# 2360. Longest Cycle in a Graph
###### tags: `leetcode`
## Description
You are given a directed graph of `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1`, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size `n`, indicating that there is a directed edge from node `i` to node `edges[i]`. If there is no outgoing edge from node `i`, then `edges[i] == -1`.
Return the length of the longest cycle in the graph. If no cycle exists, return `-1`.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node.
- Example 1:
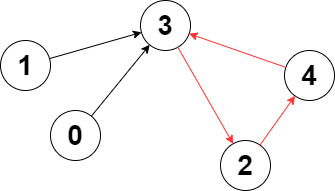
>Input: edges = [3,3,4,2,3]
Output: 3
>>Explanation: The longest cycle in the graph is the cycle: 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2.
The length of this cycle is 3, so 3 is returned.
- Example 2:
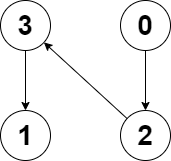
>Input: edges = [2,-1,3,1]
Output: -1
>>Explanation: There are no cycles in this graph.
- Constraints:
>n == edges.length
$2 \leq n \leq 10^5$
$-1 \leq edges[i] < n$
$edges[i] \neq i$
## Solution
- The problem can be regarded as the permutation of `DFS` iteration issue
- Because of the structure, we can make sure that each node only has one outgoing edge at most, which means that there is no chance for a graph containing multiple circle with the same node
- To leverage on the fact, cosntruct a visit vector and store if it has been visited with the value for the `visit sequence`. When we iterate through the nodes, mark it as the current index
```cpp=
global_cnt = 0;
// in DFS, current updating cnt
visit[idx] = cnt;
```
- When the dfs meets dead end, update the global cnt for the cycle and return -1
```cpp=
if (edges[idx] == -1)
{
global_cnt = cnt + 1;
return -1;
}
```
- When the pointing node is not iterated yet, return the dfs for next
```cpp=
if (visit[edges[idx]] == 0) return dfs(edges[idx], cnt + 1, edges);
```
- When the visit value of the pointing node is in the current iteration, which means that the starting point is smaller than the one gets meet, update new global value and return it back
```cpp=
if (visit[edges[idx]] > global_cnt)
{
global_cnt = visit[edges[idx]];
return cnt + 1 - visit[edges[idx]];
}
```
- If the meeting node is not in the current cycle, update the new global value and return it
```cpp=
global_cnt = cnt + 1;
return -1;
```