# Express.js 入門
- Express.js 是以 **Node.js 為基礎的 web 框架**
- 常用來 **開發 API** 或是 **web 應用程式**
- 可以快速的開發 [RESTful API](https://aws.amazon.com/tw/what-is/restful-api/)
- 支援多種模板引擎,可以產生動態網頁
- Express.js 提供多種不同的物件和機制,**簡化專案的複雜度**
- 開發者可以專注於應用程式的功能本身
:::info
**更多閱讀**:
- [Express.js 官網](https://expressjs.com/)
- [Express.js 中文文件](https://expressjs.com/zh-tw/)
:::
## 如何開始開發 Express.js APP
- 必須先安裝 [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/download/current)
- 通常會新建一個資料夾,作為專案的目錄
- 透過 Node.js 的 `npm` 工具,下載 Express.js 的套件到專案目錄中
- 打開任意的終端機軟體(如: Power Shell, CMD, git bash...)
- 輸入以下指令,將 Express.js 的檔案下載到專案目錄中
```
npm install express
```
- 在此目錄中的程式碼檔案,即可存取 Express.js 中的功能和套件
## Express.js 基本概念
Express.js 中有兩個重要的機制
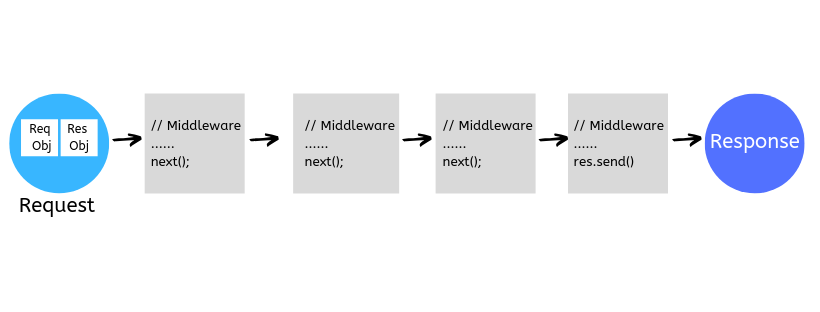
- **Middleware**
- 系統中的主要功能都必須用 middleware 的形式表示
- 目的是提供一個**簡單易讀的開發標準**,降低專案的複雜度
- 把複雜的功能拆成多個 middleware
- 透過 Express.js 將這些 middleware 串接在一起
- 使用者只需要思考每個 middleware 該執行的任務,和執行的順序
- 資料傳遞和函式呼叫由 Express.js 負責
- **Route**
- 根據 request 中的 URL,將 request 轉發給對應 middleware 的流程
- 可讓應用程式根據不同的 URL,執行不同的功能
- 同時提供一組簡潔的方法,解析、取得 URL 中的參數和資料
### Express.js 應用程式架構
在 Node.js 中,可以用 `require()` 引入外部的模組和套件
```javascript=
const express = require("express");
```
在 Epress 應用程式中,會先宣告一個 **`Application` 物件**
- 此**物件用來代表整個應用程式**,包含整個應用程式的功能和設定
```javascript=
const express = require("express");
/* 建立 Application 物件 */
let app = express();
/* 加入應用程式的功能和設定 */
// ...
```
完成 `app` 的設定後,需要建立 HTTP Server,啟動應用程式
- 可以透過 Node.js 原生的 HTTP 模組,建立 Server 物件
```javascript=
const express = require("express");
const http = require("http");
/* 建立 Application 物件 */
let app = express();
/* 加入應用程式的功能和設定 */
// ...
/* 建立 Server 物件並使用 port 3000 */
let server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000, function () {
/* 當 server 成功啟動後 顯示一下訊息 */
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
- `app` 物件也提供 `listen()` 方法,可以直接啟動 HTTP Server
```javascript=
const express = require("express");
/* 建立 Application 物件 */
let app = express();
/* 加入應用程式的功能和設定 */
// ...
/* 啟動 HTTP Server 並使用 port 3000 */
app.listen(3000, function () {
/* 當 server 成功啟動後 顯示一下訊息 */
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
### 基礎 Middleware
Express.js 中的所有功能都要以 middleware 的形式表示
- 可以把應用程式的一個功能,想成工廠上的一條產線
- 每一個 middleware 就像產線上的一台機器
- 每個 middleware 都負責完成某個小工作
- 應用程式收到 request 之後,會傳遞給 middleware
- 當 middleware 結束他的工作時,就會將資料傳遞給下一個 middleware
- 每個 middleware 完成一個小功能,直到產出 response
- Middleware 本質上是有固定格式的 function
- 包含三個參數,分別代表:
- request: 來自 user 的請求
- response: 傳回給 user 的回應
- next: 下一個 middleware
- 呼叫 `app.use()` 可以將 middleware 串接到 `app` 中
```javascript=
const express = require("express");
const http = require("http");
/* 建立 Application 物件 */
let app = express();
/* 加入 middleware */
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
/* middleware 內容 */
});
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
/* middleware 內容 */
});
...
/* 建立 Server 物件並使用 port 3000 */
let server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000, function () {
/* 當 server 成功啟動後 顯示一下訊息 */
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
:::success
**舉個 🌰**
```javascript
const express = require("express");
const http = require("http");
/* 建立 Application 物件 */
let app = express();
/* 加入 middleware */
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
/* 當收到 request 時 輸出以下訊息 */
console.log("Hello Express!");
next(); // 進入下一個 middleware
});
/* 建立 Server 物件並使用 port 3000 */
let server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000, function () {
/* 當 server 成功啟動後 顯示一下訊息 */
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
:::
### 產出 Response
Express 中有許多產出 response 的方法,以下列出較簡易的幾個方法
:::warning
- 由於產出 response 的 middleware,必須是最後被執行的 middleware,所以不會呼叫 `next()`
- 故該 middleware 的 `next` 參數可以省略
:::
#### `res.send(body)`
- 將 `body` 中的內容加入 response body,並馬上送出
- 因為會馬上將 response 送回給 user,無法和其他方法一起使用
:::success
**舉個 🌰**
```javascript
const express = require("express");
const http = require("http");
let app = express();
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
console.log("hello!");
next();
});
/* 產出 response 可以省略 next 參數 */
app.use(function(req, res) {
/* 回應 HTML 字串 */
res.send("<h1>Hello, World!</h1>");
});
let server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000, function () {
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
- 打開 http://localhost:3000/ ,可以看到應用程式回應的內容

:::
### 基礎 Route
- 在串接 middleware 時,可以設定 route 的參數 (虛擬路徑)
- 當 URL 的開頭和該路徑相同時,request 將會傳遞給該 middleware
:::success
```javascript
const express = require("express");
const http = require("http");
let app = express();
/* 當 URL 的開頭是 / 時 將執行這個 middleware */
app.use("/", function(req, res, next) {
/* 輸出 Hello Express! */
console.log("Hello Express!");
next();
});
/* 當 URL 的開頭是 /hello 時 將執行這個 middleware */
app.use("/hello", function(req, res, next) {
/* 輸出 hello! */
console.log("hello!");
next();
});
/* 當 URL 的開頭是 /world 時 將執行這個 middleware */
app.use("/world", function(req, res, next) {
/* 輸出 world! */
console.log("world!");
next();
});
app.use(function(req, res) {
/* 回傳 HTML 字串 */
res.send("<h1>Hello, World!</h1>");
});
/* 建立 Server 物件並使用 port 3000 */
let server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000, function () {
/* 當 server 成功啟動後 顯示一下訊息 */
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
在 URL 中加入不同的路徑,觀察程式的輸出
- http://localhost:3000/
- http://localhost:3000/hello
- http://localhost:3000/hello/123
- http://localhost:3000/world
- http://localhost:3000/world/abc
:::
## 根據不同 URL 回應不同內容
結合 route,和 middleware,可以根據不同的 URL 回應不同內容
:::info
```javascript
const express = require("express");
const http = require("http");
let app = express();
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
console.log("Hello Express!");
next();
});
app.use("/hello", function(req, res) {
res.send("<h1>Hello</h1>");
});
app.use("/world", function(req, res, next) {
res.send("<h1>World</h1>");
});
app.use("/", function(req, res, next) {
res.send("<h1>Home</h1>");
});
/* 建立 Server 物件並使用 port 3000 */
let server = http.createServer(app);
server.listen(3000, function () {
/* 當 server 成功啟動後 顯示一下訊息 */
console.log("Server listening on port 3000 ...");
});
```
- http://localhost:3000/
- http://localhost:3000/
- http://localhost:3000/world
:::
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet