# 1319. Number of Operations to Make Network Connected
###### tags: `leetcode`
## Description
There are n computers numbered from `0` to `n - 1` connected by ethernet cables connections forming a network where `connections[i] = [ai, bi]` represents a connection between computers `ai` and `bi`. Any computer can reach any other computer directly or indirectly through the network.
You are given an initial computer network connections. You can extract certain cables between two directly connected computers, and place them between any pair of disconnected computers to make them directly connected.
Return the minimum number of times you need to do this in order to make all the computers connected. If it is not possible, return `-1`.
- Example 1:
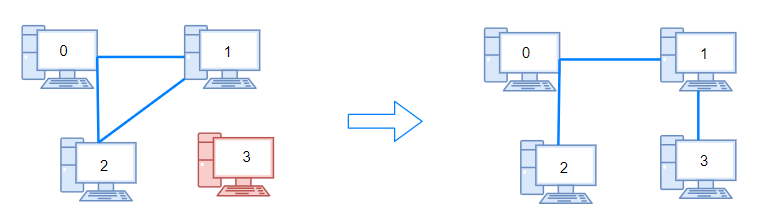
>Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
Output: 1
>>Explanation: Remove cable between computer 1 and 2 and place between computers 1 and 3.
- Example 2:
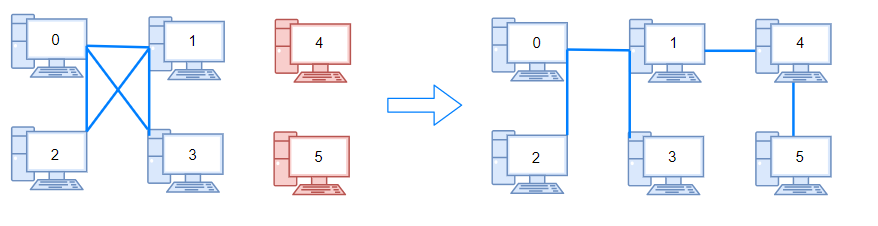
>Input: n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: 2
- Example 3:
>Input: n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]]
Output: -1
Explanation: There are not enough cables.
- Constraints:
>$1 \leq n \leq 10^5$
$1 \leq connections.length \leq min(n \times (n - 1) / 2, 10^5)$
$connections[i].length == 2$
$0 \leq a_i, b_i < n$
$a_i != b_i$
There are no repeated connections.
No two computers are connected by more than one cable.
## Solution
- The key point is to find the closing set of the connected computers
- By connecting the whole machines, we must have at least `n-1` lines, so check it beforehand
```cpp=
if (connections.size() + 1 < n)
return -1;
```
- To do so, we can iterate through all the machines and check if it is visited, and do `DFS`
- Before start, construct a graph that is the connected dots for each of the node
```cpp=
graph.resize(n);
vector<bool> visit(n);
for (auto &i : connections)
{
graph[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);
graph[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);
}
```
- Calculate the time initiating `dfs` can count the set number
```cpp=
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (visit[i] == false)
{
cnt++;
dfs(i, visit);
}
}
return cnt - 1;
```
- For `dfs`, just iterate through the node graph and check if recursive is needed when the node is not iterated yet
```cpp=
void dfs(int node, vector<bool>& visit) {
visit[node] = true;
for (auto &i : graph[node])
{
if (visit[i] == false)
dfs(i, visit);
}
}
```