# Running Oracle 19c Database with Docker
Reference: [https://dev.to/udara\_dananjaya/running-oracle-19c-database-with-docker-1akg](https://dev.to/udara_dananjaya/running-oracle-19c-database-with-docker-1akg)
---------------
```ebnf
su root
```
### 打包 oracle19C docker image
後面發現用下面的安裝發法需要連到外網,所以我直接打包安裝好的image
If you want to compress it to save space (recommended for a 6.54GB image):
```
# Save and compress using gzip
docker save oracle/database:19.3.0-ee | gzip > oracle_database_19.3.0-ee.tar.gz
```
[oracle_database_19.3.0-ee.tar.gz](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VuZDNQ9sDsvnKFHc_3rDoC1Wo7w-t_sb/view?usp=drive_link)
On the destination system, you can load this image using:
```
gunzip -c oracle_database_19.3.0-ee.tar.gz | docker load
```
After loading, verify the image is available with:
```
docker images | grep oracle/database
```
--------------------
#### 1\. Clone the Oracle Docker Repository
Begin by cloning the Oracle Docker images repository to your local machine:
```awk
git clone https://github.com/oracle/docker-images.git
```
[https://drive.google.com/file/d/1YzNrAKZiFAHhECBdG_ldzFtIDZ5_RkON/view?usp=drive_link](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1YzNrAKZiFAHhECBdG_ldzFtIDZ5_RkON/view?usp=drive_link)
#### 2\. Navigate to the 19c Directory
After cloning the repository, navigate to the Oracle 19.3.0 database directory:
```plain
cd docker-images/OracleDatabase/SingleInstance/dockerfiles/19.3.0
```
#### 3\. Download the `LINUX.X64_193000_db_home.zip` file from Oracle's website
[https://www.oracle.com/tw/database/technologies/oracle19c-linux-downloads.html](https://www.oracle.com/tw/database/technologies/oracle19c-linux-downloads.html)
I put it on my drive(private)
[LINUX.X64_193000_db_home.zip](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WQgCRDotpLCKY-N3IAO6IQFzm6GUDjno/view?usp=drive_link)
#### 4\. Copy the Installation File
Download the `LINUX.X64_193000_db_home.zip` file from Oracle's website and copy it to the `19.3.0` directory:
```awk
cp $HOME/Downloads/LINUX.X64_193000_db_home.zip .
```
#### 5\. Adjust the Slim Option (Optional)
To avoid issues when patching the database in the future, modify the `Dockerfile` in the `19.3.0` directory to disable the slim option by setting `SLIMMING=false`:
```nginx
ARG SLIMMING=false
```
#### 6\. Build the Docker Image
Move back to the parent directory and run the [`buildDockerImage.sh`](http://buildDockerImage.sh) script. Specify the version (`-v`) as `19.3.0` and use the enterprise edition (`-e`):
```plain
cd ..
chmod +x buildContainerImage.sh
./buildContainerImage.sh -v 19.3.0 -e
```
The build process typically takes 20–30 minutes, depending on your system resources. Once complete, you'll see a "Build Complete" message.
To view this image in your local registry, you can run:
```plain
docker images | grep oracle/database
```

#### 7\. Run the Oracle 19c Docker Container
Fix permissions on the host, 54321 is the typical UID/GID for the oracle user in Oracle containers
```plain
sudo mkdir -p /opt/oracle/oradata
sudo chown -R 54321:54321 /opt/oracle/oradata
```
--------------
Run the Docker container using the following command:
```plain
docker run --name "oracle19.3" -p 1521:1521 -p 5500:5500 \
-e ORACLE_PDB=orapdb1 \
-e ORACLE_PWD=topsecretpass \
-e ORACLE_MEM=4000 \
-v /opt/oracle/oradata:/opt/oracle/oradata \
--user 54321:54321 \
-d oracle/database:19.3.0-ee
```
* `--name`: The name of the container.
* `ORACLE_PDB`: Name of the pluggable database.
* `ORACLE_PWD`: Database password.
* `ORACLE_MEM`: Memory allocated to the database (in MB).
* `-v`: Mounts the volume to persist data outside the container.
This command creates and starts a new Docker container for Oracle Database. Let me break down each part:
- `docker run`: Command to create and start a new container
- `--name "oracle19.3"`: Assigns the name "oracle19.3" to the container
- `-p 1521:1521`: Maps port 1521 from the container to port 1521 on the host (for database connections)
- `-p 5500:5500`: Maps port 5500 from the container to port 5500 on the host (for Oracle Enterprise Manager)
- `-e ORACLE_PDB=orapdb1`: Sets an environment variable to create a pluggable database named "orapdb1"
- `-e ORACLE_PWD=topsecretpass`: Sets the password for the SYS, SYSTEM, and PDBADMIN accounts
- `-e ORACLE_MEM=4000`: Sets the memory allocation for the database to 4000MB (4GB)
- `-v /opt/oracle/oradata:/opt/oracle/oradata`: Mounts the host directory "/opt/oracle/oradata" to the container directory "/opt/oracle/oradata" for persistent storage
- `--user 54321:54321`: Runs the container with user ID and group ID 54321 (typically matches the oracle user inside the container)
- `-d`: Runs the container in detached mode (in the background)
- `oracle/database:19.3.0-ee`: Specifies the image to use (Oracle Database Enterprise Edition version 19.3.0)
-------------------
The first run initializes the database, which can take some time.
#### **8\. Verify the database is fully started**:
初始化時間通常需要 15-30 分鐘,視系統性能而定。
```plain
docker logs oracle19.3 | grep -i "DATABASE IS READY"
```
確認container運行狀態
```vim
docker ps -al
```

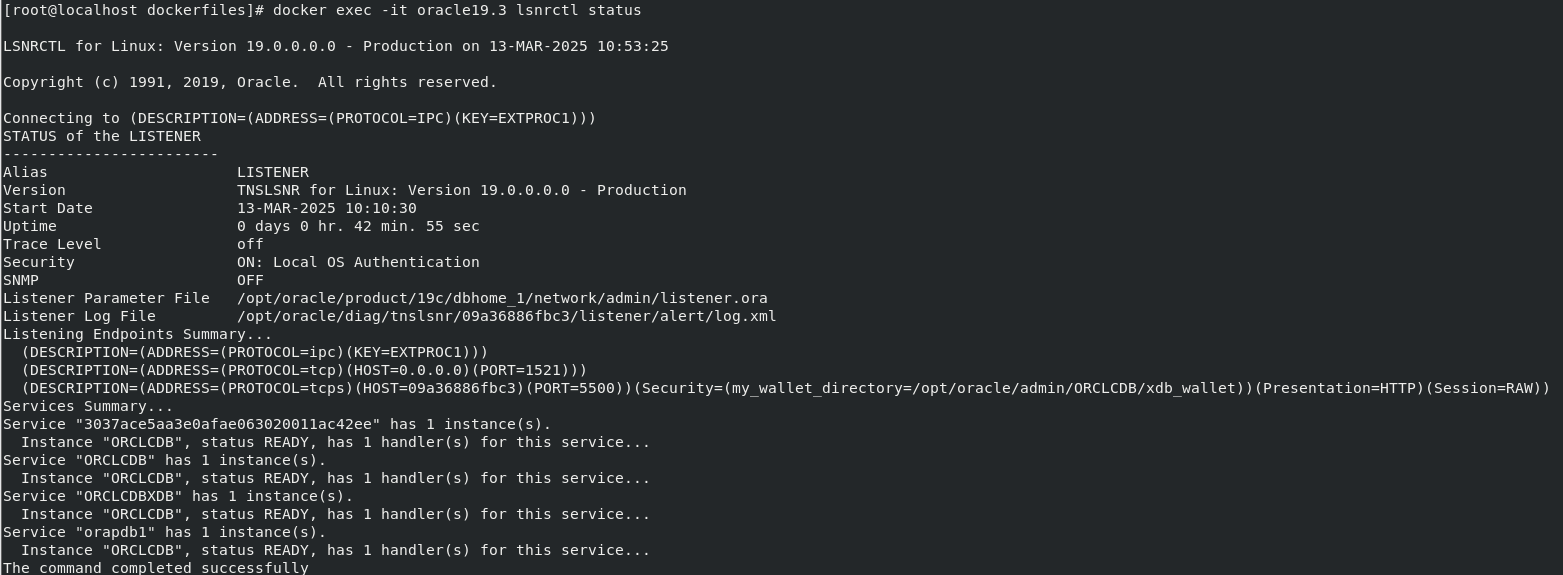
**Verify the listener is running** inside the container:
```sql
# 檢查監聽器狀態
docker exec -it oracle19.3 lsnrctl status
```
```sql
# 檢查可用服務
docker exec -it oracle19.3 lsnrctl services
```
這是**沒有**服務

這是**有**服務

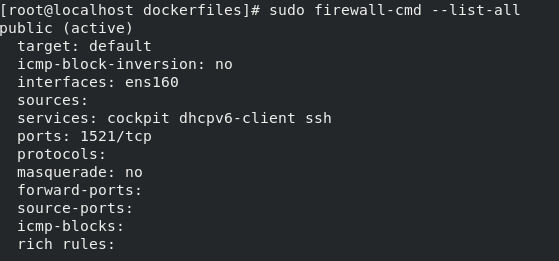
**Check firewall rules** in the VM:
```bash
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
# Add port if needed
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=1521/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
```
#### 9\. Connect to the Database
You can connect using **SQL Developer** or log into the container and use `sqlplus`:
```python
docker exec -it oracle19.3 /bin/bash
```
checks if any Oracle database instances are running on the system
```python
ps -ef | grep pmon
```
This command sources (runs) the oraenv script, which sets up the Oracle environment variables
```python
. oraenv
```
```python
sqlplus / as sysdba
```
If that doesn't work, let's try connecting with the complete connection string:
```plain
docker exec -it oracle19.3 sqlplus sys/topsecretpass@//localhost:1521/ORCLCDB as sysdba
```
#### 10\. create a user account under your PDB (orapdb1) with table creation privileges
1. **First, connect to the container database as SYSDBA**:
```bash
docker exec -it oracle19.3 sqlplus / as sysdba
```
If that doesn't work, let's try connecting with the complete connection string:
```awk
docker exec -it oracle19.3 sqlplus sys/topsecretpass@//localhost:1521/ORCLCDB as sysdba
```
2. **Switch to your pluggable database**:
```sql
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER = orapdb1;
```
3. **Create a new user with necessary privileges**:
```sql
-- Create the user with a password
CREATE USER myuser IDENTIFIED BY mypassword;
-- Grant connection privileges
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO myuser;
-- Grant table creation privileges
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO myuser;
-- Grant tablespace quota (required to create tables)
ALTER USER myuser QUOTA UNLIMITED ON USERS;
-- Optional: Grant additional privileges as needed
GRANT CREATE VIEW, CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE SEQUENCE TO myuser;
```
4. **Verify the user was created**:
```sql
SELECT username, account_status FROM dba_users WHERE username = 'MYUSER';
```
5. **Exit SQL\*Plus**:
```sql
EXIT;
```
Now you can connect to this user in SQL Developer with:
* Username: myuser
* Password: mypassword
* Hostname: Your VM IP (192.168.80.128)
* Port: 1521
* Service name: orapdb1
The user will be able to create and manage their own tables within the pluggable database.
* * *
### Useful Docker Commands
Here are some commands to manage your Docker container:
* **Stop the container**:
```apache
docker container stop oracle19.3
```
* **Start the container**:
```sql
docker container start oracle19.3
```
* **List running containers**:
```powershell
docker ps
```
* **List all images**:
```ebnf
docker images
```
* **Delete an image**:
```powershell
docker image rm "image_id_here"
```