# Extract Text from Docs - Expense API
Showcase the Amazon Textract API and how we can process Invoices programmatically in an extensible event driven workflow in under one hour!
In this lab you will process an invoice by creating a simple serverless event driven workflow by:
* Use Amazon Textract to extract form data from the [sample invoice file](https://hackmd.io/_uploads/SJYPX6uf6.jpg)
* Configure an AWS Lambda function to make an API call to Amazon Textract, then extract expense data from the sample file
* Create a simple event driven workload by adding an Amazon S3 event trigger to invoke the Lambda function for any PUT events that meet the criteria
* Validate that the response JSON file received in the S3 bucket contains the expected results.
* Review the results in Amazon CloudWatch Logs
# About Textract
[Amazon Textract](https://aws.amazon.com/textract/) is a machine learning (ML) service that automatically extracts text, handwriting, and data from scanned documents. It goes beyond simple optical character recognition (OCR) to identify, understand, and extract data from forms and tables. With Amazon Textract, you pay only for what you use. There are no minimum fees and no upfront commitments. Amazon Textract charges only for pages processed whether you extract text, text with tables, form data, queries or process invoices and identity documents. See the [FAQ](https://aws.amazon.com/textract/faqs/) for additional details about pages and acceptable use of Amazon Textract.
Amazon Textract is based on the same proven, higly scalable, deep-learning technology that was developed by Amazon's computer vision scientists to analzyze billions of images and videos daily.
# Lab
*Duration 30 minutes.*
In this lab, you create an AWS Lambda function and an IAM execution role that lets your function call the [StartExpenseAnalysis](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/textract/latest/dg/API_StartExpenseAnalysis.html) operation. API calls will be triggered from Amazon S3 events.

1. In this solution, users upload a document to an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket. Amazon textract then extracts data (automatically) from the document and stores the output in an Amazon S3 bucket for further processing.
2. The S3 bucket is configured with an AWS Lambda trigger, which invokes a Lambda function whenever a new document is uploaded.
3. The Lambda function calls the Amazon Textract API asynchronously and sends the document to Amazon Textract to initiate data extraction.
4. Amazon Textract uses optical character recognition (OCR) and machine learning (ML) models to analyze the document and exract data, including printed text, handwriting and numbers.
5. Amazon Textract queries are pretrained on a large variety of document types, reducing the need to implement post processing, reliance on manual reviews of extracted data, or the need to train ML models.
6. The Lambda function saves the extracted data in JSON format in the output folder of an S3 bucket for further processing.
## Step 1 - Create Textract Layers
The lab will be using Python 3.11 runtime for our Lambda code. Lambda Layers are particularly valuable when you're working with custom runtime modules or dependencies that are not included in the default Python runtime provided by AWS Lambda. There are two tools to use when working with Textract programmatically to either print or parse the output from the Textract API.
1. For more information on parsing Textract responses see **[Using Textractor in AWS Lambda](https://aws-samples.github.io/amazon-textract-textractor/using_in_lambda.html)**
1. For more information on printing Textract responses see **[Using Textract Pretty Printer](https://pypi.org/project/amazon-textract-prettyprinter/)**
To build the lambda layers manually perform the following in a python 3 environment
``` bash=
mkdir lambda_layers
cd lambda_layers
mkdir python
cd python
pip install amazon-textract-prettyprinter -t ./
pip install amazon-textract-textractor -t ./
cd ..
zip -r python_modules.zip .
```
1. Open the AWS Console[](https://ap-southeast-2.console.aws.amazon.com/console)
1. Go to **Lambda** > Click **Layers** > **Create layer**
1. Choose the radio button to select **Upload**, choose the zip folder `python_modules.zip`.
1. Choose **Python 3.11**
1. Click **Create**
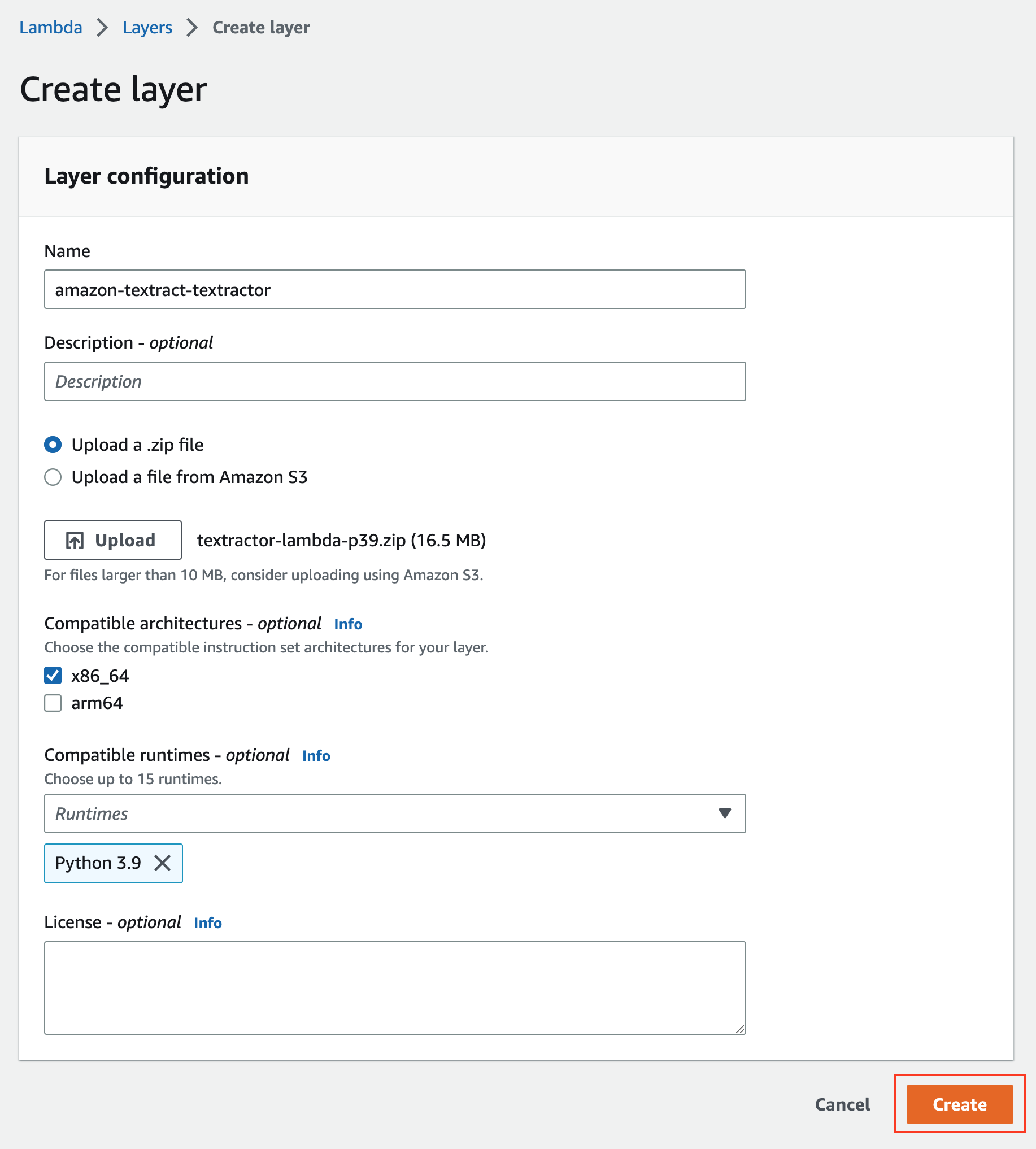
A runtime can support a single version of a language. You can choose up to 15 compatible runtimes
## Step 2 - Create Bucket
We will create a bucket for the documents to be stored.
Open the AWS Console[](https://ap-southeast-2.console.aws.amazon.com/console)
1. Go to **S3** > Click **Buckets** > **Create bucket**
1. Bucket name: **amazon-textract-bucket-*xxxxxx***
:::info
:warning: **Note** the bucket must be unique, hint use your AWS Account ID in replace of *xxxxxx*
:::
3. AWS Region: **ap-southeast-2**
1. Click **Create bucket**
1. Search for your newly create Bucket, click the bucket name `amazon-textract-bucket-xxxxxx`
1. In Objects > select **Create folder**
1. Folder name: **input**
1. Click **Create folder**
:::info
:warning: **Note** Copy the bucket name as you will use it later.
:::
## Step 4 - Create IAM Excecution Role
1. Go to **IAM** Console > Click **Roles** > **Create role**
1. Trusted entity type choose **AWS service**
1. For **Service or use case** select **Lambda**
1. Click **Next**
1. Add permission screen, assign the AWS Managed policies:
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AmazonTextractFullAccess
- AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
1. Click **Next**
1. Role name: `LambdaS3TextractExecRole`
1. Click **Create role**
## Step 5 - Create Function
1. Go back to the Lambda console.
1. In the **Functions** section click **Create function**
1. Choose **Author from scratch**
1. Function Name: `labFunction`
1. Runtime: **Python 3.11**

6. Click **Change the default execution role**
1. Select **Use an existing role**
1. Role Name: **LambdaS3TextractExecRole**
1. Click **Create function**
:::info
:warning: **INFO** A Lambda function's execution role is an AWS IAM role that grants the function permissions to access AWS services and resources. The Lambda will assume the role when it is invoked.
:::
## Step 6 - Lambda Code
1. On the **labFunction** page
1. In the IDE window, **double click** the **lambda_function.py** file.
1. **Highlight all** the default code and **replace** it with the code block below:
```python=
import json
import io
import boto3
from textractprettyprinter.t_pretty_print_expense import get_string
from textractprettyprinter.t_pretty_print_expense import Textract_Expense_Pretty_Print, Pretty_Print_Table_Format
# Function to print labels and values from the AWS Textract response
def print_labels_and_values(blocks):
pretty_printed_string = get_string(textract_json=blocks, output_type=[Textract_Expense_Pretty_Print.SUMMARY, Textract_Expense_Pretty_Print.LINEITEMGROUPS], table_format=Pretty_Print_Table_Format.fancy_grid)
print(pretty_printed_string)
# Function to process an expense analysis using AWS Textract asynchronously
def process_expense_analysis_async(client, bucket, document):
# Start asynchronous text detection job
response = client.start_expense_analysis(
DocumentLocation={'S3Object': {'Bucket': bucket, 'Name': document}}
)
# Get the JobId for the analysis
job_id = response['JobId']
# Wait for the job to complete
while True:
job_info = client.get_expense_analysis(JobId=job_id)
status = job_info['JobStatus']
if status in ['SUCCEEDED', 'FAILED']:
break
# If the job succeeded, process the results
if status == 'SUCCEEDED':
print_labels_and_values(job_info)
return job_info
else:
# Handle the case when the job fails
print(f"Textract job with JobId {job_id} has failed.")
return None
# Function to upload the Textract response to an S3 bucket
def upload_response_to_s3(s3_client, bucket, document_key, response):
# Remove "input/" from the start of the document_key
response_key = f"output/{document_key.replace('input/', '')}.json"
print("Output File - File: {}".format(str(response_key)))
s3_client.put_object(
Bucket=bucket,
Key=response_key,
Body=json.dumps(response, indent=4)
)
# Lambda handler function
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Extract the S3 bucket and document key from the event
bucket = event['Records'][0]['s3']['bucket']['name']
document = event['Records'][0]['s3']['object']['key']
print("Processing File - Bucket: {}, File: {}".format(str(bucket), str(document)))
# Create a session and AWS Textract client
session = boto3.Session()
textract_client = session.client('textract', region_name='ap-southeast-2')
# Process the expense analysis asynchronously and get the response
response = process_expense_analysis_async(textract_client, bucket, document)
if response:
# Create an S3 client and upload the Textract response
s3_client = boto3.client('s3')
upload_response_to_s3(s3_client, bucket, document, response)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('Expense analysis complete!')
}
```
## Step 7 - Review Code
1. Review the codes functions
1. **Line 8**, the function `print_labels_and_values` prints all the defined values from Textract Pretty Printer defined.
1. **Line 13**, the function `process_expense_analysis_async` performs the API call to the Textract service.
1. **Line 38**, the function `upload_response_to_s3` performs the API PUT request to the S3 service with the Textract API response.
2. **Line 49**, the function `lambda_handler` is the entry point for the Lambda process.
3. In the code editor, click **File** > **Save**.
4. Followed by the **Deploy** button
## Step 8 - Review Event Structure
1. Now you’ve deployed your function code, here is what an example Amazon S3 trigger event that will invoke your function typically looks like.
```json=
{
"Records": [
{
"eventVersion": "2.0",
"eventSource": "aws:s3",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"eventTime": "1970-01-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"eventName": "ObjectCreated:Put",
"userIdentity": {
"principalId": "EXAMPLE"
},
"requestParameters": {
"sourceIPAddress": "127.0.0.1"
},
"responseElements": {
"x-amz-request-id": "EXAMPLE123456789",
"x-amz-id-2": "EXAMPLE123/5678abcdefghijklambdaisawesome/mnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGH"
},
"s3": {
"s3SchemaVersion": "1.0",
"configurationId": "testConfigRule",
"bucket": {
"name": "my-bucket",
"ownerIdentity": {
"principalId": "EXAMPLE"
},
"arn": "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket"
},
"object": {
"key": "test%2Fkey",
"size": 1024,
"eTag": "0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef",
"sequencer": "0A1B2C3D4E5F678901"
}
}
}
]
}
```
3. In the sample Event JSON, you'll notice the following values.
* **us-east-1** with the region the Amazon S3 bucket is in.
* **my-bucket** with the name of your own Amazon bucket
* **test%2FkKey** with the name of the the object that was uploaded to your bucket (for example `invoice.jpg`).
The Lambda function will retrieve the key name of the uploaded object and the name of the bucket from the event parameter it receives from Amazon S3 with the following lines of python.
```python=
bucket = event['Records'][0]['s3']['bucket']['name']
document = event['Records'][0]['s3']['object']['key']
```
## Step 9 - Lambda Timeout
1. Click **Configuration** tab, click **General configuration**
1. Click **Edit**
1. Increase the **Lambda function timeout**. Change to **1 minute**.
1. Click **Save**.
:::info
:warning: **INFO** Lambda allocates CPU power in proportion to the amount of memory configured. Memory is the amount of memory available to your Lambda function at runtime.
:::
## Step 10 - Add Layers
1. Click the **Code** tab
1. Scroll down to **Layers**
1. Click **Add a layer**
1. In the Choose a layer section, for Layer source, choose **Custom layers**.
1. For Custom layers, choose **textract-layers**, for **Version**, choose **1**.
1. Click **Add**.

## Step 11 - Add Trigger
1. In the **Function overview** section, click **Add trigger**
1. In the Trigger configuration search box, choose **S3**
1. For Bucket, choose the bucketname that start with **amazon-textract-bucket-xxxxxx**
1. For **Event types**, choose **PUT**, and then **deselect All object** create events.
- For **Prefix type**: `input/`
- For **Suffix type**: `.jpg`
1. Review the **Recursive invocation** information and **choose** the **check box to acknowledge it**.
1. Click **Add**
:::warning
:warning: **Warning** If your notification writes to the same bucket that triggers the notification, it could cause an execution loop.
:::
To invoke you function, Amazon S3 needs permission from the function's resouce-based policy. When you configure an Amazon S3 trigger in the Lambda console, the console modifies the resouce-based policy to allow Amazon S3 to invoke the function if the bucket name and accound ID match.

## Step 12 - Upload File
1. Download [this file](https://hackmd.io/_uploads/SJYPX6uf6.jpg) and save it on your device as **invoice.jpg**
1. On the **Objects** tab, click **input/**
1. To upload a file to the bucket, on the **Objects** tab, click **Upload**
1. Click **Add files**, and then choose the **invoice.jpg** file that you downloaded at the beginning of this step.
1. Click **Upload**
:::info
:warning: **INFO** The trigger invokes your function every time you add an object that meets your criteria.
:::
## Step 13 - Bucket Output
1. Return to the S3 bucket level, on the top breadcrum menu, click the **bucketname**.

1. On the Object table click the newly formed output folder
1. You configured your Lambda function to write the Amazon Textract response to the **output** folder. The **output** folder might take a minute to load.
1. On the **Object** tab, choose the **check box** to select the **filename.pdf.json** file.
1. To download the selected file, click **Download**
## Step 14 - Review Output
On your device, open the downloaded JSON response file in your text editor, and then review the contents. (e.g Visual Studio Code)

The extraction output appears in JSON format
The contents are the response from the Amazon Textract for the AnalyzeDocument API.

A **confidence score** (line 1023) is a number between 0 and 100 that indicated the probability that a given prediction is correct. This score helps you make informed decisions about how you use the results.
A **bounding box** coordinates (line 1028) are polygon frames that encompass each piece of identifed data, such as words, a line, a table or individual cells within a table. These coordinates help you audit where a word or number came from in the source document, and they guide you when search results provide scans of original documents.
## Step 15 - Log Output
1. Back in the AWS Management Console, in the top navigation bar search box type: **cloudwatch**
1. In the left navigation pane, under **Logs**, click **Log groups**
1. In the **Log groups** section, click the log group name that ends with **labFunction**
1. On the **Log streams** tab, click the most recent log stream
1. In the Log events section, review the messages

Key-value pairs extracted from the document should be displayed. You can use the FeatureTypes input parameter to retrieve information about the key-value pairs only, use the value FORMS.
## Step 17 - Create Test
1. Scroll down to the code block, and then select and copy the **sample test code** to your clipboard.
``` json=
{
"Records": [
{
"s3": {
"bucket": {
"name": "<Your_bucket_name>"
},
"object": {
"key": "input/invoice.jpg"
}
}
}
]
}
```
2. To create a local test event, click **Test** to expand the dropdown menu. Choose **Configure test event**.
1. In the pop-up box, for Event name, type a name th you like such as `myTestEvent`.
1. In the Event JSON code window, delete the existing code and Paste the the test event code you copied earlier.
1. **Replace** the `<Your_Bucket_Name>` with the **bucket name** that you copied to your text editor earlier.
1. Click **Save**
## Step 18 - Run Test
1. To **invoke** the Lambda fuction, click **Test**.
1. You are redirected to the Execution results tab
1. Review the results.
1. The successful test returns a Respone Status of '**Success**'
1. The Fields and Search Fields **key** & **value** results are displayed

## Step 19 - Upload Overwrite
1. Navigate back to the amazon-textract-bucket **input** folder on the Amazon S3 console, and then, on the **Objects** tab, click **Upload**.
1. In the Files and folder section, click **Add files** and then choose the **invoice.jpg** file that you downloaded at the beginning of the lab.
1. Click **Upload**.

A file with tha same name will overwrite the existing file. You can turn on S3 Versioning to keep multiple versions of an object in one bucket.
:::info
:warning: **INFO** If your notification writes to the same bucket that triggers the notification, it could cause an execution loop.
:::
## Step 20 - Review Log Stream
1. Navigate back to the AWS Lambda console, and then, in the left navigation page, click **Functions**
1. In the Functions section, click **labFunction**
1. On the labFunction page, click the **Monitor** tab
1. On the Log streams tab, click the most recent log stream
1. Review the messages
## On your own
Update the Lambda code to only provide summary data
Validate that the response received in the CloudWatch logs contains no line items.
### Validation
Validate that the textract_response.json file has table data from the sample image.
You python function should now only have
```python=
import json
import io
import boto3
from textractprettyprinter.t_pretty_print_expense import get_string
from textractprettyprinter.t_pretty_print_expense import Textract_Expense_Pretty_Print, Pretty_Print_Table_Format
# Function to print labels and values from the AWS Textract response
def print_labels_and_values(blocks):
pretty_printed_string = get_string(textract_json=blocks, output_type=[Textract_Expense_Pretty_Print.SUMMARY], table_format=Pretty_Print_Table_Format.fancy_grid)
print(pretty_printed_string)
```
# Useful Links
Processing Documents with Synchronous Operations
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/textract/latest/dg/sync.html
Processing Documents with Asynchronous Operations
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/textract/latest/dg/async.html
Architecture Patterns
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/architecture/category/artificial-intelligence/amazon-textract/
AWS Prescriptive Guidance
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/prescriptive-guidance/latest/patterns/automatically-extract-content-from-pdf-files-using-amazon-textract.html
Using Amazon Augmented AI to Add Human Review to Amazon Textract Output
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/textract/latest/dg/a2i-textract.html
Tutorial: Using an Amazon S3 trigger to invoke a Lambda function
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/with-s3-example.html
## AWS Samples
Build a receipt and invoice processing pipeline with Amazon Textract
https://github.com/aws-samples/amazon-textract-invoice-processor
A sample pipeline that takes as input bank statements, extracts transaction information from tables within the statements using Textract, stores, and classifies each transaction.
https://github.com/aws-samples/textract-bank-statement-processor
# Lab Artifacts
Files used for this lab stored for reference.
## CloudFormation
:::info
To run this stack you'll need to deploy to `ap-southeast-2`. If you'd like to run this in a different region you'll need to copy the lambda layers to a bucket in the region you'd like to use and update the CloudFormation stack for the layers location. Lambda and S3 need to be in the same region.
:::
1. Go to the [CloudFormation](https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation) console and click on **Create Stack** and enter the following URL `https://arranp-aws-source.s3.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/sourcefiles/textract/deployTextract.yaml` and click **Next**

3. Enter **textract-demo** as the **Stack name**, leave the default values.
4. Skip **Configure stack options** and click **Next**.
5. Review and create - check **I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources** and click **Submit**

5. Wait till the stack status turned to **CREATE_COMPLETE**. This may take up to 5 minutes.

1. Go to your S3 Bucket and upload [sample invoice file](https://hackmd.io/_uploads/SJYPX6uf6.jpg) to a folder called 'input'.
Resource handler returned message: "Error occurred while GetObject. S3 Error Code: PermanentRedirect. S3 Error Message: The bucket is in this region: ap-southeast-2. Please use this region to retry the request
### Troubleshooting CloudFormation Stack
#### Lambda and S3 need to be in the same region
:::danger
:warning: **Error Message:** Resource handler returned message: "Error occurred while GetObject. S3 Error Code: PermanentRedirect. S3 Error Message: The bucket is in this region: ap-southeast-2. Please use this region to retry the request
:::
:::spoiler
Update the `S3Bucket` and `S3Key` values for both resources in CFN.
``` yaml=
lambdaLayer1:
Type: AWS::Lambda::LayerVersion
Properties:
CompatibleArchitectures:
- x86_64
CompatibleRuntimes:
- python3.11
Content:
S3Bucket: arranp-aws-source
S3Key: sourcefiles/textract/amazon-textract-textractor.zip
Description: 'The package contains utilities to call Textract services, convert JSON responses from API calls to programmable objects, visualize entities on the document and export document data is compatible formats.'
LayerName: amazon-textract-textractor
lambdaLayer2:
Type: AWS::Lambda::LayerVersion
Properties:
CompatibleArchitectures:
- x86_64
CompatibleRuntimes:
- python3.11
Content:
S3Bucket: arranp-aws-source
S3Key: sourcefiles/textract/textractprettyprinter.zip
Description: 'Provides functions to format the output received from Textract in more easily consumable formats incl. CSV or Markdown. amazon-textract-prettyprinter'
LayerName: textractprettyprinter
```
:::
#### Download Files
To download the required files and upload to your own bucket. The following resources are needed.
:::spoiler
**CloudFormation Stack**
https://arranp-aws-source.s3.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/sourcefiles/textract/deployTextract.yaml
**Layer 1**
https://arranp-aws-source.s3.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/sourcefiles/textract/textractprettyprinter.zip
**Layer 2**
https://arranp-aws-source.s3.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/sourcefiles/textract/amazon-textract-textractor.zip
:::
## Image

## Extend Solution
To make an async API deployment, put SQS infront of lambda

1. The process is started by an event in S3
1. The S3 event triggers a worklow
1. Receive Amazon S3 notifications using Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS)
2. The call to Start Expense API
3. Textract publishes completion status to SNS Topic
4. Post completion status to SQS Queue
5. Monitor SQS queue for completion status, invokes lambda to check for analysis success/confidence scores
6. Low confidence score goes to Human in the loop
7. Ultimately it ends up in the downstream system, either a bucket or to another downstream system.
Always use DLQ on your SQS
Adjust retries and timeouts to make optimal.
Or, use state machine in Step Functions as opposed to Lambda
