---
tags: ironhack, lecture,
---
<style>
.markdown-body img[src$=".png"] {background-color:transparent;}
.alert-info.lecture,
.alert-success.lecture,
.alert-warning.lecture,
.alert-danger.lecture {
box-shadow:0 0 0 .5em rgba(64, 96, 85, 0.4); margin-top:20px;margin-bottom:20px;
position:relative;
ddisplay:none;
}
.alert-info.lecture:before,
.alert-success.lecture:before,
.alert-warning.lecture:before,
.alert-danger.lecture:before {
content:"👨🏫\A"; white-space:pre-line;
display:block;margin-bottom:.5em;
/*position:absolute; right:0; top:0;
margin:3px;margin-right:7px;*/
}
b {
--color:yellow;
font-weight:500;
background:var(--color); box-shadow:0 0 0 .35em var(--color),0 0 0 .35em;
}
.skip {
opacity:.4;
}
</style>

# Mongoose&Express | List - Read Documents
## Learning Goals
After this lesson, you will be able to:
- Query a database inside `routes`
- Pass data from a query to our render views
<br>
:::info lecture
Recap d'architecture :
:::
Remember this image - it will help you a lot in understanding of the whole process of building any full stack application.
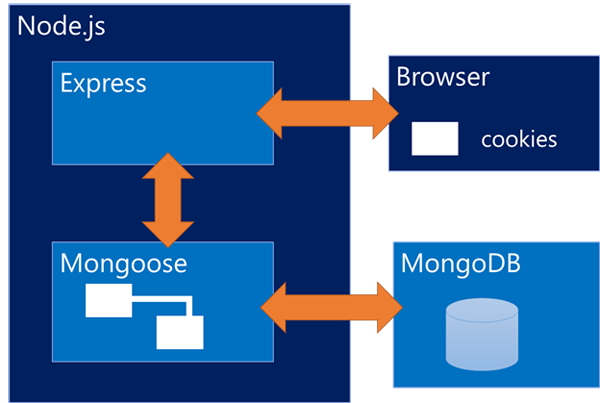
<br>
## Introduction
So far we learned how to query MongoDB using *Mongoose*, and how to render views on different routes created with *Express*. We will be finally integrating everything we've learned up to now in the second module, so we are in process of building a *full stack (JavaScript) application*.
In this lesson, we will see how to use Mongoose combined with Express, to list and read documents from our database. We will be using the same `library-project` we already created.
## List Documents
The first thing we will do is to list all the books in a new route. Let's create a `/books` route inside our `routes/index.js` file, and render a `books` view when we reach it (you should also create the `books.hbs` file inside the `views` folder).
:::info lecture
Créons notre route `/books` listant tous les livres de notre DB :
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books', (req, res, next) => {
res.render('books');
});
```
Our view is empty, and we are not passing any data to render. Let's query our `Book` collection to bring all the books we have in our database. First, we will need to require our collection model in the `index.js` file where we created the route.
:::info lecture
Nous allons devoir interroger notre modèle de livre :
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const Book = require('../models/book.js'); // 👈 add this line
```
Now we are ready to start doing some **Mongoose** queries inside the route:
:::info lecture
Maintenant que nous disposons de `Book`, servons-nous en pour interroger la DB :
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books', (req, res, next) => {
Book.find()
// 👇 allTheBooksFromDB is a placeholder, it can be any word
.then(allTheBooksFromDB => {
console.log('Retrieved books from DB:', allTheBooksFromDB);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('Error while getting the books from the DB: ', error);
});
res.render('books'); // ⚠️
});
```
If our query goes ok, we should get all the *books* we have in the database.
- **How we can pass that info to our view?**
- **Where we should call the `res.render()` method?**
We know we can add a second parameter to the `res.render()` method, where we can pass some data, so that's easy. But, where should we put our `res.render()` method at the first place?
The Mongoose query is asynchronous and if we put the `res.render()` outside the `promise` part it will render before the data is retrieved, so we won't be able to display the information in the view.
:::danger lecture
⚠️ Nous ne devons faire le `render` qu'une fois les données récupérées depuis la base :
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books', (req, res, next) => {
Book.find()
.then(allTheBooksFromDB => {
res.render('books', { books: allTheBooksFromDB }); // 👈
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('Error while getting the books from the DB: ', error);
})
});
```
Finally, we can add some code to our `books.hbs` to display every book. Remember we can iterate over the array so go ahead and add the following code:
:::info lecture
Ne manque plus que notre template :
:::
```htmlmixed
{{! views/books.hbs }}
<h1>Books</h1>
{{#each books}}
<p>{{this.title}}</p>
{{/each}}
```
Awesome! We have our `library` displaying all the books we have!

## Show detailed Document
Now we have displayed only the title of each book but we want the users of our app to be able to see all the other information. We can *take them* to the **detailed** view where they can see everything we have saved in our DB related to that specific book. Let's create a view inside *views* folder **views/book-details.hbs**, where all these data will be displayed. For sure we won't create a view per book, we know how to manipulate data so the view gets changed dynamically.
### Adding the routes
:::info lecture
Occupons-nous maintenant des pages détail de chaque livre...
:::
First, let's turn all the *titles* on the *books.hbs* into hyperlinks. The link should include a field that we can use to query the database to find a specific book.
**Which field can we use?** Yes! It seems that the `id` is the best one.
Replace the code on `books.hbs`:
:::info lecture
Chaque élément de la liste doit être un lien vers la page détail du livre en question. Ajoutons pour cela L6 un lien `<a href="">` avec pour URL `/books/5a79d85fd642ff1f1e6a479e`
:::
```htmlmixed=
{{! views/books.hbs }}
<h1>Books</h1>
{{#each books}}
<p>
<a href="/books/{{this.id}}">{{this.title}}</a>
</p>
{{/each}}
```
**When we click on one of the titles, where we will navigate?**
:::info lecture
Ainsi, chaque lien aura sa propre URL liée à l'ID de chaque livre.
:::
Exactly! We will navigate to a route like the following: `http://localhost:3000/books/5a79d85fd642ff1f1e6a479e` (yes, the final part will be different from book to book!)
So how we have to structure the route? 🤔 Hm, it should be something like this: `http://localhost:3000/books/:bookId`.
Let's add this route to our project and make it render a `book-details` view, for now.
:::info lecture
Une fois le lien cliqué, le navigateur va accéder à l'URL. Notre serveur doit être capable d'y répondre et de délivrer la page demandée. Créons pour cela une nouvelle route `/books/:bookId` :
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books/:bookId', (req, res, next) => {
res.render('book-details');
});
```
### Get the `id`
**How we can get the `id` from the URL?**
There are a different ways to get the `id` info, but the best one is using `req.params`.
:::info lecture
`req.params.bookId` nous permet de récupérer le paramètre de l'URL :
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books/:bookId', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('The ID from the URL is: ', req.params.bookId);
res.render('book-details');
});
```
:bulb: Is there any other way we can do this rather than using the route params?
Go ahead and click on different books, and you should see on the console the `_id` field of each book you clicked on.
### Querying the DB
We have all we need to query our database, retrieve all the info about the clicked book and pass the data to our view.
**Which Mongoose method should we use to query?**
We have a couple of options: `find()`, `findOne()`, `findById()` are the most common ones. After having the information about the book we are looking for, we should pass that data to the view.
:::info lecture
Utilisons ce paramètre pour interroger notre DB et récupérer les datas de notre livre en question : L4
:::
```javascript=
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books/:bookId', (req, res, next) => {
Book.findOne({'_id': req.params.bookId})
.then(theBook => {
res.render('book-details', { book: theBook });
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('Error while retrieving book details: ', error);
})
});
```
<div class="skip">
:::info
We use `findOne()`, so the database retrieves an object with the book. If we use the `find()` method, it will return an array with the objects that match the criteria, but in our case there's only one object with the passed `id` so we will get the array with one element. Although we showed you how to use `find()` method, we will keep using `findById()` method since it's the most self-explanatory.
:::
```javascript
// routes/index.js
router.get('/books/:bookId', (req, res, next) => {
Book.findById(req.params.bookId)
.then(theBook => {
res.render('book-details', { book: theBook });
})
.catch(error => {
console.log('Error while retrieving book details: ', error);
})
});
```
</div>
Let's add some code to the `book-details.hbs` so we can display the information we've got from the DB:
:::info lecture
Enfin, n'oublions pas le template `views/book-details.hbs`
:::
```htmlmixed
{{! views/book-details.hbs }}
<h1>{{book.title}}</h1>
<span>Written by: {{book.author}}</span>
<p>Summary: {{book.description}}</p>
<p>Rating: {{book.rating}}/10</p>
<a href="/books">Return</a>
```
When clicking in any of the books, we should see this:

## Summary
We've started creating robust project combining all the concepts we learned so far in the module 2.
Using *Mongoose queries* in the routes will be one of the main tasks you will do at your projects, and it's essential to understand the process we follow to do them.