2017q3 Homework1 (ternary)
===
contributed by <`river85511`>
###### tags: `sysprog2017`
---
## Homework Requirements
- [x] 解釋 Balanced Ternary 原理
- [x] Balanced Ternary 的設計要解決什麼類型的問題,需要詳述實際應用案例 (如 IOTA/Tangle)
- [ ] 針對特定的領域 (如加密貨幣),列出在 GitHub 裡頭可找到的應用案例,不僅列出程式碼,還要解說
- [ ] 在研究的過程中,應該會對既有工具進行修改或者重新開發 (不限程式語言),也該一併指出,程式碼應該維護在 GitHub 上
## Balanced Tenary
### Introduction to Balanced Ternary
相較於以 `0` 和 `1` 來表示數值的二進位 (Binary),三進位 (Ternary) 則是以 `0`、`1`、`2` 來表示數值。而在 Balanced Ternary 中,Ternary 的 `0`,`1`,`2` 則是改以 `-1`、`0`、`1` 或是更簡略的以 `T`、`0`、`+` 來表示。
>中英文字間請記得空白
>[name=課程助教][color=red]
>謝謝助教提醒!
>[name=David Kuo][color=blue]
除此之外,在二進位的電腦中的 bit 和 byte, 在三進位的電腦中則變為 trit 和 tryte。一個 trit 能夠表達三種數值 `T`、`0`、`+`,而一個 tryte 有 6 個 trits。
### Conversion to Balanced Ternary Representation
接著,透過以下的公式就能將不同整數基底 (integer base) 的數字以 Balanced Ternary 表示:
$(a_n a_{n-1} \dotsi a_1 a_0. c_1 c_2 c_3 \dotsi)_b = \sum_{k=0}^{n}a_kb^k + \sum_{k=0}^{n}c_kb^{-k}$,其中
* ${a_n a_{n-1} \dotsi a_1 a_0. c_1 c_2 c_3 \dotsi}\ is\ the\ representation\ in\ the\ original\ numerical\ system$
* $b\ is\ the\ original\ radix$
* $a_k\ and\ c_k\ are\ the\ digits\ places\ to\ the\ left\ or\ right\ of\ the\ radix\ point\ respectively$
舉例來說, 若以 Balanced Ternary 來表示整數,如:$20_{dec}$ 和 $-20_{dec}$ 時,其表示法為:
* $1T1T_{bal3} = 1\cdot3^3 + (-1)\cdot3^2 + 1\cdot3^1 + (-1)\cdot3^0 = 20_{dec}$
* $T1T1_{bal3} = (-1)\cdot3^3 + 1\cdot3^2 + (-1)\cdot3^1 + 1\cdot3^0 = -20_{dec}$
>由此例子可以發現,若想要用 Balanced Ternary 表達負數,只需要將正數的 $+$ 和 $T$ 對調即可。[color=red]
若以 Balanced Ternary 來表示小數,如: ${(\frac{1}{20})}_{dec}$ 、${(\frac{-1}{20})}_{dec}$ 、${(\frac{19}{20})}_{dec}$,其表示法為:
* $0.0\overline{1T} = 0\cdot3^0 + 0\cdot3^{-1} + 1\cdot3^{-2} + (-1)\cdot3^{-3} + \dotsi = \frac{1}{20}$
* $0.0\overline{T1} = 0\cdot3^0 + 0\cdot3^{-1} + (-1)\cdot3^{-2} + 1\cdot3^{-3} + \dotsi = \frac{-1}{20}$
* $1.0\overline{T1} = 1\cdot3^0 + 0\cdot3^{-1} + (-1)\cdot3^{-2} + 1\cdot3^{-3} + \dotsi = \frac{19}{20}$
>由此例子可以發現,若想要從 $\frac{1}{20}$ 得到 $\frac{19}{20}$,只需要在 $\frac{1}{20}$ 小數點前的第一位改成 $1$ 然後小數點後的 $1$ 和 $T$ 對調即可。[color=red]
參考資料:[Wikipedia: Balanced Ternary](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balanced_ternary)、[Number Systems 3: Ternary](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vOyiHMa-mtQ)
### Balanced Ternary Arithmetic
#### Addition
|+ | T | 0 | 1 |
|-------|---|---|---|
| T |T1 | T | 0 |
| 0 |T | 0 | 1 |
| 1 |0 | 1 | 1T|
#### Subtraction
|- | T | 0 | 1 |
|-------|---|---|---|
| T |0 | T | T1|
| 0 |1 | 0 | T |
| 1 |1T | 1 | 0 |
> 1~bal3~ + 1~bal3~ 可以表示成 1T~bal3~ = 3~dec~ - 1~dec~
> T~bal3~ + T~bal3~ 可以表示成 T1~bal3~ = -3~dec~ + 1~dec~
#### Multiplication
|× | T | 0 | 1 |
|-------|---|---|---|
| T |1 | 0 | T |
| 0 |0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 |T | 0 | 1 |
#### Division
|÷ | T | 0 | 1 |
|-------|---|---|---|
| T |1 |NaN| T |
| 0 |0 |NaN| 0 |
| 1 |T |NaN| 1 |
>需要特別注意的是,減法和除法是不符合交換律(communicative)的
基於上述四則運算規則,接著我們來談 multi-trits 的加減乘除。
#### multi-trits addition
以 $11_{dec} + 4_{dec} = 15_{dec}$ 或 $11T_{bal3} + 11_{bal3} = 1TT0_{bal3}$ 為例:
11T
+ 11
--------------
1T0
+ 1
--------------
TT0
+ 1
--------------
1TT0
#### multi-trits subtraction
以 $11_{dec} - 4_{dec} = 7_{dec}$ 或 $11T_{bal3} - 11_{bal3} = 10T_{bal3}$ 為例:
11T
- 11
--------------
101
+ T
--------------
1T1
#### multi-trits multiplication
以 $11_{dec} \times 4_{dec} = 7_{dec}$ 或 $11T_{bal3} \times 11_{bal3} = 1TT0T_{bal3}$ 為例:
11T
x 11
--------------
11T
+ 11T
--------------
1T0T
+ 1
--------------
TT0T
+ 1
--------------
1TT0T
#### multi-trits division
以 $30_{dec} \div 6_{dec} = 5_{dec}$ 或 $1010_{bal3} \div 1T0_{bal3} = 1TT_{bal3}$ 為例:
>根據 [Wikipedia: Balanced Ternary](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balanced_ternary),若
> 被除數 > (除數/2) -> 商 = 1
> 被除數 < -(除數/2) -> 商 = T
> -(除數/2) <= 被除數 <= (除數/2) -> 商 = 0
01TT
-------
Divisor 1T0 )1010 T0<1<10, set 0
- 0
-------
1010 10 = 10, but 10.1 > 10, set 1
-1T0
-------
TT0
+ 1
-------
0T01 T01<T0, set T
- T10
------
0T10 T10=T10, set T
- T10
------
0
>上述的規則其實我想了很久,後來我的想法是:除法的目的在於,使被除數扣掉除數的某個倍數後,能使餘數為0(整除),若不為零則得最接近0。另外,在 Balanced Ternary 中,除數能夠除的倍數只有 `-1`、`0`、`1`。因此,若以上面的例子來解釋的話,第一次的商為0的原因是因為,`1` 這個數字不管 - (1 * 6) 或是 - (-1 * 6)都會使 `1` 遠離 `0`,只有 - (0 * 6) 才能使餘數最接近 `0`。同理類推第二次的商為`1` 的原因是因為 `10.1` - (1 * 6) 比 -(0 * 6) 和 -(-1 * 6)更能讓餘數接近零。
### Ternary Logic
>In logic, a three-valued logic (also ternary logic or 3VL) is a logic systems in which there are three truth values indicating true, false and some indeterminate third value. -- Wikipedia: Three-valued logic
根據維基百科的定義,三元邏輯就是一種有三種可能值(正、負、中間值)的邏輯系統。而在 Balanced Ternary 中,此三種可能值就是 `-1`、`0`、`1`。
#### Ternary Logic Operators in True Tables
下表彙整了 Balanced Ternay 的 OR、AND、XOR、NEG 的邏輯運算子(Logic Operator)
|A |B |A ∨ B|A ∧ B|A ⊕ B|¬ A |
|-----|-----|-----|-----|-----|-----|
|1 |1 |1 |1 |-1 |-1 |
|1 |0 |1 |0 |0 |-1 |
|1 |-1 |1 |-1 |T |-1 |
|0 |1 |1 |0 |0 |0 |
|0 |0 |0 |0 |0 |0 |
|0 |-1 |0 |-1 |0 |0 |
|-1 |1 |1 |-1 |T |1 |
|-1 |0 |0 |-1 |0 |1 |
|-1 |-1 |-1 |-1 |-1 |1 |
接著,我們來談應該要怎麼實做這些邏輯運算子,並延伸到半加器及全加器的設計上。首先,下圖列出了一個多工器(multiplexer),這個多工器上有五個 pin,其中4個 pin (sel、N、0、P) 為 input pin,剩下的一個 pin 為 output,其功能為:
* 當 sel 的輸入值為 `-1` 時,out 就會為 N 的輸入值;
* 當 sel 的輸入值為 `0` 時,out 就會為 0 的輸入值;
* 當 sel 的輸入值為 `1` 時,out 就會為 P 的輸入值;
>空白!!
>[name=課程助教][color=red]
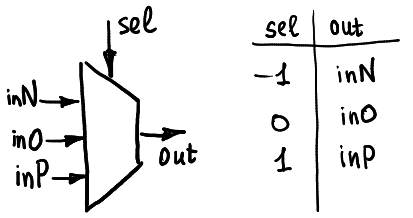
透過這個多工器,我們就能先實作出一些 Balanced ternary 的單元運算子(unary operator),包括: increment、decrement、 max(A,0) (或稱為 OR )、min(A,0) (或稱為 AND )。如下列圖片所示:
##### increment
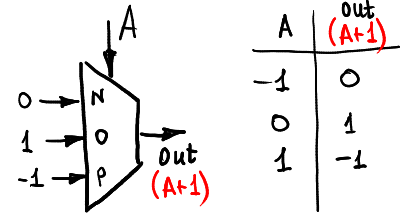
##### decrement
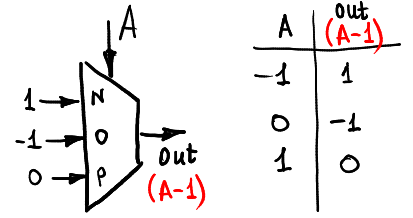
##### max(A,0) (或是 OR)
.png)
##### min(A,0) (或是 AND)
.png)
有了這些單元運算子(Unary Operator)以後,就能夠將半加器(Half Adder) 和全加器(Full Adder)實現,如下列圖片所示:
### Half Adder and Full Adder
#### 半加器 (Half Adder)
##### Sum of two trits
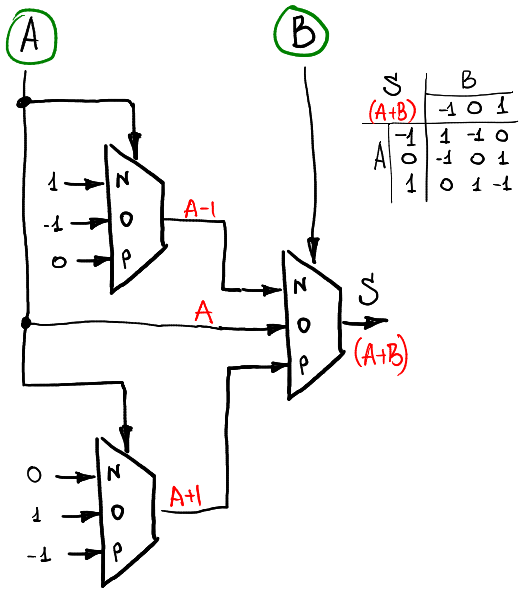
>從這個電路得到的結果,就如同上面在 Balanced Ternary Arithmics 中介紹的 Addition 部份相同,至於紀錄進位(carry)的部份,則會由下面的 Consensus 來實現
##### Consensus
.png)
#### 全加器 (Full Adder)
##### Sum of three trits
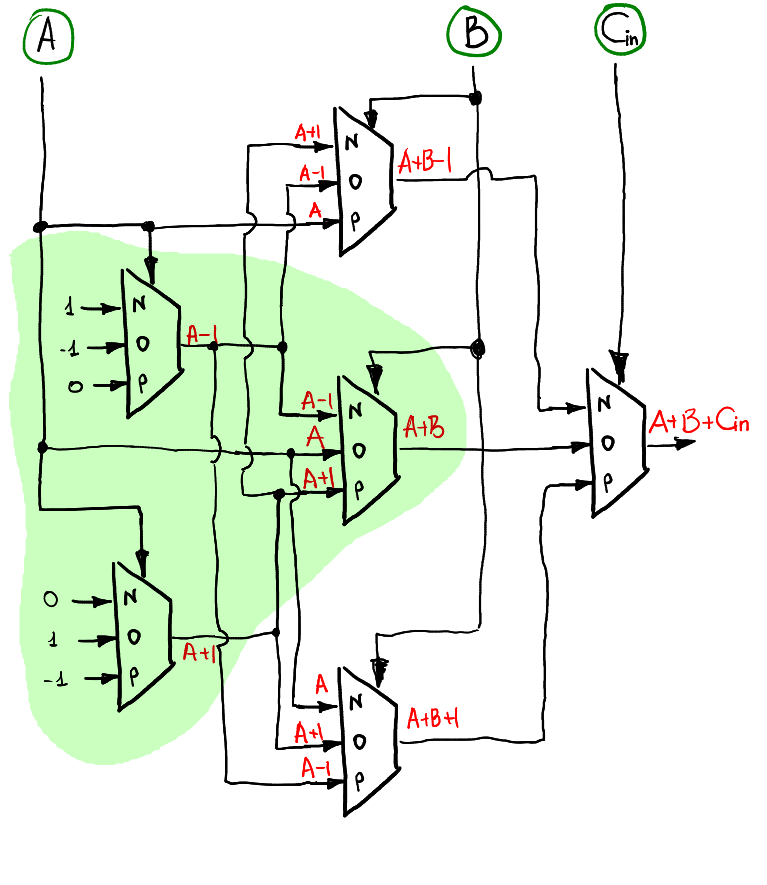
>可以特別注意到的地方是:若 Carry (Cin)為0的話,從全加器得到的結果就會如同半加器一樣,也就是圖中的綠色部份。至於若要檢查是否在加的過程中有 overflow 發生,則是由下面的電路實現。
##### Overflow - carry flag
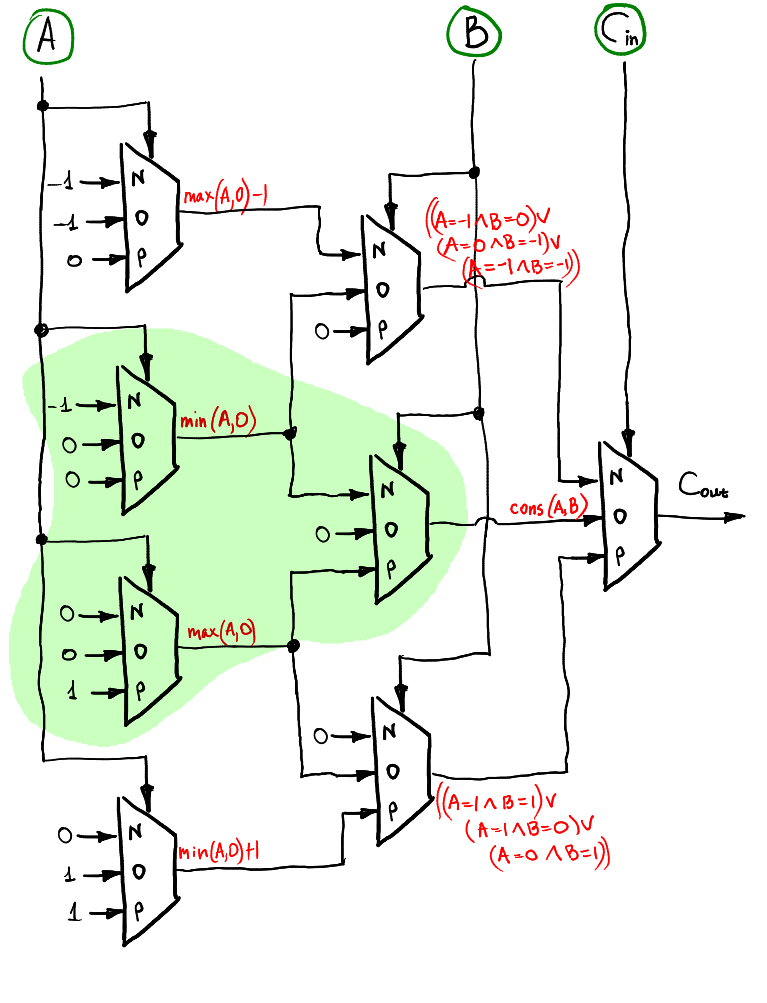
#### Application of Ternary Logic
[SQL(NULL)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Null_(SQL))
參考資料:[Wikipedia: Three-valued logic](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three-valued_logic)、 [Wikipedia: 三值邏輯](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E4%B8%89%E5%80%BC%E9%80%BB%E8%BE%91)、
[Ternary logic](https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Ternary_logic)、[Ternary Computing Basics](https://github.com/ssloy/tutorials/wiki/Ternary-computing:-basics)
## Balanced Ternary 的設計要解決什麼類型的問題
### Setun - A Balanced Ternary Based Computer
在1956年的蘇聯,由 S. L. Sobolev 帶領的團隊希望能夠創造出一台便宜、便於學校、實驗室、設計機構、或製造場使用的電腦,但由於電晶體在當時非常難取得,而真空管又非常容易損毀,促使他們重新檢視了電腦的架構,並討論了未來電腦的雛型。在這個背景下誕生的電腦就是一台 Balanced Ternary 的電腦 Setun。
透過在當時取得容易的微型鐵氧極線圈(miniature ferrite cores) 和半導體二極體(semiconductor diodes) 來當作變流器(controlled current transform) 能夠輕易的實現 Balanced Ternary 中的邏輯運算,同時,Balanced Ternary 的邏輯運算比二進位的邏輯運算還快,耗能也較少。這些都是促使他們打造一台 Balanced Ternary 電腦的原因之一。
在1960年的4月,這台電腦通過測試,並展現了驚人的可靠度和不同環境的適應性(例如溫差)。同時,Setun 由於便於製造及使用,不只被列入建議生產的清單上,還接收到國外的訂單。然而,即使在以上種種優點下,在1965年,Setun 仍在蘇聯電腦生產局官員的反對下,被迫停止生產。而後用來取代 Setun 的則是一台擁有同等效能但比 Setun 還貴的2.5倍的二進位的電腦。
參考資料:[Development of ternary computers at Moscow State University](http://www.computer-museum.ru/english/setun.htm)
### 與其他數值系統的比較
透過分析不同底數的底數經濟(Radix Economy),就能夠比較以不同底數來表示數值的效率,根據[Wikipedia: Radix Economy](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_economy),用一個底數 $b$ 來表達數值 $N$ 的底數經濟之計算公式為:
$E(b,N)=b\lfloor \log _{b}(N)+1\rfloor$
從這個公式,可以得知若以自然常數 $e$ 當底數來表達數值時,其底數經濟最低,也就代表,理論上自然常數 $e$ 才是用來表達數值時最理想的底數。若是整數的話,$3$ 則是最有效率的底數,其次則是以 $2$。下表列出了我們常見的底數,以及他們各自在表達不同數值範圍大小時的平均底數經濟。

若就以這張圖表中的 $E(b)\over E(e)$ 來看的話,可以發現其實以 $3$ 為 底數來表達數值的底數經濟比以 $2$ 為底數還要低,也就是以 $3$ 為底數來表達數值其實比以 $2$ 還有效率。但值得注意的是,在表達數值的範圍為 $1-43$ 時,以 $2$ 為底數來表達數字,其實也比以 $3$ 還要來的有效率的。但在表達更大的數字範圍時,以 $3$ 為底數還是比以 $2$ 為底數有效率。
那為什麼現代的電腦系統仍以 $2$ 為底數(二進位)來表達數值呢? 原因如下:
* 只需要透過開關,就能夠輕易表達兩個不同數值(0,1)。因此,相對來說,區分三個不同電壓區間,以表達三個數值就相對困難
* 二進位的系統比較不會因為電壓的隨機震盪產生錯誤的訊號(數值) (greater noise immunity)
* 二進位電腦的歷史發展悠久,若想把電腦的數值表達系統改變成以 $3$ 為底數,將會是十分浩大的工程....
但是從底數經濟的分析中我們可以得知,在表達數字時,以 $3$ 為底數反而會是更好的選擇。
參考資料:[How efficient is Binary system compared to other number systems for use in computers?](https://www.quora.com/How-efficient-is-Binary-system-compared-to-other-number-systems-for-use-in-computers)、[What is the most efficient numerical base system?](https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/446664/what-is-the-most-efficient-numerical-base-system)、[Wikipedia: Radix Economy](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_economy)
### IOTA / Tange 之應用
#### IOTA介紹
首先,我們來看看 IOTA 和 其他加密貨幣(如 Bitcoin)之間的差異是什麼。根據 [IOTA BREAKDOWN: The Tangle Vs. Blockchain Explained](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I_jNH9BlEEo),可以知道 IOTA 是基於 Tangle 的結構而其他加密貨幣則是基於 Blockchain 的結構,而這兩種不同結構的差異,以下列出比較:
| | Blockchain | Tangle |
| -------- | -------- | ------- |
| Miners | Yes | No |
| Fee | Yes | No |
| Blocks | Yes | No |
| Hard/Soft fork capability | Yes | No |
| Hashcash | Yes | Yes (Lite) |
| Distributed consensus | Yes | Yes |
| Quantum security | No | Yes |
| Scalability | No | Yes |
| Offline capability | No | Yes |
從這個比較表中,可以得知使用 IOTA 交易時,由於免手續費(Fee),也沒有 Block,所以也不需要礦工。除此之外,IOTA 同時也能處理使用者大幅增加時的情況 (Scalable),還可以避免量子電腦的威脅。那是什麼樣的條件,使得 IOTA 能夠擁有這些能力呢?根據 [IOTA 白皮書](https://iota.org/IOTA_Whitepaper.pdf),可以了解到 Tangle 的底層其實是一種稱為 Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) 的結構,如下圖所示:
>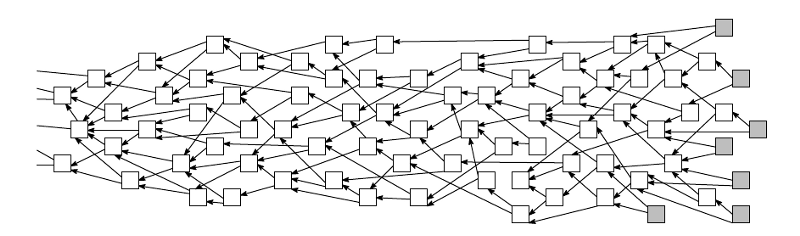
在這種結構底下,每次新的交易產生時(如圖中的灰色方塊),都得先驗證兩個根據 [Monte Carlo 演算法](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AyBNnkYrSWY)隨意取出的交易,該次交易才能成立。而此設定,不只使 IOTA 免除了如 Bitcoin 需要礦工幫忙驗證交易並支付手續費必要,同時也確保 IOTA 在使用者增加時的仍能順利進行交易。同時,IOTA 也提供了一個稱為 [Masked Authenticated Messaging](https://lab.ruuvi.com/iota/) 的功能,來保護並加密傳遞的訊息。
這些優點實際上為 [Internet of Thing (IOT)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things) 提供了相當好的環境。而從 IOTA 的[發展歷史](https://medium.com/@MartinRosulek/how-iota-makes-future-for-internet-of-things-af14fd77d2a3),如下所示:
* **第一階段**
* IOTA core live
* establishing the IOTA Foundation
* moving the community’s chat over to Slack
* completing some partnerships
* IOTA on exchange market
* spreading into the world
* **第二階段**
* extending IOTA’s utillity
* open IOTA to anyone that want to build on top of the IOTA network
* **第三階段**
* development of hardware (project's name is Jinn project), a brand new type of microprocessor for IoT, a hardware implementation hasher for IOTA’s ‘Curl hash function’
也可以得知 IOTA 希望能與 IOT 的發展結合。從 IOTA 已經公開釋出[程式碼](https://github.com/iotaledger),到目前正在打造一個專門處理 IOTA 的 Hashcash 所需要的運算的微型處理器,稱為 Jinn Processor,都可以發現 IOTA 對於 IOT 的野心。
值得特別注意的是,IOTA 正在開發的 Jinn Processor 內部並不是以二進位來表達數值,而是以 Balanced Ternary 來表示數值,以及進行運算。正是因為以 Balanced Ternary 來表達數值的 Radix Economy 較二進位低、同樣的空間下能表達的數值範圍也比二進位來的更廣、操作起來也更快更直觀、耗能也較小等優點。
參考資料:[How IOTA makes bright future for Internet of Things](https://medium.com/@MartinRosulek/how-iota-makes-future-for-internet-of-things-af14fd77d2a3)、[IOTA BREAKDOWN: The Tangle Vs. Blockchain Explained](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I_jNH9BlEEo)、[The Tech Behind IOTA Explained](http://www.tangleblog.com/2017/01/25/the-tech-behind-iota-explained/)、[IOTA Development Roadmap](https://blog.iota.org/iota-development-roadmap-74741f37ed01)、[OUR FIRST INVESTMENT IN TOKENS IS.. IOTA](https://outlierventures.io/research/our-first-investment-in-tokens-is/)
## Balanced Ternary 在 GitHub 裡頭可找到的應用案例
[IOTA_kerl](https://github.com/iotaledger/kerl)
* IOTA is adding an additional hashing function, based on Keccak, with conversion to ternary.
* CheckSums are calculated using the last 9 trytes.
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet