# TypeScript
---
FAC 17 (Nov 2019)➡️
Freelance until Sep 2020 ➡️
Heka until March 2022 ➡️
Unmind June 2023 ➡️
TravelPerk Oct 2023 ⭐️
---
## 4 stages of competence

---
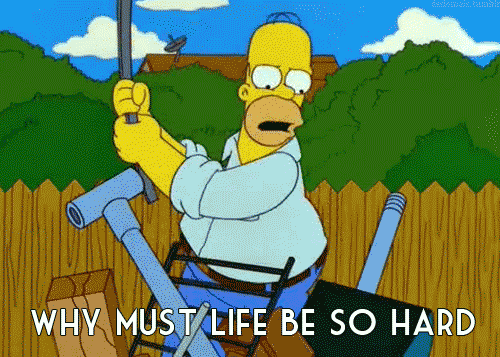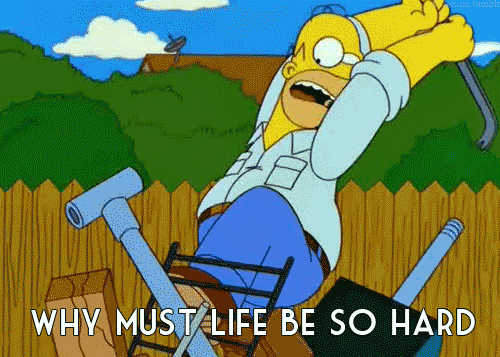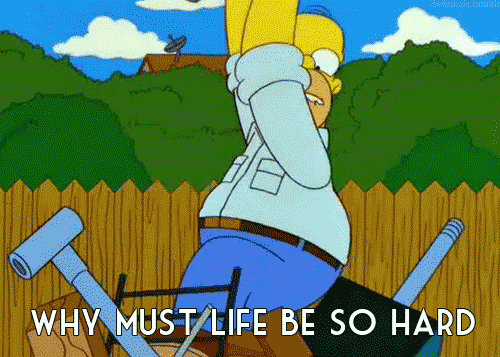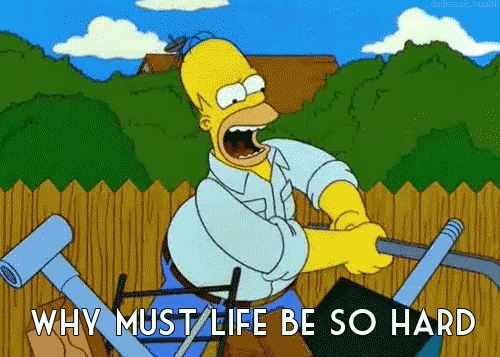
The 3 stages of typescript grief 😖🙄😍
---
# 1
---
# 2

---
# 3

---
## Types
(Strings, Numbers, Boolean, Null, Undefined, BigInt, Symbol, <span style="color:blue">Object</span>)
---
Javascript is an interpreted (or just-in-time compiled) **dynamic** (not static) and **weakly** (not strongly) typed language
---
## Static vs Dynamic
"Statically-typed programming languages do type checking at compile-time (TS), whereas dynamically-typed languages do type checks at runtime. (JS)"
([source](https://www.educative.io/answers/statically-v-dynamically-v-strongly-v-weakly-typed-languages))
---
## Weak vs Strong
"Weakly-typed languages make conversions between unrelated types implicitly (JS); whereas, strongly-typed languages don’t allow implicit conversions between unrelated types.(TS)"
([source](https://www.educative.io/answers/statically-v-dynamically-v-strongly-v-weakly-typed-languages))
---
"JavaScript provides language primitives like string and number, but it doesn’t check that you’ve consistently assigned these. TypeScript does." - Someone
---
# Examples
---
# Interesting Concepts
---
# Duck typing
"If it looks like a duck, swims like a duck, and quacks like a duck, then it probably is a duck"
If an object that has no defined type is "compatible" with a type definition then it's fine.
---
# Generics
---
## How is TS run?
- JS is usually run in JIT compilation
- TS must be compiled into JS to then be run
- When compilation happens types are removed so these aren't accessible at run time!
"X only refers to a type, but is being used as a value here"
---
## ts.config
"The presence of a tsconfig.json file in a directory indicates that the directory is the root of a TypeScript project. The tsconfig.json file specifies the root files and the compiler options required to compile the project."
---
## Things to avoid
<img src="https://hackmd.io/_uploads/rJHDAEHfT.jpg" alt="drawing" width="400"/>
---
Using ```any```
```typescript
let something: any = "Hello World!";
something = 23;
something = true;
```
---
Avoid type assertion e.g.
```typescript
const name = "tony" as number;
console.log(add(name, 2));
```
---
Make sure you're using the lowercase versions of types e.g. `string` not `String`
---
## Almost done...
---
# Why a presentation on TypeScript?
---
## Questions?
## FAQ
- How does duck typing work?
- This is because TypeScript uses structural typing (not nominative), which relies on the shape of the objects rather than their explicit class names.
- Types vs interfaces
- it depends
- We can use define a type alias for a primitive type: type userName = string | undefined, const myAddress: userName = "tonylomax" . Can't do that with interfaces
- Can only do union types with types e.g. type Transport = 'Bus' | 'Car' | 'Bike' | 'Walk';
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-17T11:11:24.408Z","metaMigratedFrom":"Content","title":"TypeScript","breaks":true,"description":"FAC 17 (Nov 2019) ➡️ Freelance until Sep 2020 ➡️ Heka until March 2022 ➡️ Unmind","contributors":"[{\"id\":\"5da6f9cf-649f-4aef-9a8d-c3c402e0a647\",\"add\":7153,\"del\":3813}]"}