## Functional Programming with React Redux
:::info
#### Leo Fan
:::success
#### @ RDME Recharge, 2022/10/11
:::
Note: test note
---
### What is Functional Programming?
Functional programming is the process of building software by
:::info
composing pure functions
:::danger
avoiding shared state, mutable data, and side-effects.
:::
[@wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_programming)
Note:
Coding style
----
1. Function 必須作為一級公民。意即,Function 可以像一般變數一般被當作參數傳入、被當作結果輸出、被任意 assign 給其他變數、被任意進行運算。
2. Function 中只能有 Expression 而非指令( instructions )。
3. Function 必須是 「Pure」、沒有 Side Effect。
4. Function 「不可改變 Input 的資料」、「不可 改變狀態」。
5. Function 「可以任意『組合』得到新的 Function,且依然滿足以上這些守則」。
---
### Benefits
* No observable side-effects. Easy to read and reason about.
* Explicit arguments. Expressions are self-documenting and portable.
* Cacheable. Based on arguments.
* Easily testable. Assert output by input. No mocking.
* Safe parallelization. No race conditions.
Note:
mock object,模擬對象
似汽車設計者使用碰撞測試假人來模擬車輛碰撞中人的動態行為。
----
### KISS principle: Keep it simple and stupid

---
### Main Concepts
* First-class and higher-order functions
* Pure functions
* Declarative vs Imperative
* Currying
* Composing
---
### First-class and higher-order functions
* 可以將函式(至少一個)當成參數傳入另一個函式。
* 可以將函式當成另一個函式的回傳值。
```javascript=
const add = function(x){ //add函式接收參數並且回傳一個 Function 作為回傳值
return function(y){
return x + y;
};
};
const addFive = add(5);
const addTen = add(10);
addFive(2) // ans : 7
addTen(2) // ans : 12
```
---
### Pure Functions
Pure Functions 意指將相同的input丟入函式,永遠會回傳相同的output結果,而且在過程中完全沒有任何的"副作用"。
* 更改外部變數或者物件屬性(例如:全域變數、父類別範圍內的變數等)
* 寫入console.log、檔案
* 觸發外部流程
* 呼叫任何有副作用的函式(Functions)
----
```javascript=
// slice: Pure Function
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
arr.slice(0, 3); // output = [1, 2, 3], arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
arr.slice(0, 3); // output = [1, 2, 3], arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// splice: not Pure Function
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
arr.splice(0, 3); // output = [1, 2, 3], arr = [4, 5, 6]
arr.splice(0, 3); // output = [4, 5, 6], arr = []
```
---
### Declarative vs Imperative
* Declarative Paradigm (宣告式編程)一 較為抽象的程式碼,可以藉由自然語言直觀的理解該行程式碼想要達到什麼樣的結果。描述該在哪做什麼(what to do)以及資料流程(data flow)
* Imperative Paradigm (指令式編程) 一 程式碼具體表達需要做什麼來達到目標。描述該做什麼(how to do)以及流程控制(flow control)
----
```javascript=
const a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Declarative Programming
declarativeSquare = (arr) => arr.map((val) => val*val)
declarativeSquare(a); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
// Imperative Programming
imperativeSquare = (arr) => {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] *= arr[i];
}
return arr;
}
imperativeSquare(a); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
```
---
### Currying
```javascript
f(x)(y)(z) === f(x, y)(z) === f(x, y, z)
```
Allows to call a function with fewer arguments. It returns a function that takes the remaining arguments until all arguments are there.
----
```javascript=
function curry(fn) {
const arity = fn.length; // 4
return function resolver() {
if (arguments.length >= arity) {
return fn.apply(null, arguments); // => output
}
const memory = Object.values(arguments);
return function () {
return resolver.apply(null, [...memory, ...arguments]);
};
};
}
function add(a, b, c, d) {
return a + b + c + d;
}
curry(add)(1, 2, 3, 4) // 10
curry(add) // fn
curry(add)(1, 2) // fn
curry(add)(1, 2)(3, 4) // 10
```
Note:
Like Python partial()
---
### Composing
```javascript
f(a) === b
g(b) === c
g(f(a)) === c
```
**Function breeding**
Takes functions with traits you'd like to combine and mashes them together to spawn a brand new one.
----
```javascript=
function emphasize(string) {
return string + '!';
}
function uppercase(string) {
return string.toUpperCase();
}
const yell = compose(
emphasize,
uppercase,
);
yell('hello') // 'HELLO!'
```
---
### Using pure functions in React
```javascript
const Counter = ({ count }) => {
return <h3>{`Count: ${count}`}</h3>;
};
```
```javascript
// Use memo
const CounterComponent = React.memo(function Counter({ count }) {
return <h3>{`Count: ${count}`}</h3>;
});
```
Note:
React.memo 只會確認 props 的改變。如果你的 function component 被 wrap 在 React.memo 內,實作中具有一個 useState、useReducer 或 useContext Hook,當 state 或 context 改變時,它仍然會持續 rerender。
----
### Avoiding side effects
```javascript
const Counter = ({ count }) => {
useEffect(() => {
document.title = `Number of click: ${count}`;
}, [count]);
return <h3>{`Count: ${count}`}</h3>;
};
```
----
### Higher-Order Component
```javascript=
// Javascript
function hof(firstName) {
return function (lastName) {
return '$(firstName) $(lastName)';
};
}
hof('Leo')('Fan') // Leo Fan
const leoNamer = hof('Leo')
leoNamer('Pan') // Leo Pan
leoNamer('Lan') // Leo Lan
// ReactJS
const createHOC = (WrappedComponent, data) => {
class HocClass extends React.Component {
render() {
return <dic> <WrappedComponent {...data} /> </div>;
}
}
return HocClass;
};
```
----
### Currying
```javascript=
// ReactJS
const reverse = PassedComponent => ({ children, ...props }) => (
<PassedComponent {...props}>
{children.split("").reverse().join("")}
</PassedComponent>
);
// Redux
export const withMiddleware = store => next => action => {
// do something, next(action) or state.dispatch();
}
```
---
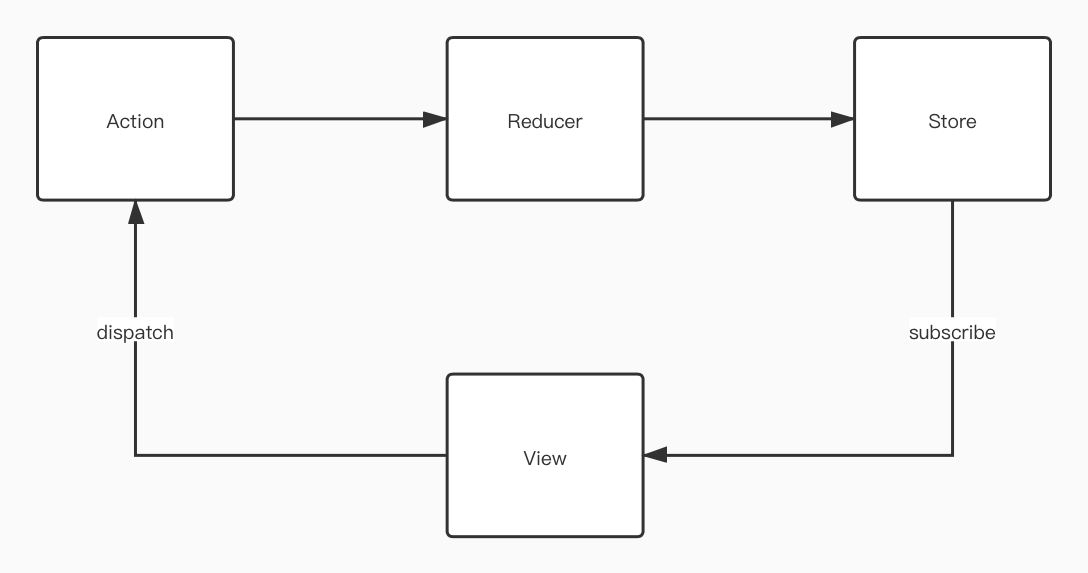
### How Redux Works
* Create a **store** for data and let the view subscribe to it
* The view **dispatch**es an **action** to submit the changs
* The **reducer** changes the **state** based on the action type
* Finally return the new state and triggers the view to change
----
----
### Wonderful Redux FP Design
* createStore: returns new **Object** { getState, dispatch, subscribe }
* combineReducers: returns new **Function**
* applyMiddleware: returns new **Function**
----
### createStore
<div style="font-size: 32px">
createStore defines those APIs that can be used within components. It’s more like setter and getter
</div>
```javascript=
export default function createStore (reducer, enhancer) {
if (enhancer) {
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer);
}
let currentState;
// Redux now uses a shallow copy `nextListeners` via `ensureCanMutateNextListeners()`
// to prevent bugs in the middle of `dispatch`
let currentListeners = [];
function getState () {
return currentState;
}
// Register callbacks to execute after changes
function subscribe (listener) {
currentListeners.push(listener);
return () => {
// empty listeners
const index = currentListeners.indexOf(listener);
currentListeners.splice(index, 1);
};
}
function dispatch (action) {
currentState = reducer(currentState, action);
// state changes, notify to invoke callbacks
currentListeners.forEach(listener => listener());
}
// Initialize Redux by calling a virtual reducer
dispatch({ type: "MY-MINI-REDUX" });
return {
getState,
dispatch,
subscribe
};
}
```
----
### combineReducers
<div style="font-size: 32px">
Returns a new function that can return the new state. Can’t be any purer.
</div>
```javascript=
// This is just a helper function to map through the Object
function mapValues(obj, fn) {
return Object.keys(obj).reduce((result, key) => {
result[key] = fn(obj[key], key);
return result;
}, {});
}
export default function combineReducers (reducers) {
return function combination (state = {}, action) {
// Official Redux uses `pick` on filtering reducers.
// Let's trust reducers are functions here
return mapValues(reducers, (reducer, key) => reducer(state[key], action))
};
}
```
----
### applyMiddleware: Redux Thunk
<div style="font-size: 32px">
redux-thunk allows to use function as dispatch parameter so that I could do something right before “dispatching”
</div>
```javascript=
// Allow passing function to dispatch
export default function thunk({ dispatch, getState }) {
return next => action => {
if (typeof action === "function") {
return action(dispatch, getState);
}
return next(action);
};
}
// without redux-thunk
dispatch({ type: 'action', payload: 'value' })
// with redux-thunk
// the dispatch is wrapped up by a new function
dispatch(function (dispatch, getState) {
console.log('redux-thunk')
dispatch({ type: 'action', payload: 'value' })
})
```
----
### applyMiddleware: Redux Logger
<div style="font-size: 32px">
It’s easy to guess what this middleware does. It simply outputs the state changes.
</div>
```javascript=
// Output the previous and current state in console
export default function logger({ getState }) {
return next => action => {
console.log("======== Redux Logger ========");
console.log("Action Type: ", action.type);
const prevState = getState();
console.log("Prev: ", prevState);
const returnValue = next(action);
const nextState = getState();
console.log("Next: ", nextState);
console.log("==============================");
return returnValue;
};
}
```
----
### Redux Middlewares
<div style="font-size: 32px">
All of the middlewares are curry functions.
</div>
```javascript=
const store = createStore(
combineReducers({
one: oneReducer,
two: twoReducer
}),
applyMiddleware(ReduxThunk, ReduxLogger)
);
```
```javascript=
// Combine the functions
// a(b(c())) => compose(a, b, c)
function compose(...funcs) {
return funcs.reduceRight((composed, f) => f(composed));
}
export default function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return next => (reducer, initialState) => {
const store = next(reducer, initialState);
let dispatch = store.dispatch;
const middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: action => dispatch(action)
};
const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI));
// Enhance the `dispatchers` by applying middlewares to each of them
dispatch = compose(...chain, store.dispatch);
return {
...store,
dispatch
};
};
}
```
---
### Reference
* [Functional programming @wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_programming)
* [Functional Programming and React](https://slides.com/sebastiansiemssen/functional-programming-and-react)
* [React JS & Functional Programming Principles](https://www.slideshare.net/landike/react-js-functional-programming-principles)
* [Functional Programming with React/Redux](https://medium.com/nmc-techblog/functional-programming-with-react-redux-6228906edbe3)
* [Fundamentals of functional programming with React](https://blog.logrocket.com/fundamentals-functional-programming-react/)
* [React 大小事之 Functional Programming](https://hackmd.io/@iJKONXzbT461MONF6A2rCA/HySYSpW1o)
* [談談 JavaScript 那些常見的 Functional Programming 的概念帶來了怎樣的好處](https://jason-memo.dev/posts/whats-the-benefit-from-javascript-functional-programing/)
* [Learn Functional Progamming Design from Redux - Pitayan](https://pitayan.com/posts/redux-fp-design/)
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-17T11:13:25.939Z","metaMigratedFrom":"YAML","title":"Functional programming with React Redux","breaks":true,"slideOptions":"{\"theme\":\"serif\",\"transition\":\"slide\",\"slideNumber\":true,\"center\":true,\"display\":\"block\",\"spotlight\":{\"enabled\":false}}","contributors":"[{\"id\":\"d4f3b938-9e48-40a8-ac07-9fb3b744b9fd\",\"add\":14538,\"del\":3138}]"}