# RH134 Red Hat System Administration II notes in the margin
###### tags: `red hat, rhel8`
> You will find here notes and links to official docs with information on products and technologies that described on RedHat Training.
> THIS DOCUMENT DOES NOT REPRINT ANY COPYRIGHTED CONTENT FROM REDHAT TRAINING. You will find here only public accessible outline.
[Course description: RH134 Red Hat System Administration II](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/rh134-red-hat-system-administration-ii)
## :memo: Table of contents
[ToC]
### 1. Improve command line productivity
Run commands more efficiently by using advanced features of the Bash shell, shell scripts, and various utilities provided by Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
[Book: Introduction to Linux](https://tldp.org/LDP/intro-linux/html/intro-linux.html)
[Book: Advanced Bash-Scripting Guide](https://tldp.org/LDP/abs/html/abs-guide.html)
[Книга: Искусство программирования на языке сценариев командной оболочки](http://rus-linux.net/MyLDP/BOOKS/abs-guide/flat/abs-book.html)
```
#!/bin/bash
# this sample script is ping computers in loop.
# It uses conditional expression with color echo
for HOST in f{1..7}
do
echo -en "\nlets try ping $HOST: "
if ping -c 1 -W 1 $HOST >/dev/null 2>&1
then
echo -e "\e[1;32m alive \e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[1;41m DEAD \e[0m"
fi
done
```
[YouTube Video: "Where GREP Came From - Computerphile" with Brian Kernighan](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NTfOnGZUZDk)
[GNU website: GNU Grep 3.5 manual](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/manual/grep.html)
[Почему работать в консоли настолько приятно? Так задумано отцами-основателями Unix](https://habr.com/ru/company/vdsina/blog/552536/)

### 2. Schedule future tasks
Schedule commands to run in the future, either one time or on a repeating schedule.
[Cron в Linux: история, использование и (внутреннее) устройство](https://habr.com/ru/company/badoo/blog/468061/)
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 System Administrator’s Guide: CHAPTER 24. AUTOMATING SYSTEM TASKS](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/system_administrators_guide/ch-automating_system_tasks)
[Techmint Article: Cron Vs Anacron: How to Schedule Jobs Using Anacron on Linux](https://www.tecmint.com/cron-vs-anacron-schedule-jobs-using-anacron-on-linux/)
[Putorius Article: Cron vs Anacron - Different Ways of Scheduling Jobs on Linux](https://www.putorius.net/cron-vs-anacron.html)
| Cron | Anacron |
| ---- | ------- |
It’s a daemon | It’s not a daemon
Appropriate for server machines | Appropriate for desktop/laptop machines
Enables you to run scheduled jobs every minute | Only enables you to run scheduled jobs on daily basis
Doesn’t executed a scheduled job when the machine if off | If the machine if off when a scheduled job is due, it will execute a scheduled job when the machine is powered on the next time
Can be used by both normal users and root | Can only be used by root unless otherwise (enabled for normal users with specific configs)
[Fedora Magazine: Systemd Timers for Scheduling Tasks](https://fedoramagazine.org/systemd-timers-for-scheduling-tasks/)
>Let's create an alternative for this crontab job:
>```
>*/10 * * * * /usr/bin/date >> /tmp/date
>```
>
>Timers work directly with services' units. So we have to create /etc/systemd/system/date.service first:
>```
>[Unit]
>Description=Prints date into /tmp/date file
>
>[Service]
>Type=oneshot
>ExecStart=/usr/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/date >> /tmp/date'
>```
> Then we have to create timer unit with the same name but with *.timer suffix /etc/systemd/system/date.timer:
>```
>[Unit]
>Description=Run date.service every 10 minutes
>
>[Timer]
>OnCalendar=*:0/10
>
>[Install]
>WantedBy=timers.target
>```
>
>This config will run date.service every 10 minutes. You can also list all timers enabled in your system using systemctl list-timers command or systemctl list-timers --all to list all timers. Run systemctl start date.timer to enable timer.
>
>You can also create timer with different name, i.e. task.timer. In this case you have specify service unit name:
>```
>Unit=date.service
>```
[Freedesktop man page: systemd.timer — Timer unit configuration](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.timer.html)
[Freedesktop man page: systemctl — Control the systemd system and service manager](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemctl.html)
[RedHat Knowledgebase: Why are there many tmpfs filesystems mounted on the server?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/2435631)
[RedHat Knowledgebase: How to work with /dev/shm in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 and later](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/1384183)
[RedHat Knowledgebase: How do I restrict or modify size of /dev/shm?](https://access.redhat.com/articles/7081)
[RedHat Knowledgebase: How do I modify the size of tmpfs?](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/2843)
By default tmpfs is half of available system RAM
[What Is /dev/shm And Its Practical Usage](https://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/what-is-devshm-and-its-practical-usage.html)
[Freedesktop man journald.conf: journald disk usage can grow up to 4GB ](https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/journald.conf.html)
https://www.loggly.com/ultimate-guide/managing-journal-size/
https://www.loggly.com/ultimate-guide/linux-logging-with-systemd/#journald-configuration
### 3. Tune system performance
Improve system performance by setting tuning parameters and adjusting scheduling priority of processes.
[Tuned is a system tuning service for Linux.](https://tuned-project.org)
[RedHat Blog: Tuning Your System With Tuned](https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/tuning-your-system-tuned)
[RHEL8 Docs: Monitoring and managing system status and performance: CHAPTER 2. GETTING STARTED WITH TUNED](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/monitoring_and_managing_system_status_and_performance/getting-started-with-tuned_monitoring-and-managing-system-status-and-performance)
[RHEL8 Docs: Monitoring and managing system status and performance: CHAPTER 3. CUSTOMIZING TUNED PROFILES](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/monitoring_and_managing_system_status_and_performance/customizing-tuned-profiles_monitoring-and-managing-system-status-and-performance)
[YouTube Video: Linux processes, init, fork/exec, ps, kill, fg, bg, jobs](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TJzltwv7jJs)
### 4. Control access to files with ACLs
Interpret and set access control lists (ACLs) on files to handle situations requiring complex user and group access permissions.
### 5. Manage SELinux security
Protect and manage the security of a server by using SELinux.
Manage basic storage
https://people.redhat.com/dwalsh/
https://danwalsh.livejournal.com/
[YouTube: Red Hat Summit: Are you listening to what SELinux is telling you?](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wv9kwlabdlo)

[SELinux Coloring Book](https://developers.redhat.com/books/selinux-coloring-book)
https://selinuxproject.org/page/Category:Notebook
https://freecomputerbooks.com/The-SELinux-Notebook-The-Foundations.html
https://www.amazon.com/SELinux-System-Administration-Sven-Vermeulen/dp/1787126951
https://www.amazon.com/SELinux-Example-Using-Security-Enhanced/dp/0131963694
https://www.amazon.com/Selinux-Source-Security-Enhanced-Linux/dp/0596007167
### 6. Create and manage storage devices, partitions, file systems, and swap spaces from the command line.
https://www.thomas-krenn.com/en/wiki/Linux_Storage_Stack_Diagram
[RHEL8 Docs: Considerations in adopting RHEL 8: Btrfs has been removed](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/considerations_in_adopting_rhel_8/file-systems-and-storage_considerations-in-adopting-rhel-8)
```
12.1.1. Btrfs has been removed
The Btrfs file system has been removed in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
This includes the following components:
- The btrfs.ko kernel module
- The btrfs-progs package
- The snapper package
You can no longer create, mount, or install on Btrfs file systems in
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. The Anaconda installer and the Kickstart
commands no longer support Btrfs.
```
### 7. Manage logical volumes
Create and manage logical volumes containing file systems and swap spaces from the command line.
[RHEL8 Docs: Configuring and managing logical volumes](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_logical_volumes/index)
[The Status of Storage Within Linux: LVM, Btrfs, and ZFS comparison](https://blog.jenningsga.com/status-of-storage-within-linux/)

### 8. Implement advanced storage features
Manage storage using the Stratis local storage management system and use VDO volumes to optimize storage space in use.
[Stratis Project ](https://stratis-storage.github.io/)
https://opensource.com/article/18/4/stratis-easy-use-local-storage-management-linux
https://opensource.com/article/18/4/stratis-lessons-learned
[RHEL8 Docs: Managing file systems: Chapter 17. Managing layered local storage with Stratis](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/managing_file_systems/managing-layered-local-storage-with-stratis_managing-file-systems)
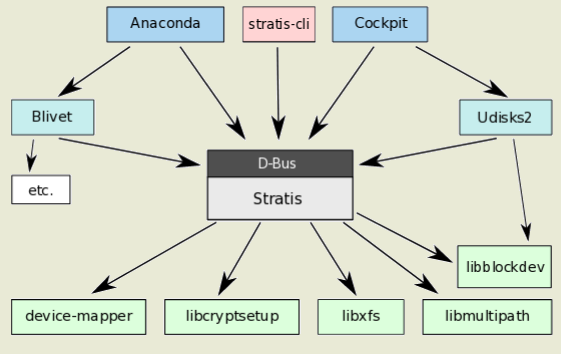
[Red hat Interactive Lab: Stratis](https://lab.redhat.com/stratis)
[RHEL8 Docs: Deduplicating and Compressing storage](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html-single/deduplicating_and_compressing_storage/index)


https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/introducing-virtual-data-optimizer-reduce-cloud-and-premise-storage-costs
[Red hat Interactive Lab: VDO](https://lab.redhat.com/vdo-configure)
https://www.opennet.ru/opennews/art.shtml?num=51828
### 9. Access network-attached storage
Use the NFS protocol to administer network-attached storage.
[RHEL8 Docs: System Design Guide Chapter: 29. Mounting NFS shares](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/system_design_guide/mounting-nfs-shares_system-design-guide)
[RHEL8 Docs: Considerations in adopting RHEL 8 Chapter 12. File systems and storage](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/considerations_in_adopting_rhel_8/file-systems-and-storage_considerations-in-adopting-rhel-8)
https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/filesystems/autofs.html
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/storage_administration_guide/nfs-autofs
https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.automount.html
https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.mount.html
Альтернатива демону autofs.Автомонтирование при помощи, юнитов systemd mount и automount.
[Habr: Автомонтирование файловых систем с systemd](https://habr.com/ru/post/331240)
```bash
cat /etc/systemd/system/media-nfs.mount
[Unit]
Description=NFS share
[Mount]
What=server.url.example.com:/srv/nfs_share
Where=/media/nfs
Type=nfs4
Options=rw
DirectoryMode=0755
cat /etc/systemd/system/media-nfs.automount
[Unit]
Description=NFS share
Requires=network-online.target
[Automount]
Where=/media/nfs
TimeoutIdleSec=301
[Install]
WantedBy=graphical.target
```
### 10. Control the boot process
Manage the boot process to control services offered and to troubleshoot and repair problems.
[Red Hat KB: Resetting the Root Password of RHEL8 ](https://access.redhat.com/solutions/3889671)
http://onreader.mdl.ru/HandsonBooting/content/index.html
### 11. Manage network security
Control network connections to services using the system firewall and SELinux rules.
### 12. Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux on servers and virtual machines.
[RHEL Overview](https://developers.redhat.com/products/rhel/overview)
[RHEL 8 Bare Metal Quick Install](https://developers.redhat.com/rhel8/install-rhel8#)
[RHEL8 Administration guid:Installation](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/performing_a_standard_rhel_installation/index)
[RHEL 8 VirtualBox Quick Install](https://developers.redhat.com/rhel8/install-rhel8-vbox)
[Red Hat Enterprise Linux Hello World](https://developers.redhat.com/products/rhel/hello-world)
[Red Hat Customer Portal Labs](https://access.redhat.com/labs/)
### 13. Run Containers
Obtain, run, and manage simple, lightweight services as containers on a single Red Hat Enterprise Linux server.
https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2018/02/22/container-terminology-practical-introduction/
https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2018/08/29/intro-to-podman/
https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/behind-scenes-podman
https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/image-stores-podman
https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/rootless-podman
https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/09/25/rootless-containers-with-podman-the-basics/
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/building_running_and_managing_containers/index
https://access.redhat.com/solutions/3911401
https://catalog.redhat.com/software/containers/explore
https://developers.redhat.com/products/rhel/ubi
https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/introducing-red-hat-universal-base-image
### 11. Comprehensive review
https://www.certdepot.net/
https://www.server-world.info/en/
[Snap vs Flatpack vs AppImage](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BdCPODLqf_E)
[DJ Ware - The CyberGizmo](https://www.youtube.com/c/DJWareCG)
[Brian Will](https://www.youtube.com/user/briantwill)
[Chris Titus Tech](https://www.youtube.com/c/ChrisTitusTech)
[Bryan Lunduke](https://www.youtube.com/user/BryanLunduke)
[Learn Linux TV](https://www.youtube.com/c/LearnLinuxtv)
[Jeff Geerling](https://www.youtube.com/c/JeffGeerling)
[DistroTube Linux enthusiast & free software advocate](https://www.youtube.com/c/DistroTube)
[Luke Smith](https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC2eYFnH61tmytImy1mTYvhA)
[Tyler's Tech](https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC3LqPyZ9818X8EM9e9mJMwQ)
[Craft Computing](https://www.youtube.com/c/CraftComputing)
[Christian Lempa](https://www.youtube.com/@christianlempa)