# Get Into IoT Activity Sheets
[TOC]
# Setup
## Prerequisites
For this session you will need:
* A laptop or PC
* Raspberry Pi Zero (provided)
* IoT LoRa Node pHAT (provided)
* Sensors and Breadboard (provided)
## Procedure
1. Connect your PC or laptop to the `DMC-Tenant1` WiFi network using the password `DMC2-PsK2020`.
2. Download and install [Thonny Python IDE](https://thonny.org/) (free software).
3. Configure Thonny to connect to your Raspberry Pi Zero by going to `Tools-->Options`
<br/><br/>
4. Select the Interpreter tab and from the dropdown choose `Remote Python 3 (SSH)`
<br/><br/>
5. In the Host field, enter the IP address for your Raspberry Pi Zero as provided by the session facilitator. Enter `pi` in the Username field and click OK.
<br/><br/>
6. In the prompt that appears, enter the password `raspberry`, check remember password then click OK.
<br/><br/>
7. Wait for the Raspberry Pi Zero to connect. When it does, the Thonny window should look something like the following:
<br/><br/>
8. In the directory listing for the Rasperry Pi Zero, double click the `hello_world.py` script and press the green run button in the Thonny menu bar. If all went well, you should see the following output in the Shell:
```
>>> %Run hello_world.py
Hello, world!
>>>
```
# Introduction
## Raspberry Pi Zero W

Our embedded system is a [Raspberry Pi Zero W](https://www.raspberrypi.com/products/raspberry-pi-zero-w/) single board computer. It runs a version of Linux called Raspbian from an included SD card and has interfaces for WiFi, Bluetooth, HDMI, USB, a camera, and several general purpose inputs and outputs (GPIO).
To power the board, plug the provided USB cable into an USB port on your PC or laptop or a micro USB phone charger.
## IoT Lora Node pHAT
Here is an overview of the IoT LoRa Node pHAT for reference when connecting up your sensor(s).

|Pin|Description|
|--|--|
|5V|Provides 5 volt power output|
|3V3|Provides 3.3 volt power output|
|GND|Provides ground for either 3.3V or 5V power|
|GPIO2|I2C data pin by default, can be reconfigured
|GPIO3|I2C clock pin by default, can be reconfigured
|GPIO4|1-wire serial pin or general purpose digital I/O|
# Sensors
## Smart Temperature & Humidity Sensor
### Sensor Overview
The [DHT11](https://www.mouser.com/datasheet/2/758/DHT11-Technical-Data-Sheet-Translated-Version-1143054.pdf) is a low cost Temperature and Humidity sensor which is commonly used in IoT projects. The breakout module has three pins: power, ground, and Signal. The sensor uses a single wire serial protocol known as 1-wire.

### Hardware Setup
Attach the sensor to the pHAT using the jumper wires provided using the following connections:
|Sensor Pin| pHAT Pin|
|--|--|
|Signal| GPIO4|
|Vcc (+)| 3V3|
|Ground (-) | GND|
### Python Code
You can test that the sensor is connected correctly by running the `dht11_test.py` script from Thonny.
```python=
from rak811.rak811 import Mode, Rak811 #Lora Chip driver
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO # RPi GPIO library
import dht11 # Sensor library
from time import sleep # Timing library
from cayennelpp import LppFrame # LoRaWAN payload library
# Initialize GPIO
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.cleanup()
# Read DHT11 data using pin 4
sensor = dht11.DHT11(pin = 4)
# Initialize RAK811 LoRa module
lora = Rak811()
lora.hard_reset()
lora.mode = Mode.LoRaWan
lora.band = 'EU868'
# Configure TTN credentials
lora.set_config(app_eui='0101010101010101',
app_key=''
)
# Join TTN LoRaWAN
lora.join_otaa()
lora.dr = 5
# Read and publish sensor data forever
while True:
# Read from sensor
result = sensor.read()
# If results are valid, publish readings to TTN
if result.is_valid():
print("Temperature: %-3.1f C" % result.temperature)
print("Humidity: %-3.1f %%" % result.humidity)
# Create a Cayenne data frame
frame = LppFrame()
# Add readings to data frame
frame.add_temperature(0, result.temperature)
frame.add_humidity(0, result.humidity)
# Publish data frame to TTN
print("Publishing to TTN")
lora.send(bytes(frame))
# Sleep for 5 seconds to adhere to LoRaWAN duty cycle limits
sleep(5)
lora.close()
```
## Sound Threshold Detector
### Sensor Overview
This module uses an electret microphone in conjuction with an amplifer. It has two outputs:
* AO: analog output, real-time output voltage signal of the microphone
* DO: when the intensity of the sound reaches a certain threshold, the output is a high or low level signal. The threshold sensitivity can be achieved by adjusting the potentiometer.
:::info
The sound threshold level will need to be set manually using the screw on the sensor. Turn the screw on the blue potentiometer until the LED is off but flashes for loud sounds. Anticlockwise is less sensitive and it can take several turns before you see a response.
:::

### Hardware Setup
Because the Raspberry Pi cannot directly read analog voltages, we are constrained to use on the digital output from this sensor.
Attach the sensor to the pHAT using the jumper wires provided using the following connections:
|Sensor Pin| pHAT Pin|
|--|--|
|DO (1)| GPIO4|
|VCC (2)| 3V3|
|GND (3) | GND|
### Python Code
```python=
from rak811.rak811 import Mode, Rak811 # LoRa chip driver
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO # RPi GPIO library
from time import sleep # Time delay library
from cayennelpp import LppFrame # LoRa payload library
# Define a flag to indicate whether the sound threshold was exceeded or not
alert = False
# Callback function to set this flag when sound level is exceeded
def threshold_cb(channel):
global alert
alert = True
# initialize GPIO
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# Set up pin 2 as input and attached interrupt on rising edge
GPIO.setup(2, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.add_event_detect(2, GPIO.RISING, callback=threshold_cb, bouncetime=100)
# Initialize RAK811 LoRa module
lora = Rak811()
lora.hard_reset()
lora.mode = Mode.LoRaWan
lora.band = 'EU868'
# Configure TTN credentials
lora.set_config(app_eui='0101010101010101',
app_key=''
)
# Join TTN LoRaWAN
lora.join_otaa()
lora.dr = 5
# Read and publish sensor data forever
while True:
# Create a Cayenne data frame
frame = LppFrame()
frame.add_digital_input(0, alert)
# Publish data frame to TTN
print("Publishing to TTN")
lora.send(bytes(frame))
# Reset alert flag
alert = False
# Sleep for 5 seconds to adhere to LoRaWAN duty cycle limits
sleep(5)
lora.close()
```
## Light Level Sensor
### Sensor Overview
An LDR (sometimes called a photocell) is a special type of resistor. When light hits the LDR, its resistance is very low, but when it’s in the dark its resistance is very high.
By placing a capacitor in series with an LDR, the capacitor will charge at different speeds depending on whether it’s light or dark. When the capacitor is charged, it will activate a digital input on the Raspberry Pi. By measuring the time it takes to charge the capacitor, we can estimate the resistance of the LDR and hence the incident light level.
### Hardware Setup
Setup the LDR and capacitor as shown below.
:::danger
Ensure the white stripe on the capacitor is orientated as shown otherwise it will be damaged!
:::
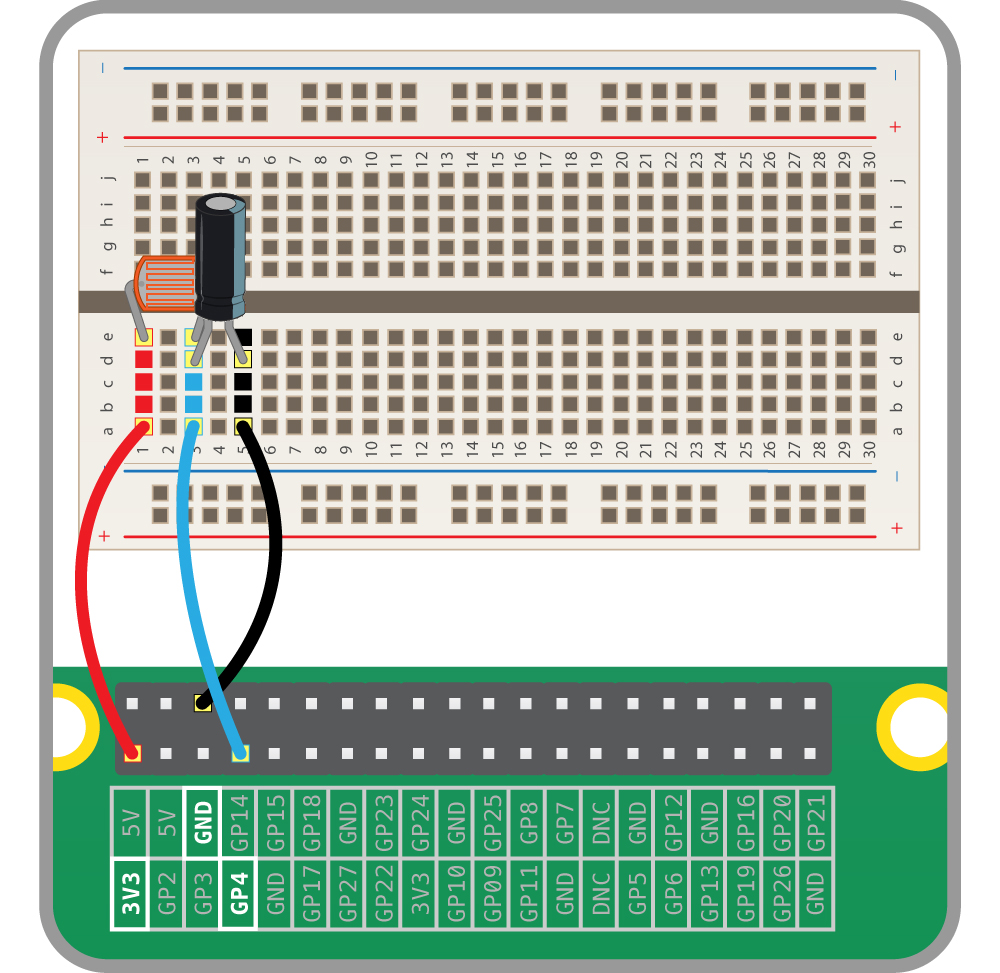
Attach the sensor to the pHAT using the jumper wires provided using the following connections:
|Sensor Pin| pHAT Pin|
|--|--|
|LDR (red)| 3V3|
|Midpoint (blue)| GPIO4|
|Capacitor tail (black) | GND|
### Python Code
```python=
from rak811.rak811 import Mode, Rak811 # LoRa chip driver
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO # RPi GPIO library
import time # timing library
from cayennelpp import LppFrame # LoRa payload library
from gpiozero import LightSensor # Light sensor library
import math # maths function library (for statistics)
# initialize GPIO
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# Initialize light sensor on GPIO pin 4
ldr = LightSensor(4)
# Read LDR sensor over given time period and calculate
# sensor statistics
def sample_ldr(sample_duration=1):
t_start = time.time()
samples = []
while time.time() < t_start + sample_duration:
samples.append(ldr.value*10000)
stats = {}
n = len(samples)
mean = sum(samples) / n
std = math.sqrt(sum((s-mean)**2 for s in samples) / n)
return {
"min": min(samples),
"max": max(samples),
"mean": mean,
"std": std
}
# Initialize RAK811 LoRa module
lora = Rak811()
lora.hard_reset()
lora.mode = Mode.LoRaWan
lora.band = 'EU868'
# Configure TTN credentials
lora.set_config(app_eui='0101010101010101',
app_key=''
)
# Join TTN LoRaWAN
lora.join_otaa()
lora.dr = 5
# Read and publish sensor data forever
while True:
# Create a Cayenne data frame
frame = LppFrame()
# Sample light level for 10 seconds
light_stats = sample_ldr(10)
# Publish sensor stats
frame.add_luminosity(0, light_stats['min'])
frame.add_luminosity(1, light_stats['max'])
frame.add_luminosity(2, light_stats['mean'])
frame.add_luminosity(3, light_stats['std'])
# Publish data frame to TTN
print("Publishing to TTN")
lora.send(bytes(frame))
lora.close()
```
## Ultrasonic Range Sensor
### Sensor Overview
In air, sound travels at a speed of 343 metres per second. An ultrasonic distance sensor sends out pulses of ultrasound which are inaudible to humans, and detects the echo that is sent back when the sound bounces off a nearby object. It then uses the speed of sound to calculate the distance from the object.
### Hardware Setup
:::info
Due to the potential for damage to the Raspberry Pi, the breadboard has been pre-populated for you.
:::
This sensor needs a 5V power supply so your Raspberry Pi Lora Node pHAT has been modified to provide an additional power pin for this purpose (see [here](#IoT-Lora-Node-pHAT) for reference). This means that the output voltage from this sensor is too high for the inputs on the Raspberry Pi, so to prevent damage the voltage is stepped down by the two resistors on the breadboard.
Attach the sensor to the pHAT using the jumper wires provided using the following connections:
|Sensor Pin| pHAT Pin|
|--|--|
|Power (red)| 5V|
|Trigger (green)| GPIO2|
|Echo (yellow) | GPIO4 |
|Ground (black) | GND|
### Python Code
```python=
from rak811.rak811 import Mode, Rak811 # LoRa chip driver
from gpiozero.pins.pigpio import PiGPIOFactory # RPi GPIO pin driver
from gpiozero import DistanceSensor # Sensor library
import time # Timing library
from cayennelpp import LppFrame # LoRa payload library
import math # Math functions library (for statistics)
# Instantiate sensor
factory = PiGPIOFactory()
ultrasonic = DistanceSensor(echo=4,
trigger=2,
max_distance=4,
pin_factory=factory)
# Take readings from sensor over a given period and summarise with descriptive statistics
def sample(sample_duration=1):
t_start = time.time()
samples = []
while time.time() < t_start + sample_duration:
samples.append(ultrasonic.distance)
stats = {}
n = len(samples)
mean = sum(samples) / n
std = math.sqrt(sum((s-mean)**2 for s in samples) / n)
return {
"min": min(samples),
"max": max(samples),
"mean": mean,
"std": std
}
# Initialize RAK811 LoRa module
lora = Rak811()
lora.hard_reset()
lora.mode = Mode.LoRaWan
lora.band = 'EU868'
# Configure TTN credentials
lora.set_config(app_eui='0101010101010101',
app_key=''
)
# Join TTN LoRaWAN
print("Joining LoRaWAN...")
lora.join_otaa()
lora.dr = 5
# Read and publish sensor data forever
while True:
# Create a Cayenne data frame
frame = LppFrame()
range_stats = sample(10)
frame.add_analog_input(0, range_stats['min'])
frame.add_analog_input(1, range_stats['max'])
frame.add_analog_input(2, range_stats['mean'])
frame.add_analog_input(3, range_stats['std'])
print(frame)
# Publish data frame to TTN
print("Publishing to TTN")
lora.send(bytes(frame))
lora.close()
```
## PIR Motion Sensor
## Sensor Overview
Humans and other animals emit radiation all the time. This is nothing to be concerned about, though, as the type of radiation we emit is infrared radiation (IR), which is pretty harmless at the levels at which it is emitted by humans. In fact, all objects at temperatures above absolute zero (-273.15C) emit infrared radiation.
A PIR sensor detects changes in the amount of infrared radiation it receives. When there is a significant change in the amount of infrared radiation it detects, then a pulse is triggered. This means that a PIR sensor can detect when a human (or any animal) moves in front of it.
## Hardware Setup

This sensor requires 5V power instead of 3.3V, so your Raspberry Pi LoRa Node pHAT has been modified to provide an additional 5V pin. See [here](#IoT-Lora-Node-pHAT) for reference.
Attach the sensor to the pHAT using the jumper wires provided using the following connections:
|Sensor Pin| pHAT Pin|
|--|--|
|Output| GPIO4|
|Power| 5V |
|Ground | GND|
## Python Code
```python=
from rak811.rak811 import Mode, Rak811 # LoRa chip driver
from gpiozero import MotionSensor # Sensor library
import time # Timing library
from cayennelpp import LppFrame # LoRa payload library
# Variables to keep track of when we last transmitted, and how often we want to transmit
last_transmit_time = time.time()
transmit_interval = 5 # seconds
# Instantiate the motion sensor
pir = MotionSensor(4)
# Initialize RAK811 LoRa module
lora = Rak811()
lora.hard_reset()
lora.mode = Mode.LoRaWan
lora.band = 'EU868'
# Configure TTN credentials
lora.set_config(app_eui='0101010101010101',
app_key=''
)
# Join TTN LoRaWAN
print("Joining LoRaWAN...")
lora.join_otaa()
lora.dr = 5
# Read and publish sensor data forever
while True:
motion = False
# Create a Cayenne data frame
frame = LppFrame()
pir.wait_for_motion(5)
if pir.motion_detected:
motion = True
frame.add_presence(0,motion)
# Publish data frame to TTN
print("Publishing to TTN")
lora.send(bytes(frame))
time.sleep(max(0, transmit_interval - (time.time() - last_transmit_time)))
last_transmit_time = time.time()
lora.close()
```
# Device Allocations
|LoRa Device EUI| RPi MAC Address|IP Address| Role|
|--|--|--|--|
|60C5A8FFFE78++B303++|B8:27:EB:85:0C:7C|172.17.111.217|PIR Motion Sensor|
|60C5A8FFFE78++B2D0++|B8:27:EB:C6:AF:A8|172.17.111.240|Light Level Sensor|
|60C5A8FFFE78++B223++|B8:27:EB:0D:34:F1|172.17.111.238|Ultrasonic Distance Sensor|
|60C5A8FFFE78++B345++|B8:27:EB:62:EE:ED|172.17.111.239|Temperature and Humidity Sensor|
|60C5A8FFFE78++B22E++|B8:27:EB:3E:48:2A|172.17.111.241|Sound Threshold Detector|
<!--
:::warning
60C5A8FFFE78++B2C5++ is possibly damaged
:::
-->
# Node Red Example
```javascript=
[
{
"id": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"type": "tab",
"label": "Flow 1",
"disabled": false,
"info": "",
"env": []
},
{
"id": "338ce01dc6cd3d45",
"type": "mqtt in",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"topic": "#",
"qos": "2",
"datatype": "json",
"broker": "b0479d9283a99332",
"nl": false,
"rap": true,
"rh": 0,
"inputs": 0,
"x": 70,
"y": 180,
"wires": [
[
"a33fef212b79cdfb",
"a8642d722d010b7d"
]
]
},
{
"id": "a33fef212b79cdfb",
"type": "debug",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"active": false,
"tosidebar": true,
"console": false,
"tostatus": false,
"complete": "payload",
"targetType": "msg",
"statusVal": "",
"statusType": "auto",
"x": 250,
"y": 60,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "a8642d722d010b7d",
"type": "switch",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"property": "topic",
"propertyType": "msg",
"rules": [
{
"t": "eq",
"v": "v3/dmc02-makerlab@rjc-home/devices/dmc-lora-phat-60c5a8fffe78b223/up",
"vt": "str"
},
{
"t": "eq",
"v": "v3/dmc02-makerlab@rjc-home/devices/dmc-lora-phat-60c5a8fffe78b22e/up",
"vt": "str"
},
{
"t": "eq",
"v": "v3/dmc02-makerlab@rjc-home/devices/dmc-lora-phat-60c5a8fffe78b2d0/up",
"vt": "str"
},
{
"t": "eq",
"v": "v3/dmc02-makerlab@rjc-home/devices/dmc-lora-phat-60c5a8fffe78b303/up",
"vt": "str"
},
{
"t": "eq",
"v": "v3/dmc02-makerlab@rjc-home/devices/dmc-lora-phat-60c5a8fffe78b345/up",
"vt": "str"
}
],
"checkall": "true",
"repair": false,
"outputs": 5,
"x": 230,
"y": 180,
"wires": [
[
"56f29c40d810e578"
],
[
"2bebbd1a3b9c4cf2"
],
[
"6c8ca1c4058f047f"
],
[
"99d88abdad548205"
],
[
"d30888b9bcbd593c"
]
]
},
{
"id": "b9e1933908a6e7a2",
"type": "link out",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "ultrasonic-distance-sensor",
"mode": "link",
"links": [
"938f62da889d1c32"
],
"x": 515,
"y": 100,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "0ccfd39fce55e47b",
"type": "link out",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "sound-threshold-detector",
"mode": "link",
"links": [
"938f62da889d1c32"
],
"x": 515,
"y": 140,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "4806fc7172f307b1",
"type": "link out",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "light-level-sensor",
"mode": "link",
"links": [
"938f62da889d1c32"
],
"x": 515,
"y": 180,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "998fb78920616d2f",
"type": "link out",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "pir-motion-sensor",
"mode": "link",
"links": [
"938f62da889d1c32"
],
"x": 515,
"y": 220,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "644f4c8b8ccabc60",
"type": "link out",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "temp-humid-sensor",
"mode": "link",
"links": [
"938f62da889d1c32",
"1918a9db9abfcb72"
],
"x": 515,
"y": 260,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "59a54f228cf5f17c",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "ultrasonic-distance-sensor",
"info": "",
"x": 650,
"y": 100,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "19afda2ec546e2b0",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "sound-threshold-detector",
"info": "",
"x": 650,
"y": 140,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "f69ea66a6e0ab03f",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "light-level-sensor",
"info": "",
"x": 620,
"y": 180,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "7f4f93583105eae2",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "pir-motion-sensor",
"info": "",
"x": 620,
"y": 220,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "6341ba603ff6c1fa",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "temp-humid-sensor",
"info": "",
"x": 630,
"y": 260,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "d30888b9bcbd593c",
"type": "function",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"func": "msg.topic = \"temp-humid-sensor\";\nconst data = msg.payload.uplink_message.decoded_payload;\nmsg.payload = {\n humidity: data.relative_humidity_0,\n temperature: data.temperature_0\n};\nreturn msg;",
"outputs": 1,
"noerr": 0,
"initialize": "",
"finalize": "",
"libs": [],
"x": 420,
"y": 260,
"wires": [
[
"644f4c8b8ccabc60"
]
]
},
{
"id": "99d88abdad548205",
"type": "function",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"func": "msg.topic = \"pir-motion-sensor\";\nmsg.payload = msg.payload.uplink_message.decoded_payload.presence_0;\nreturn msg;",
"outputs": 1,
"noerr": 0,
"initialize": "",
"finalize": "",
"libs": [],
"x": 420,
"y": 220,
"wires": [
[
"998fb78920616d2f"
]
]
},
{
"id": "6c8ca1c4058f047f",
"type": "function",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"func": "msg.topic = \"light-level-sensor\";\nconst data = msg.payload.uplink_message.decoded_payload;\nmsg.payload = {\n min: data.luminosity_0,\n max: data.luminosity_1,\n mean: data.luminosity_2,\n std: data.luminosity_3\n}\nreturn msg;",
"outputs": 1,
"noerr": 0,
"initialize": "",
"finalize": "",
"libs": [],
"x": 420,
"y": 180,
"wires": [
[
"4806fc7172f307b1"
]
]
},
{
"id": "2bebbd1a3b9c4cf2",
"type": "function",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"func": "msg.topic = \"sound-threshold-detector\";\nmsg.payload = msg.payload.uplink_message.decoded_payload.digital_in_0;\nreturn msg;",
"outputs": 1,
"noerr": 0,
"initialize": "",
"finalize": "",
"libs": [],
"x": 420,
"y": 140,
"wires": [
[
"0ccfd39fce55e47b"
]
]
},
{
"id": "56f29c40d810e578",
"type": "function",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"func": "msg.topic = \"ultrasonic-distance-sensor\";\nconst data = msg.payload.uplink_message.decoded_payload;\nmsg.payload = {\n min: data.analog_in_0,\n max: data.analog_in_1,\n mean: data.analog_in_2,\n std: data.analog_in_3\n}\nreturn msg;",
"outputs": 1,
"noerr": 0,
"initialize": "",
"finalize": "",
"libs": [],
"x": 420,
"y": 100,
"wires": [
[
"b9e1933908a6e7a2"
]
]
},
{
"id": "938f62da889d1c32",
"type": "link in",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"links": [
"0ccfd39fce55e47b",
"4806fc7172f307b1",
"644f4c8b8ccabc60",
"998fb78920616d2f",
"b9e1933908a6e7a2"
],
"x": 515,
"y": 340,
"wires": [
[
"b0f3e60a43f7d99a"
]
]
},
{
"id": "b0f3e60a43f7d99a",
"type": "debug",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"active": false,
"tosidebar": true,
"console": false,
"tostatus": false,
"complete": "false",
"statusVal": "",
"statusType": "auto",
"x": 620,
"y": 340,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "bd971507f05f8f2a",
"type": "ui_chart",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"group": "0f9f2919eea37f6f",
"order": 1,
"width": 12,
"height": 11,
"label": "chart",
"chartType": "line",
"legend": "true",
"xformat": "HH:mm:ss",
"interpolate": "linear",
"nodata": "",
"dot": false,
"ymin": "",
"ymax": "",
"removeOlder": 1,
"removeOlderPoints": "",
"removeOlderUnit": "3600",
"cutout": 0,
"useOneColor": false,
"useUTC": false,
"colors": [
"#1f77b4",
"#c01c28",
"#ff7f0e",
"#2ca02c",
"#98df8a",
"#aec7e8",
"#ff9896",
"#9467bd",
"#c5b0d5"
],
"outputs": 1,
"useDifferentColor": false,
"className": "",
"x": 570,
"y": 520,
"wires": [
[]
]
},
{
"id": "dfa4182eed238352",
"type": "split",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"splt": "\\n",
"spltType": "str",
"arraySplt": 1,
"arraySpltType": "len",
"stream": false,
"addname": "topic",
"x": 430,
"y": 520,
"wires": [
[
"bd971507f05f8f2a"
]
]
},
{
"id": "1918a9db9abfcb72",
"type": "link in",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "",
"links": [
"644f4c8b8ccabc60"
],
"x": 335,
"y": 520,
"wires": [
[
"dfa4182eed238352"
]
]
},
{
"id": "c467a0fe0721b1b6",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "Dashboard Widget Example",
"info": "",
"x": 480,
"y": 480,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "1ab9691461215172",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "Debug sensor data",
"info": "",
"x": 810,
"y": 340,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "090e2f38a2317158",
"type": "comment",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "Debug incoming messages",
"info": "",
"x": 290,
"y": 20,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "15a6ed11e4709d39",
"type": "inject",
"z": "0379d6b85cd091e6",
"name": "Clear chart",
"props": [
{
"p": "payload"
}
],
"repeat": "",
"crontab": "",
"once": false,
"onceDelay": 0.1,
"topic": "",
"payload": "[]",
"payloadType": "json",
"x": 420,
"y": 580,
"wires": [
[
"bd971507f05f8f2a"
]
]
},
{
"id": "b0479d9283a99332",
"type": "mqtt-broker",
"name": "",
"broker": "eu1.cloud.thethings.industries",
"port": "8883",
"tls": "",
"clientid": "",
"autoConnect": true,
"usetls": true,
"protocolVersion": "4",
"keepalive": "60",
"cleansession": true,
"birthTopic": "",
"birthQos": "0",
"birthPayload": "",
"birthMsg": {},
"closeTopic": "",
"closeQos": "0",
"closePayload": "",
"closeMsg": {},
"willTopic": "",
"willQos": "0",
"willPayload": "",
"willMsg": {},
"sessionExpiry": "",
"credentials": {}
},
{
"id": "0f9f2919eea37f6f",
"type": "ui_group",
"name": "Default",
"tab": "6aa60a85c8c12573",
"order": 1,
"disp": true,
"width": 12,
"collapse": false,
"className": ""
},
{
"id": "6aa60a85c8c12573",
"type": "ui_tab",
"name": "Home",
"icon": "dashboard",
"disabled": false,
"hidden": false
}
]
```
<!--
# MPU6050 Accelerometer & Gyroscope
```python=
from rak811.rak811 import Mode, Rak811
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from time import sleep
from cayennelpp import LppFrame
from mpu6050 import mpu6050
import math
import time
# initialize GPIO
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.cleanup()
# Initialize RAK811 LoRa module
lora = Rak811()
lora.hard_reset()
lora.mode = Mode.LoRaWan
lora.band = 'EU868'
# Configure TTN credentials
lora.set_config(app_eui='0101010101010101',
app_key=''
)
# Join TTN LoRaWAN
lora.join_otaa()
lora.dr = 5
# Initialise Accelerometer & Gyroscope
sensor = mpu6050(0x68)
# Generate a list of statistics about a collection of datasets
def describe(collection):
stats = {}
for name, samples in collection.items():
n = len(samples)
mean = sum(samples) / n
std = math.sqrt(sum((s-mean)**2 for s in samples) / n)
stats[name] = {
"min": min(samples),
"max": max(samples),
"mean": mean,
"std": std
}
return stats
# Generate a list of samples of accelerometer and gyroscope readings
# over a given duration
def sample_IMU(sample_duration=1):
t_start = time.time()
samples = {
"ax": [],
"ay": [],
"az": [],
"rx": [],
"ry": [],
"rz": []
}
while time.time() < t_start + sample_duration:
acc = sensor.get_accel_data()
gyr = sensor.get_gyro_data()
samples['ax'].append(acc['x'])
samples['ay'].append(acc['y'])
samples['az'].append(acc['z'])
samples['rx'].append(gyr['x'])
samples['ry'].append(gyr['y'])
samples['rz'].append(gyr['z'])
return samples
# Read and publish sensor data forever
while True:
# Create a Cayenne data frame
frame = LppFrame()
# Sample Accelerometer and Gyroscope for 15 seconds
samples = sample_IMU(15)
# Extract statistics from data sample
stats = describe(samples)
# Display statistics about sensor readings
print(stats)
# Add statistics to data frame
frame.add_accelerometer(0, stats['ax']['min'], stats['ay']['min'], stats['az']['min'])
frame.add_accelerometer(1, stats['ax']['max'], stats['ay']['max'], stats['az']['max'])
frame.add_accelerometer(2, stats['ax']['mean'], stats['ay']['mean'], stats['az']['mean'])
frame.add_accelerometer(3, stats['ax']['std'], stats['ay']['std'], stats['az']['std'])
frame.add_gyrometer(0, stats['rx']['min'], stats['ry']['min'], stats['rz']['min'])
frame.add_gyrometer(1, stats['rx']['max'], stats['ry']['max'], stats['rz']['max'])
frame.add_gyrometer(2, stats['rx']['mean'], stats['ry']['mean'], stats['rz']['mean'])
frame.add_gyrometer(3, stats['rx']['std'], stats['ry']['std'], stats['rz']['std'])
# Publish data frame to TTN
print("Publishing to TTN")
lora.send(bytes(frame))
lora.close()
```
-->