# 2090. K Radius Subarray Averages
###### tags: `leetcode`
## Description
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
For example, the average of four elements 2, 3, 1, and 5 is (2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to 2.
- Example 1:
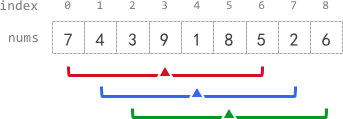
>Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3
Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1]
>>Explanation:
- avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index.
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37.
Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5.
- For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4.
- For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4.
- avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
- Example 2:
>Input: nums = [100000], k = 0
Output: [100000]
>>Explanation:
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000.
avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
- Example 3:
>Input: nums = [8], k = 100000
Output: [-1]
>>Explanation:
- avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
- Constraints:
>n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 105
0 <= nums[i], k <= 105
## Solution
- We need to check whether the boundary contains any element that needs to be calculated
```cpp=
vector<int> ans(nums.size(), -1);
if (k * 2 >= nums.size()) return ans;
```
- The ending posing is the last one that needs to be calculated, and the length is the total length of the anverage size. We can accumulate all the stuff together first
```cpp=
int end = nums.size() - k - 1, len = k * 2 + 1, i = 0;
for (; i < len; i++) sum += nums[i];
```
- In the cycle, update the value for answer by calculating the average, and substract the first element in the current array and add the new one awaiting
```cpp=
for (i = k; i < end; i++)
{
ans[i] = sum / len;
sum -= nums[i - k], sum += nums[i + k + 1];
}
```
- After all, update the final one and return
```cpp=
ans[end] = sum / len;
return ans;
```