例外處理時, 不會再進入try裡面, 如範例中的"inside the try block after the exception"就不會顯示出來
```java=
System.out.println("before the try-catch block");
try {
System.out.println("inside the try block before an exception");
//it throws ArithmeticException
System.out.println(2 / 0);
System.out.println("inside the try block after the exception");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Division by zero!");
}
System.out.println("after the try-catch block");
```
- Java7 支援multi-catch
```java=
try{
xxxxxx
} catch(yyyException){
} catch(zzzException){
}
```
- 使用mutli-catch時, base class的exception要放在最後判斷, 如範例IOException要放在Exception之前
```java=
try{
} catch(IOException e){
} catch(Exception e){
}
```
- 如有多個exception要放在同個catch判斷時, 用`|`符號作分隔, 寫成`catch(Exception1 | Exception2 e)`, 可以利用`e.getClass().getSimpleName()`得知所handle的exception class, 特別注意到在catch判斷式中, 其中任一一個exception不能是任意其他一個的subclass, 如catch(RuntimeException | Exception e)就會出錯
## Generic Programming
- 類似c++的template ([這裡講的很詳細](https://ethan-imagination.blogspot.com/2018/11/javase-gettingstarted-017.html))
- 注意到`<>` 裡面放的type==不能是primitive type==, 只允許reference type, 包含array (因此primitive array是可以使用的, 如int[]), custom class, standard class (Integer, Double, Boolean, ...)
```java=
class urGenericType<T> {
T t;
//constructor
public urGenericType(T t){
this.t = t;
}
```
- 也允許多個type參數
```java=
class urGenericType<T, U, V> {
T t;
U u;
V v;
...
}
```
- 在使用時直接`urGenericType gtn = new GenericTypeName<>(...)`, 例如`urGenericType<Integer> obj1 = new urGenericType<>(10);`
- 當然也可以建立generic array
```java=
public class urImmutableArray<T>{
T [] tArr;
//constructor
public urImmutableArray(T [] tArr){
this.tArr = tArr;
}
...
}
```
- 在使用時直接`var urArrName = new urImmutableArray<>(...)`, 例如`var stringArray = new urImmutableArray<>(new String[] {"item1", "item2", "item3"});`
[序列化](https://lolikitty.pixnet.net/blog/post/36759934-java-%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96-%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96-%28serialization-deserialization%29)
## Gson
- 序列化(serialization): java物件 → String
```java=
publi class MyObject(){
private BigInteger id;
private static String userName;
private transient Data date;
}
List<MyObject> myObjectList = new ArrayList<MyObject();
MyObject myObject = new MyObjec();
myObjectList.add(myObject);
myObjectList.add(myObject);
//List<MyObject> -> String
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().create();
String myObjectStr = gson.toJson(myObjectList);
//允許序列化null
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().serializeNulls().create();
//排除那類不序列化
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().excludeFieldsWithModifiers(Modifier.TRANSIENT).create();
```
- 反序列化(deserialization): String → java物件
```java=
JsonReader jsonReader = new JsonReader(new StringReader(xxx));
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().excludeFieldsWithModifiers(Modifier.TRANSIENT).create();
List<MyObject> myObjectList = gson.fromJson(jsonReader, new TypeToken<ArrayList<MyObject>>() {}.getType());
```
- `transient`要小心使用, ==transient = 不序列化 + @Transient==, 如有用到JPA repository的function, 當寫某張table的某個non-nullab欄位, 就會出問題
## Reflection
- 改變modifier (常用在unit test,要mock無法直接access的field)
```java=
public class MyObject(){
private static final String USERNAME = "HBY";
}
Field userNameField = MyObject.class.getDeclaredField("USERNAME");
Field modifierField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
//access private member
modifierField.setAccessible(true);
//set modifier to public
modifierField.setInt(userNameField, userNameField.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
//set USERNAME to ...
userNameField.set(MyObject, "New_HBY");
```
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet